Chapter 1: Brain imaging, lesion, brain as models
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
EEG
Electrodes on the scalp; subject performs perceptual task
Map signal strength over time across cortex (not pinpoint where)
Only detect cortex (can’t detect anything below cortexes)
Sleep disorders, epilepsy, can tell only see overall state of brain, like seizure
The only direct tool (tracks brain activity—measuring voltage changes)
Good temporal resolution, poor spatial resolution
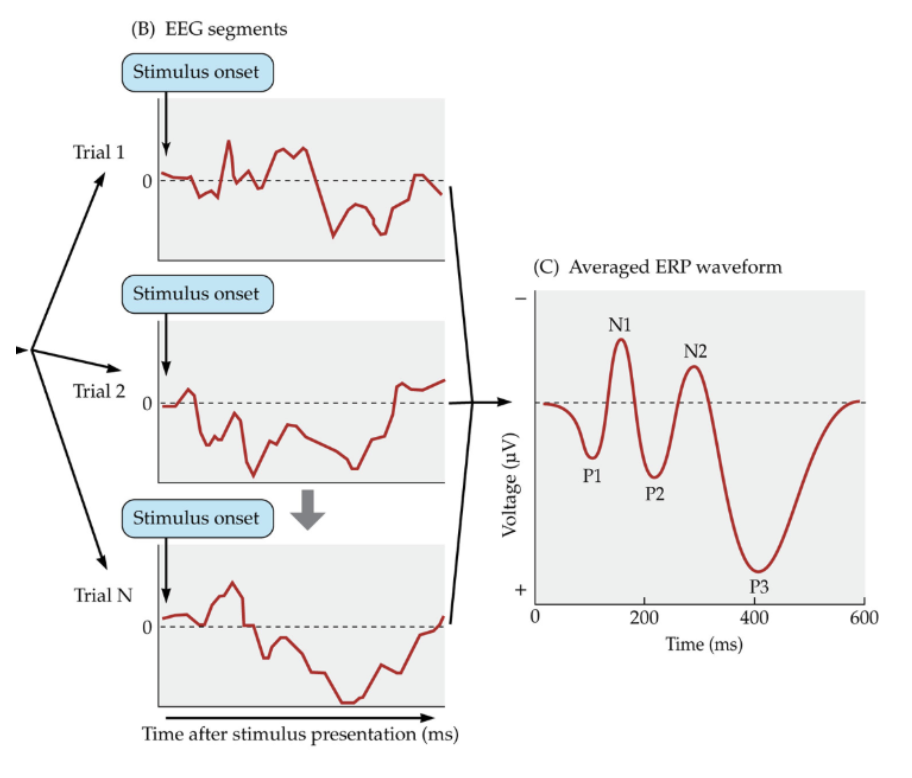
Event-related potential (ERP)
The averaged waveform from averaging all the brain responses aligned the the moment that the stimulus was present
MEG
measures magnetic fields created by the flow of ion currents between neurons when a neuron fires
High temporal resolution
Use with MRI for good spatial resolution
Difficult to measure signals deep in brain
PET
radioactive tracer injected into participant → as tracer decays, positrons are emitted and picked up by scanner → areas of high radioactivity are associated with neural activity (based on blood flow)
good for studying disease or brain chemicals; poor spatial resolution, but can be improved if used with MRI; invasive procedure (cocaine, glucose)
MRI
Large magnet obtains high res images of body based on differences in water content
Detects magnetic force → measure a signal that indicates the presence of specific elements in the tissue
Overlay plot (bringing a lot of ppl with the overlapping damage → take all the structural MRI images and overlay them on top of one another to see the ppl’s common damages, common loss)
fMRI
Detects changes in oxygenation (blood-oxygen level)
BOLD signal (takes a few secs, that’s why temporal resolution is slower than EEG & MEG)
When a brain region becomes more active, neurons need more high oxygen blood (and glucose in blood)
Non-invasive procedure
Best spatial resolution, poorer temporal resolution
Animal lesion studies (MT and V4)
MT lesion, but not V4 lesion, disrupts motion perception
V4 lesion, but not MT lesion, disrupts color perception
Human clinical studies
E.g. specific type of speech deficit based on location of lesion in left hemis
Damage to Broca’s area interferes w production of speech
Damage to Wernicke’s area interferes w understanding speech
Brain as Mathematical model
Based on giant squid axons study in 1950s
Describe how action potentials in neurons are initiated and propagated
Use math lang, concepts and equations to closely mimic psychological and neural processes w math precision
Brain as Computational models
programed to process step-by-step in perceptual or cognitive process.
Brain as Statistical optimization models
Stats we have amassed through perceptual exp, like the experience of holding a pencil or listening to someone speak
Used to make some aspect of perception function at its best
Efficient coding & max likelihood est
Efficient coding model
Maximize information transmission with minimal redundancy (economically encode the world)
E.g. Do I need to code this pixel in the view from the purple boat
Maximum likelihood estimation
estimation optimizes outcomes by integrating multiple information sources and cues, favoring reliable ones
E.g. Which boat’s view gives a more reliable estimation of the distance from Green island to Blue Island (ans. Red boat)
Bayesian models
Use past experiences to interpret current sensory input, predicting future events and adapting to reduce prediction errors
Deep neural networks (DNNs)
Mimics human biology and strengthens or weakens connections between computational units over time.
Artificial neural networks are made of many nodes, where each node mimics the functioning of a human neuron.
Nodes are arranged in layers and layers are massively interconnected.
Each connection between nodes has a weight which reflects the excitatory or inhibitory relationship between the nodes.
The network learns over time, either with or without supervision and feedback.
Influence of Prior Knowledge and Context
DNNs can perform like humans, but may not model the way humans perform tasks, so the process is not always explainable .
Our physical surrounding is influenced by past and current experience .
Perception fills in with statistical guesses, rules of thumb, and expectations creating perceptual illusions, individual differences, and failures