EX2 Alpha Agonists (MC)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Tyrosine hydroxylase catalyzes the
rate limiting (slowest) step in the biosynthesis of NE and DA
What is the key difference between tyrosine and metyrosine? What is the effect of adding this additional group?
adding an alpha methyl group inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase
What is an alternate substrate?
a drug that acts like the substrate but does not produce a biologically relevant product
in the presence of methyldopa, what happens to the conversion of DOPA to dopamine?
decrease in the rate of conversion → less produced over time
a1 receptor
postsynaptic, mediates smooth muscle contraction
subtypes a, b, d
a2 receptor
presynaptic in CNS, postsynaptic in periphery
regulates release and biosynthesis of NE
increases uptake of NE into presynaptic neuron
alpha1 agonist uses
management of shock
decongestant
vasoconstriction
alpha2 agonist uses
HTN
Glaucoma
Spasticity
a1 antagonists
HTN
BPH
a2 antagonists
mild depression (CNS)
How does neurotransmission differ if its primary post synaptic vs pre synaptic?
presynaptic → decreased NE neurotransmission
postsynaptic → increased NE neurotransmission
two chemical classes of alpha agonists
phenethanolamines and 2-aryl imidazolines
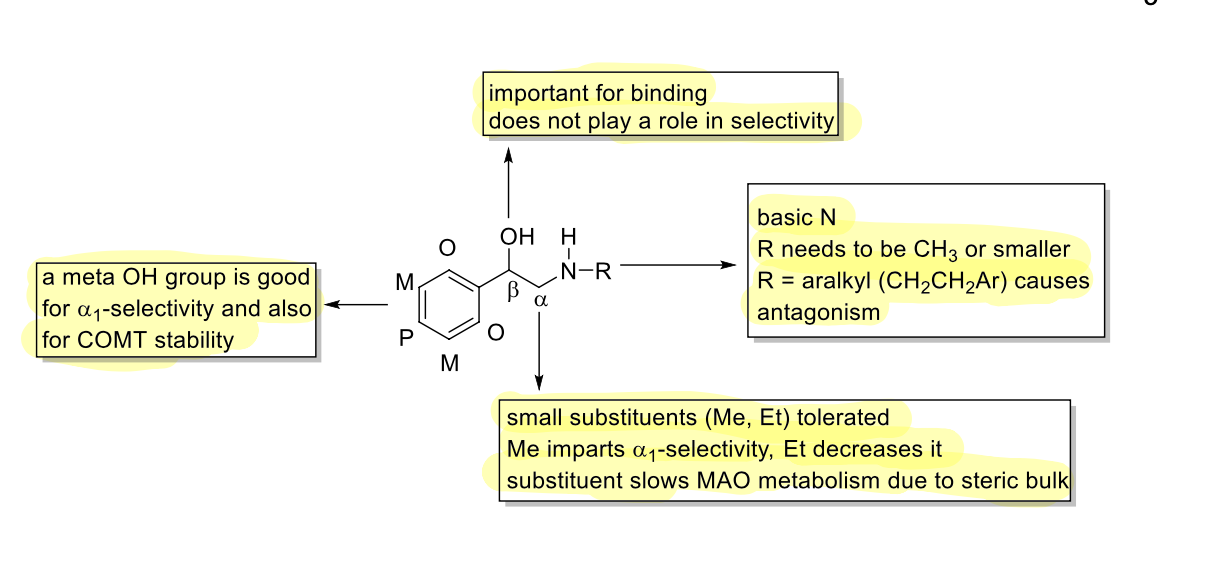
phenethanolamines SAR
alpha agonist
phenethanolamine derivatives
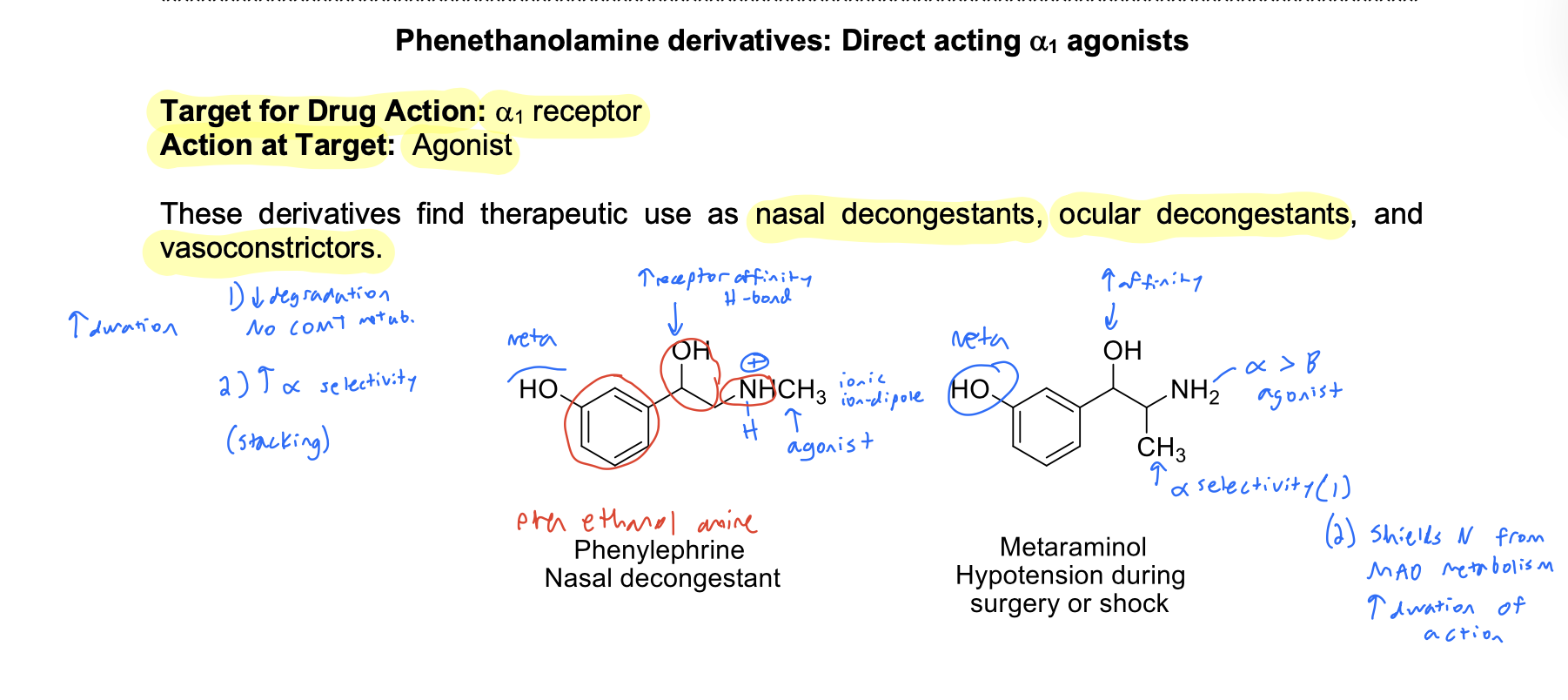
Which OH configuration increases receptor affinity?
R
Which functional group imparts a1 selectivity at the a carbon?
CH3
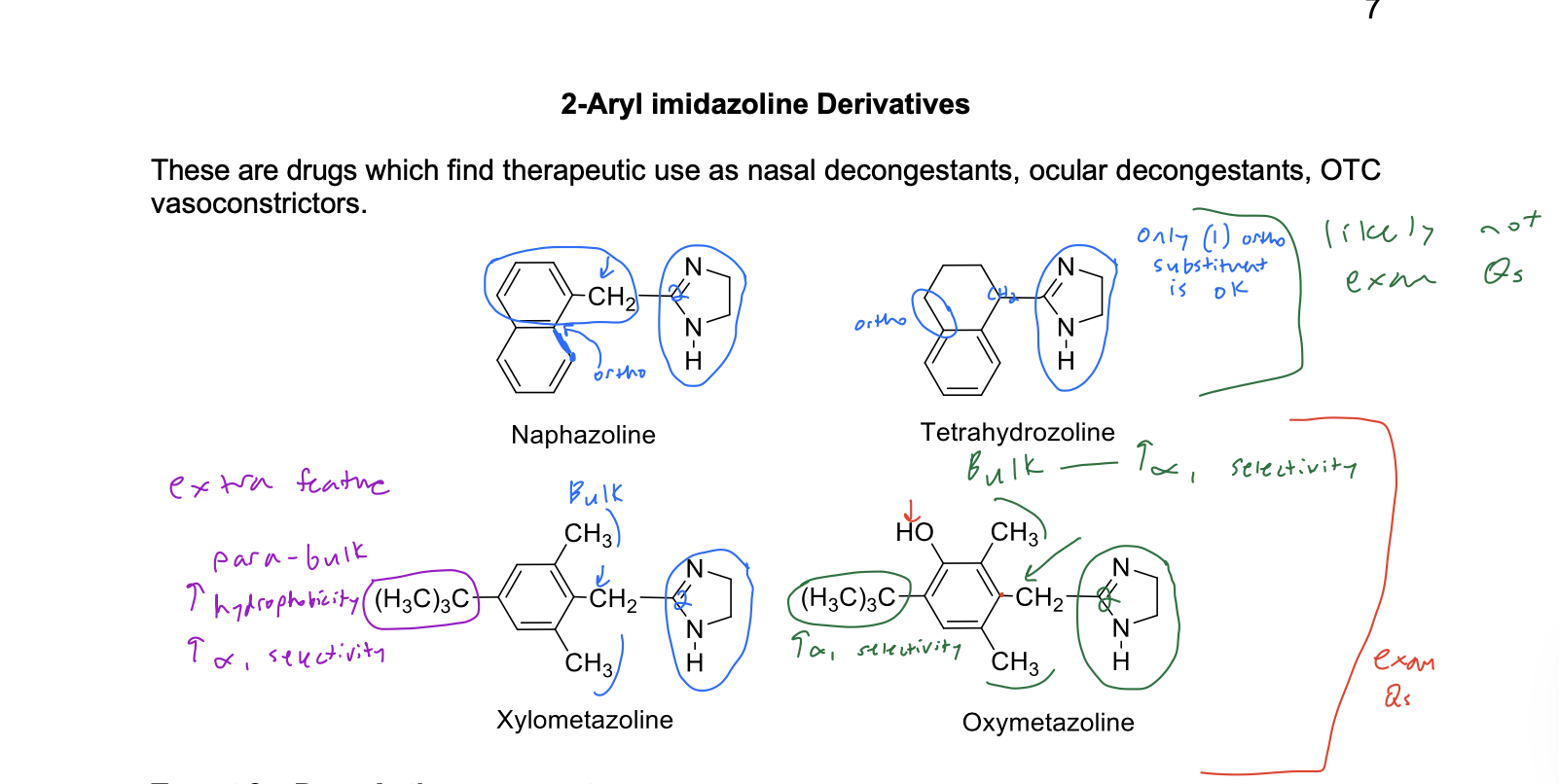
2-aryl imidazolines SAR
direct acting a1 agonists

which structural features are responsible for selective a1 receptor agonist activity?
ortho alkyl groups on aromatic ring
2-aryl imidazoline derivatives
Indirect acting a1 agonists
promotes release of NE from synaptic vesicles
NOTE absence of OH groups
targets presynaptic storage vesicles
Mechanism of action for indirect a1 agonists (story problem)
enters presynaptic neuron (active transport)
Disrupts storage vesicle
Causes NE release (into synapse, increases NE neurotransmission)
Mixed acting a1 agonists (direct and indirect)
Phenethylamine/Phenethanolamine derivatives
These agents have a direct effect at the post-synaptic a1-receptor and have an indirect effect
Presence of one OH group imparts some direct activity at the receptor
Which functional group is responsible for the direct effect of psuedoephedrine?
B OH
If a drug has a direct effect at the post-synaptic a1-receptor, then what should you observe?
binding +activation of receptor
a2 adrenergic receptors
decreased release and biosynthesis of NE
Increased uptake of NE into presynaptic neuron
2-amino imidazoline SAR
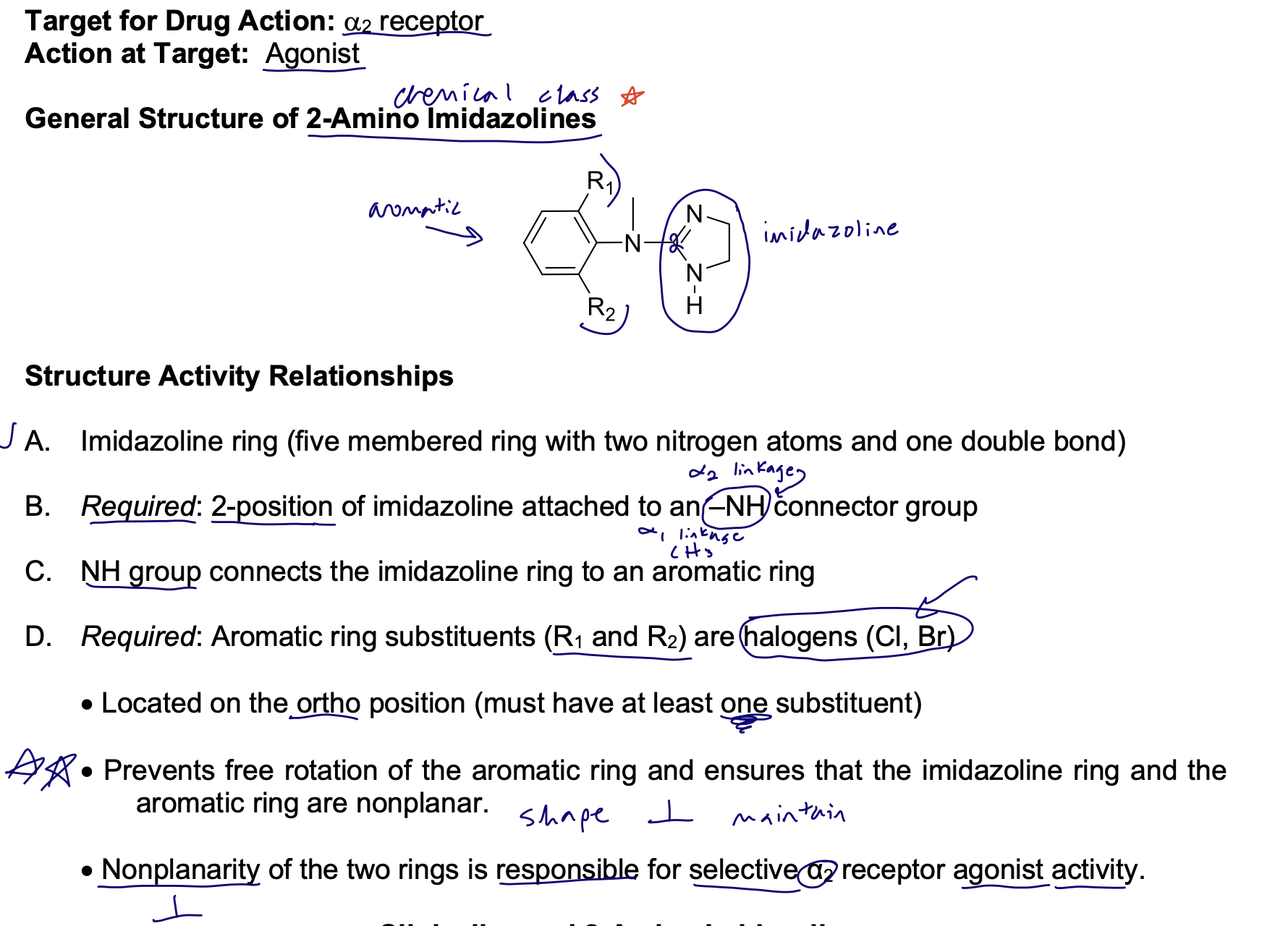
Agents are used as centrally acting antihypertensives
which form binds to receptors
IONIZED FORM
Which form of clonidine binds to receptor?
ionized form
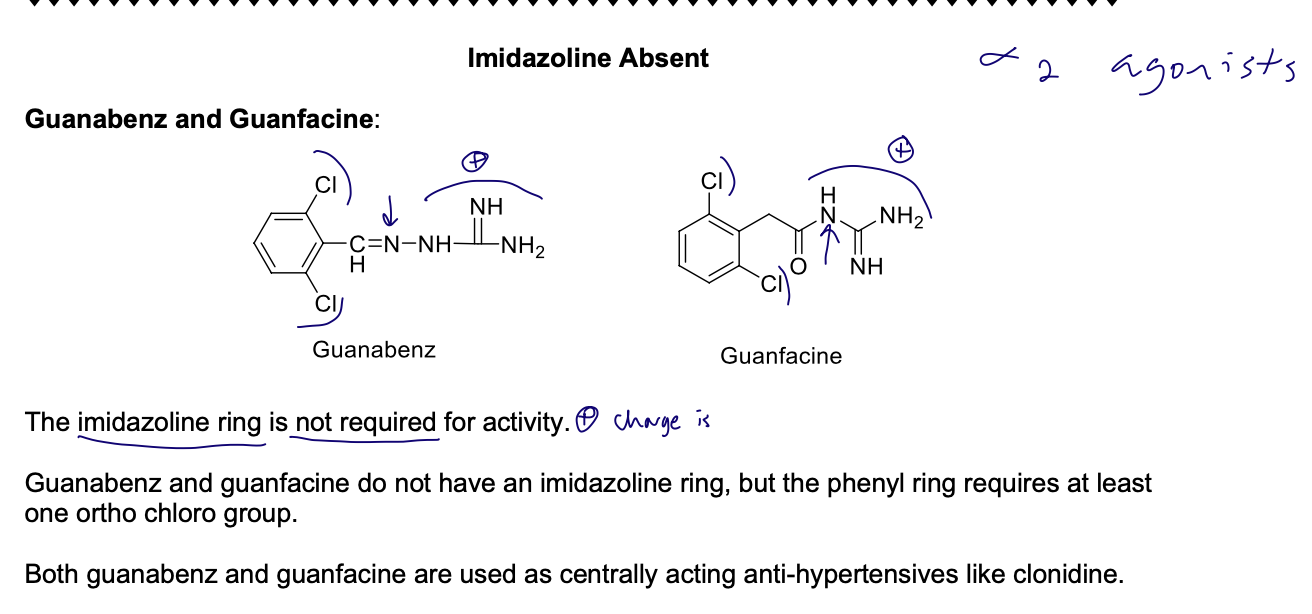
Imidazoline absent on a2 agonists