06.3C U6P1 (PART C) Contraction of Skeletal Muscle (ONLY)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Stimulated Membrane (Muscle)
Acetylcholine binds to sodium channels which results in an influx of sodium ions.
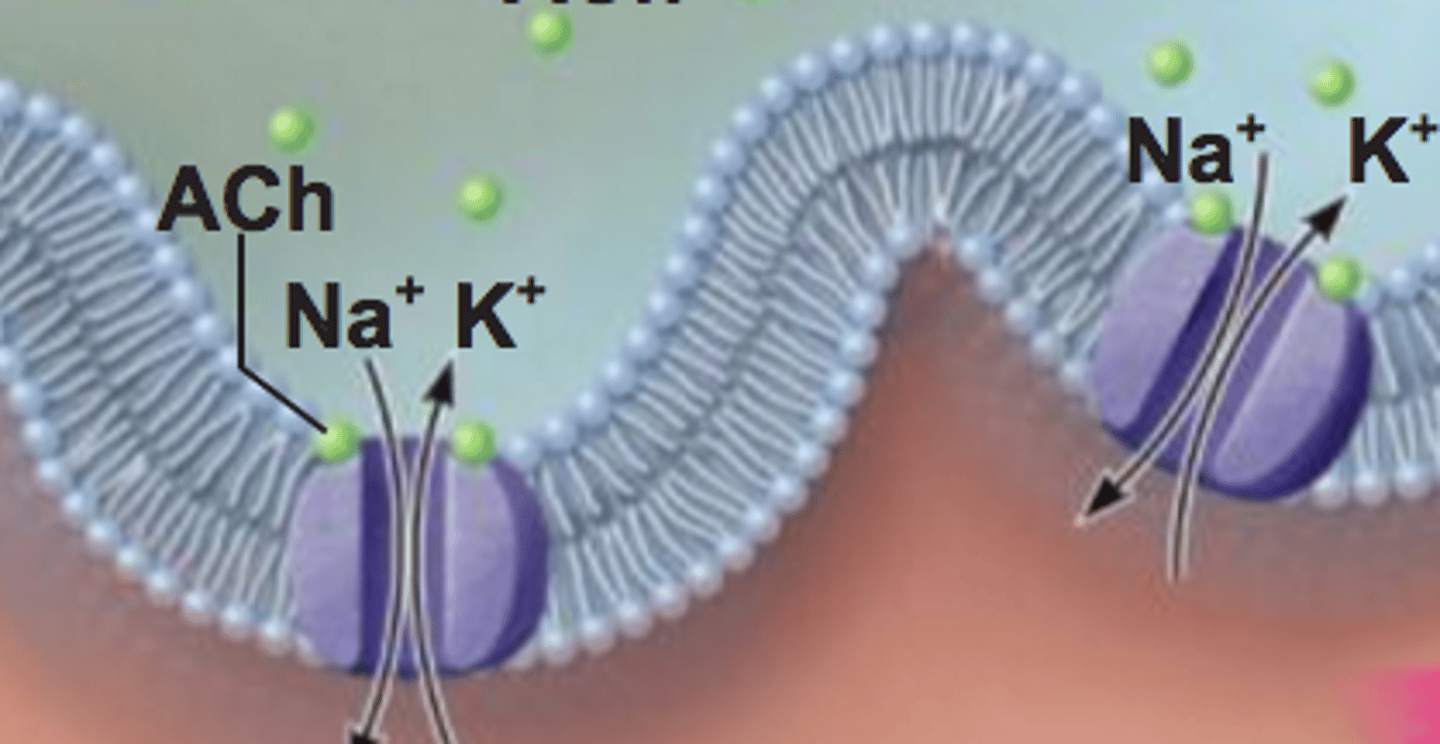
Depolarized Membrane (Muscle)
Sodium channels open allowing sodium to rush INTO the cell via facilitated diffusion that causes the membrane to become more positive on the inside than on the outside
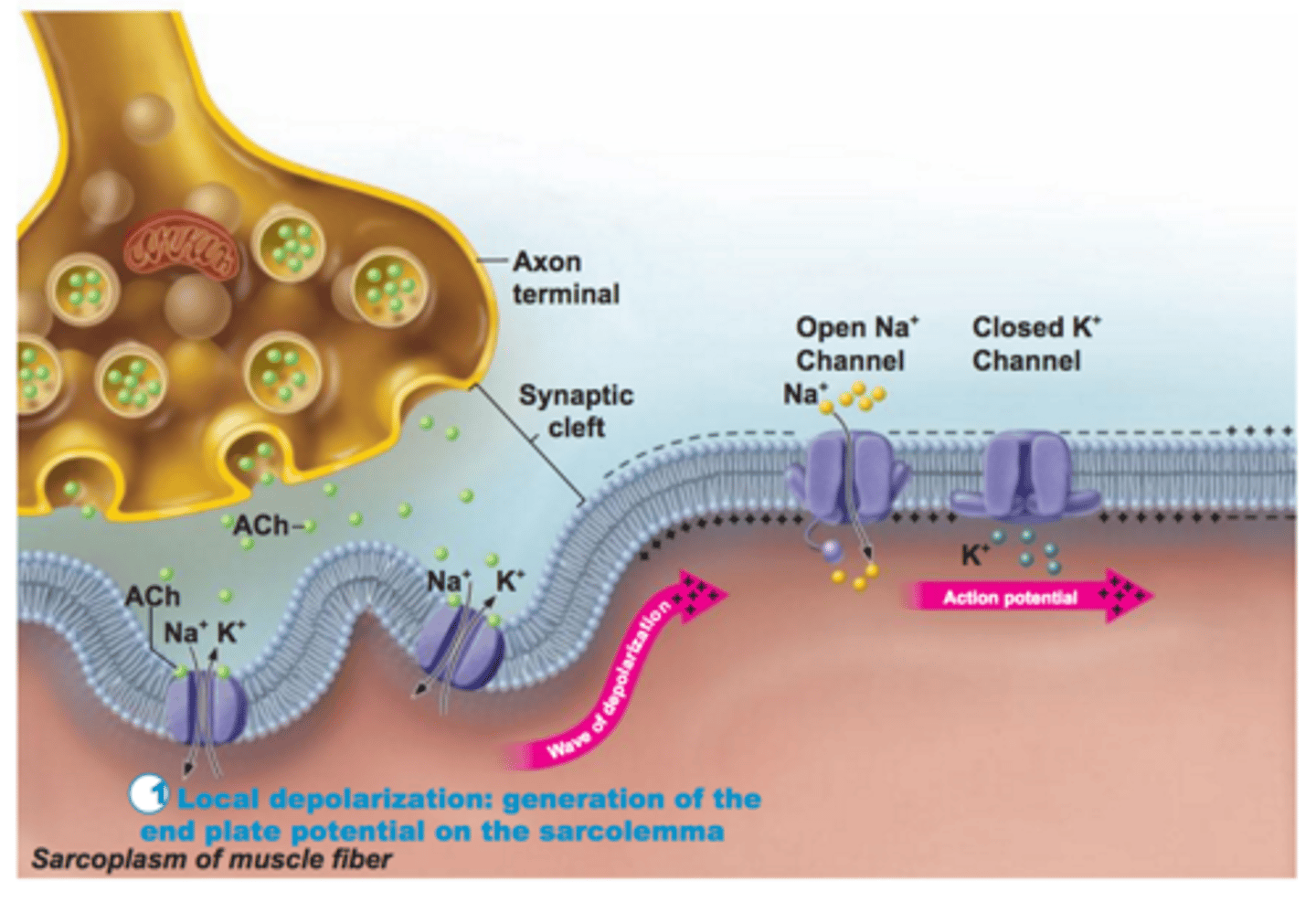
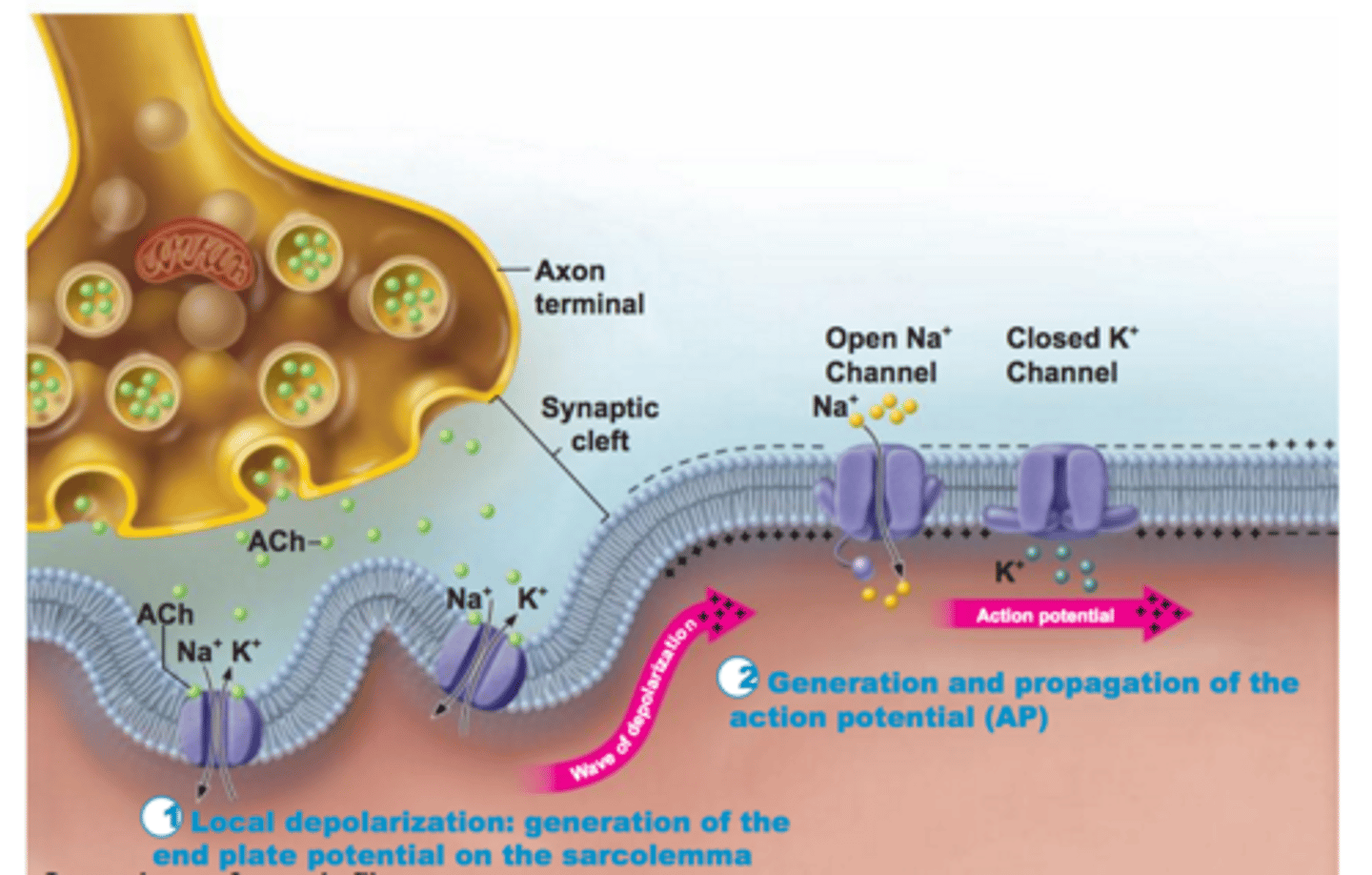
Propagation of an Action Potential (Muscle)
Occurs when sodium ions flood into the muscle fiber triggering the opening of additional sodium channels along the membrane resulting in a more positive charge inside the cell than outside the cell
Calcium ions
A type of ion that initiates the release of neurotransmitters from synaptic vesicles and also initiate muscle contractions by binding to troponin and causing troponin to pull on tropomyosin which exposes the active site on actin.
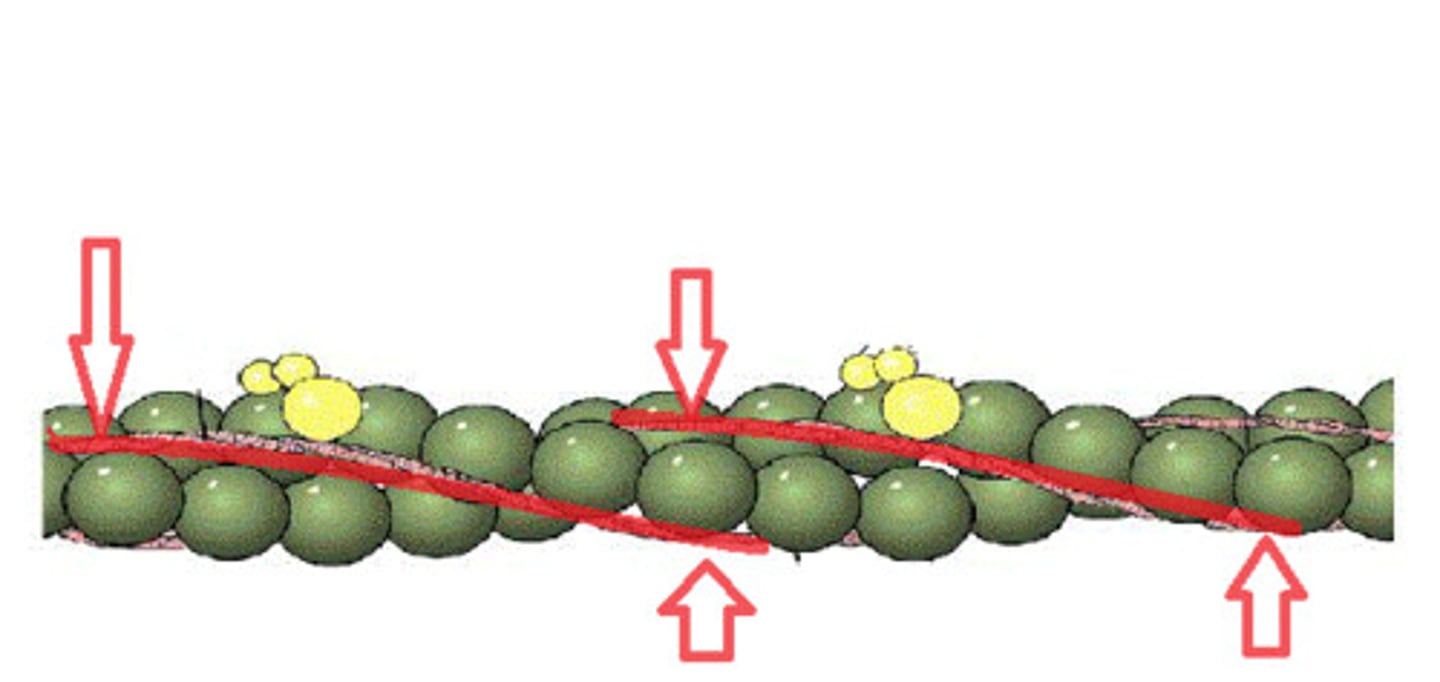
Actin
A thin globular protein that consists of two strands of proteins wound around each other (look like two strands of pearls)
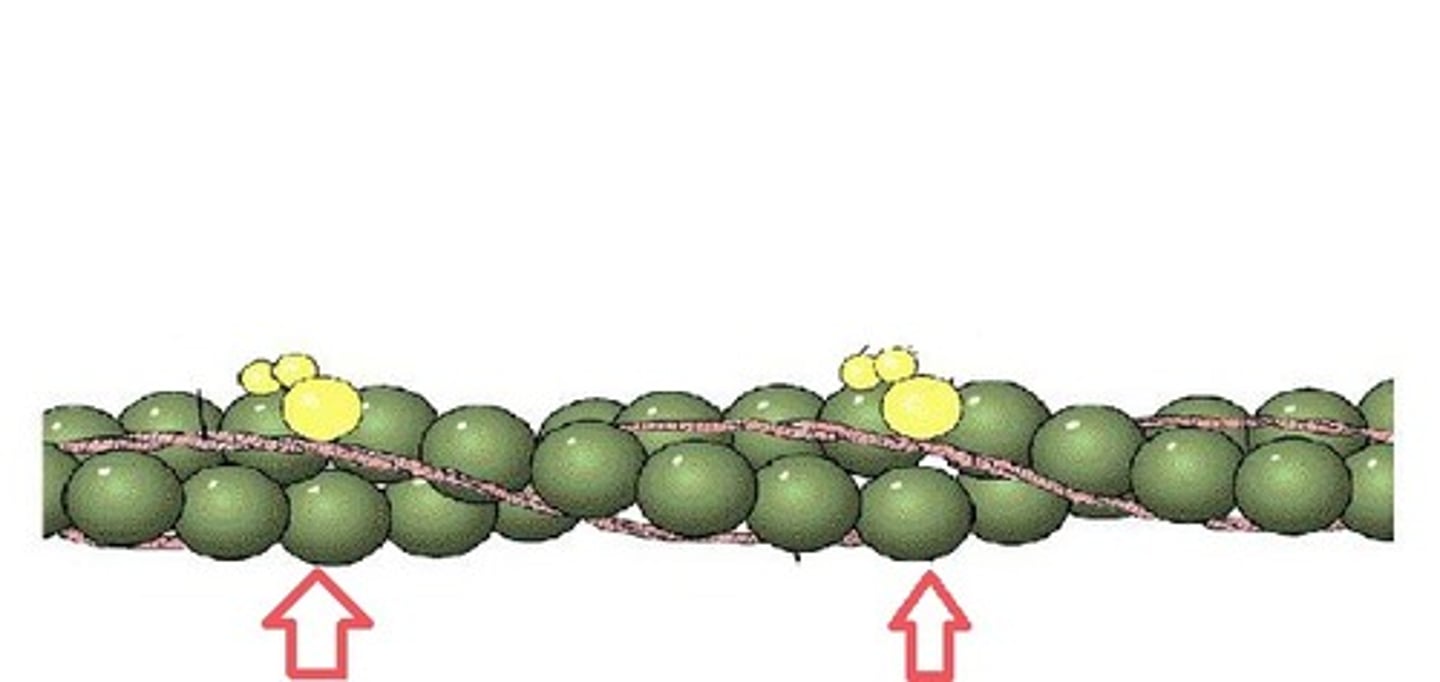
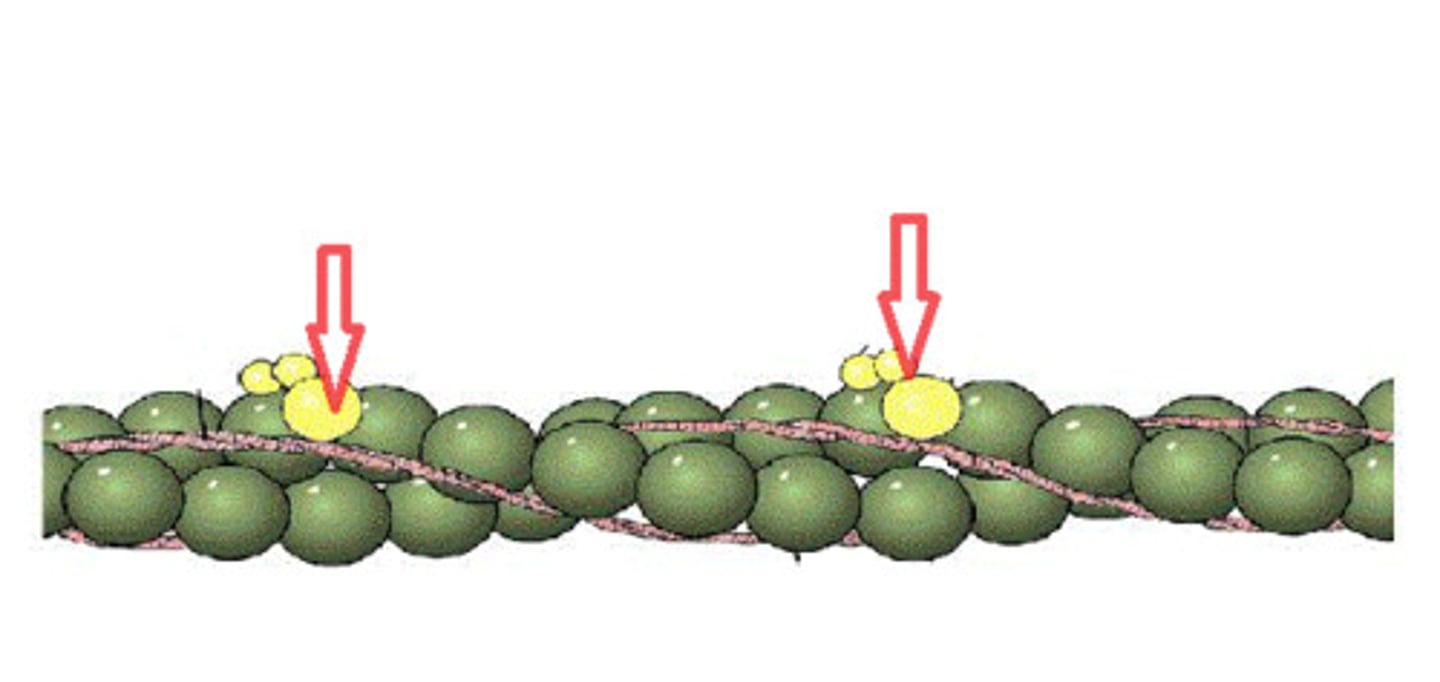
Myosin
A thick globular protein with paddle-like extension that contains binding sites for actin and ATP
Troponin
A globular protein that is associated with tropomyosin as part of the thin filament of the sarcomere that covers the binding sites on actin; provides a binding site for calcium ions which cause tropomyosin to swivel and expose active sites on actin
Tropomyosin
A regulatory protein that, on a resting muscle fiber, covers binding sites along actin, preventing actin and myosin from interacting
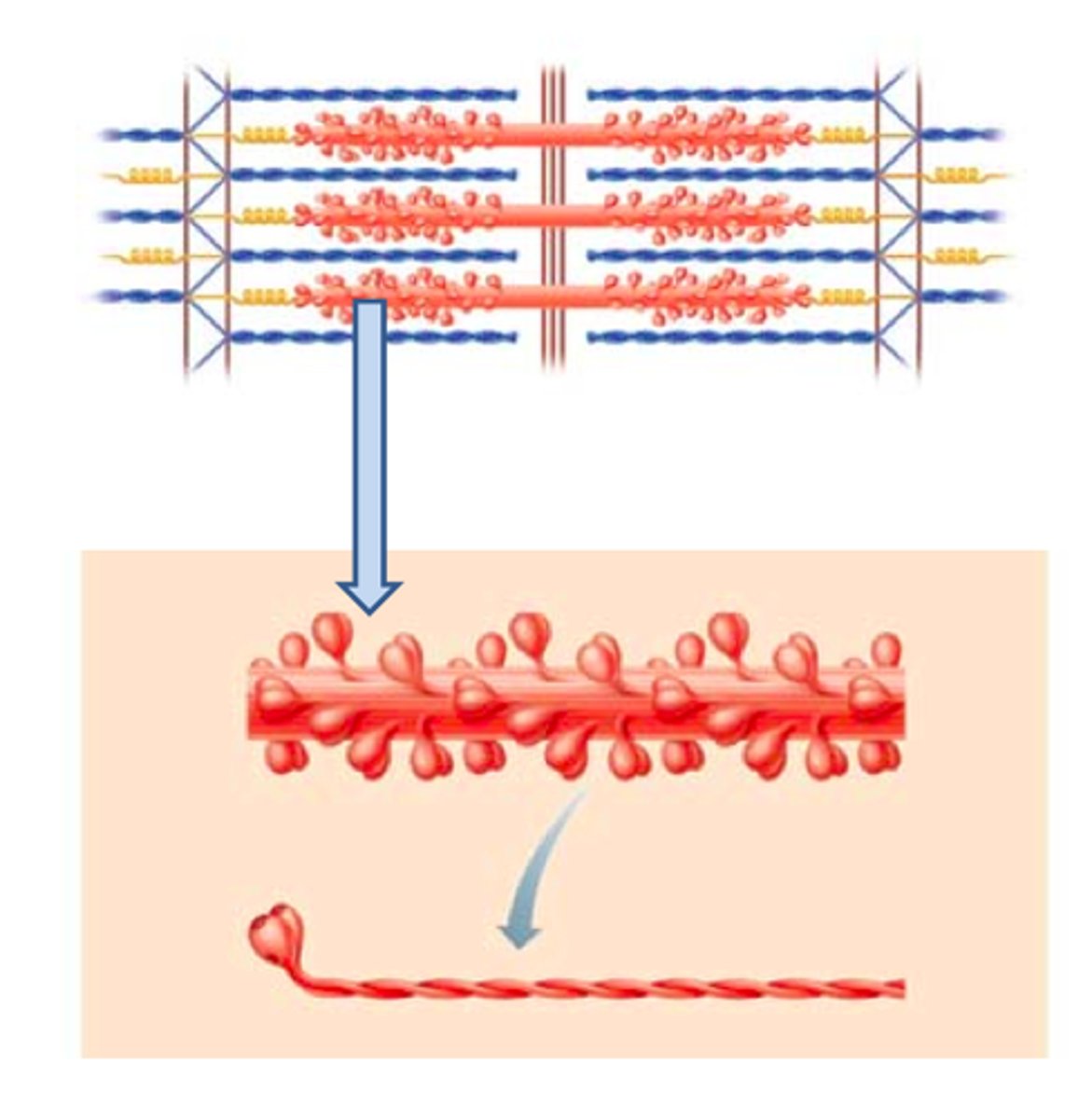
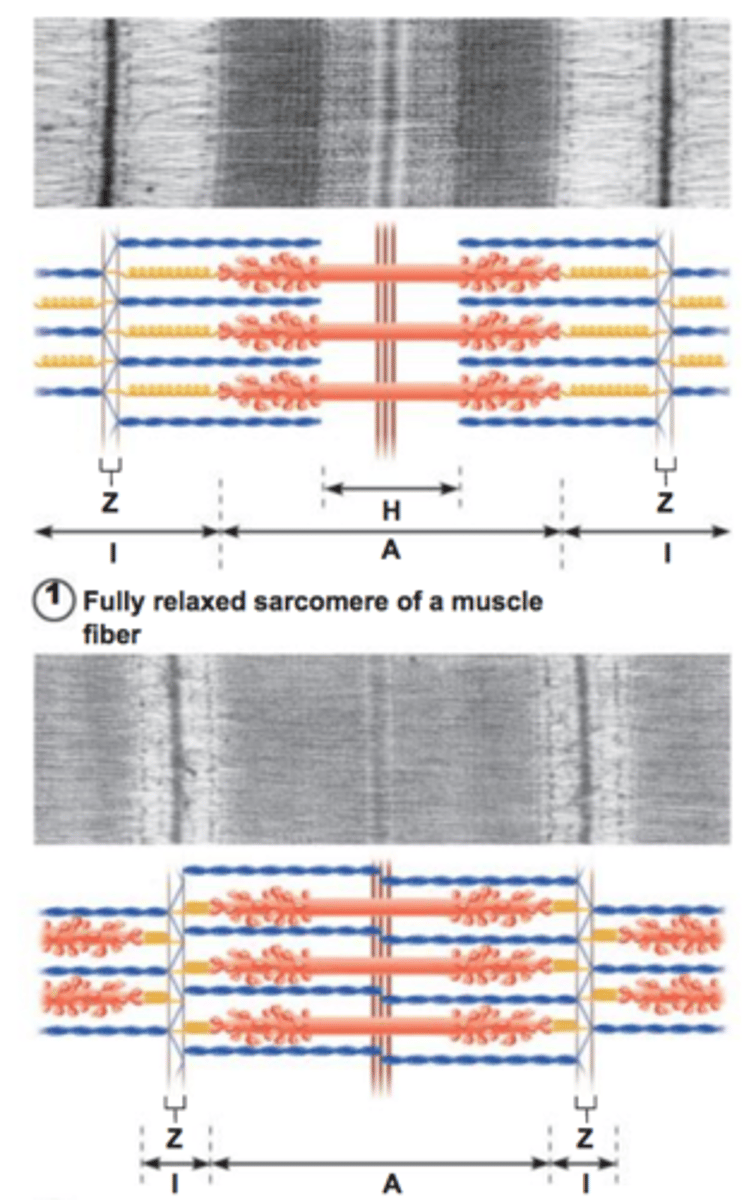
Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction
A widely accepted theory that states that the cytoplasm of skeletal muscles have thousands of myofibrils that consist of thick and thin filament that slide past one when muscles contract
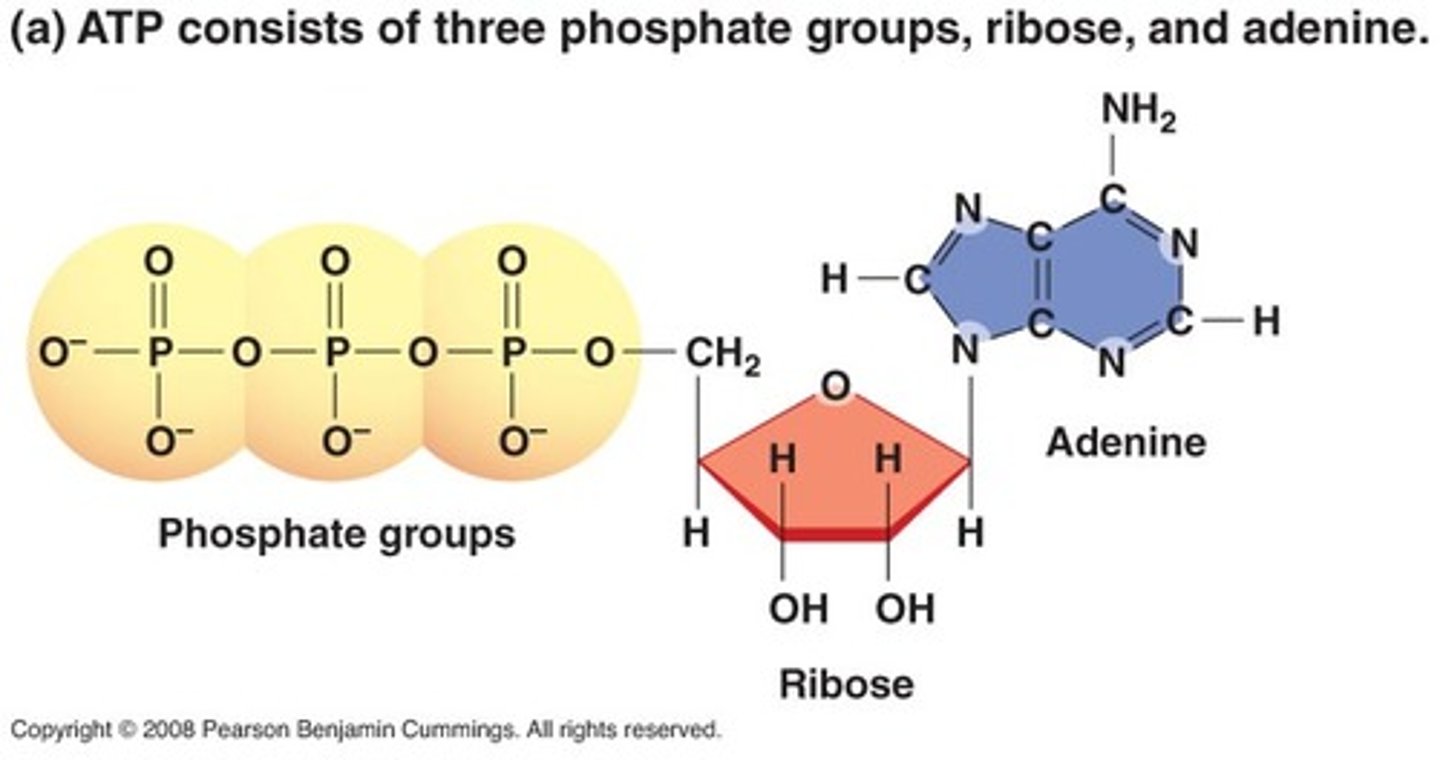
ATP (Muscle Contraction)
A compound composed of adenosine and three phosphate groups that supplies energy for many biochemical cellular processes like muscle contraction by undergoing enzymatic hydrolysis.
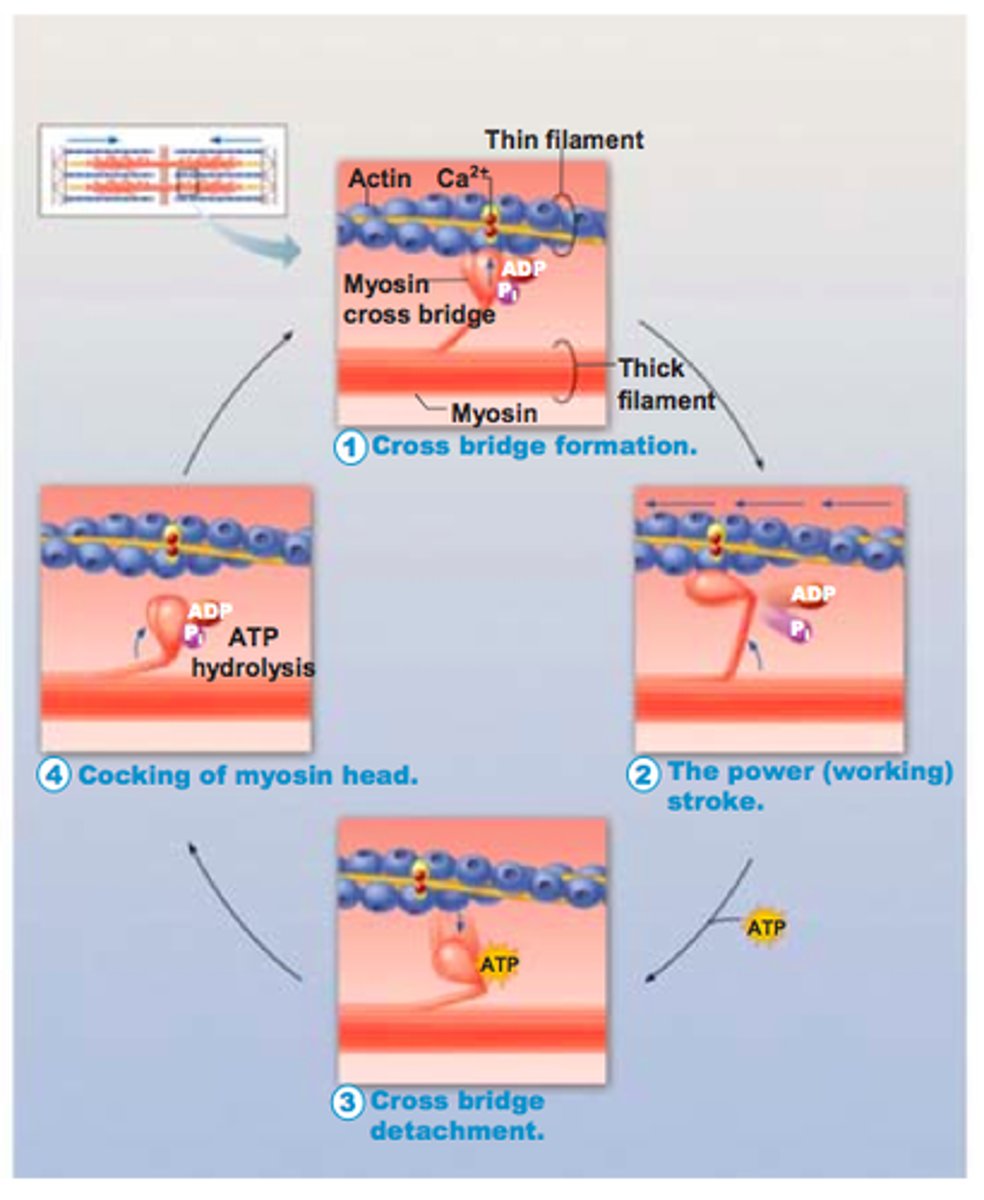
Cross bridge cycle
A series of four steps that results in the shortening of the sarcomere when the muscle is stimulate and ATP is present. Four steps include cross bridge formation (myosin head attaches to an actin myofilament , power stroke (myosin head pivots and pulls actin), cross bridge detachment (ATP binds to myosin), cocking of myosin head (hydrolysis of ATP)
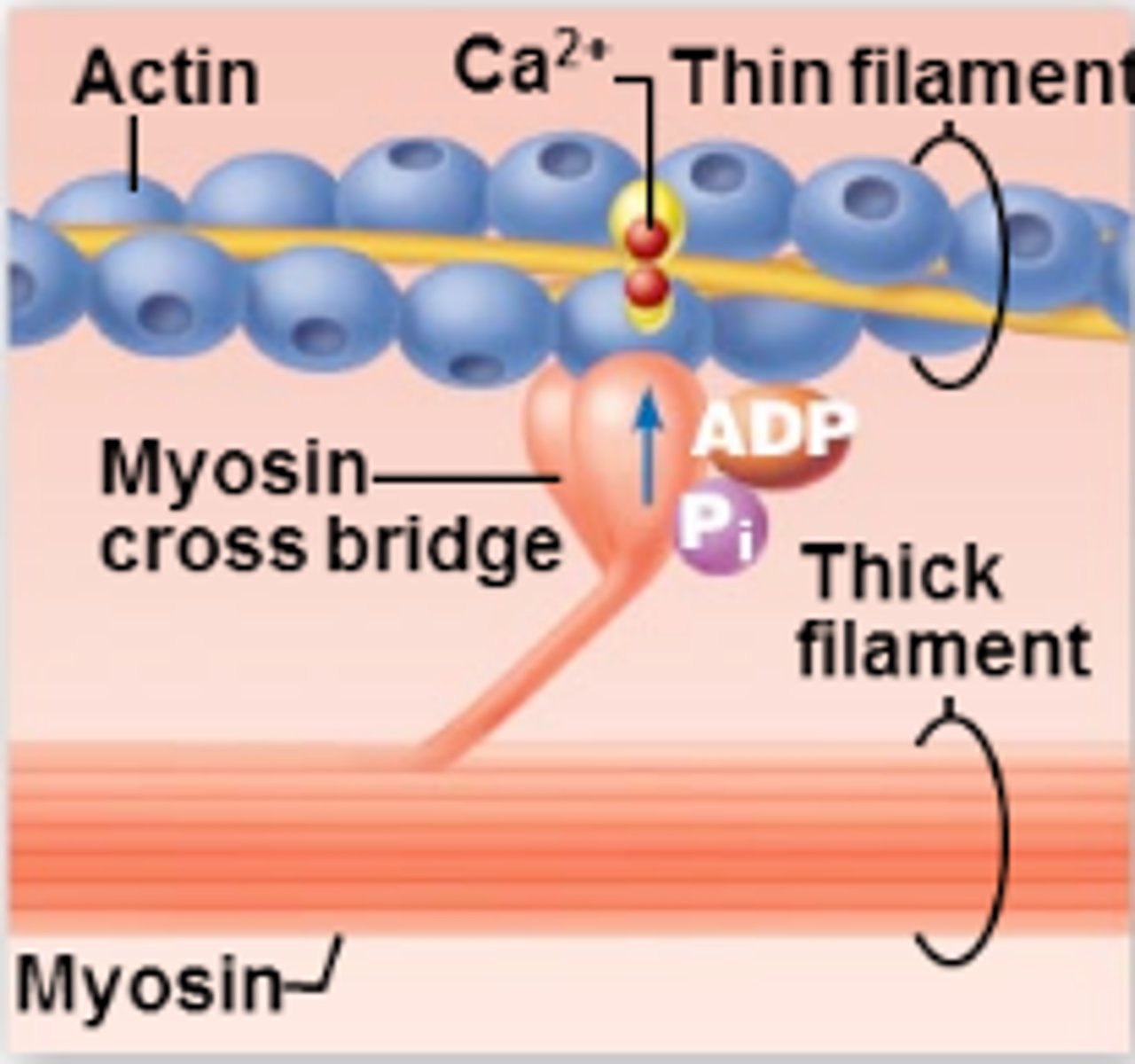
Cross bridge formation
High-energy myosin head attaches to active site on the thin filament (actin)
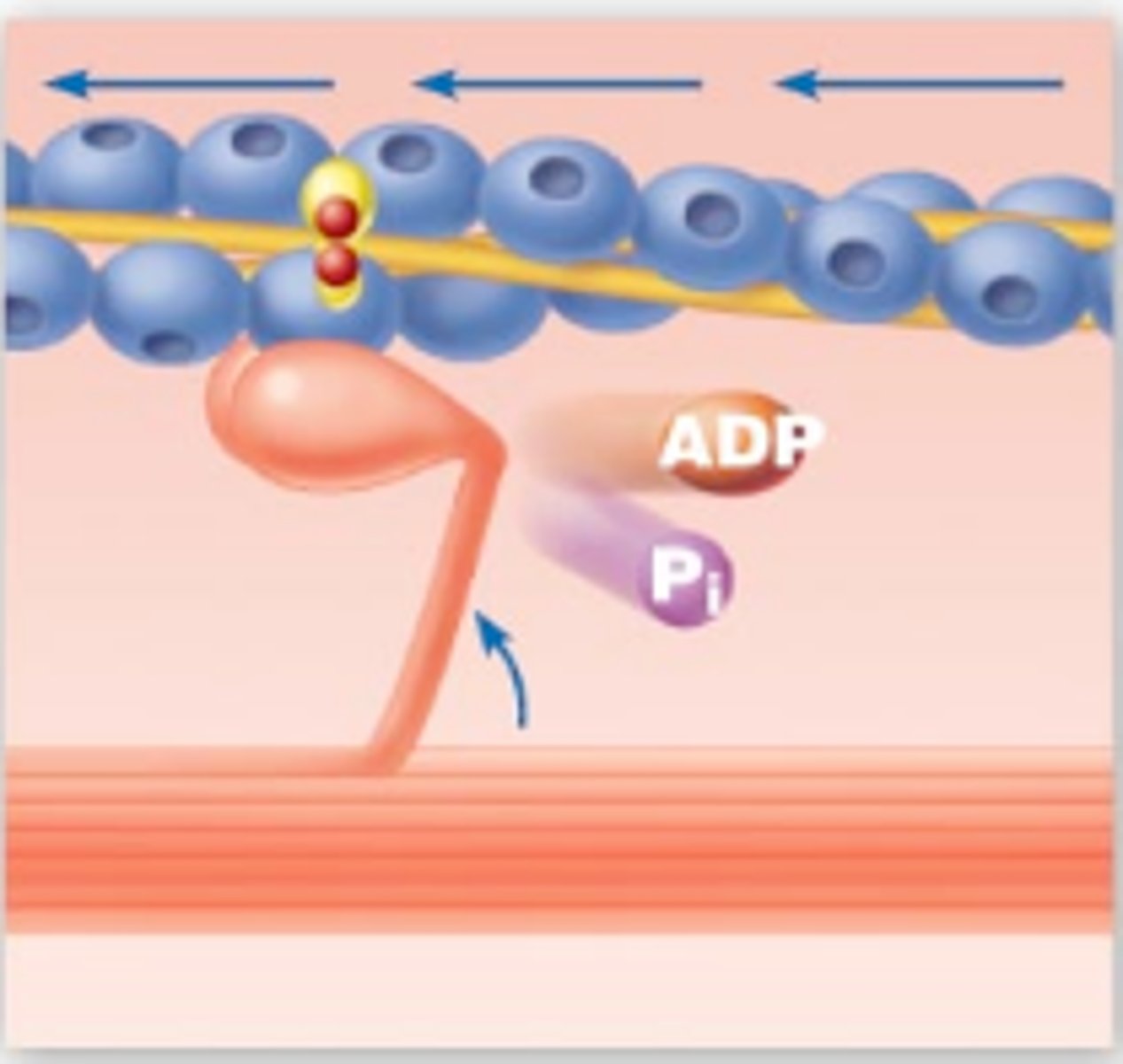
Working (power) stroke
Myosin head pivots and pulls actin toward M line
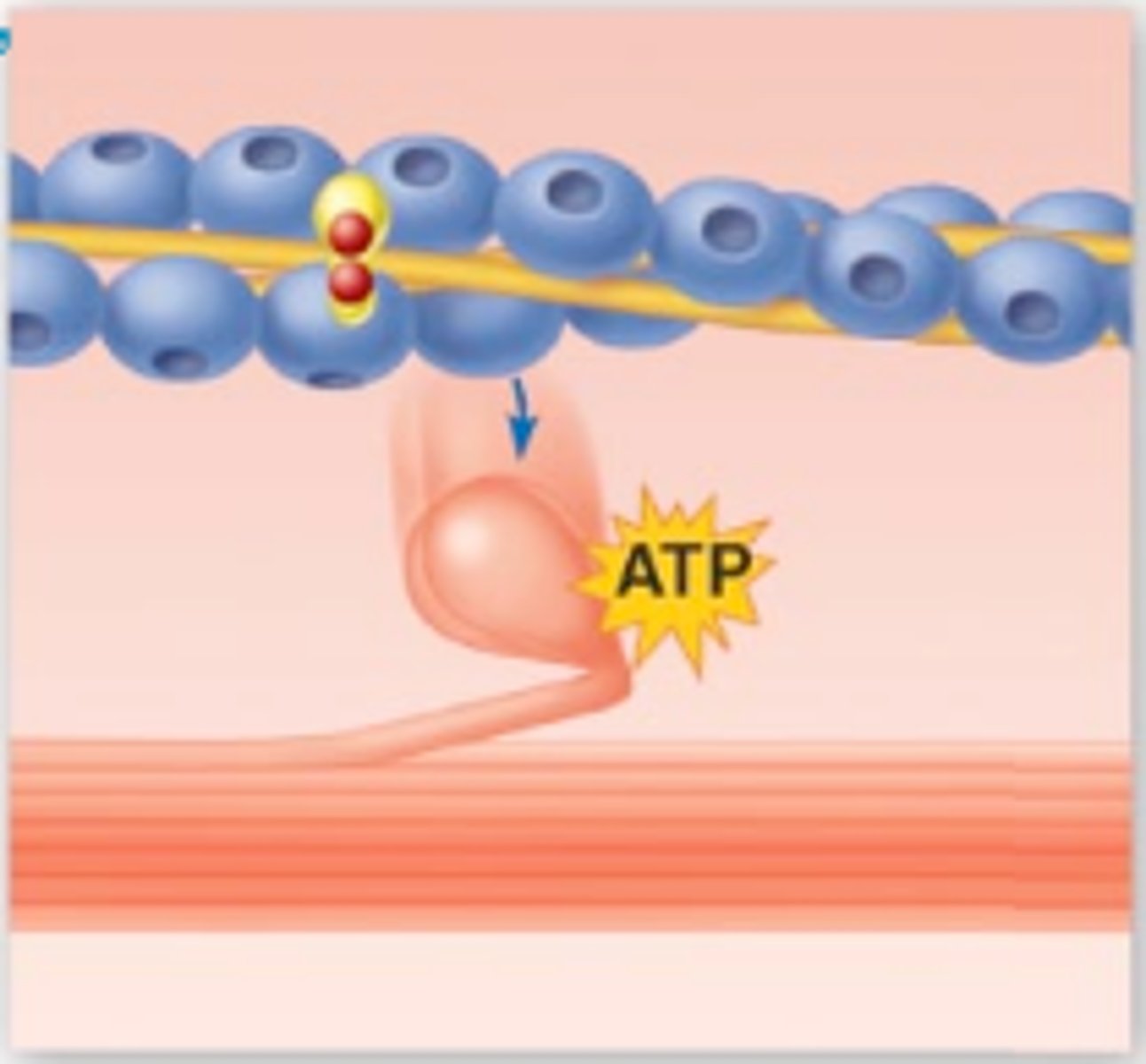
Cross bridge detachment
ATP attaches to myosin head and the cross bridge detaches
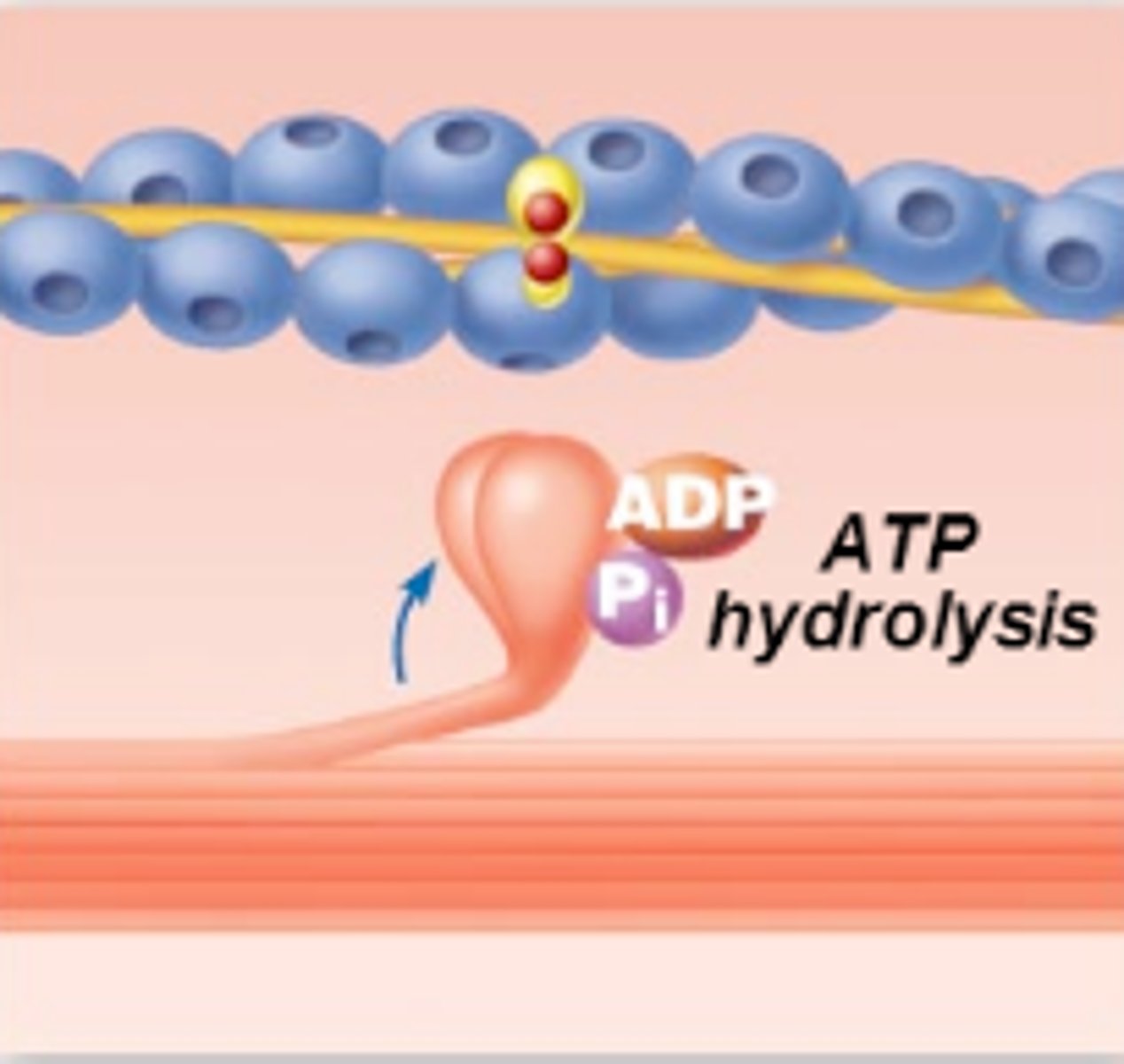
"Cocking" of the myosin head
Energy from hydrolysis of ATP cocks the myosin head into the high-energy state
T-tubule
Also called transverse tubules, these are deep invaginations of the plasma membrane found in muscle cells that allow depolarization of the membrane to quickly penetrate to the interior of the cell.
Excitation -coupling
Process in which action potentials that travel along sarcolemma and T tubules ultimately cause the release of calcium which triggers the formation of cross-bridges and the sliding of thin over thick filaments during muscle contraction