reaction rates and equilibrium
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
How does pressure effect rate of reaction?
only in gases
-higher pressure increases rate, more particles in the same volume, more frequent collisions
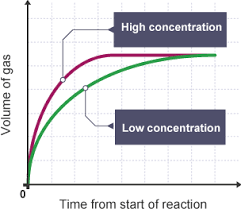
how does concentration effect rate of reaction?
-increased conc. increases reaction rate, more particles in same volume, more frequent collisions BETWEEN REACTANT PARTICLES
-graph levels off earlier
how does temperature effect rate of reaction?
-increased temperature increases rate
-reactant particles gain kinetic energy, move around faster, collide more frequently
-more particles exceed activation energy, more successful collisions
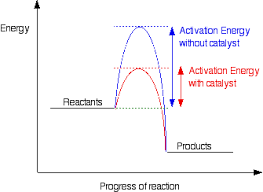
What's the role of a catalyst?
increases rate of chemical reaction
offers alternative pathway
with a lower activation energy
so more molecules exceed activation energy
remains unchanged
Whats the benefit of using catalyst (iron) in terms of economical importance in haber process
-less energy needed, reduces energy costs
-carried out at 200 instead of 400 atmospheres as there's a safety risk of explosions and it's uneconomical
-carried out at 450 degrees C, reduces equilibrium yield as forward reaction exothermic but increases rate or reaction
compromise between chemical equilibrium and reaction rate
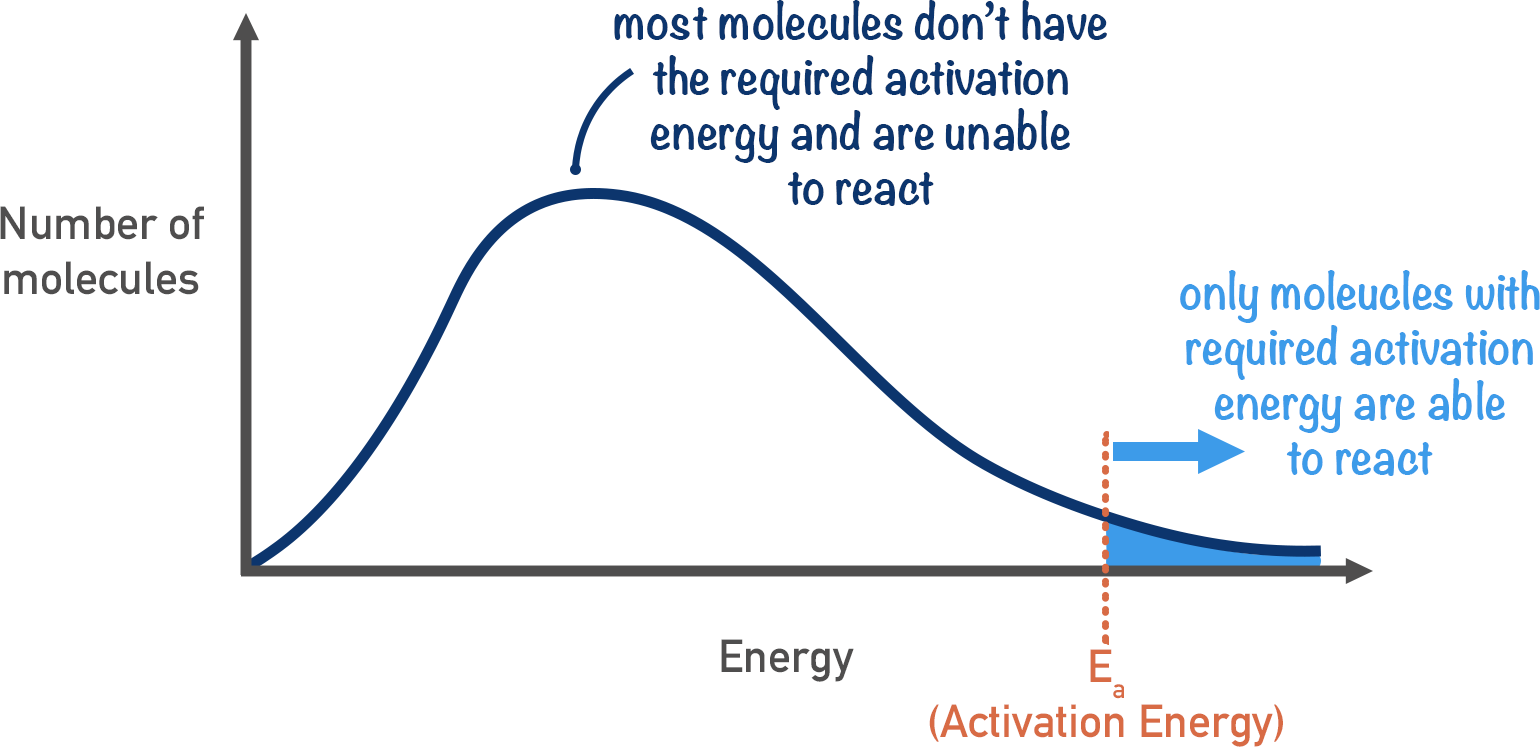
Whats the boltzmann ditribution
-peak is most probably energy
-mean energy of molecules is greater than most probably energy
-area under curve = number of particles
-graph doesn't touch x-axis at the end as there's no maximum energy that a particle can have
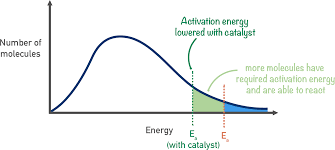
how does temperature/catalyst effect boltzmann distributuion
-as temperature increases, peak lowers and shifts to the right as more particles exceed activation energy
-GREATER AREA UNDER CURVE ABOVE Ea
-catalyst just lowers Ea
What's dynamic equilibrium?
in closed system
rate of forward reaction = rate of reverse reaction
concentrations of reactants and products remain constant
both reactions still take place
what's the equilibrium law
Kc (equilibrium constant)
bigger number means position of equilibria lies more on the right
ONLY AFFECTED BY TEMPERATURE, NOT PRESSURE
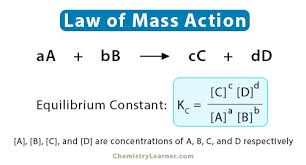
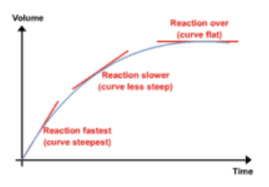
Describe how rate of reaction changes as time goes on
-rate is highest at the start, highest conc. of reactant particles, most frequent collisions
-rate decreases as products form and conc. of reactants decreases, less frequent collisions between reactant particles
-reactant stops when all of one reactant is used up (limiting reactant)
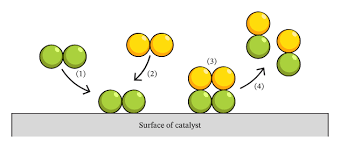
How does a catalyst work?
-reaction takes place on surface of catalyst
reactant molecules form weak temporary bonds with surface of catalyst at the expense of their existing bonds getting weaker
- 2 molecules collide on surface of catalyst, bonds break more easily
how does increasing pressure effect position of equilibrium in haber process (N2 + 3H2 = 2NH3)
system acts to decrease pressure
forward reaction favoured as less gas molecules on the right
position of equilibrium shifts to right
equilibrium yield of ammonia increases
how does increasing temperature effect position of equilibrium in haber process (forward reaction exothermic)
system acts to decrease temperature
reverse reaction favoured as it's endothermic
position of equilibrium shifts to the left
equilibrium yield of ammonia decreases
RATE of ammonia forming INCREASES
What happens to rate of reaction if you use a weaker acid?
-decrease
-less H+ ions solution PARTIALLY DISSOCIATES
-less reactant particles
-less frequent collisions
Why is the use of catalysts in industrial processes important for the environment?
-can carry out reaction at lower temperatures
-lower energy demand
-less burning/combustion of fossil fuels
-less CO2 made
quantities to monitor rate of reaction
concentration decrease, mass decrease, volume increase