Unit 1 Section 3, Neuroanatomy and Neurophysology
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Action Potential: Threshold
The strength of a signal measured in +mV. Necessary to trigger an all-or-none action potential response in a neuron
What does the Na-K ion pump do in a cell?
Uses active transport (Energy expanded in the form of ATP) To move Na ions out and K ions in
Passive transport
Ions diffuse through the cell membrane along the concentrated gradient (higher to lower) and no energy is expanded
Spatial summation
Multiple sub-threshold stimuli, in CLOSE PHYSICAL PROXIMITY to a neuron, add up to produce an action potential
Temporal Summation
When multiple sub-threshold stimuli that are close together IN TIME ADD UP to produce an action potential.
What does overshoot mean
Depolarization
What does Undershoot mean
Repolarization
What is the correct distribution/concentration of ions during resting membrane?
More sodium in the extracellular space, more potassium in the intracellular space.
Absolute refractory period
A new action potential cannot be indicated, no matter how strong the stimulus signals.
Efferent pathway
Carries motor information from the brain to the body
Relative Refractory Period
Occurs when the neurons membrane status returns to (at least) 51% restored to resting membrane potential.
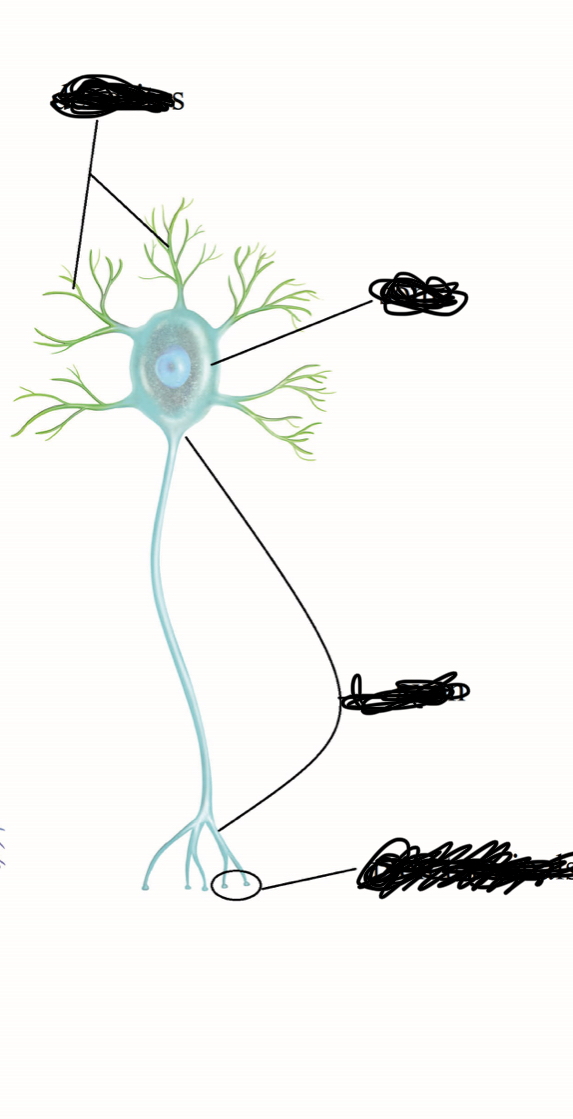
What type of cell is this?
Neuron
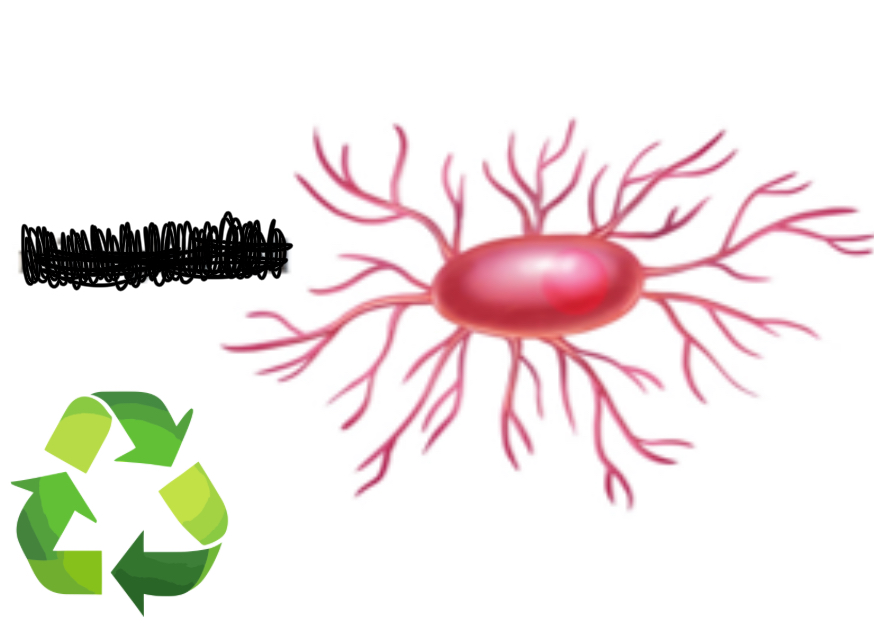

What type of cell is this?
Microglial Cell
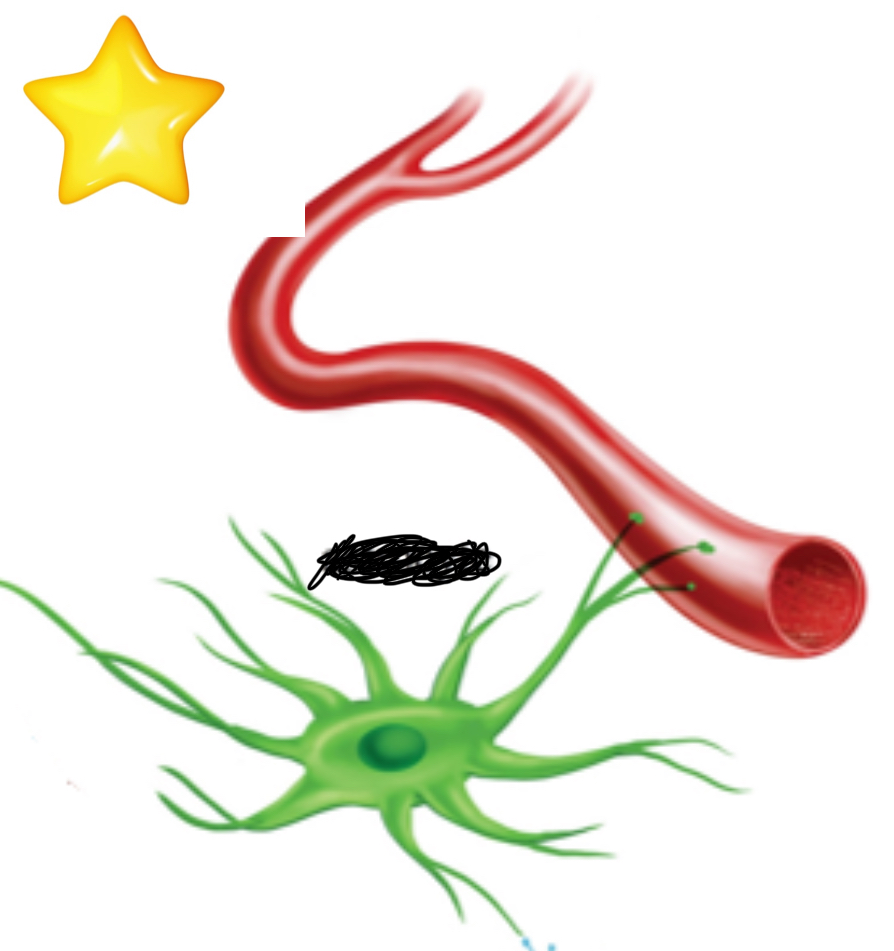
What cell is this?
Astrocyte
What do Astrocytes do?
Anchors neurons to blood supply, barriers around synapses
What does a neuron do?
Processes and transmits cellular signals inside the brain
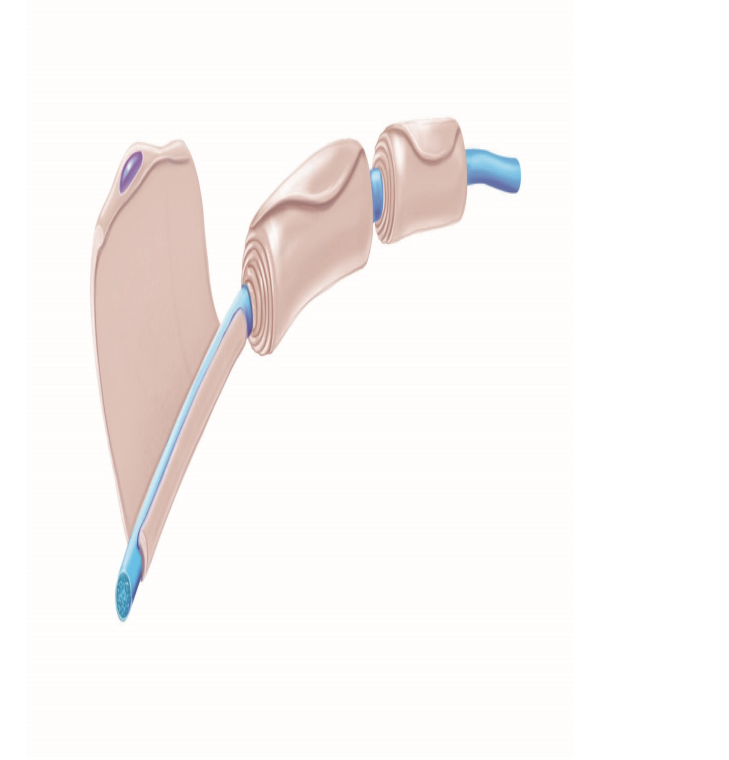
What cell is this?
Myelin Cell
What does a Myelin Cell do?
Wraps around nerves, protects them
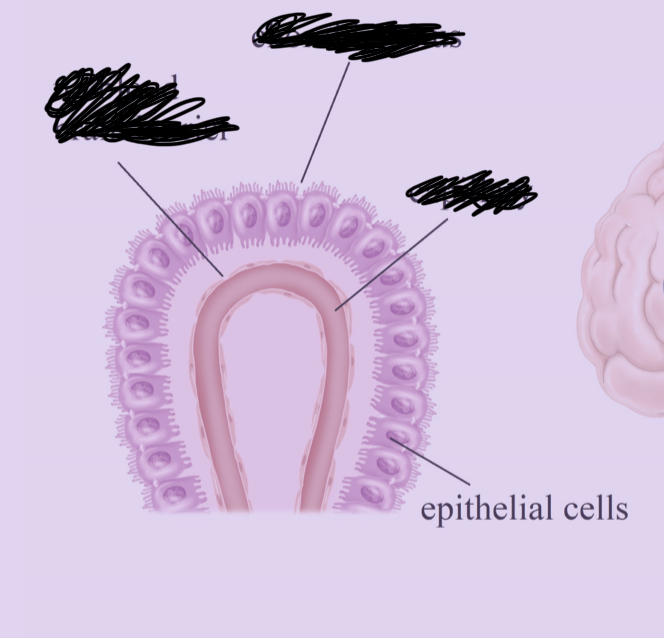
What cell is this?
Ependymal cell
What do ependymal cells do?
Produces cerebrospinal fluid
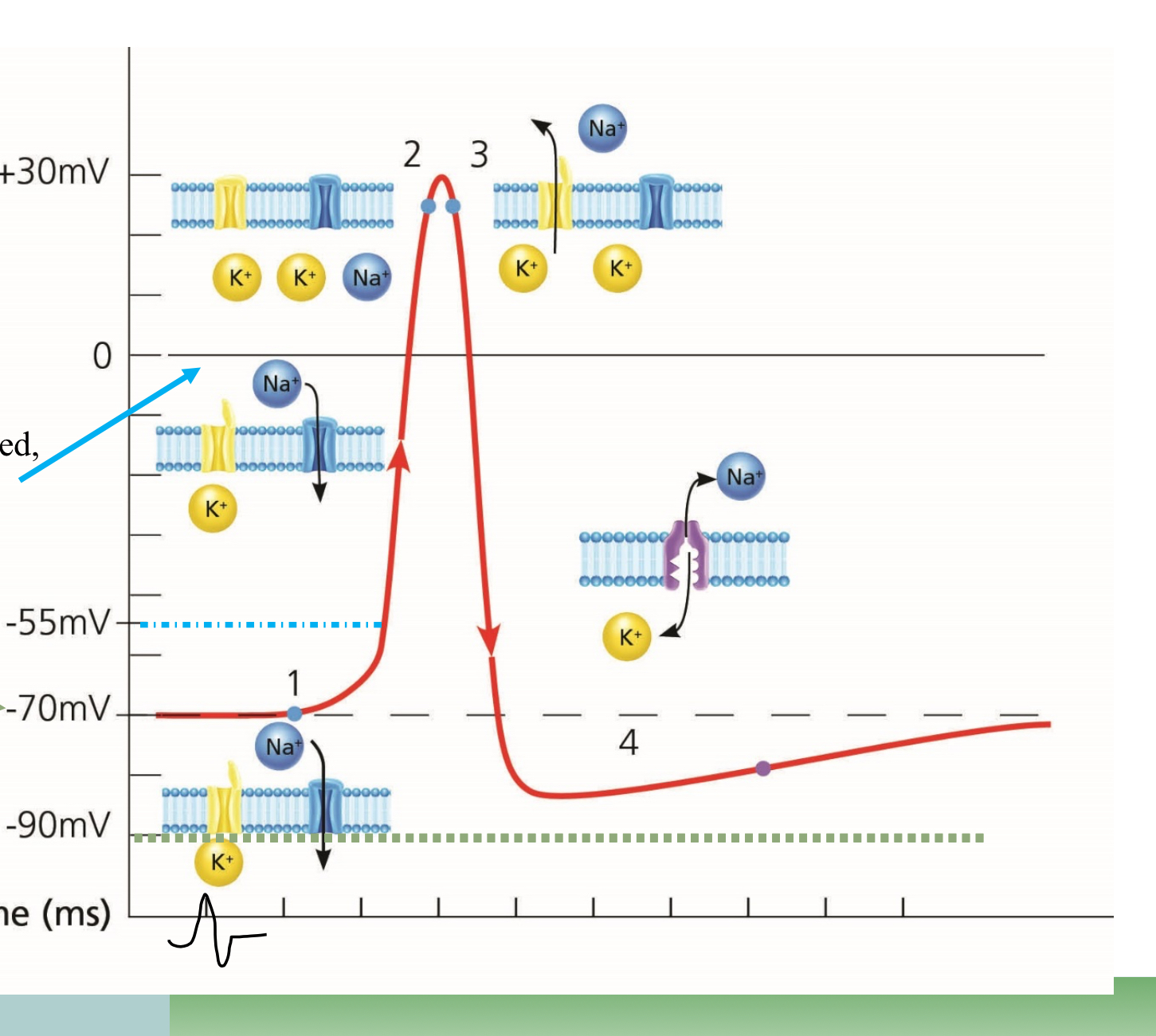
What point is #1 on the graph?
Resting
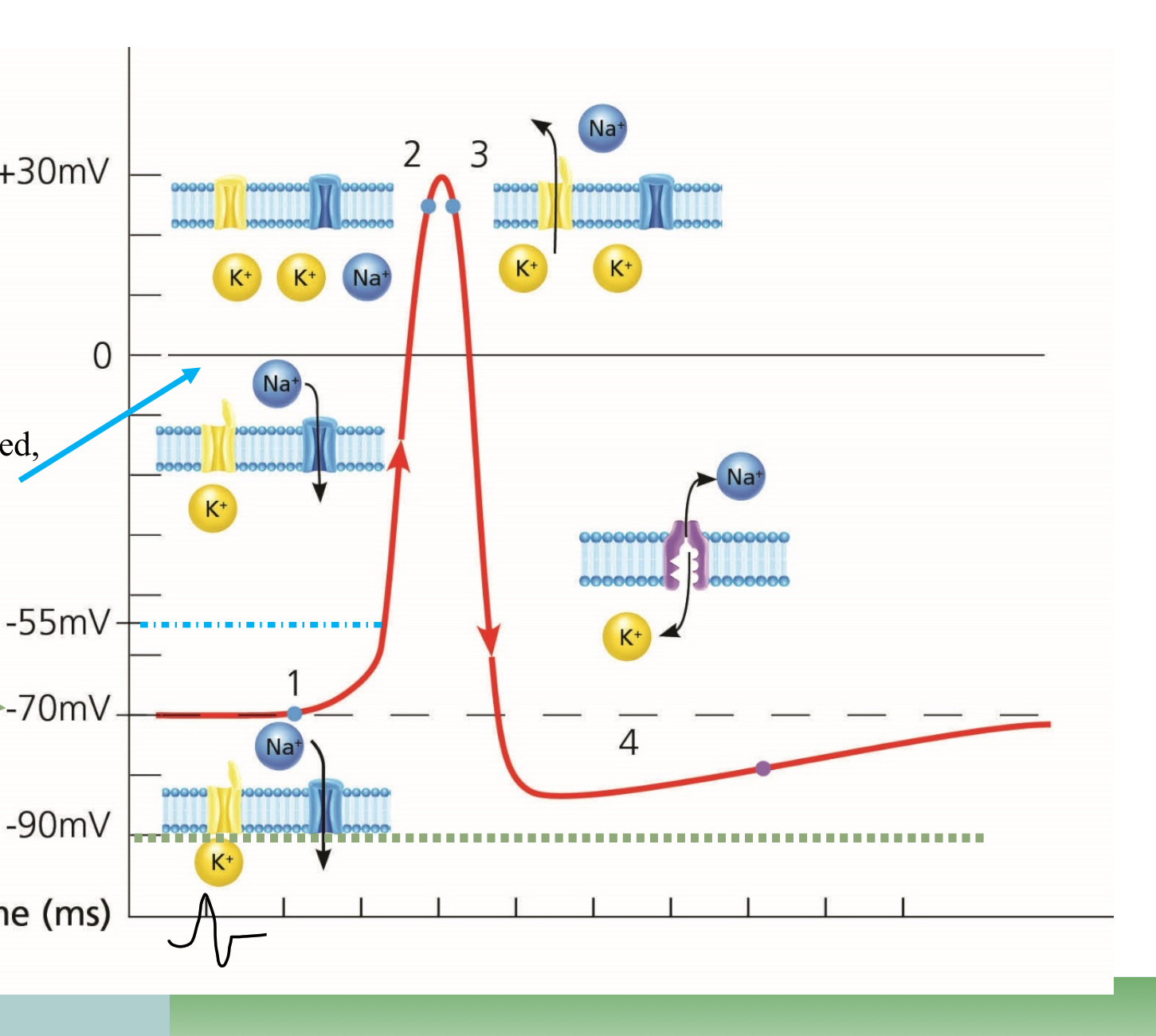
What point is #2 on the graph?
Depolarization
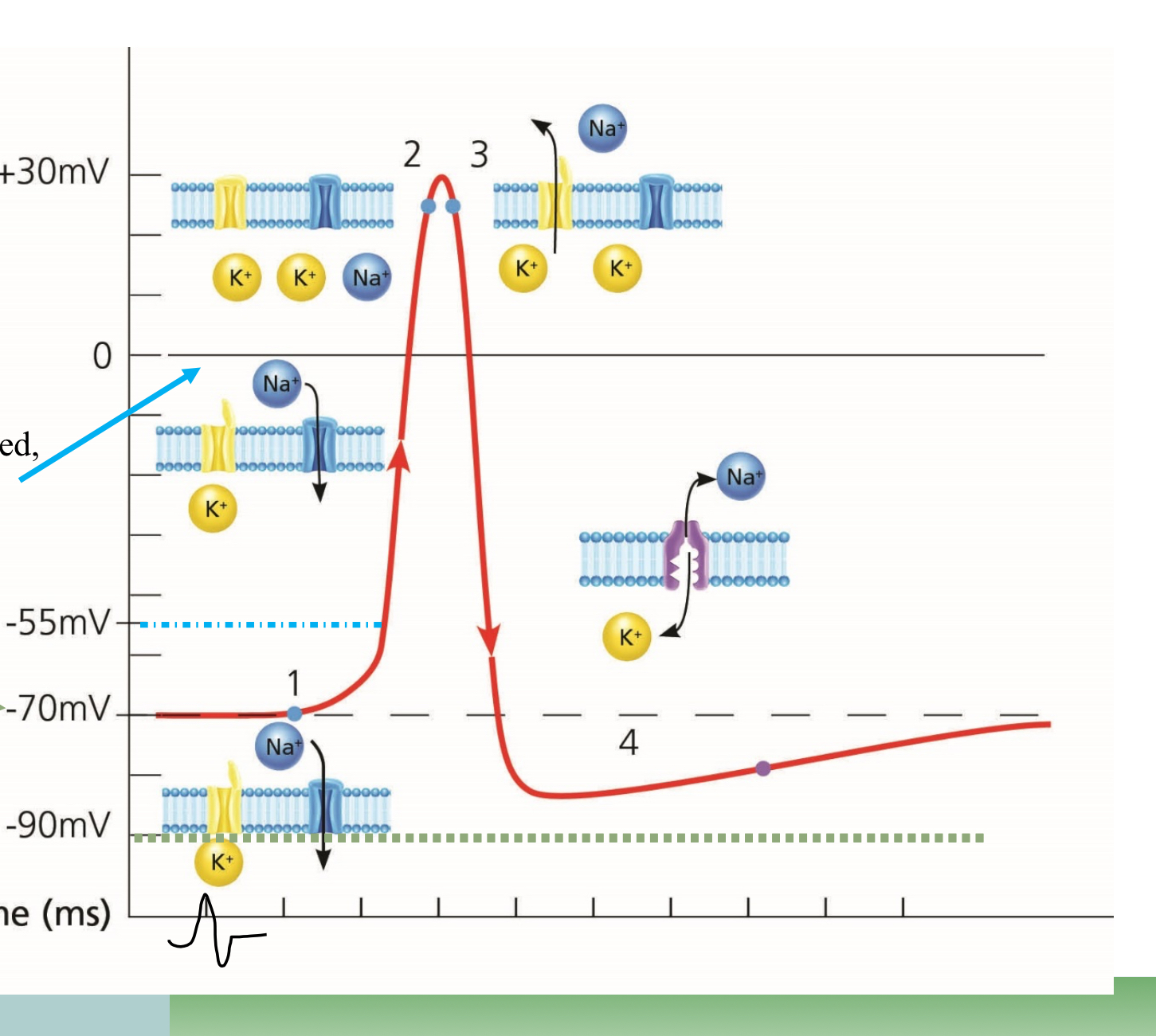
What point is #3 on the graph?
Repolarization
What happens at the top point of the graph, in the middle
Overshoot, too much Na
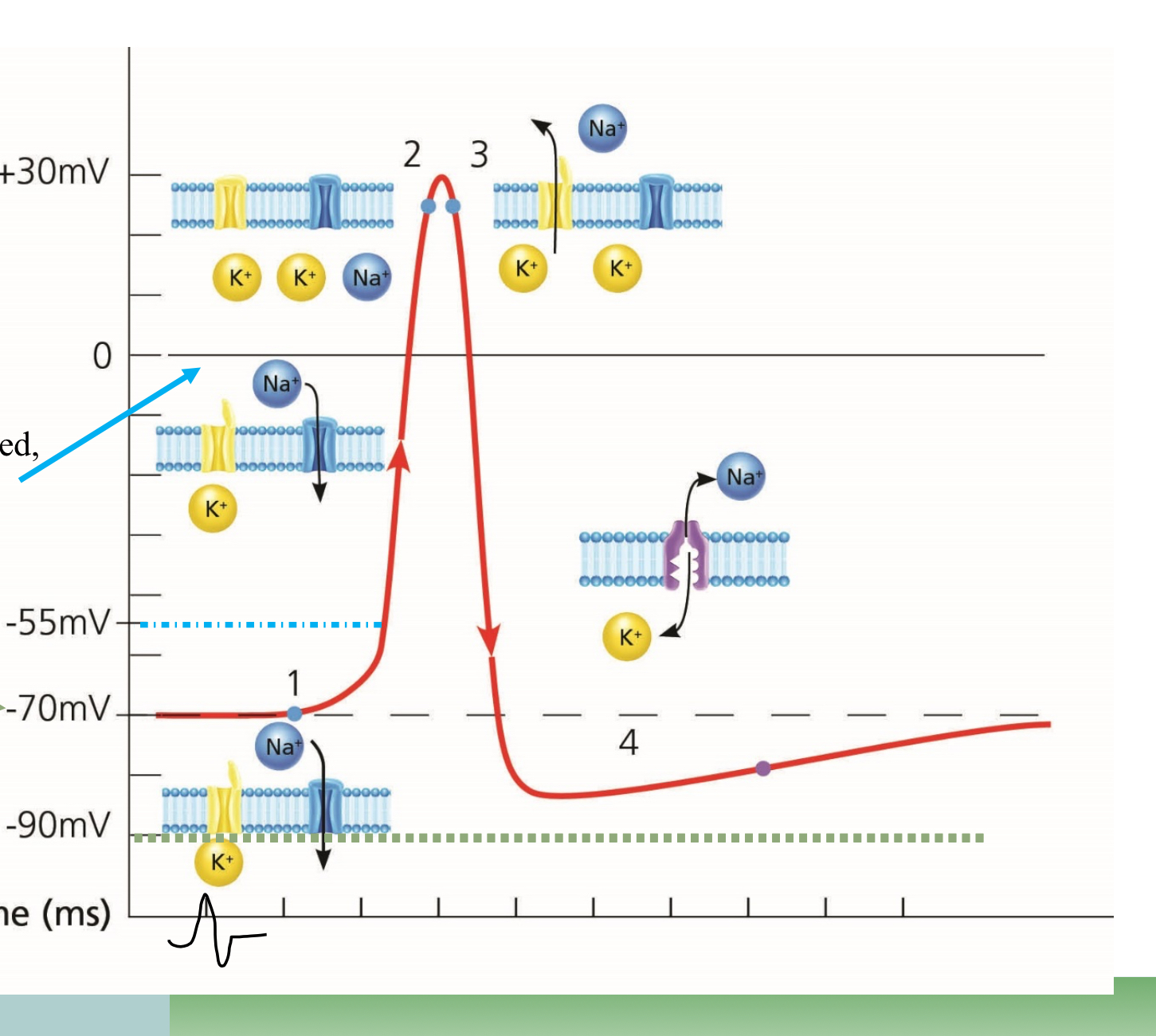
What happens at the lowest point before #4
Undershoot, too much K
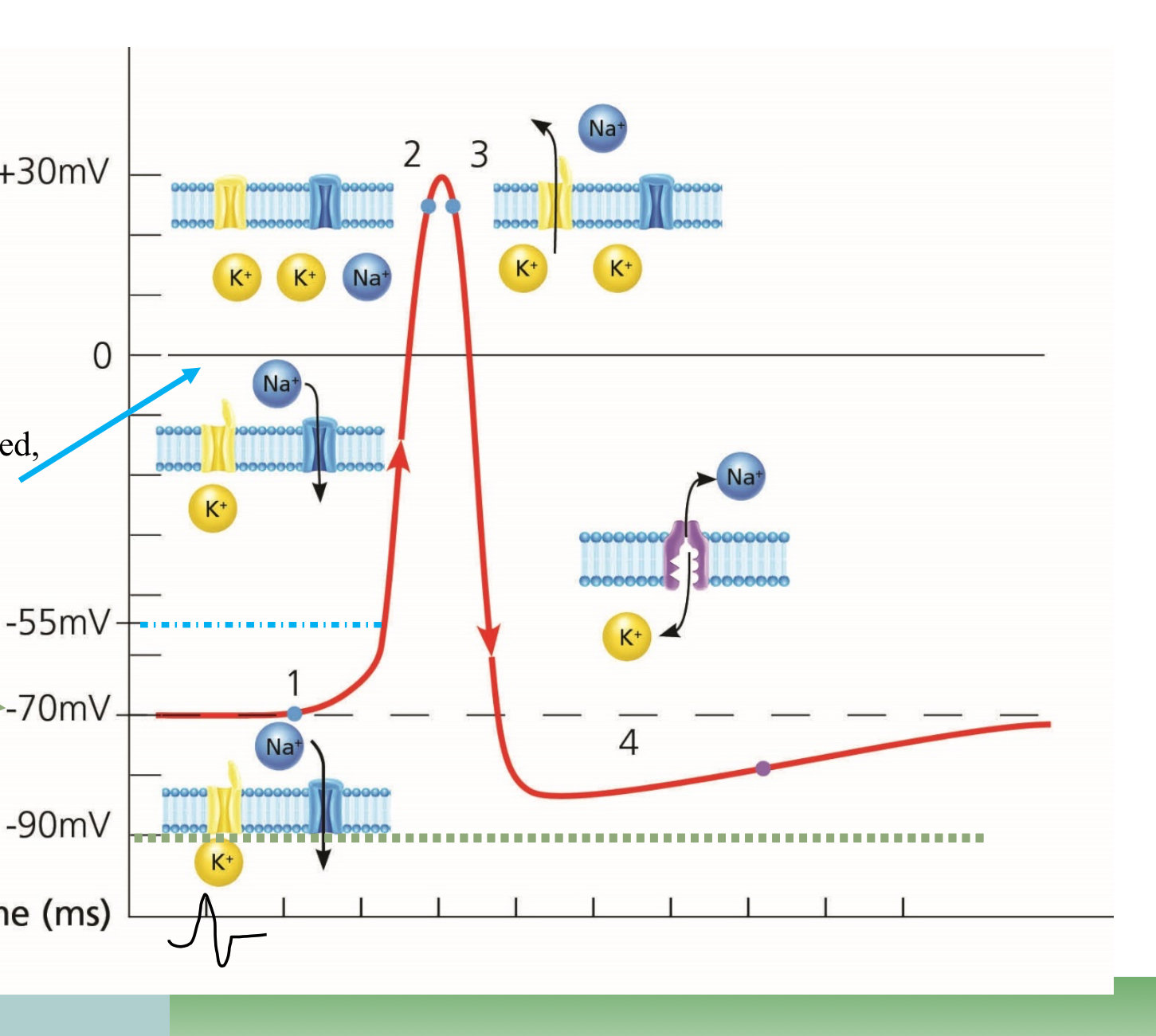
What happens in the space before #4
Absolute refractory
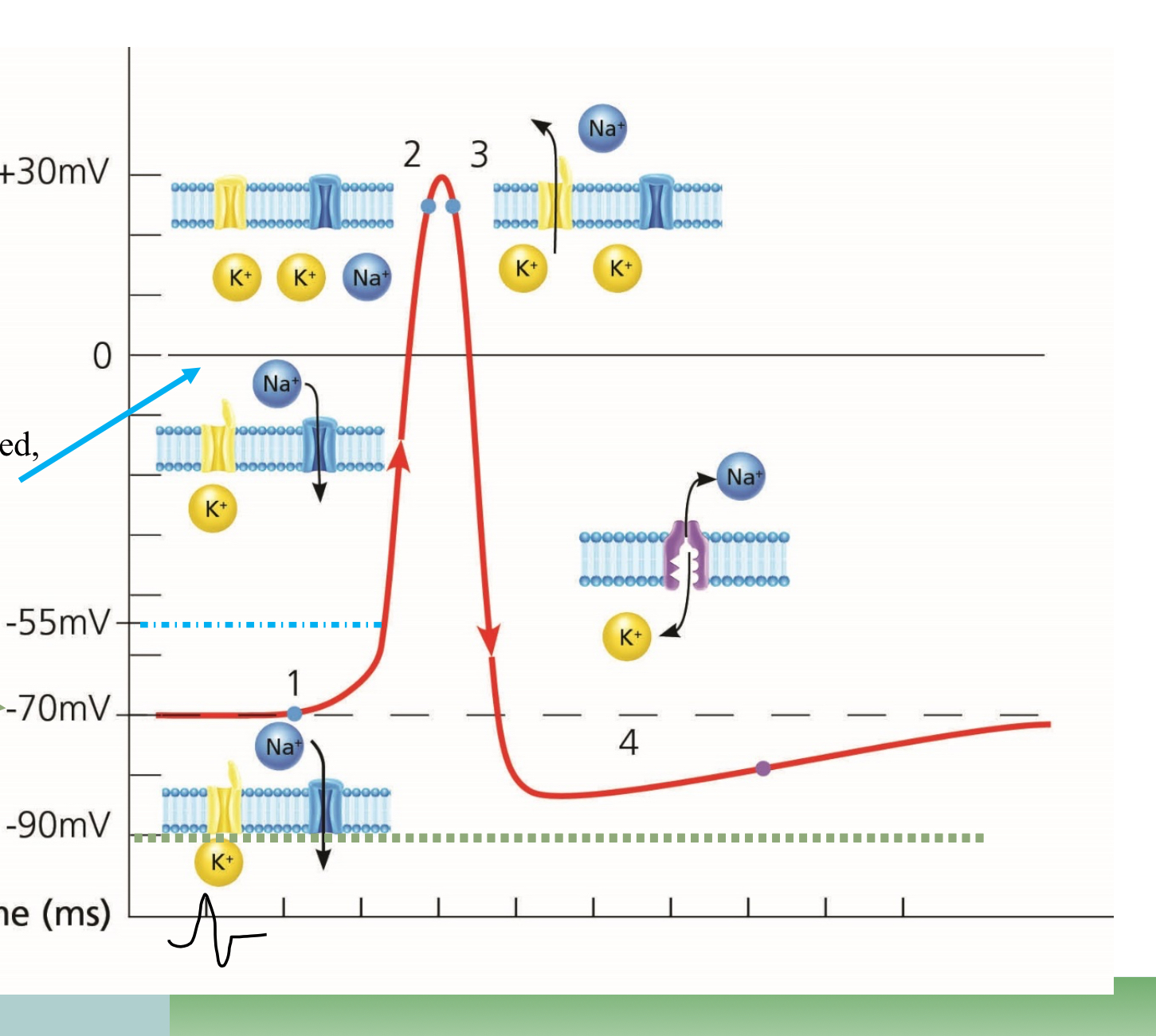
What happens at #4
Relative refractory
Which ions are more present outside the cell
Na
What ions are more present inside the cell
K
Which way does Sodium move during Depolarization
Into the cell
Which way does Potassium move during repolarization?
Outside of the cell