ICP Final
5.0(4)Studied by 178 people
Card Sorting
1/125
Last updated 5:20 PM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
1
New cards
chemistry
study of matter and energy
2
New cards
steps of the scientific method
1. Define the problem
2. Gather information
3. make a hypothesis
4. perform the experiment
5. analyze the data
6. conclusion
2. Gather information
3. make a hypothesis
4. perform the experiment
5. analyze the data
6. conclusion
3
New cards
independent variable
what you are testing; the thing being manipulated
4
New cards
dependent variable
what is being measured (changed by the independent)
5
New cards
control
the thing that stays the same
6
New cards
standard
a quality that people agree to use for comparison
7
New cards
scientific law
description of events in nature; WHAT happens
8
New cards
scientific theory
explanation of events in nature; WHY things happen
9
New cards
scientific model
representation of an object or event that can be used to understand the real thing (which may be too complex, small, or large to see)
10
New cards
science
observing, studying, or experimenting to find patterns in nature
11
New cards
technology
application of science usually resulting in an invention
12
New cards
Giga(G)
1 billion
13
New cards
Mega(M)
1 million
14
New cards
Kilo(k)
1000
15
New cards
Deci(d)
1/10
16
New cards
Centi(c)
1/100
17
New cards
Milli(m)
1/1000
18
New cards
Micro(µ)
1/1,000,000
19
New cards
Nano(n)
1/1,000,000,000
20
New cards
length
distance from one point to another (meter)
21
New cards
mass
the amount of matter in an object (gram)
22
New cards
volume(V)
the amount of space and object takes up (liter)
23
New cards
density(D)
the amount of matter in a given amount of space (mass/volume)
24
New cards
scientific notation
write a very large or small number as a power of ten (Ex: 750,000,000 = 7.5*10^8)
25
New cards
which variable goes on the x-axis?
independent variable
26
New cards
which variable goes on the y-axis?
dependent variable
27
New cards
accuracy
How close your measurement is to the real one (correct)
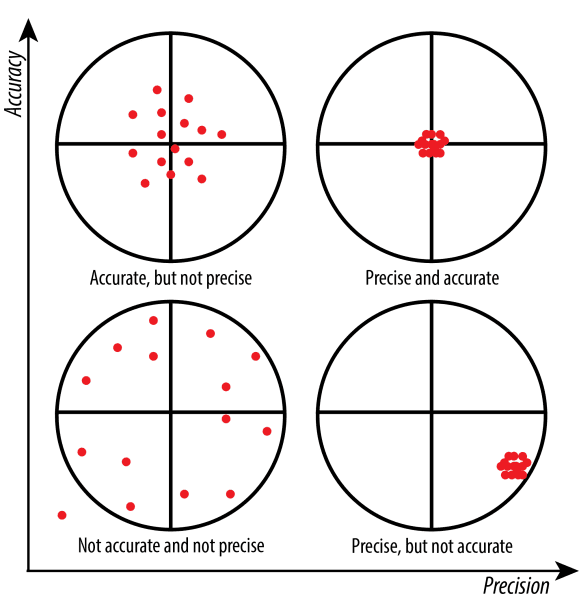
28
New cards
precision
how close your measurement is to other measurements made in the same way (repeatable)
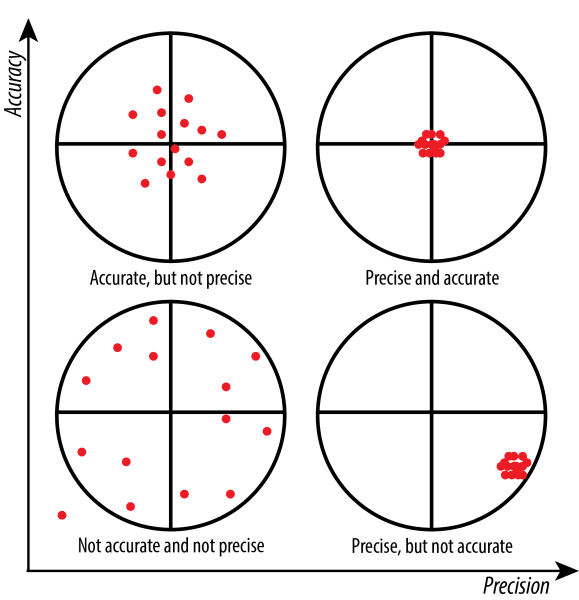
29
New cards
how do you add and subtract to correct sig figs? (1.2+2.53)
round answer to the left-most estimated digit (3.7)
30
New cards
how do you multiply and divide to correct sig figs? (125/5)
round answer to the least number of sig figs (30)
31
New cards
matter
anything that has mass and takes up space
32
New cards
pure substances
matter with a definite composition and definite properties
33
New cards
element
simplest form of matter
34
New cards
atom
the smallest particle of an element that still acts like that element
35
New cards
chemical symbol
shorthand way of writing the names of the elements
36
New cards
compound
2 or more elements that are chemically combined
37
New cards
molecule
the smallest particle of a substance that still acts like that substance
38
New cards
chemical formula
shorthand way of writing out compounds
39
New cards
mixtures
2 or more kinds of matter (pure substances) PHYSICALLY mixed together
-can be separated using physical properties
-no fixed ratio
-similar properties as substances in the mixture
-can be separated using physical properties
-no fixed ratio
-similar properties as substances in the mixture
40
New cards
homogeneous mixture
substances are spread out evenly (Ex: salt water, air)
41
New cards
heterogeneous mixture
substances are NOT spread out evenly (Ex: chocolate chip cookie, pizza, sand)
42
New cards
alloys
homogeneous mixtures of metals (Ex: bronze)
43
New cards
colloids
looks like particles are spread out evenly but aren't (Ex: butter, pearls)
44
New cards
suspension
particles that settle to the bottom (Ex: Italian dressing, hot chocolate)
45
New cards
physical properties
properties that can be observed with 5 senses and measured (Ex: color)
46
New cards
chemical properties
ability to react or the lack of ability (Ex: flammability)
47
New cards
intensive properties
does NOT depend on the amount (Ex: color, density)
48
New cards
extensive properties
depend on the amount (Ex: mass, volume)
49
New cards
physical change
-only a change in physical properties
-usually reversible
-Ex: melting, freezing
-usually reversible
-Ex: melting, freezing
50
New cards
chemical change
a process by which new substances are formed having new physical and chemical properties; not easily reversible (Ex: rusting, burning)
51
New cards
4 signs of a chemical change
1. bubbles (gas is forming)
2. heat or light (burning)
3. color change
4. precipitate (2 liquids become solid)
2. heat or light (burning)
3. color change
4. precipitate (2 liquids become solid)
52
New cards
steps for proving a calculation
1. write down the information given to you
2. write down the equation you are going to use
-use variables and move for the solved variable
3. substitute letters for units
4. answer
2. write down the equation you are going to use
-use variables and move for the solved variable
3. substitute letters for units
4. answer
53
New cards
melting point
temperature that a solid turns into a liquid
54
New cards
boiling point
temperature that a liquid turns into a gas
55
New cards
synthetic
man-made
56
New cards
solid
substance with definite shape and definite volume
57
New cards
liquid
substance with definite volume but no definite shape
58
New cards
gas
substance with no definite shape or volume; fills its container
59
New cards
plasma
similar to a gas but with charged particles (most common phase in the universe)
60
New cards
kinetic theory of matter
-all matter is made up of tiny particles in constant motion
-the higher the temperature the faster the particles move
-particles with less mass move faster
-the higher the temperature the faster the particles move
-particles with less mass move faster
61
New cards
thermal energy
higher temp. → particles move faster → more energy
62
New cards
movement in solids
particles are close together and vibrate in place
63
New cards
crystalline solid
particles are in a pattern (most common solid)
64
New cards
amorphous solid
particles are not in a pattern
65
New cards
movement in liquids
particles are close together but can slip past each other (flow)
66
New cards
viscosity
resistance to flow (high: molasses, glue ~ low: water, juice)
67
New cards
movement gas
particles move in a straights line until they collide with something and change directions
68
New cards
melting
solid → liquid
69
New cards
freezing
liquid → solid
70
New cards
vaporization
liquid → gas
71
New cards
condensation
gas → liquid
72
New cards
deposition
gas → solid
73
New cards
sublimination
solid → gas
74
New cards
endothermic phase change
requires energy to be added
-melting
-boiling
-evaporation
-sublimation
-melting
-boiling
-evaporation
-sublimation
75
New cards
exothermic phase change
releases energy
-freezing
-condensation
-deposition
-freezing
-condensation
-deposition
76
New cards
boiling vs evaporation
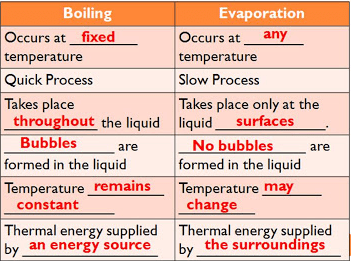
77
New cards
Archimedes Principle
the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object (duck)
78
New cards
Bernoulli's Principle
the pressure in a moving stream of fluid is less than the pressure in the surrounding fluid (hair dryer + ping pong ball)
79
New cards
Pascal's Principle
the pressure in a fluid is transmitted equally throughout the fluid (hydraulics)
80
New cards
pressure equation
F1/A1 = F2/A2
81
New cards
Boyle's Law
P1V1 = P2V2
82
New cards
Charles' Law
V1/T1 = V2/T2
83
New cards
Gay-Lussac's Law
P1/T1 = P2/T2
84
New cards
Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle
the location of an electron can only be described in terms of probabilities of where it might be located
85
New cards
protons(p+)
positive electrical charge
1 atomic mass unit(amu)
1 atomic mass unit(amu)
86
New cards
neutrons(n)
no electrical charge; neutral
1 amu (slightly larger than p+)
1 amu (slightly larger than p+)
87
New cards
electrons(e-)
negative electrical charge
1/1836 amu
1/1836 amu
88
New cards
Atoms are...
neutral; p+ = e-
89
New cards
Main energy levels
1,2,3,4,5,6,7
90
New cards
sublevels
s,p,d,f
91
New cards
s
1 orientation (max 2 e-)
92
New cards
p
3 orientations (max 6 e-)
93
New cards
d
5 orientations (max 10 e-)
94
New cards
f
7 orientations (max 14 e-)
95
New cards
orbitals
s p d f
1 1s
2 2s 2p
3 3s 3p 3d
4 4s 4p 4d 4f
5 5s 5p 5d 5f
6 6s 6p 6d 6f
7 7s 7p 7d 7f
1 1s
2 2s 2p
3 3s 3p 3d
4 4s 4p 4d 4f
5 5s 5p 5d 5f
6 6s 6p 6d 6f
7 7s 7p 7d 7f
96
New cards
Al
Aluminum
97
New cards
C
Carbon
98
New cards
Cl
Chlorine
99
New cards
H
Hydrogen
100
New cards
Mg
Magnesium