Business human resoucre management
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Human resource management (HRM) definition
managing people for optimal business performance and aligning organisation goals to employee productivity
internal influences on HR
cooperate objectives - the goals an organisation sets to guide HR policies
organisational structure - the szie, scale, and height of it can determine the influences of how employees are treated
financial strategies - a decision to reduce costs via outsourcing can result in different HR training programmes
external influences on HE
market changes - a loss in market share can switch to more competitative HR schemes
economic changes - recessions can lead to less labour force
social changes - more people demanding flexible work options
soft HRM and hard HRM
Soft HRM: an approach to HR which empasizes the human element of human resources, focusing on: employee development and well being, as well as motivation and collaboration
Hard HRM: an approach to HR that prioritizes organizational efficiency and performance, often focusing on cost control and strict performance management.
HR objective: employee engagement and ivolvement
the degree of commitment shown by employees towards the business, seen in contribution and decision making, this can be shown with employees:
being positive about the workplace
be active rather than passive
seek opportunities
HR objective: talent development
identifies employees who have potential and nurturing the process, it is important to keep these employees to allow them to shine in your business.
HR objective: talent development CYCLE
Need / talent planning – finding gaps and what the business needs
Recruitment / selection – finding the best employees to find a gap
Orientation – starting day and teaching how thing work
Skill development – developing and enhancing skills
Performance evaluation – looking if they have reached their qoue and beyond
Succession planning – promotion
HR objective: training
the process of equipping employees with the skills and knowledge to do their jobs effectively, this can take time and money but the benefits can be considered greater
HR objective: diversity
identifying the fact that all employees are different and have different backrounds, beliefs and priorities. H
HR objective: alignment of values
bringing the core values or beliefs of employees together to focusing on a common task, leading to corporate culture where all employees have the right mindset
HR objective: number, skills and location of employees
matching the workforce skills, size and location to the businesses’ needs, being important for the business to run smoothly by meeting seasonal fluctuations and meeting new challenges
name the 4 human resource data methods:
labour turnover and retention rates
labour productivity
employee costs as a percentage of turnover
labour cost per unit
labour turnover:
the amount of employees leaving the business
calculated as: number of staff who left % average number of staff X 100
over a specific period.
retention rates
a measure of a firm’s ability to keep its workforce with the business normally for more than one year
calculated as: number of employees serving for more than 1 year X 100
labiur productivity
a measure of workforce performance that looks at output per worker
calculated as: total output % number of workers
employee costs as a percentage of turnover
employee costs are all costs associated with the workforce, this helps calculate this with relation with revenue from sales
calculated as: employee costs % revenue X 100
labour costs per unit
a measure of the average employee cost per unit of output
calculated as: total labour costs % total output
organisational design and structure
organisational design: the framework which provides a structure
organisational structure: the way in which the firm is organised
centralised and decentralised authority
centralised: power is held at the top of management, with them making decision and going to them for enquiries
decentralised: distributed power among levels, greater flexibility and responsiveness
tall structure adv dis
adv: employees are closely supervised, promotion opportunites available, clear structure showing authority and repsonsibilty
dis: employees feel restricted, decisions take longer, more difficult communication
flat structure adv dis
adv: short communication, less constricted, quicker decision making
dis: fewer promotion opportunities, managers have large workloads / staff and lines of authority are not clear
centralised structure
decisions are made by the head office, which is then followed by the branches e.g. supermarkets, fast food
adv: senior management having control, customers have consistent experience, decisions are made in the interest of the whole business
dis: branch managers have limited responsibilites, fewer promotion opportunities
decentralised structure:
decision making is more regional, allowing branches and stores to make decisions
adv: workers are empowered to make decisions, they can be made quickly
dis: senior managers have no insight, reduced consistency
influence of delegation, centralisation and decentralisation:
B – Business and functional objectives
L – Legal form
O – organisational design
T – technology
S– Skills and attitudes of the workforce
P– priorities and attitudes of leaders and their preferred leadership styles
O– organisational design
D – degree of confidence and stability in the economic environment
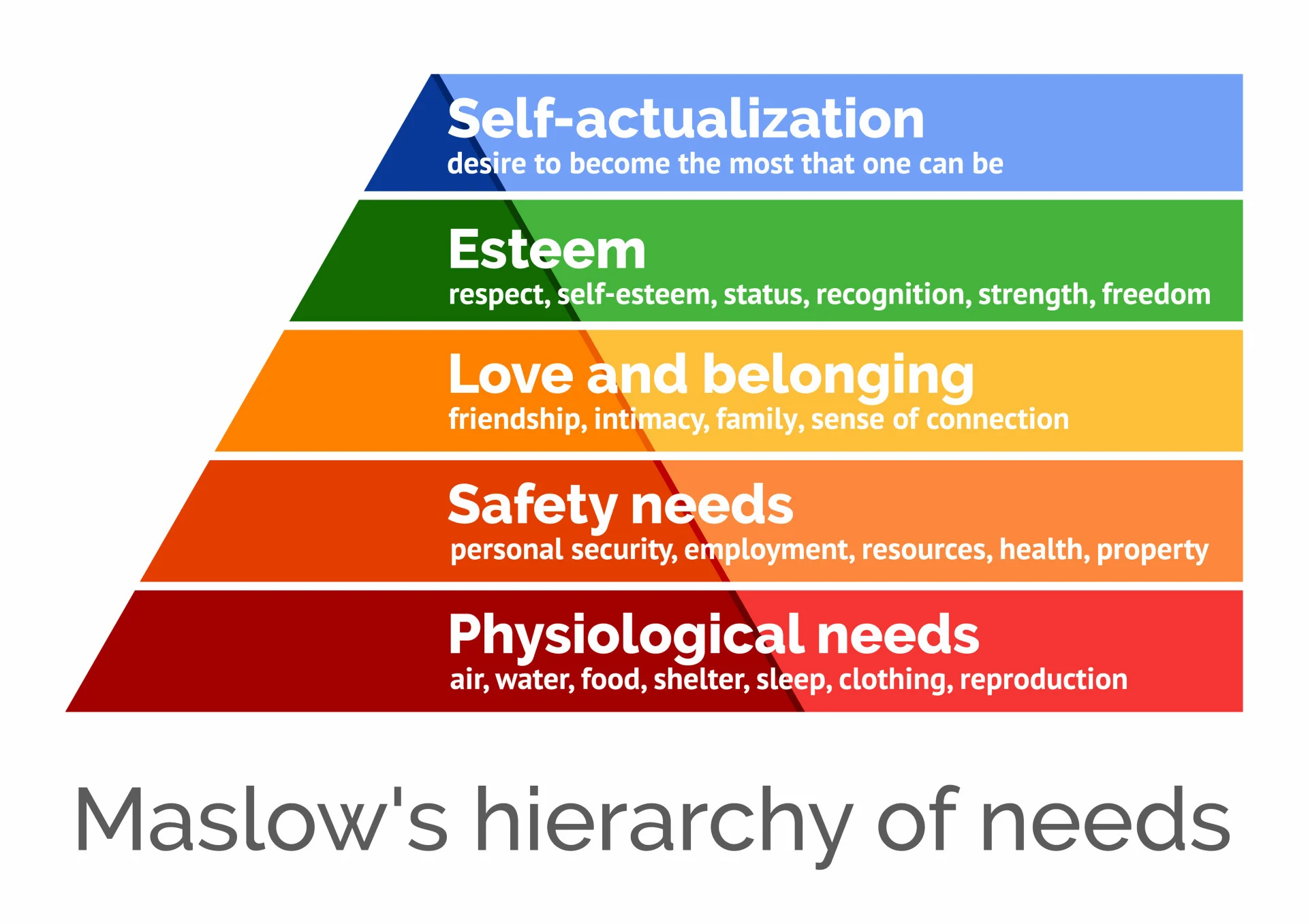
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs:
Herzberg’s two factor theory;
there are 2 key factors in motivators:
motivators: factors that motivate people more to work harder e.e.g responsibility, possibilities, and appraisal of work
hygeine (maintenance) factors: factors that can de-motivate if not present but do not motivate more e.g. working conditions, job security
Taylor’s scientific management theory:
believed in the division of labour
found the most efficient person in a job and set in as the standard
create a piece-rate-pay where you get paid for what you make
finanical and non-financial motivators
financial - using money value to reward workforce and influence work speed
non-financial - motivating employees through job design
HR flow
the movment of employees through an organisation starting at recruitment
human inflow
this encompases where and how to recruit employees, these actiosn can be planning, recruitment, selectiotion and induction
internal human flow
the flow of employees within the organisation, it includes transfers, promotions, demotions and pay terms
human outflow
regarding the release of employees
human resource planning
current workforce: size and skills → preparing for the furute workforce wants
where are they now → how are we going to get there? → where do we want to be in the future