BMS 550L Histology Lab: Cytology I Overview
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Eukaryotic cell
Cell type with a defined nucleus and organelles.
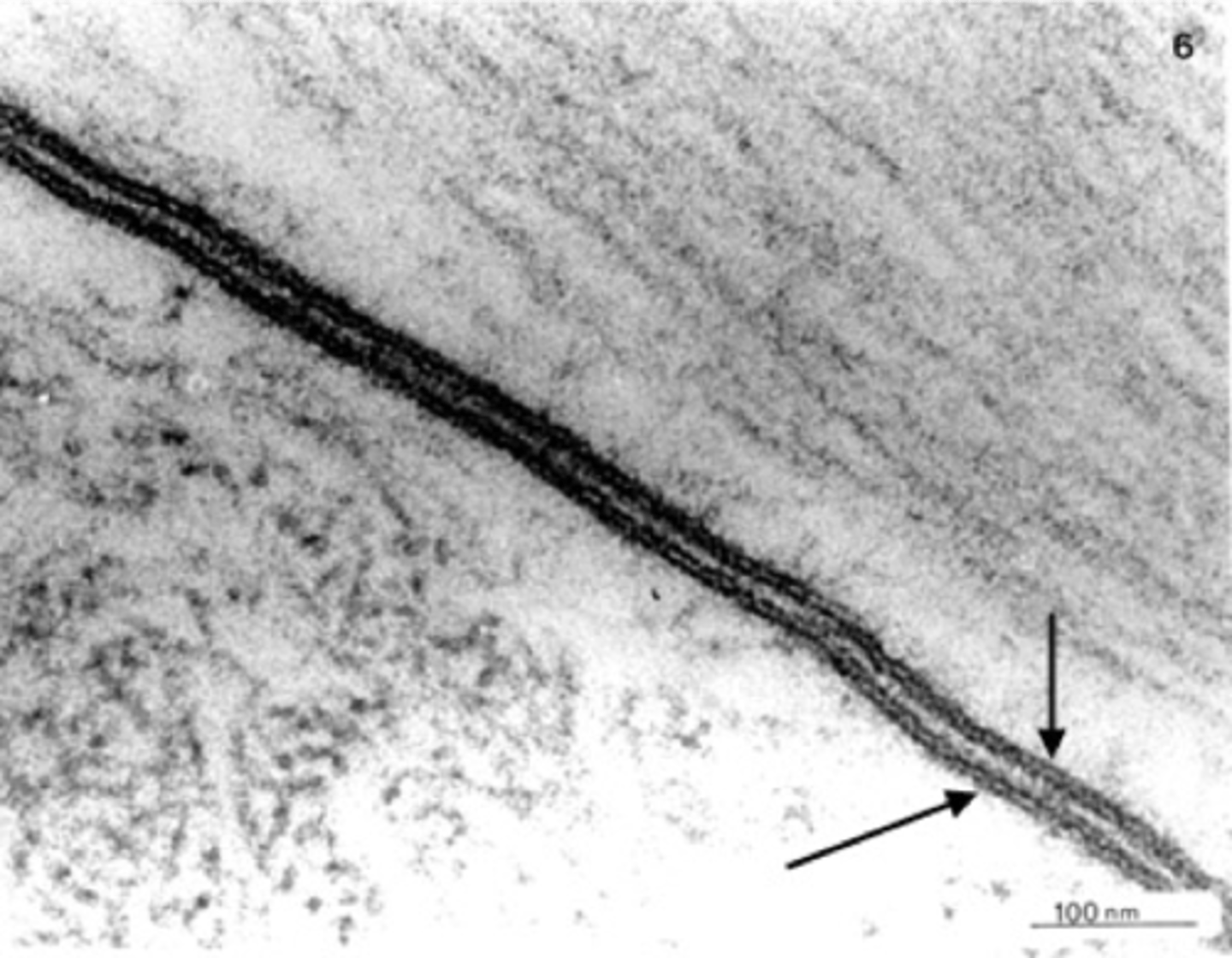
Cell membrane
Outer boundary of the cell, regulates entry/exit.
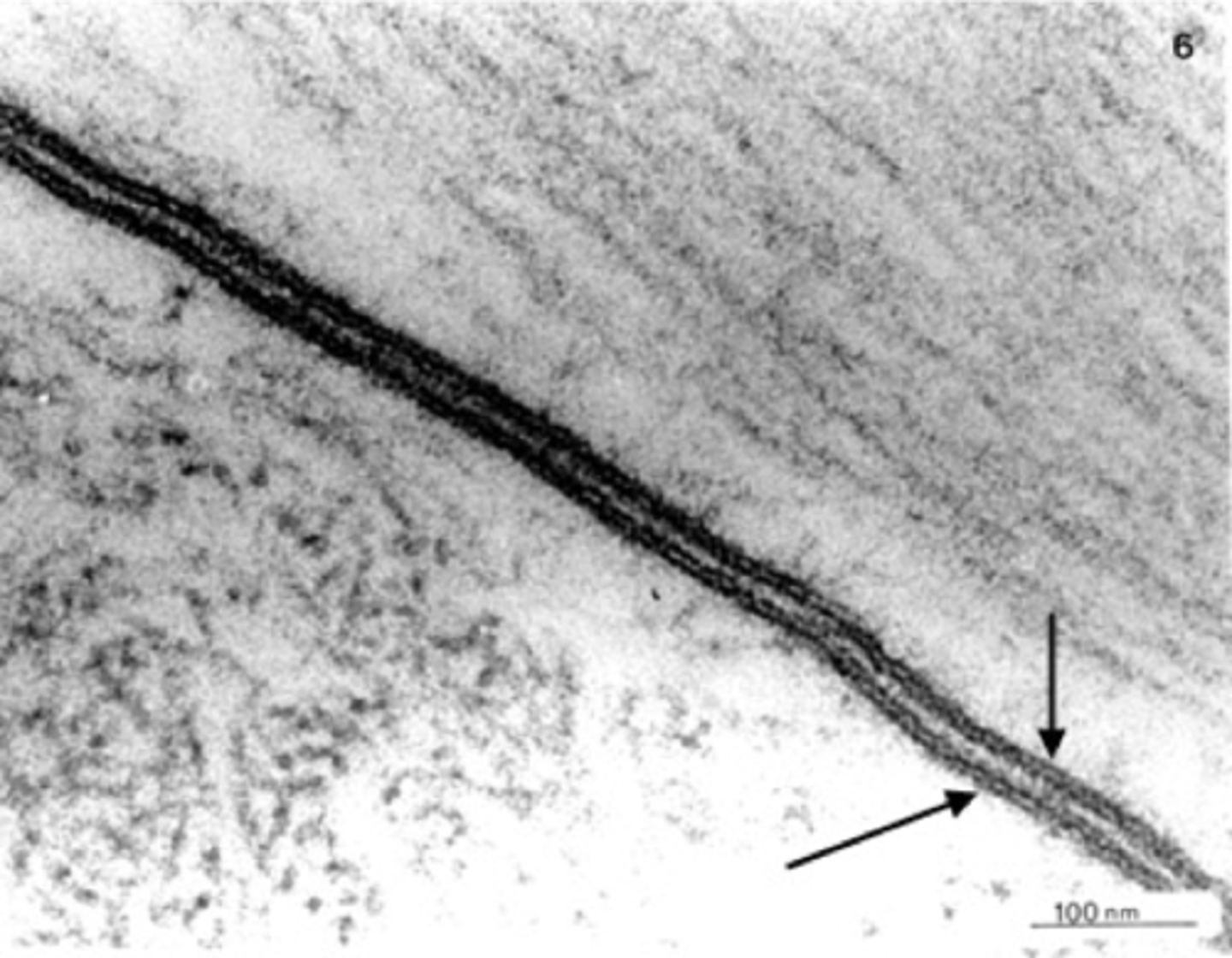
Cell membrane
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis, found free or on RER.
Ribosomes
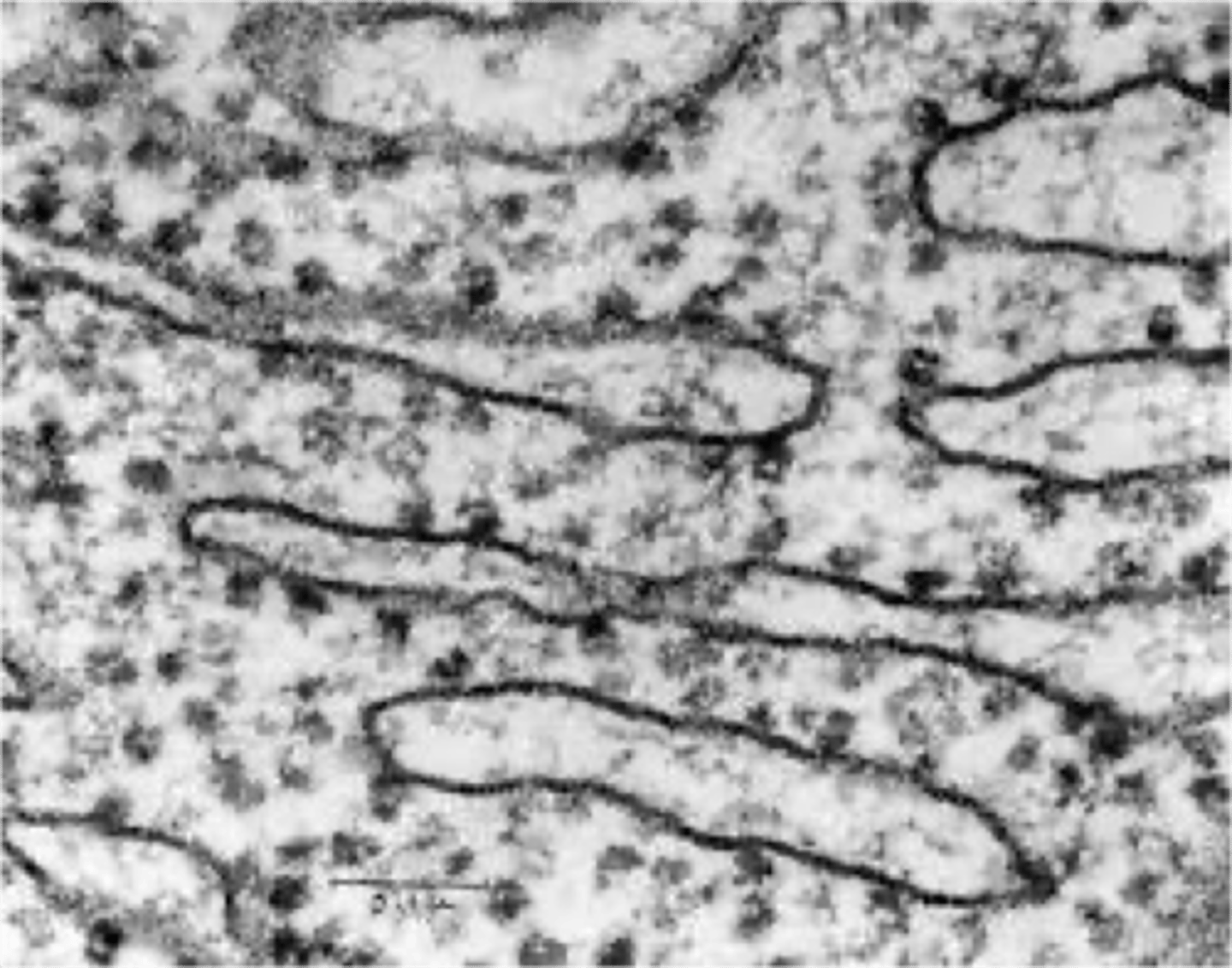
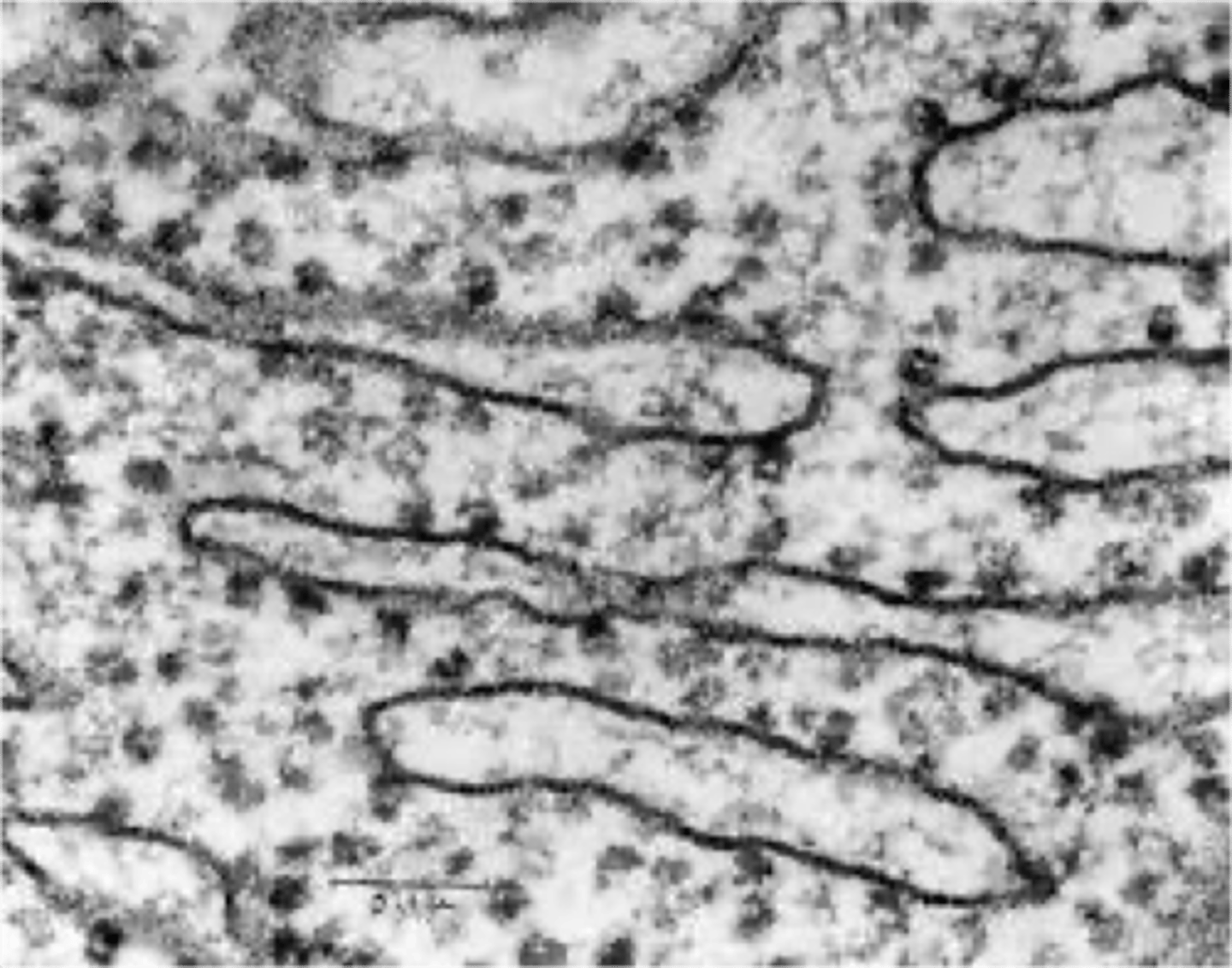
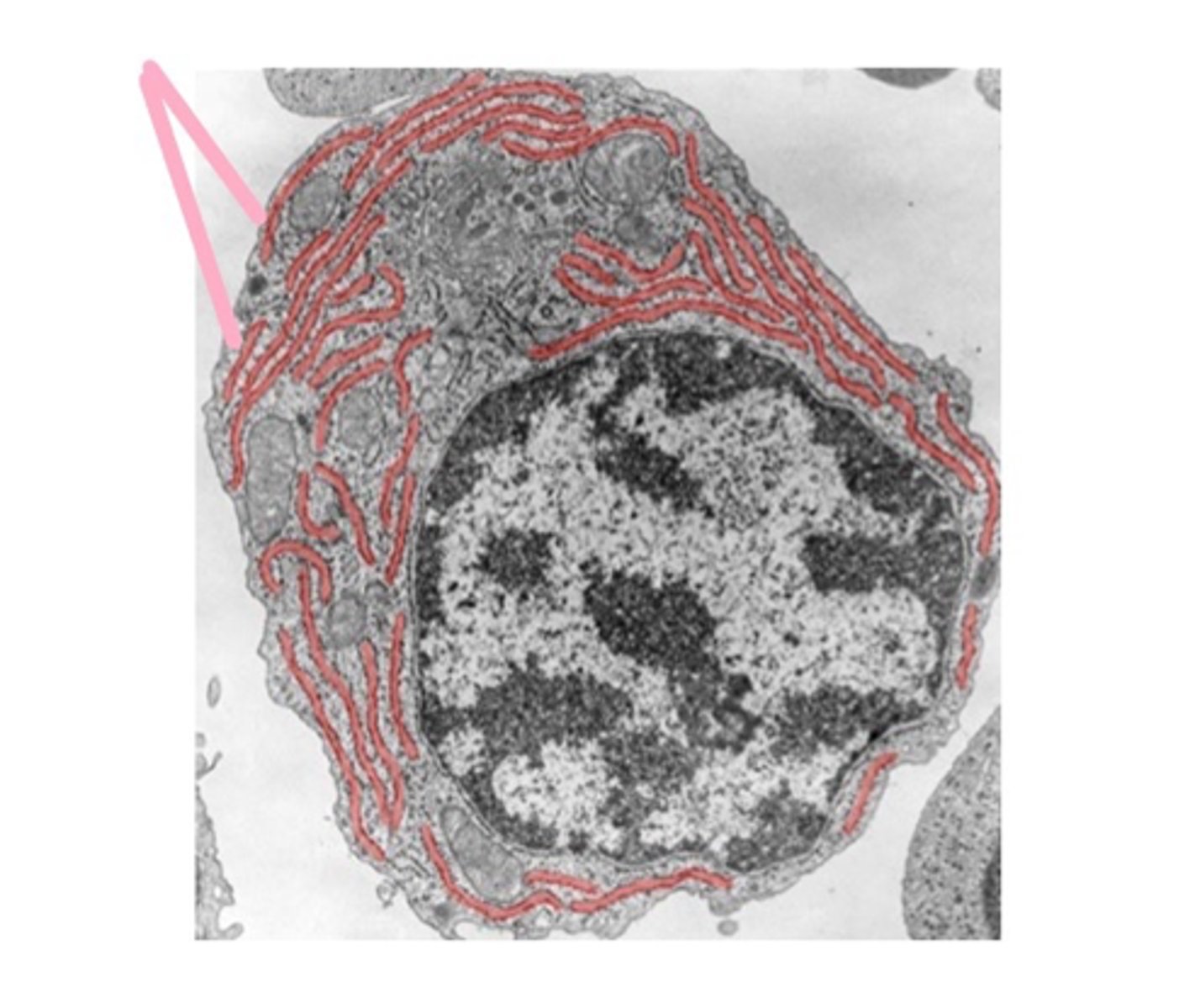
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Studded with ribosomes, synthesizes proteins.
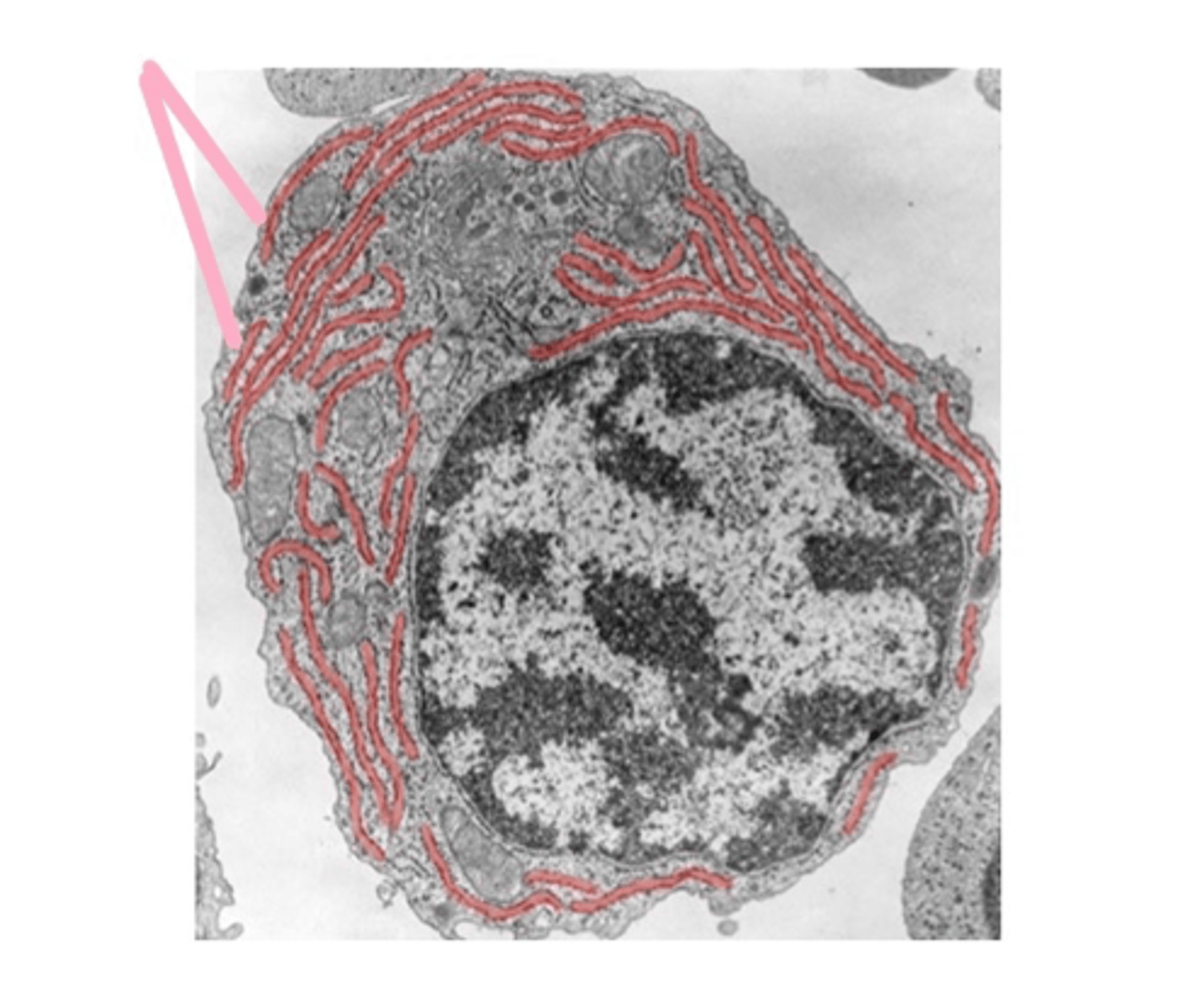
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Rough ER
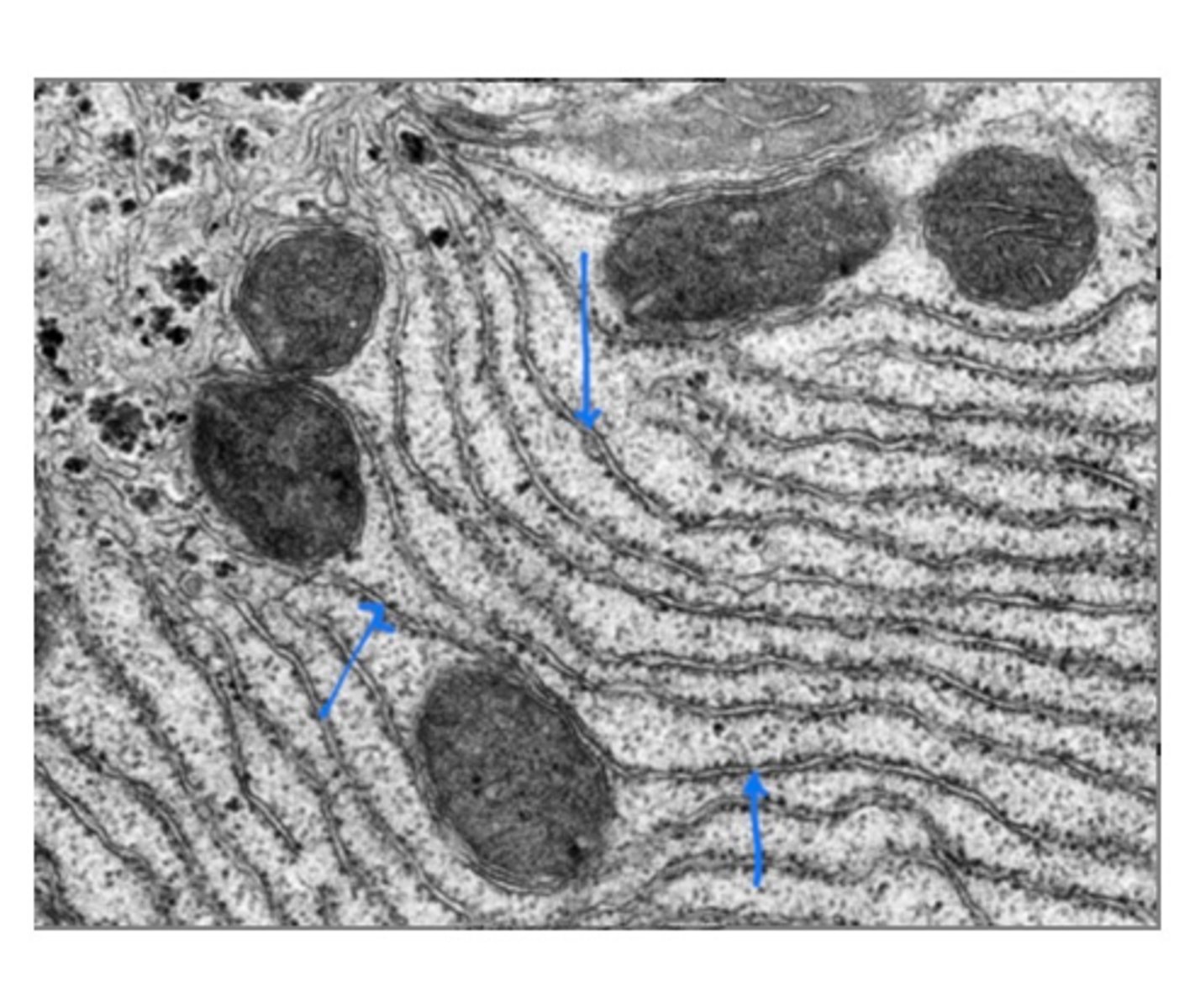
Smooth ER
Lipid synthesis and detoxification, no ribosomes.
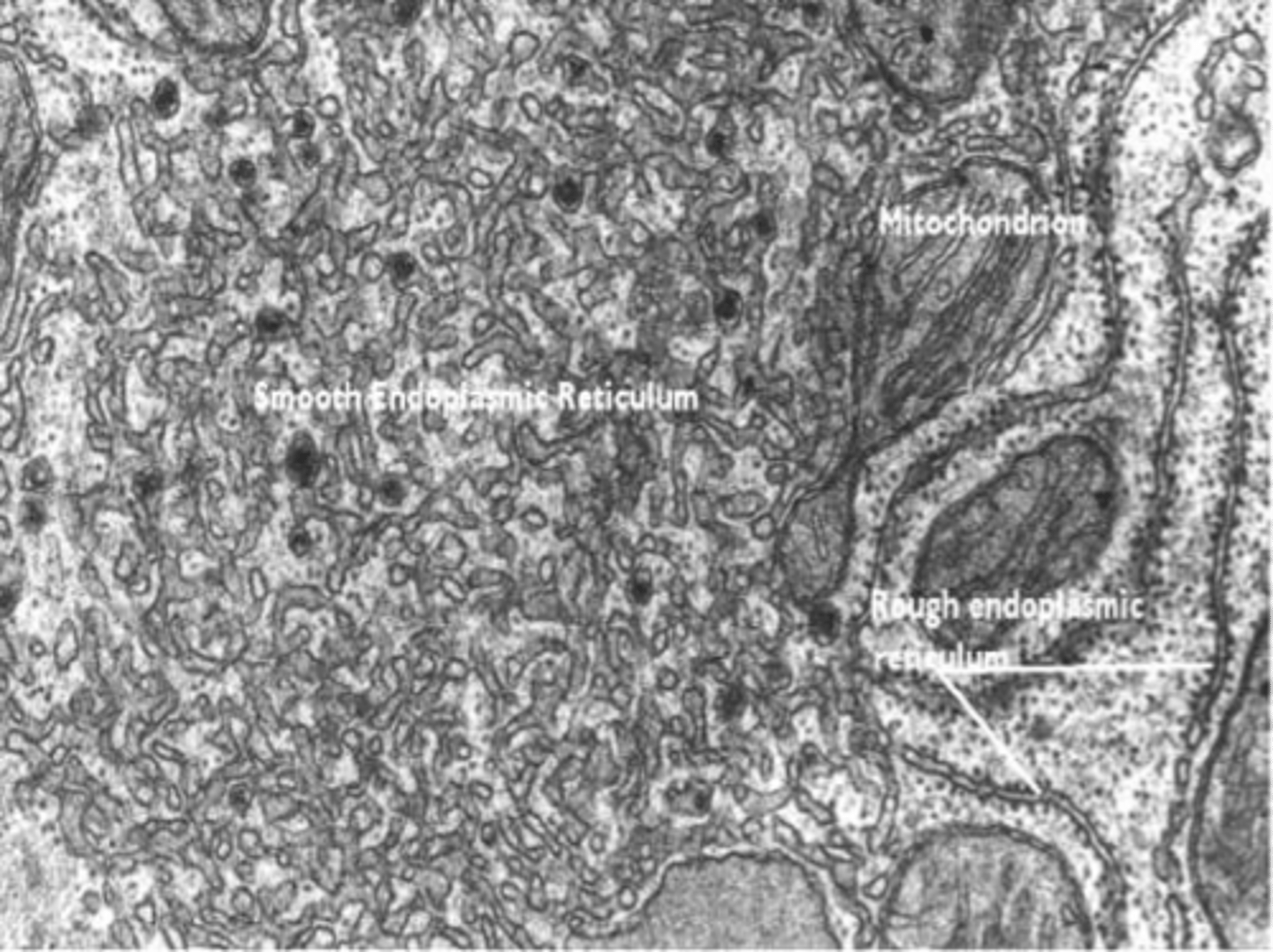
Smooth ER
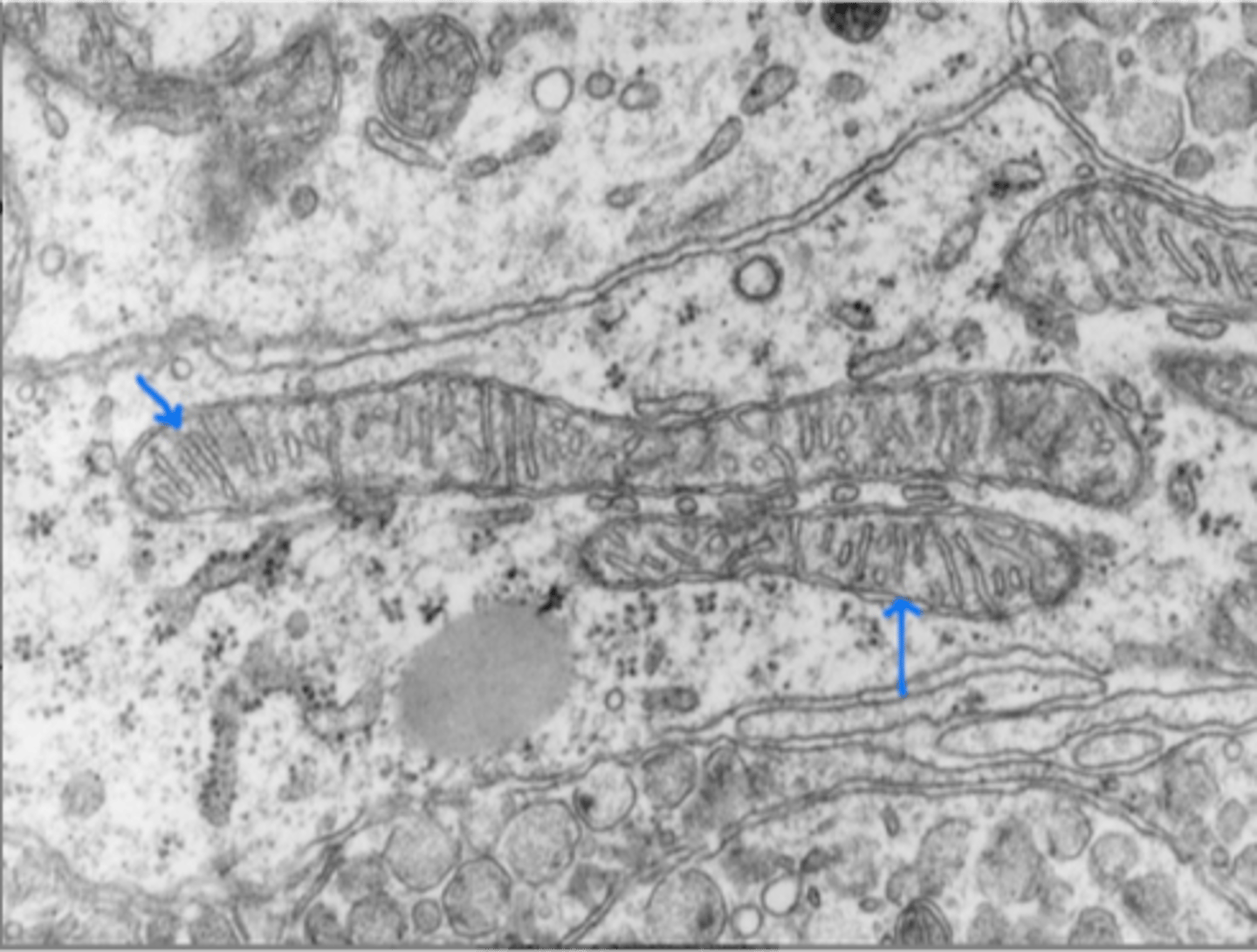
Mitochondria
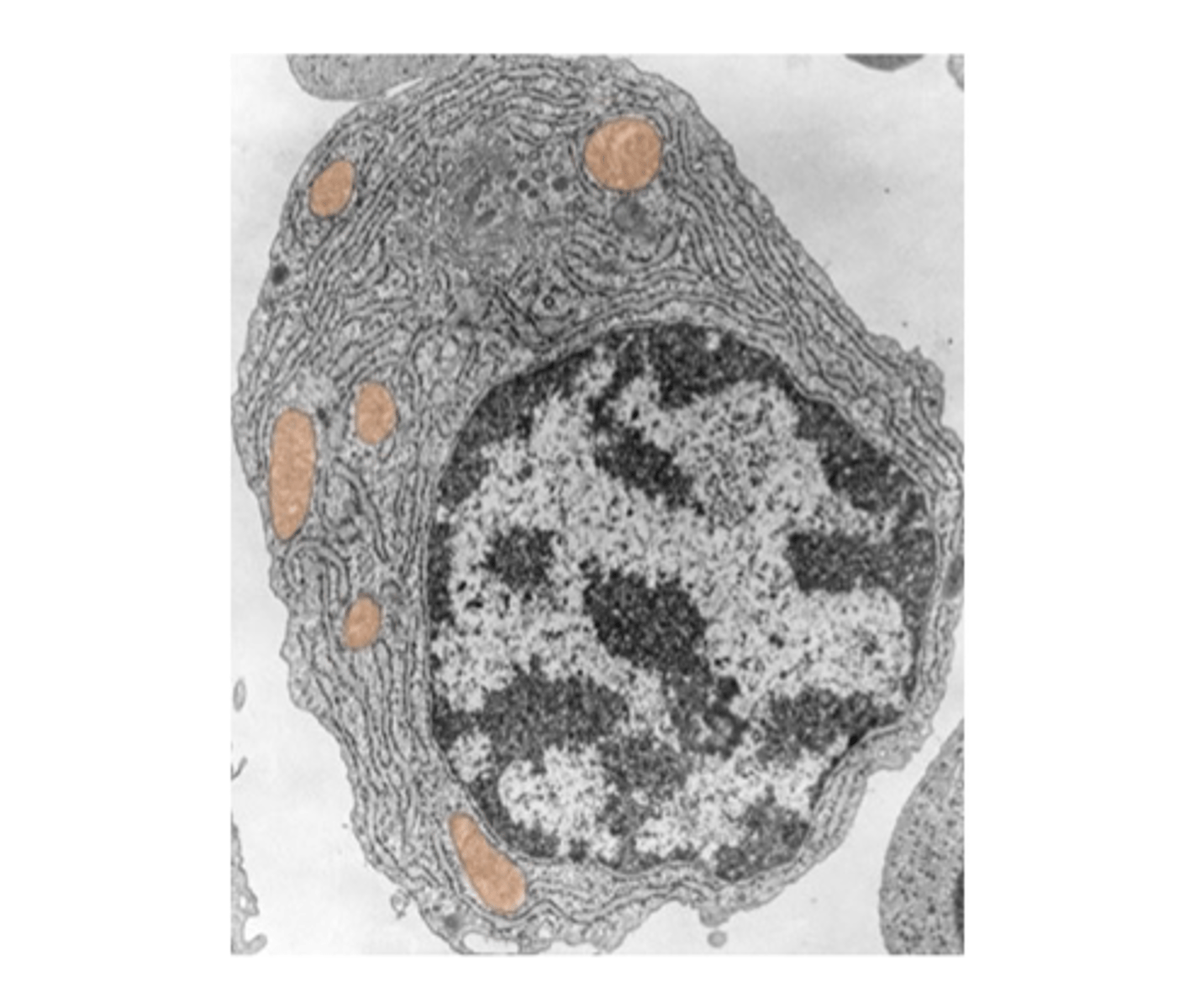
Mitochondrion
Golgi apparatus
Processes and packages proteins for secretion.
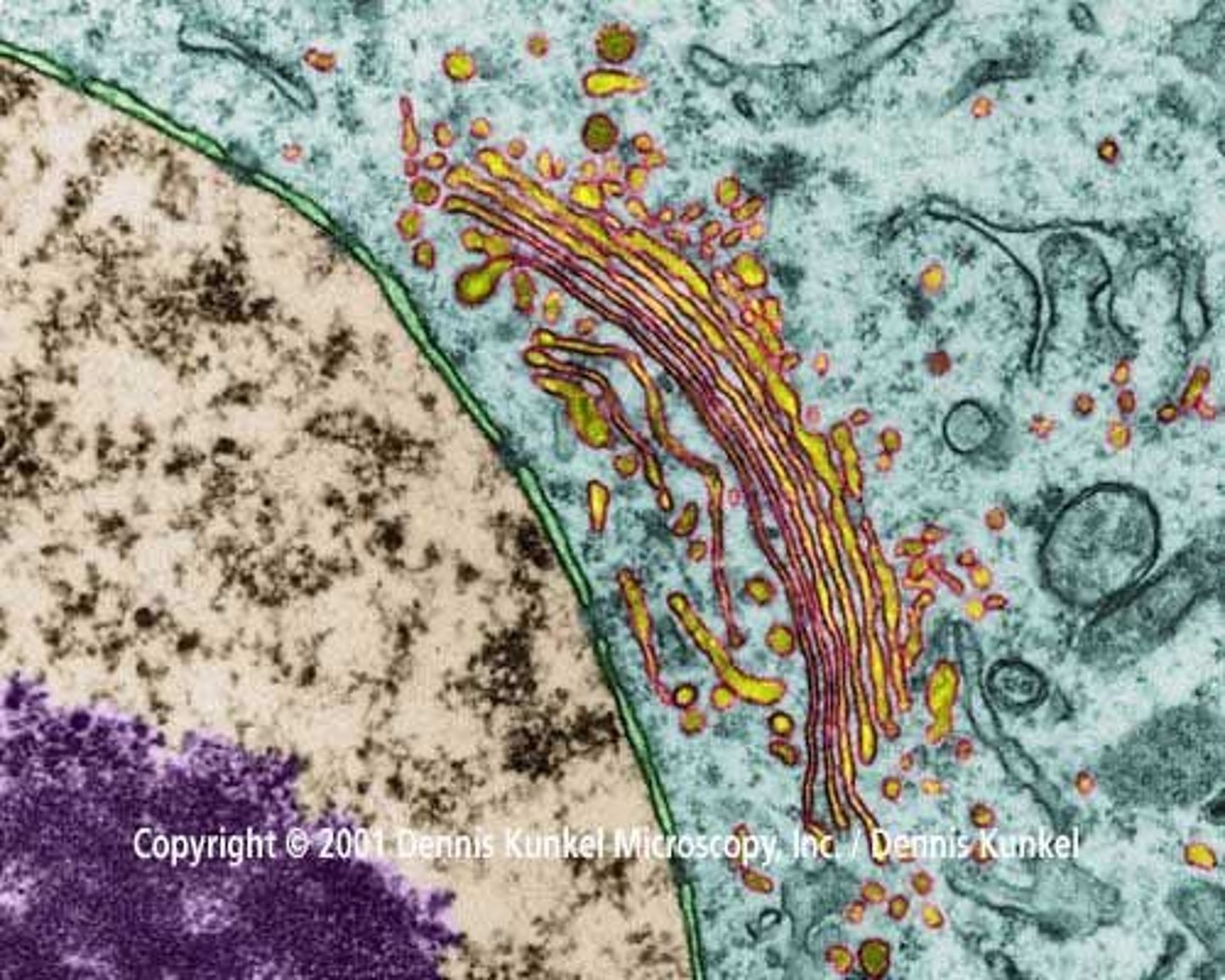
Golgi Apparatus
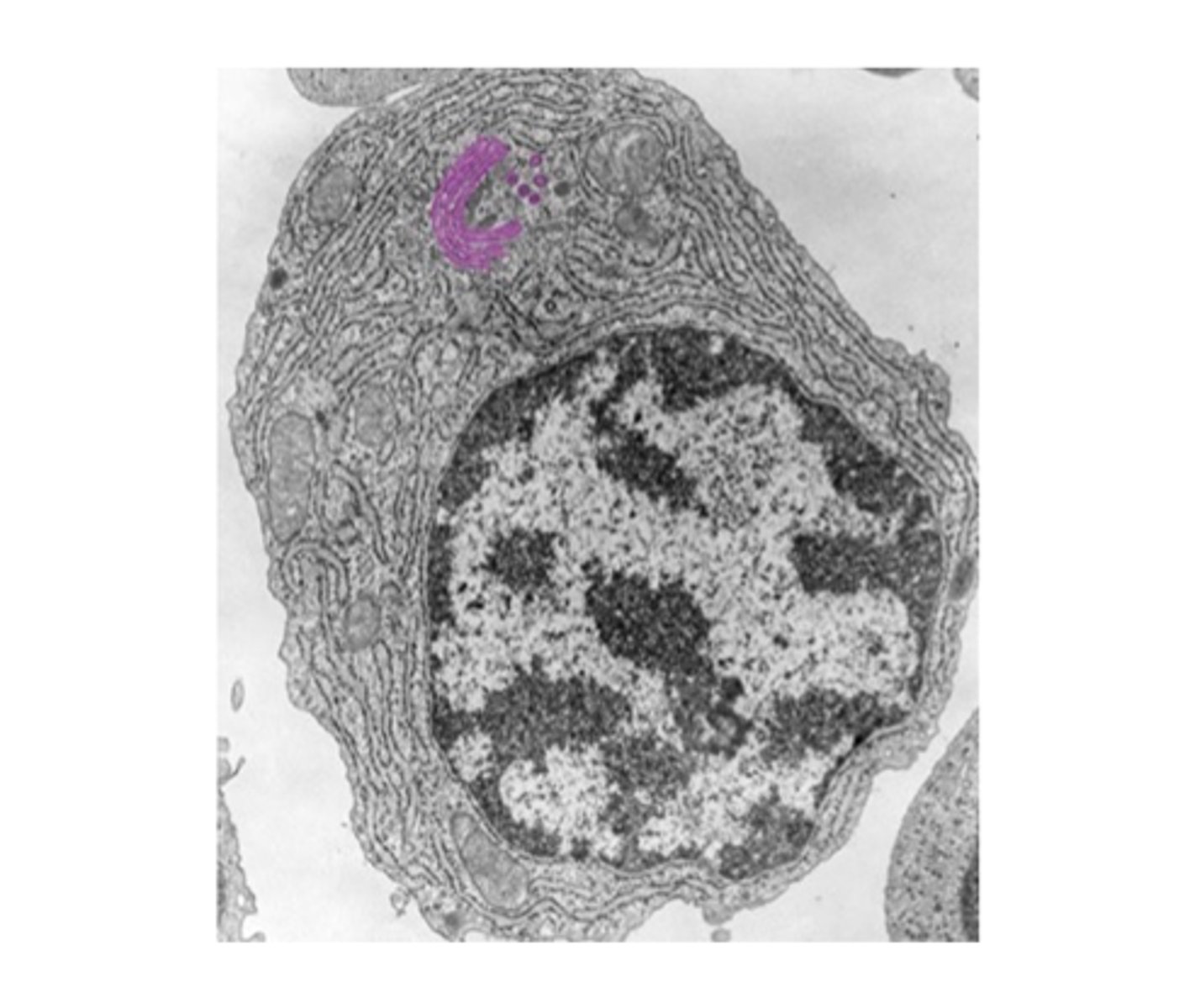
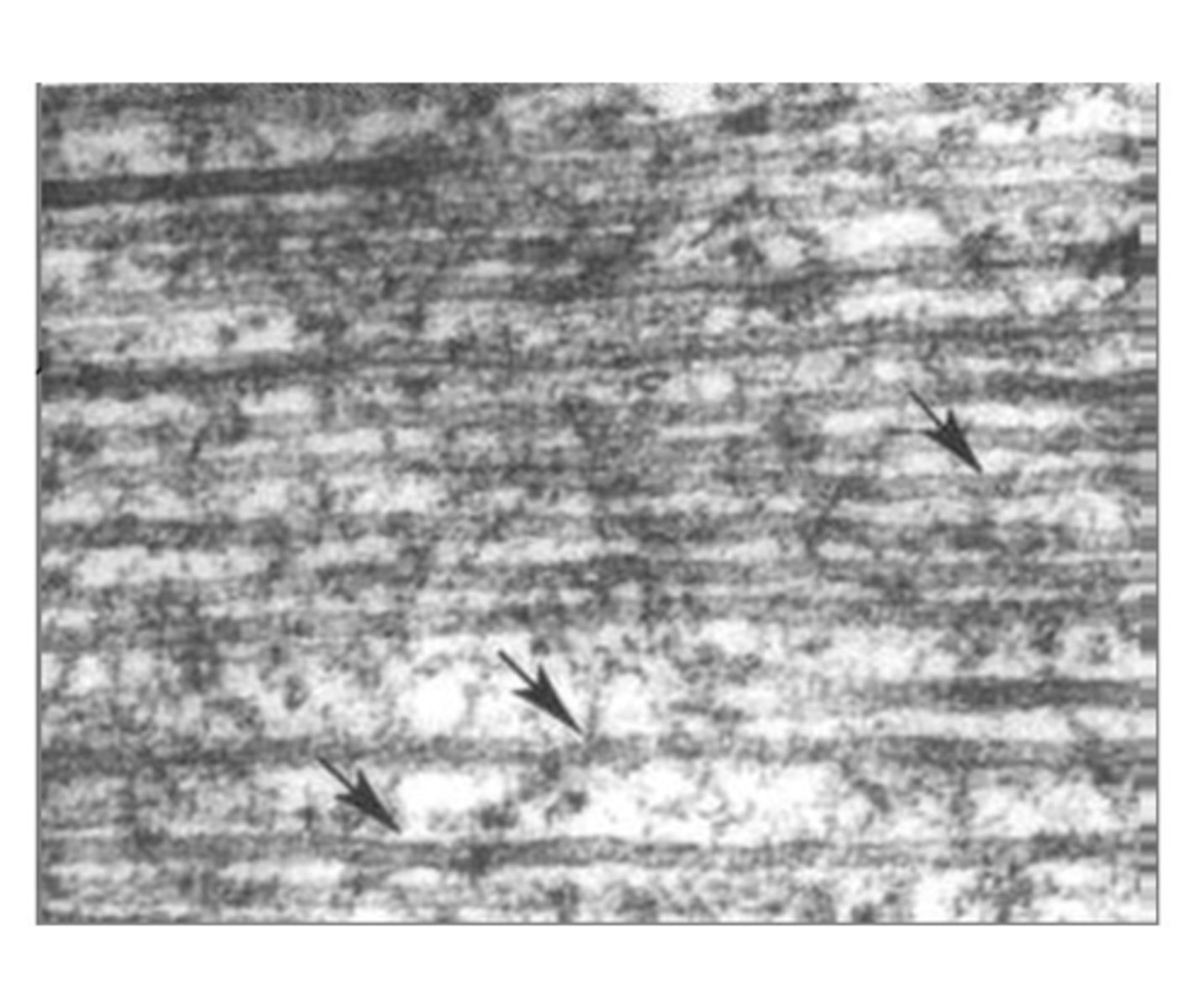
Microtubules
Cytoskeletal elements aiding in cell shape and transport.
Microtubules
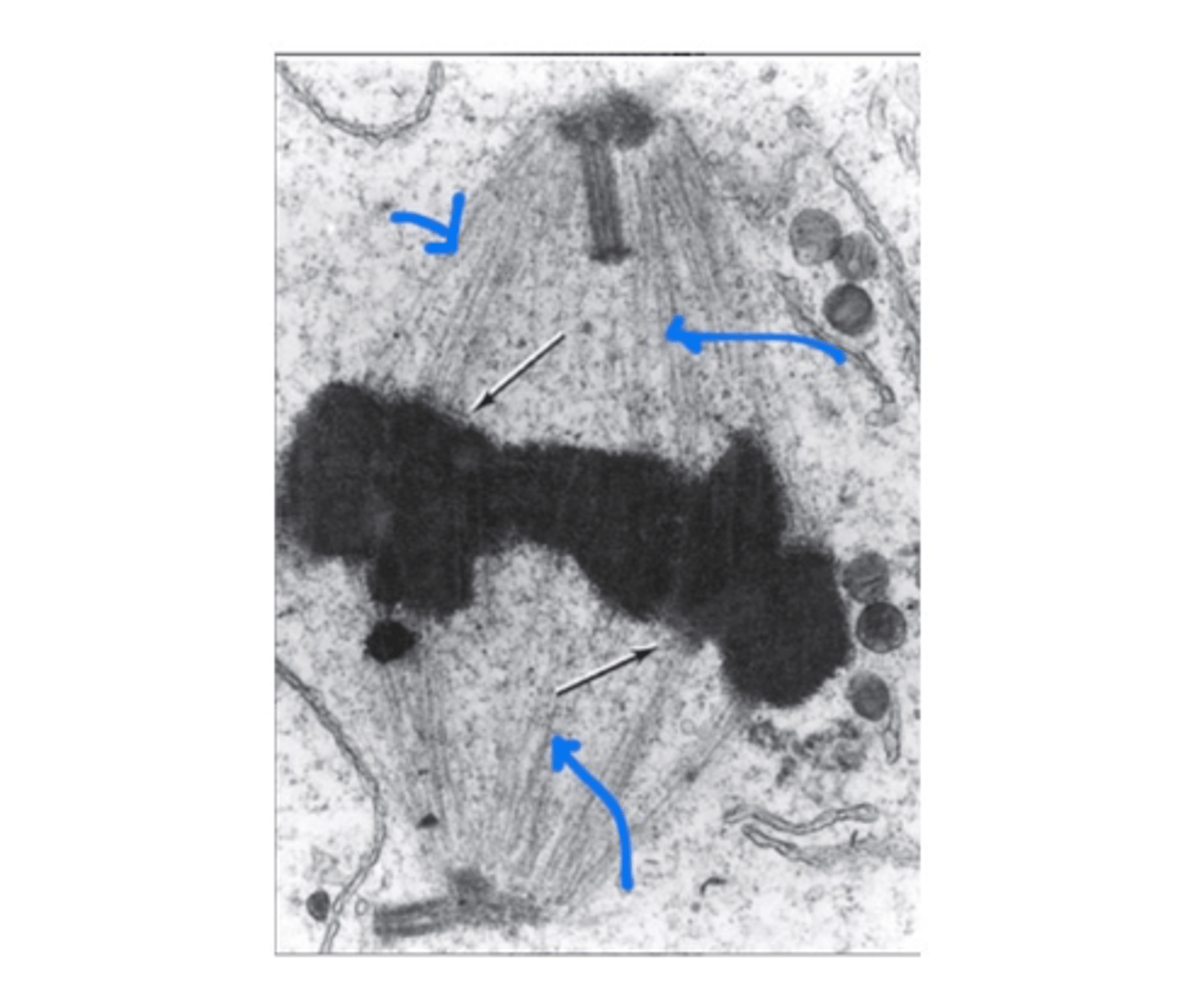
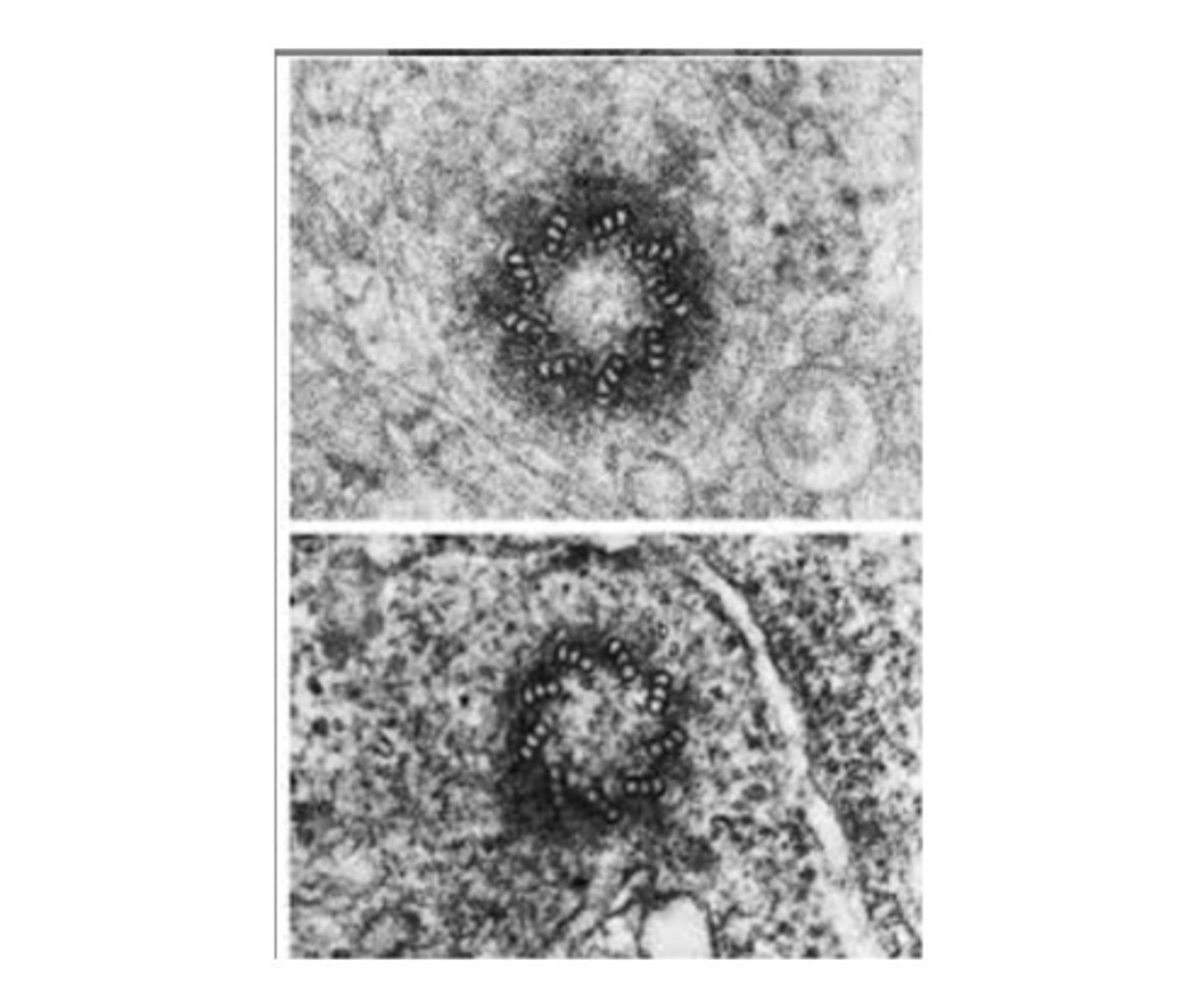
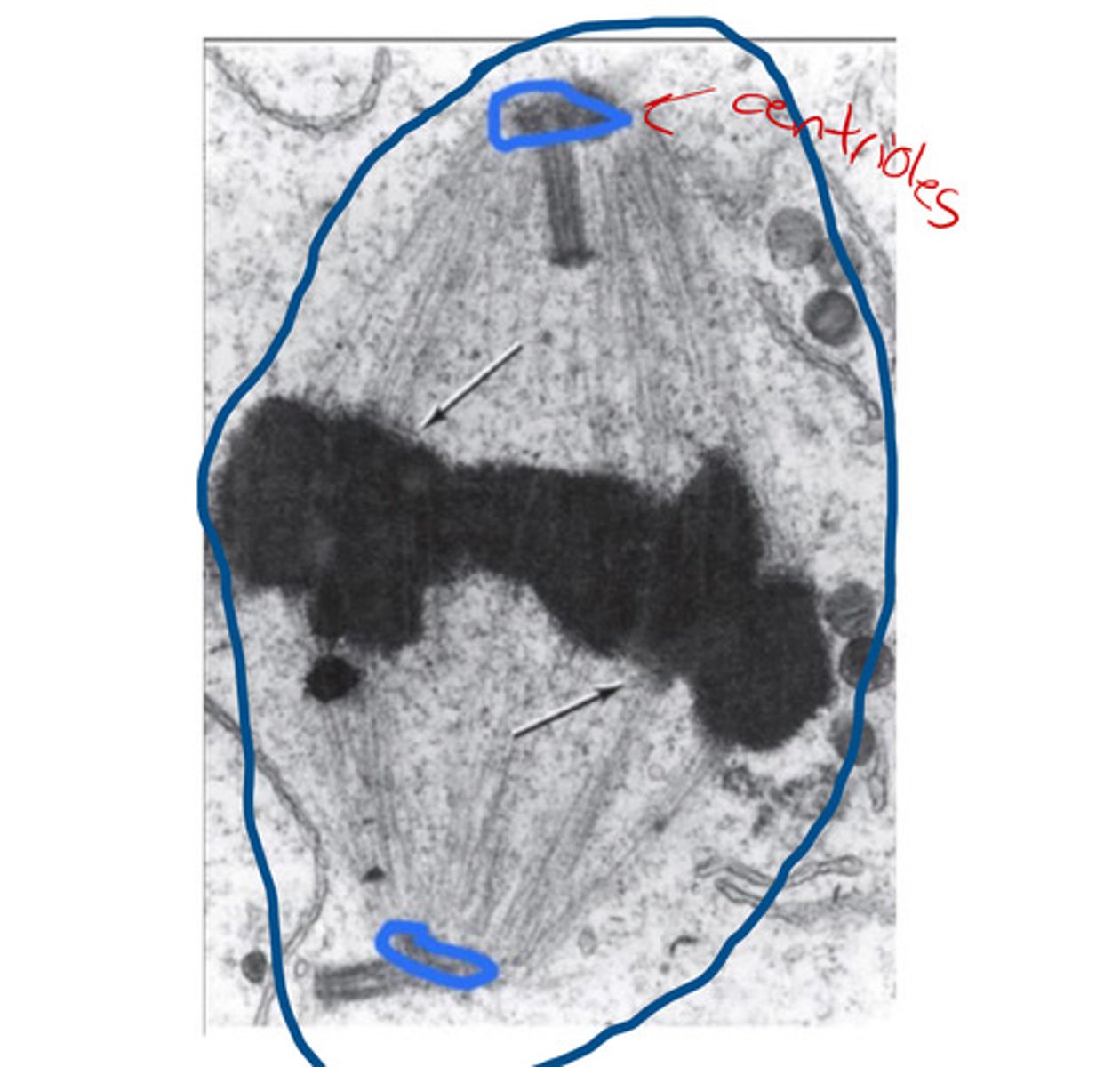
Centrioles
Structures involved in cell division and mitosis.
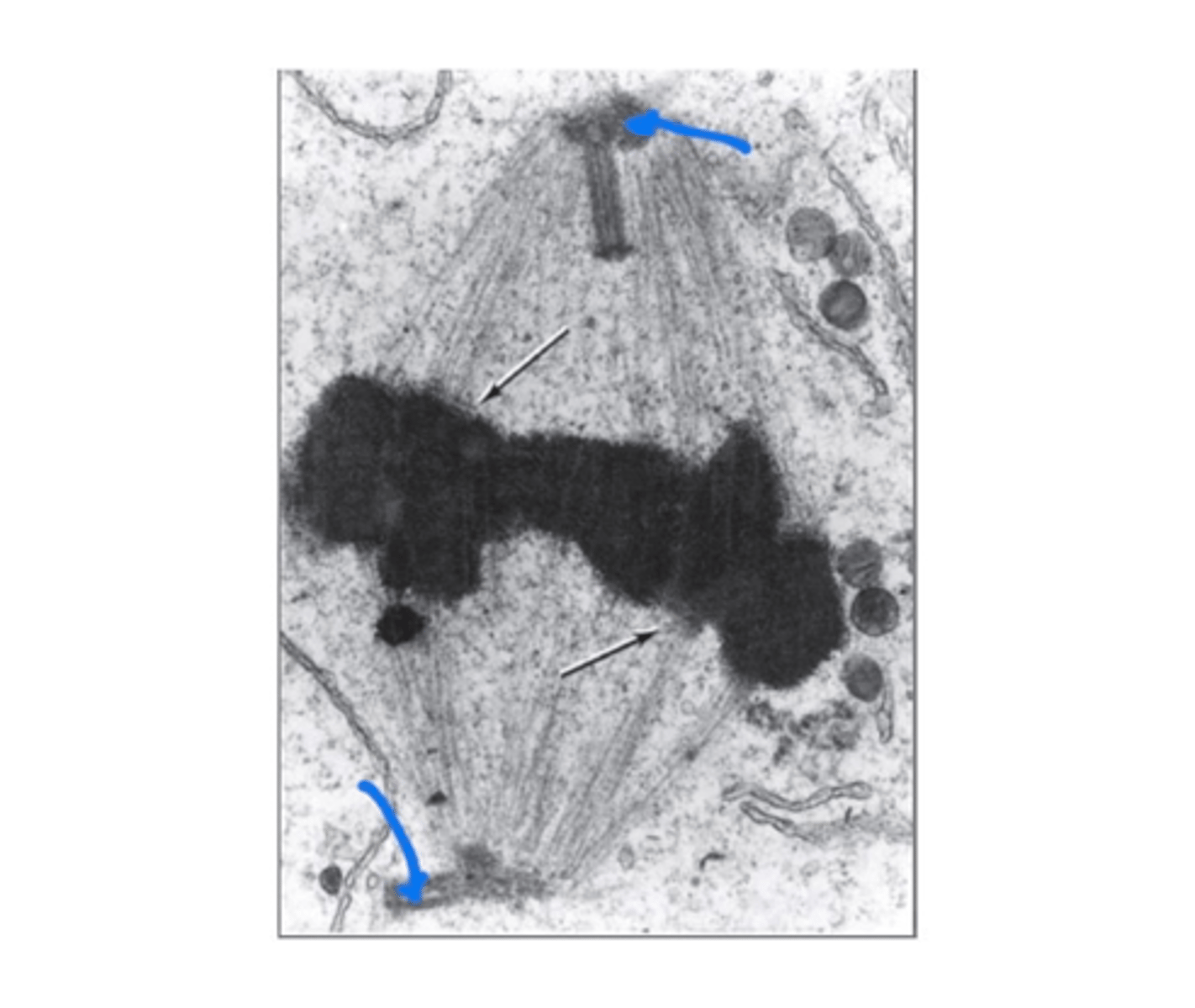
Centrioles
Centrioles
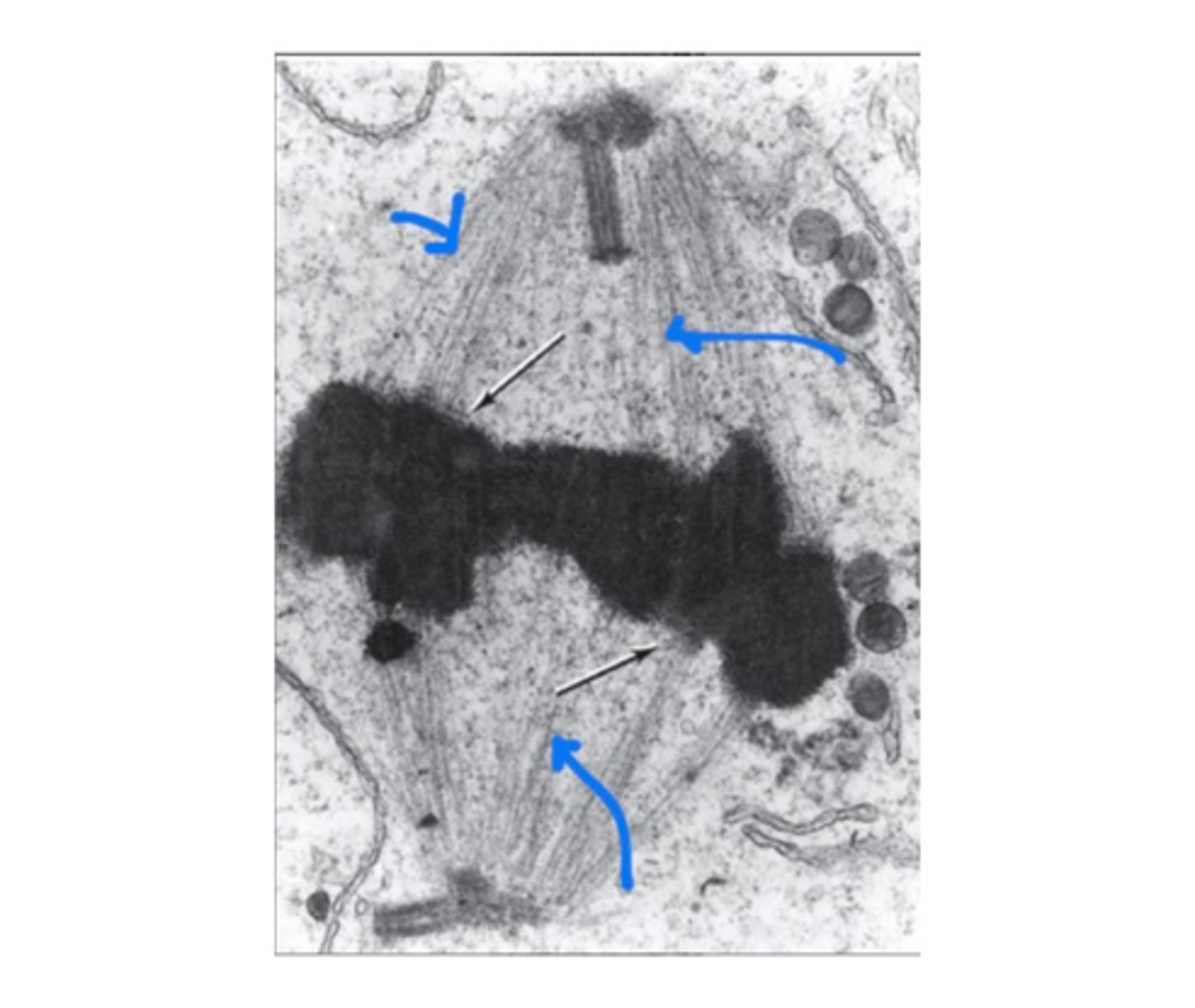
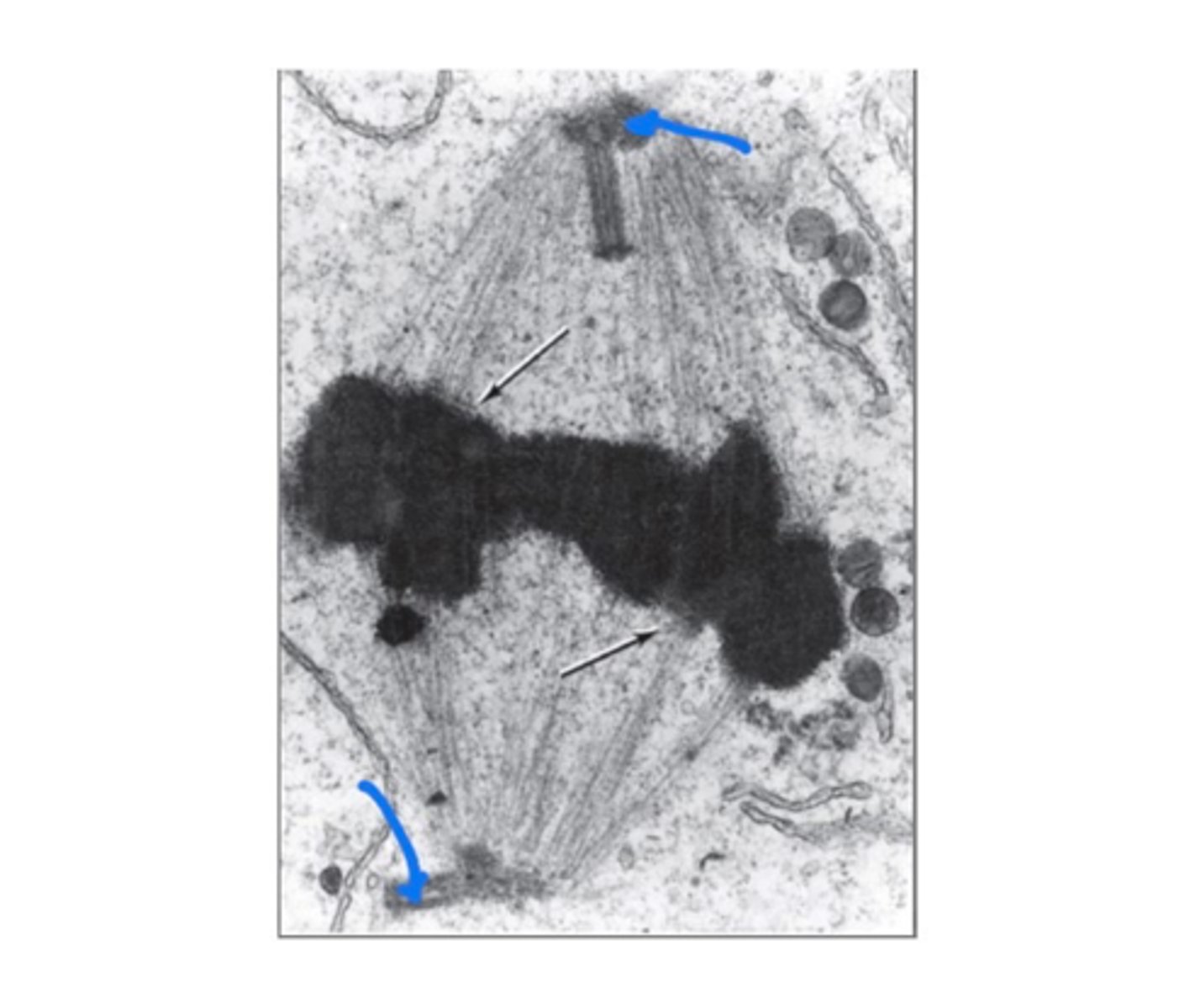
Mitotic spindle
Structure that separates chromosomes during mitosis.
Mitotic spindle
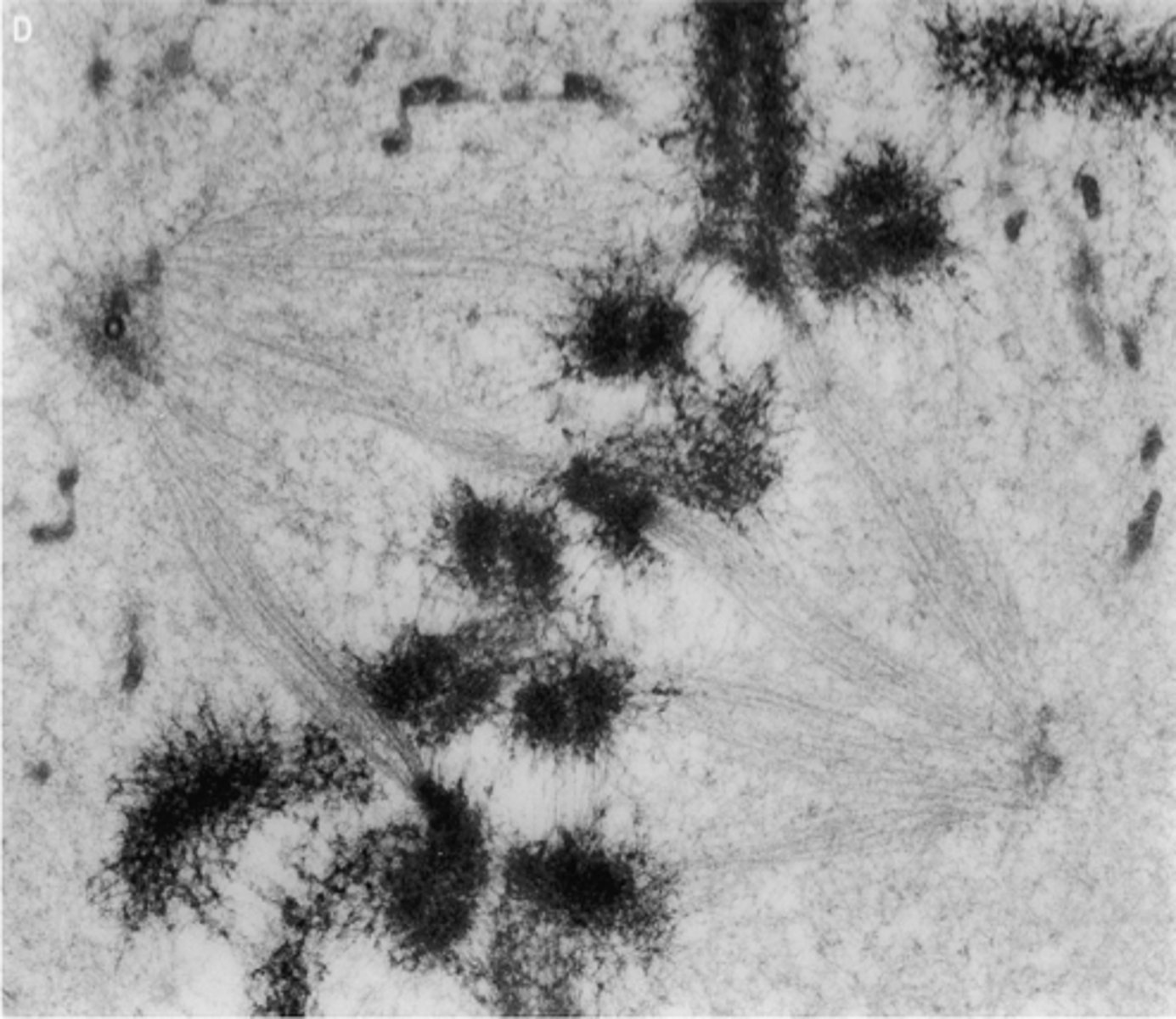
Microfilaments
Thin filaments aiding in cell movement and shape.
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, produces ATP.
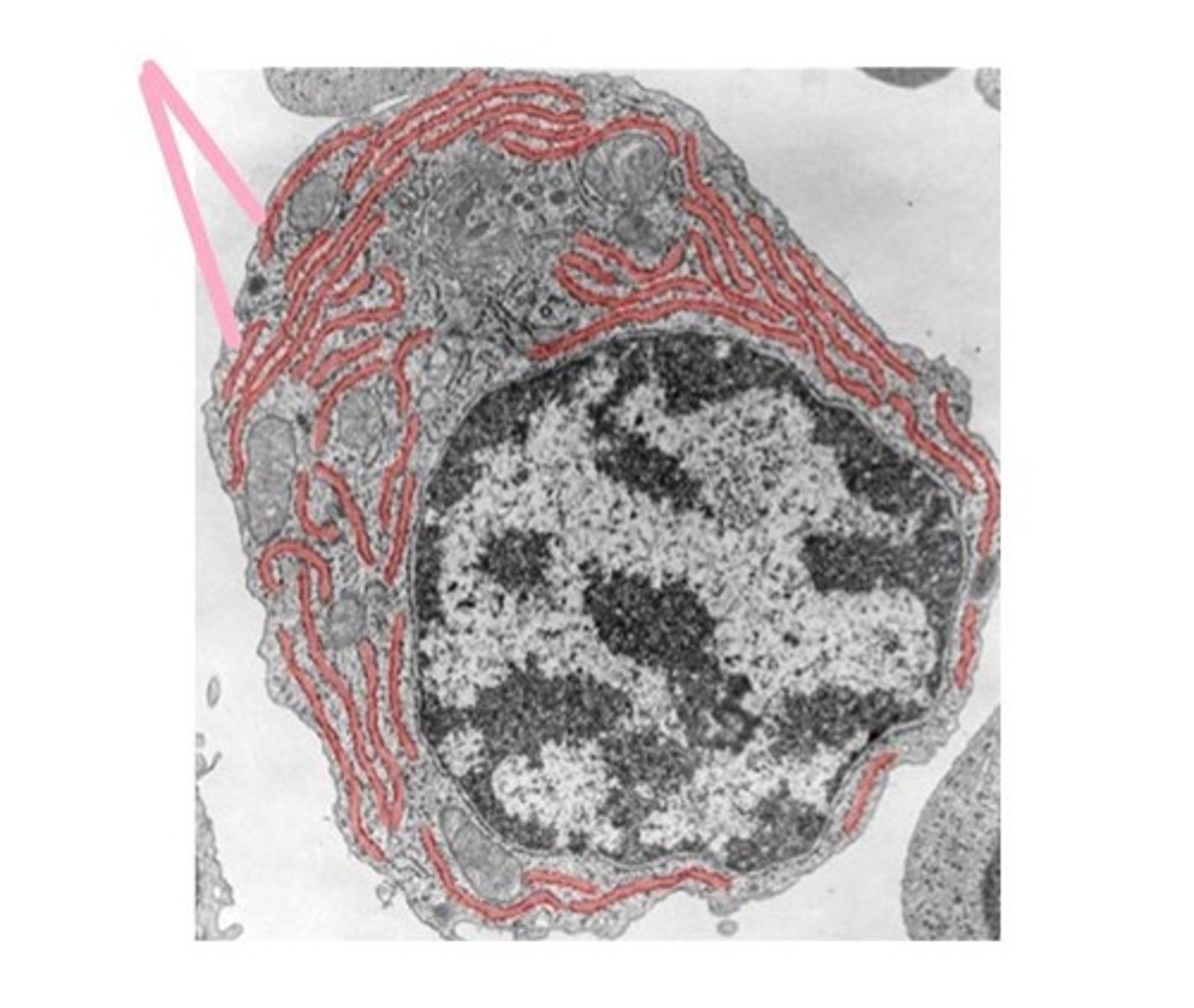
Nucleus
Contains genetic material, control center of the cell.
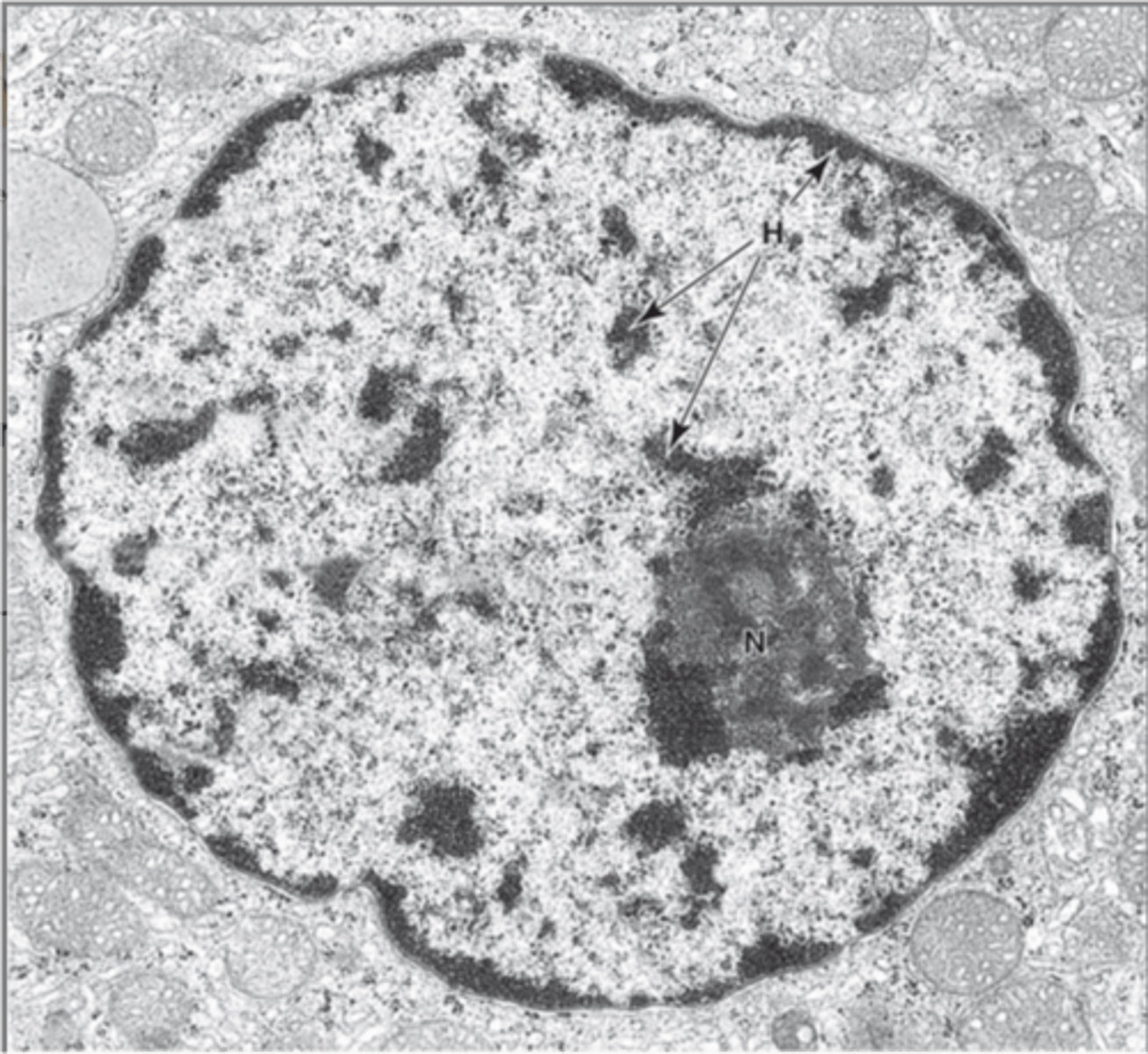
Nucleus
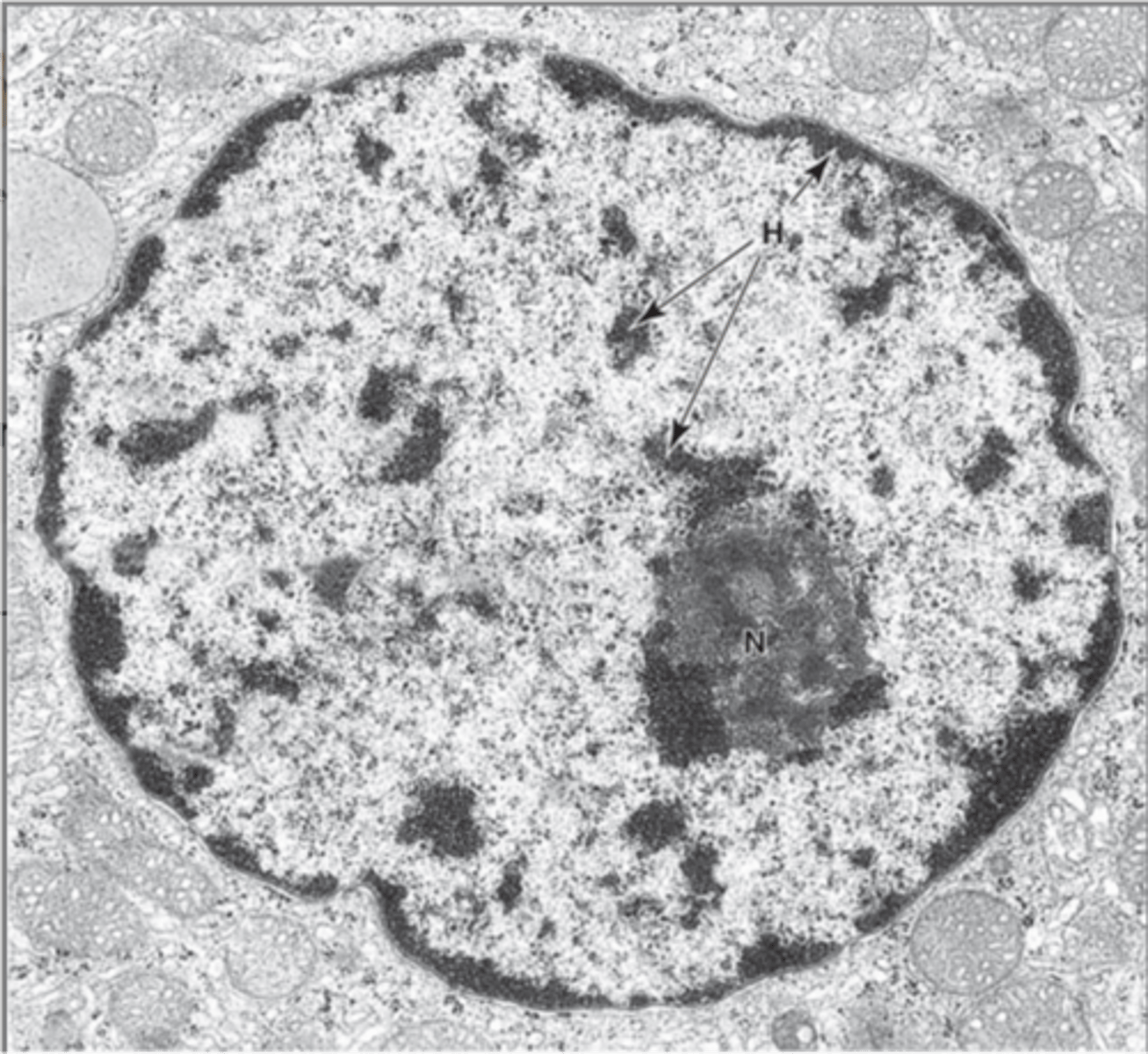
Nucleus
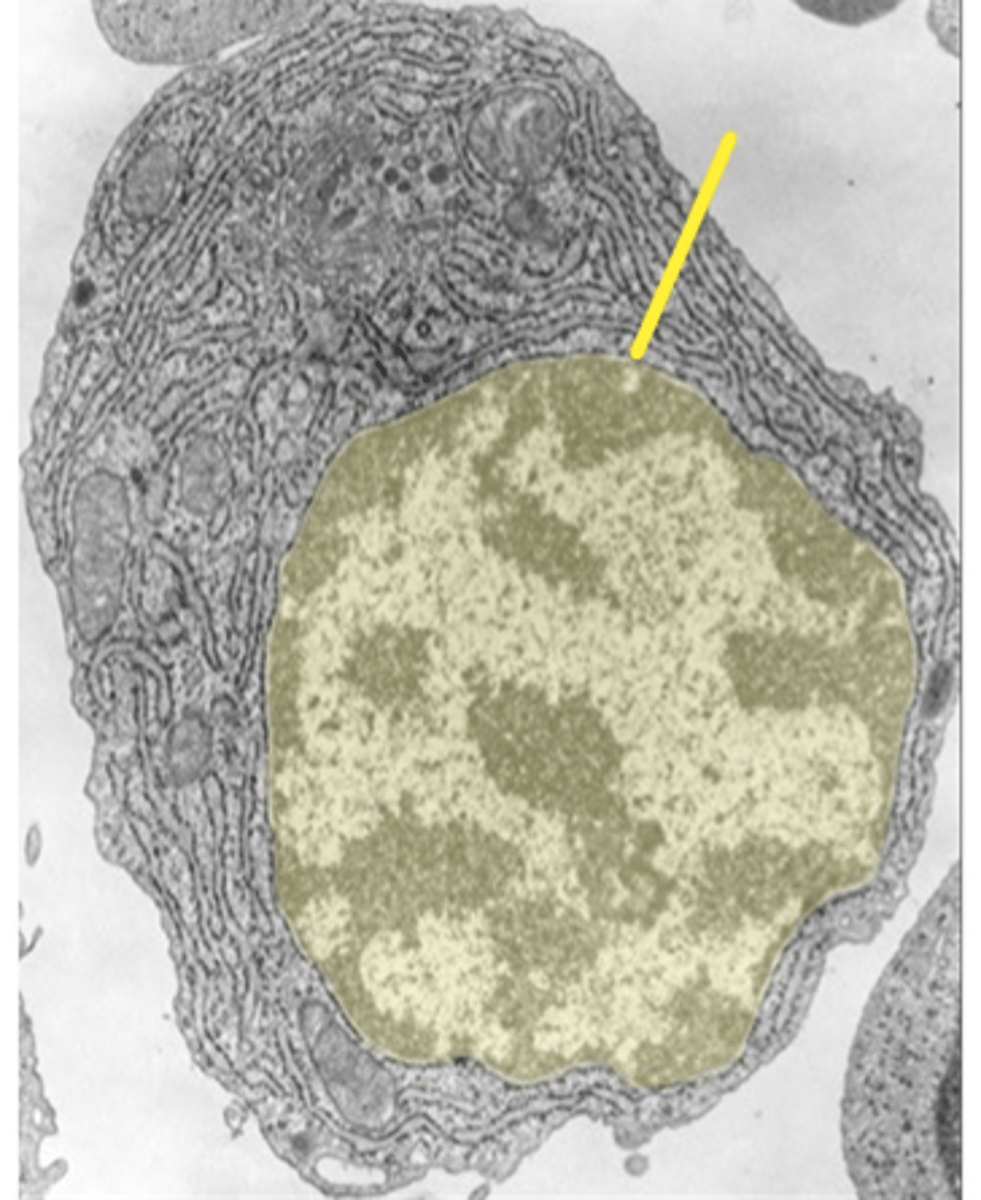
Nucleolus
Site of ribosomal RNA synthesis within the nucleus.
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane surrounding the nucleus, contains pores.
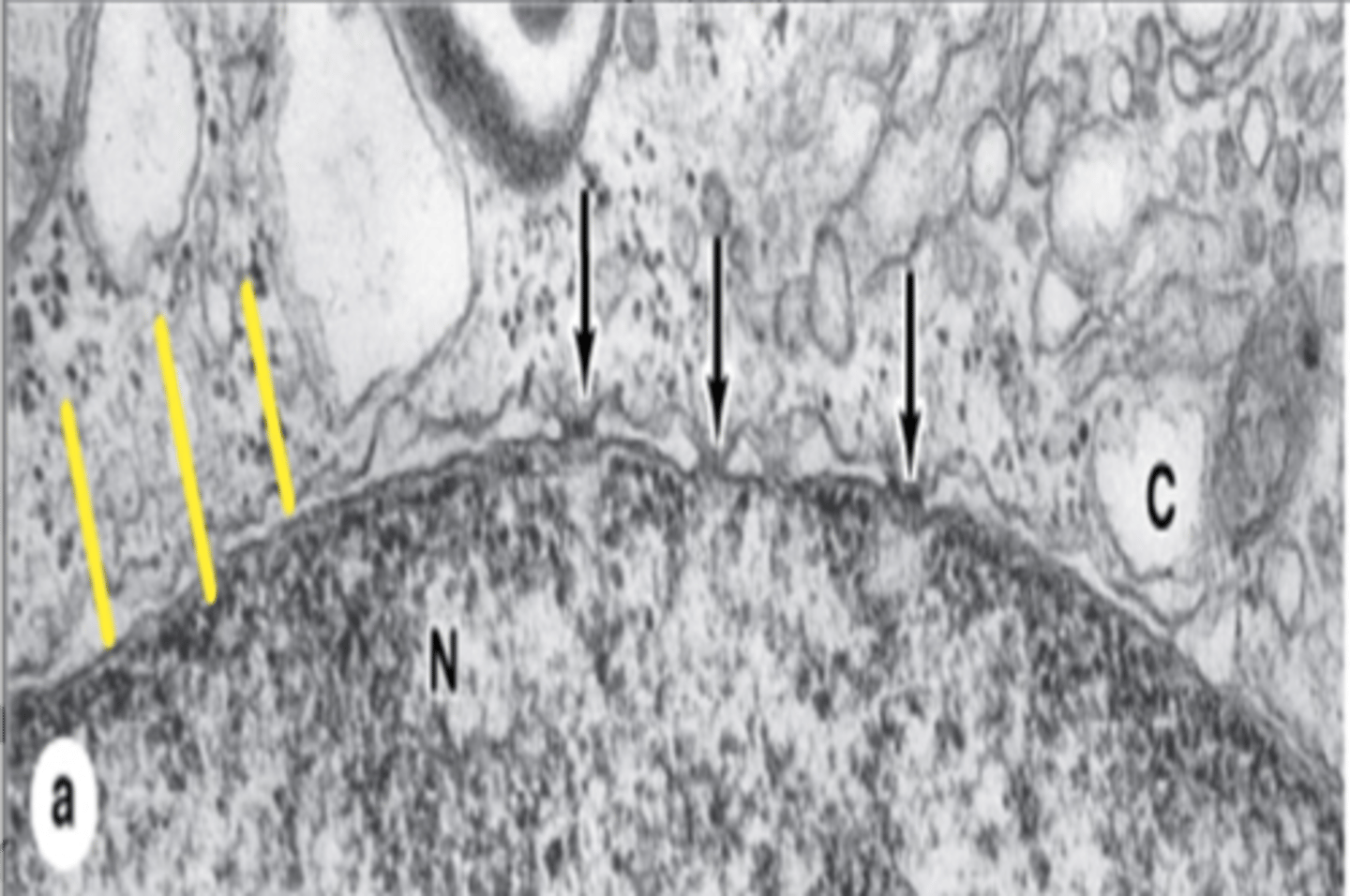
Nuclear envelope
Heterochromatin
Tightly packed, inactive form of DNA.
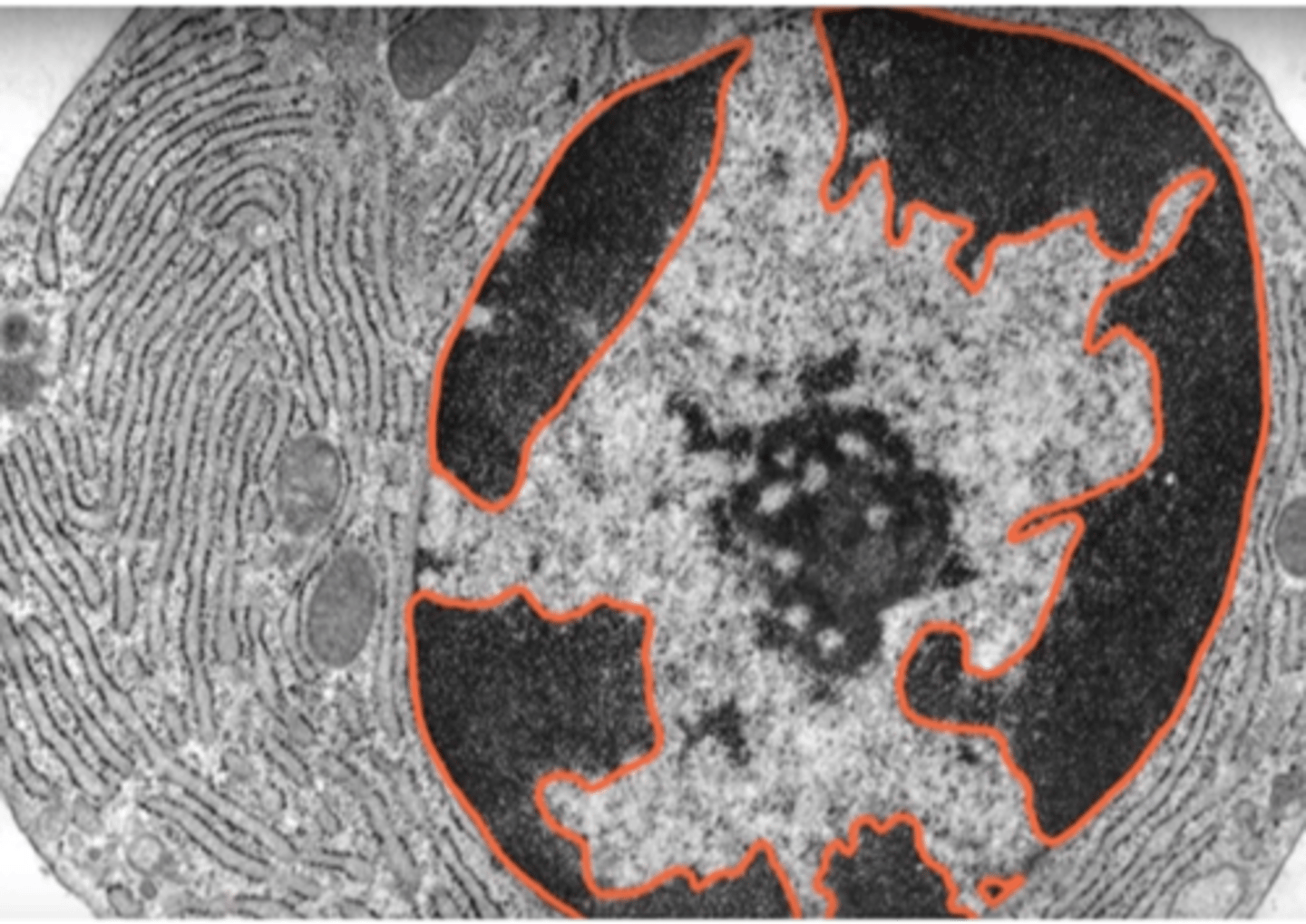
Heterochromatin
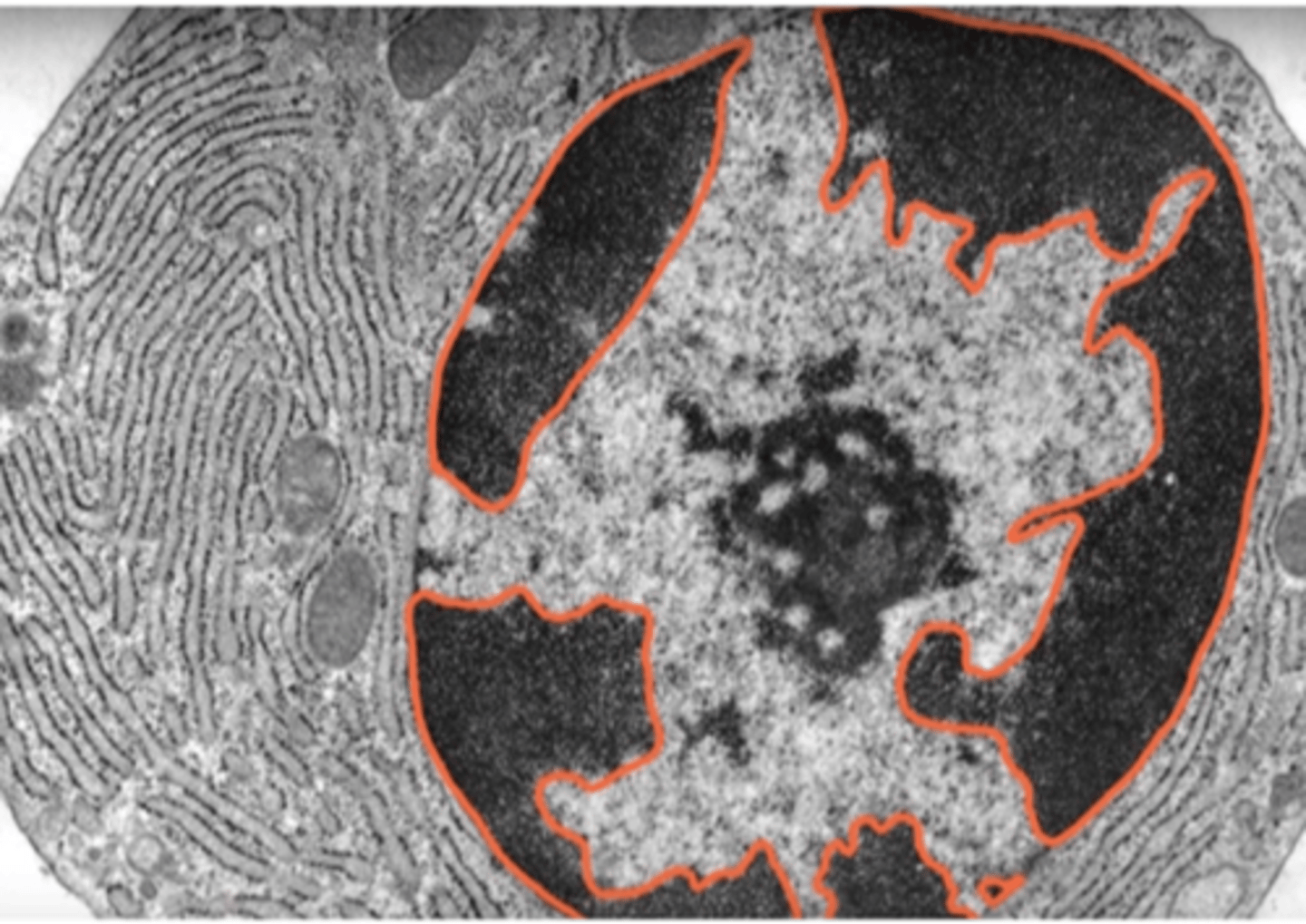
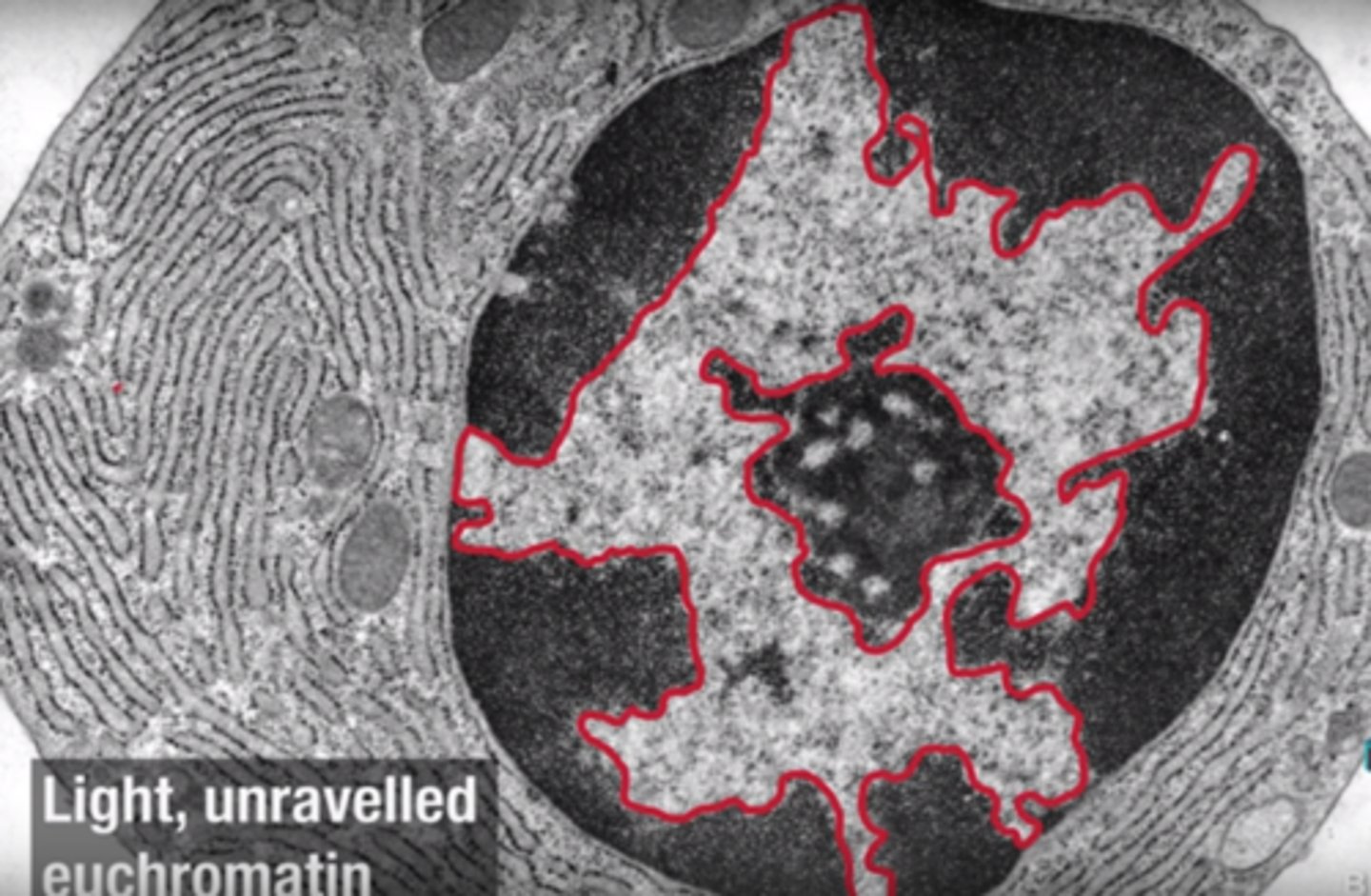
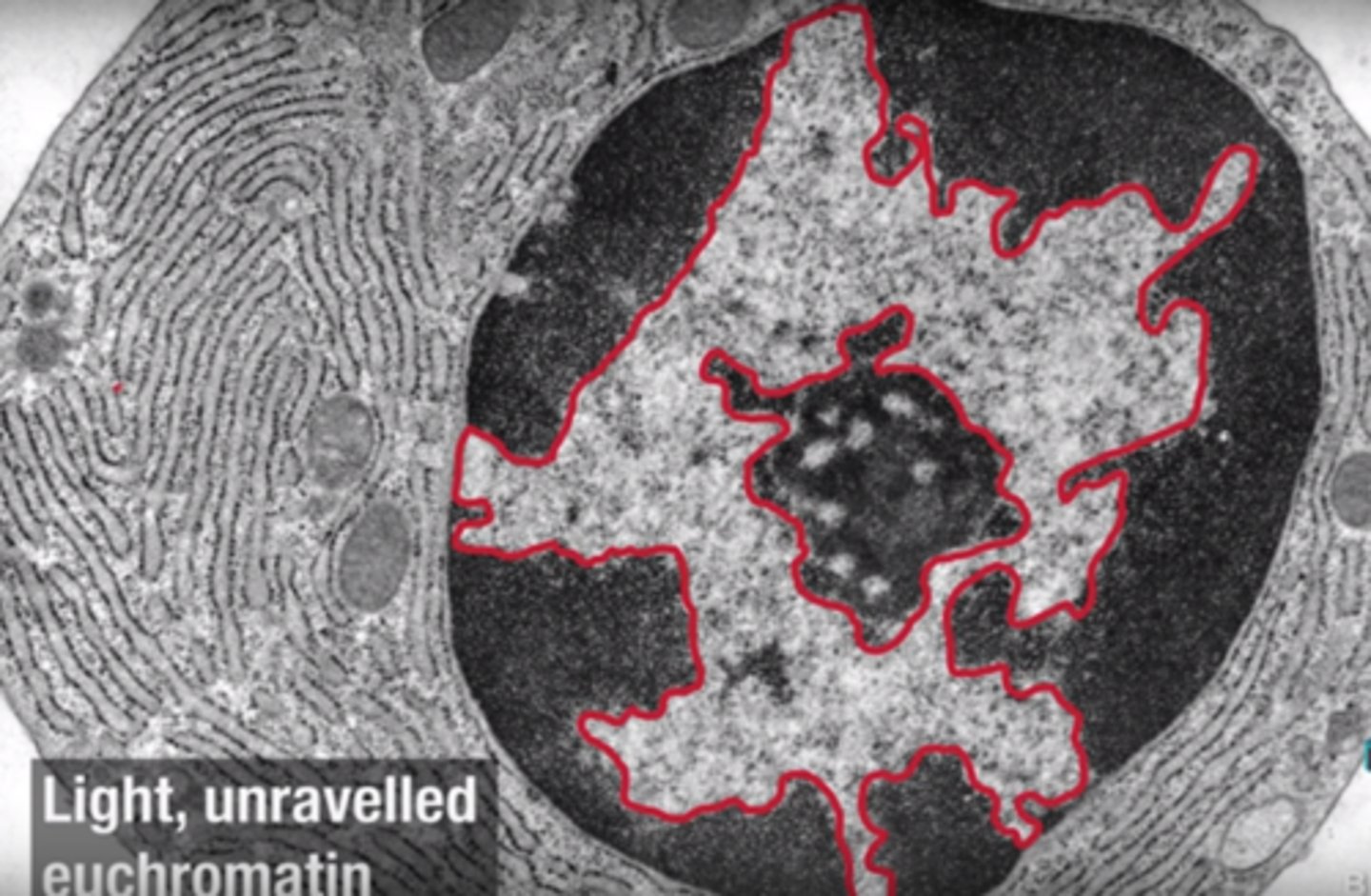
Euchromatin
Loosely packed, active form of DNA.
Euchromatin
Prophase
First stage of mitosis, chromosomes condense.
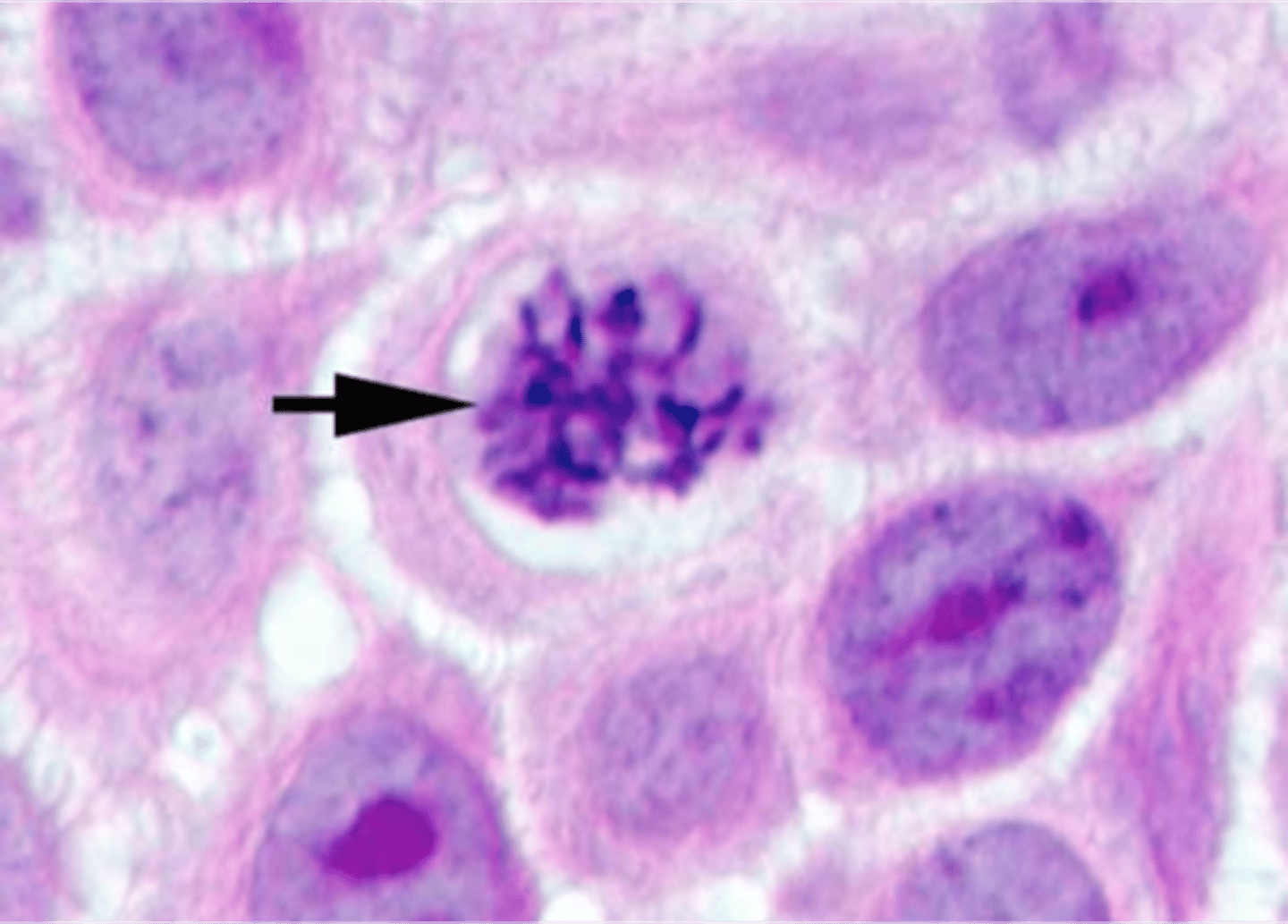
Prophase
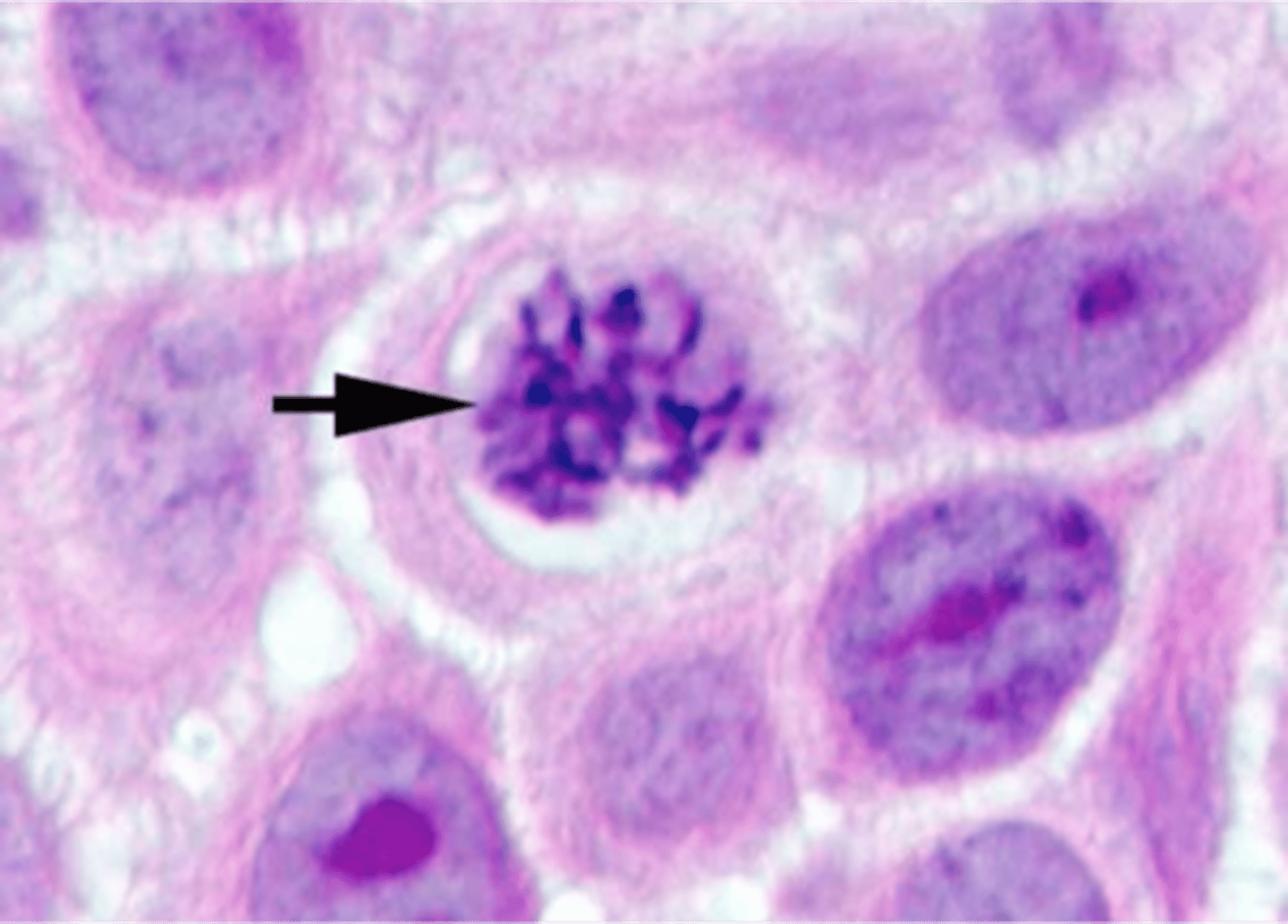
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the cell's equator.
Metaphase
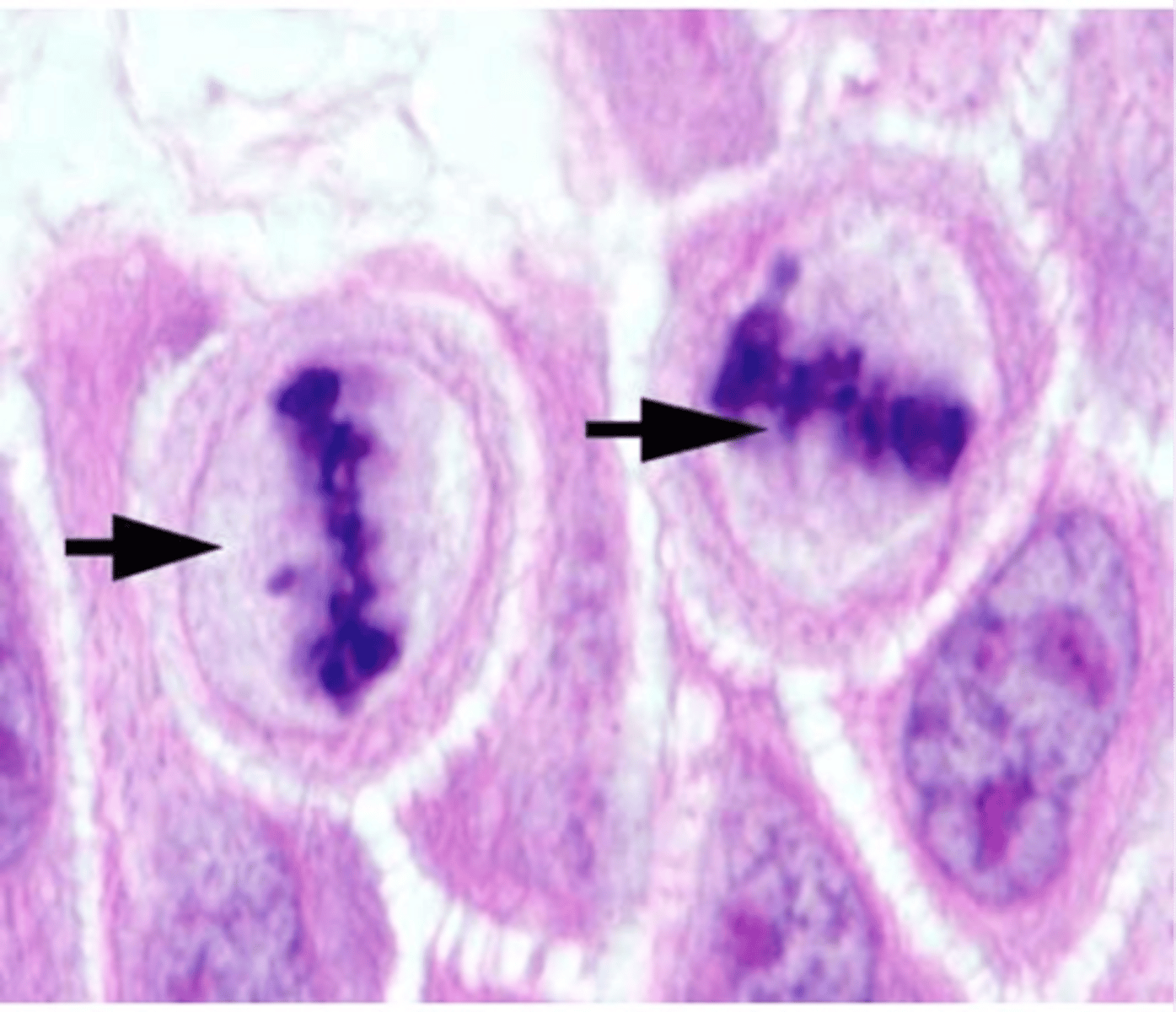
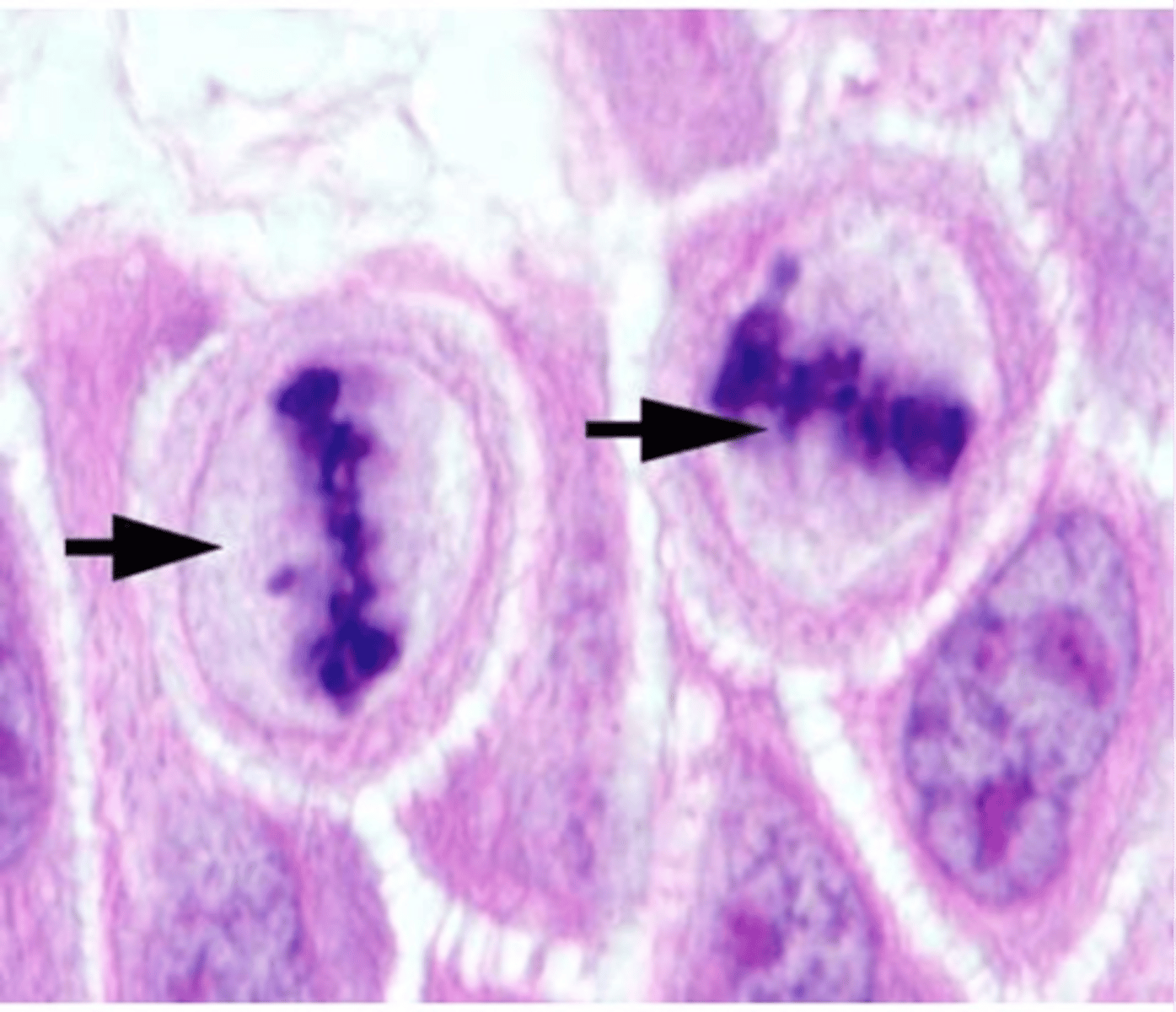
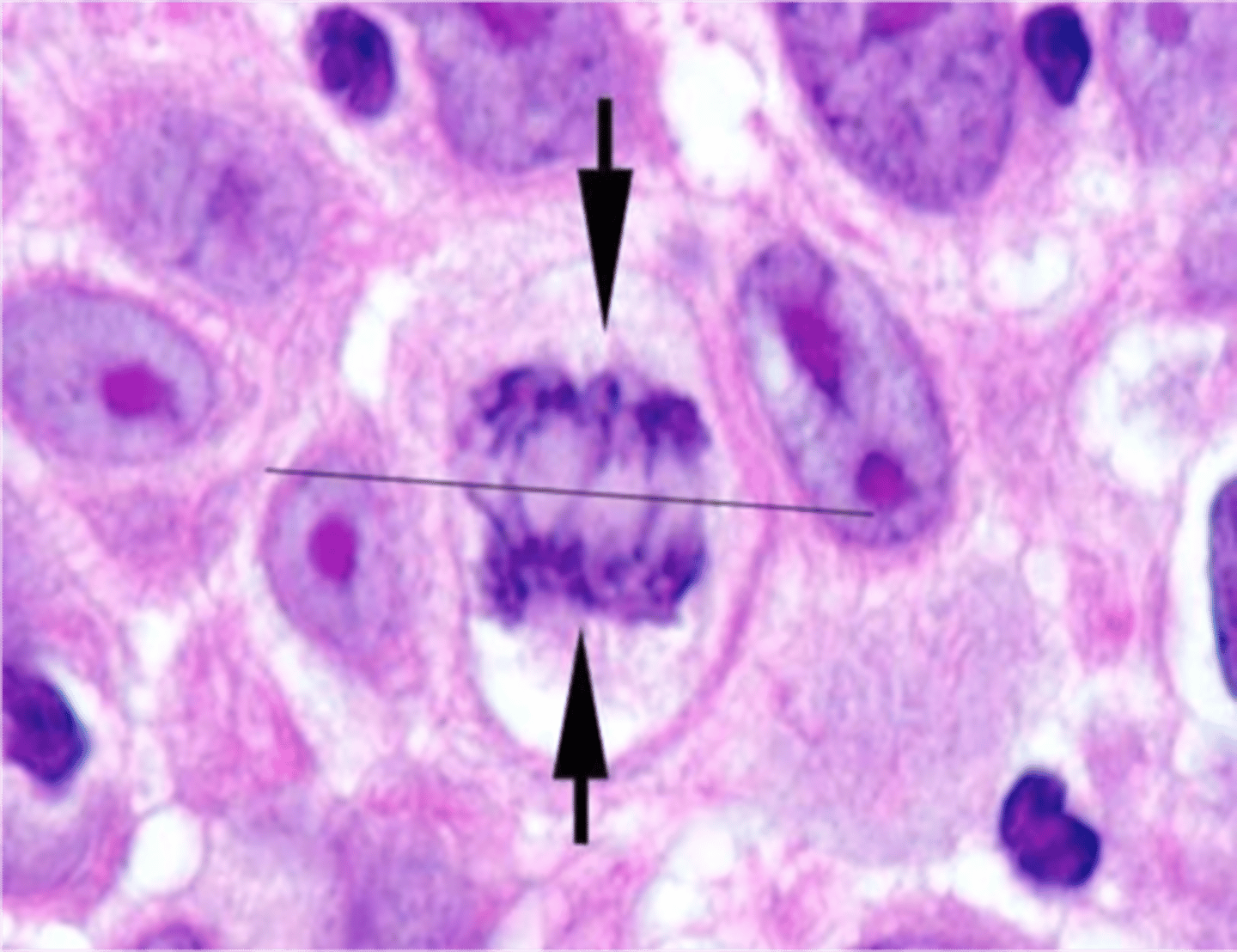
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate and move to poles.
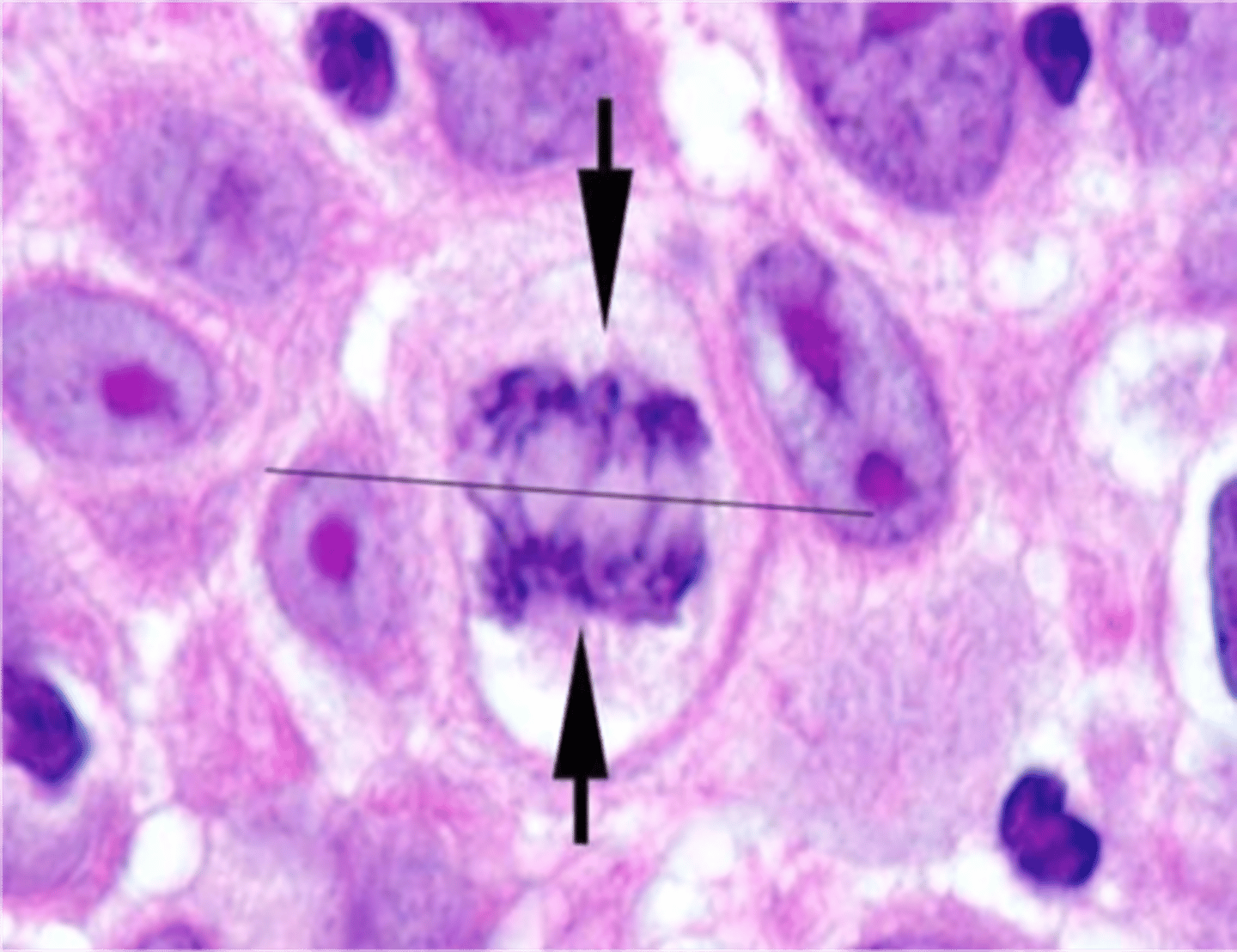
Anaphase
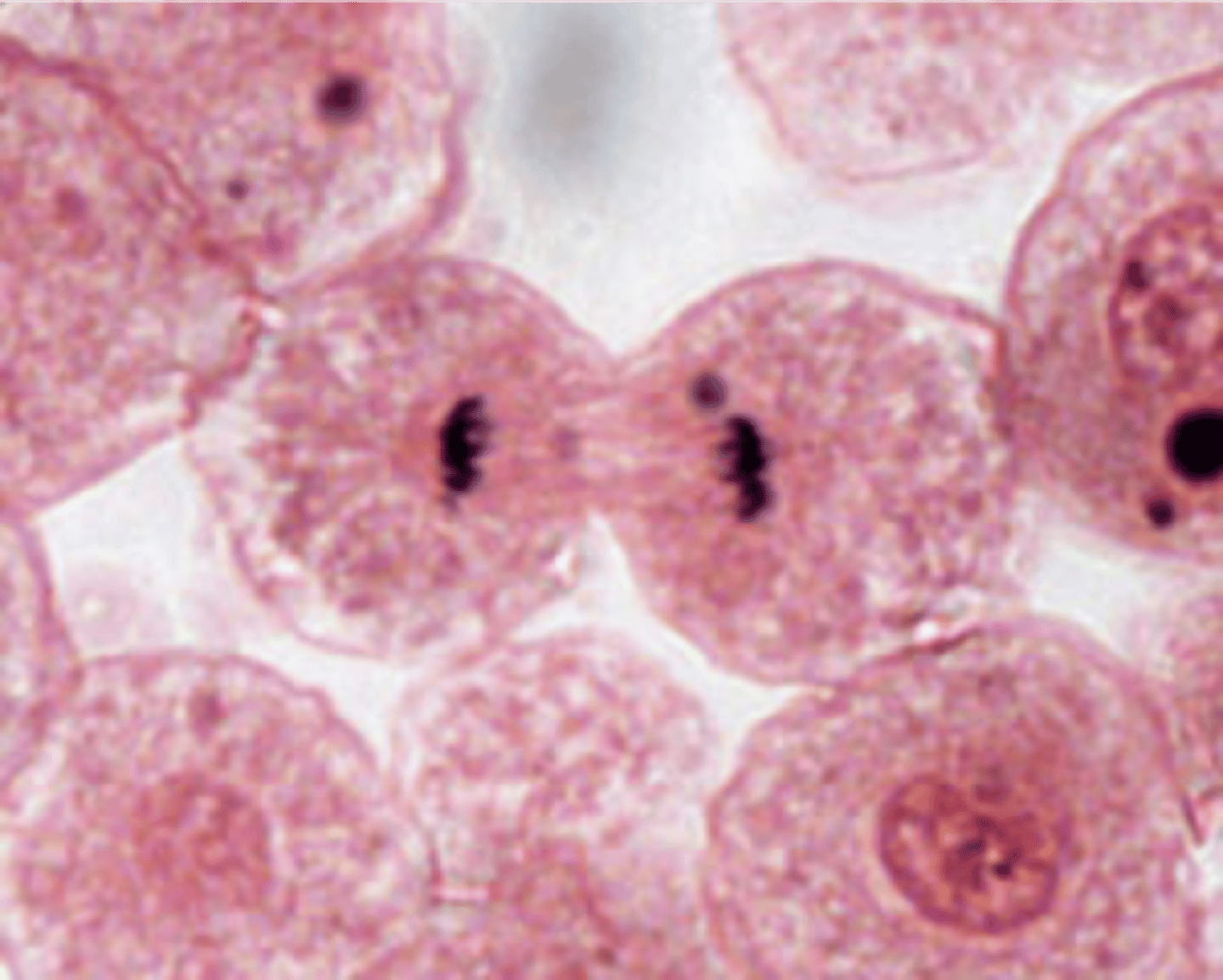
Telophase
Chromatids reach poles, nuclear envelope re-forms.
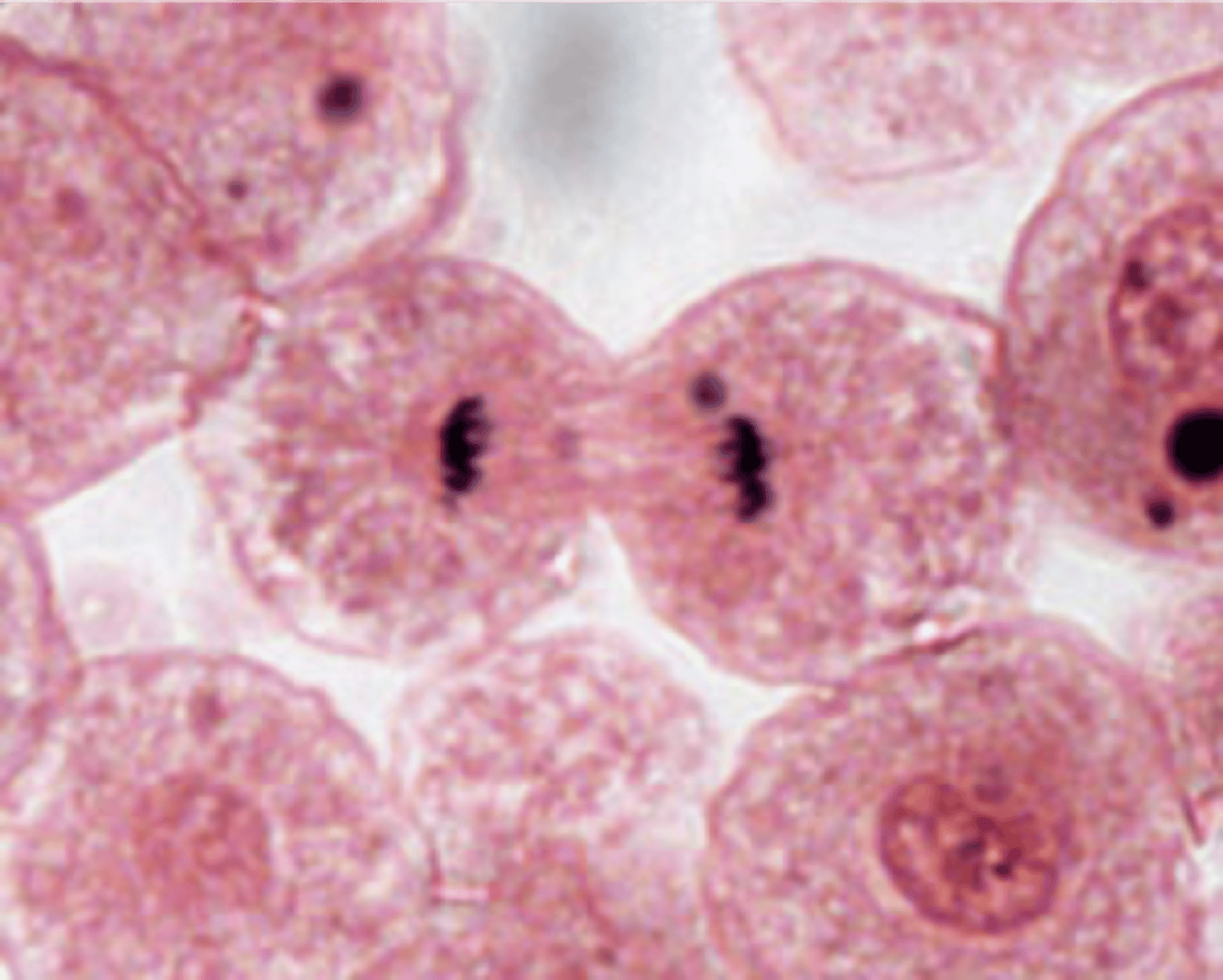
Telophase
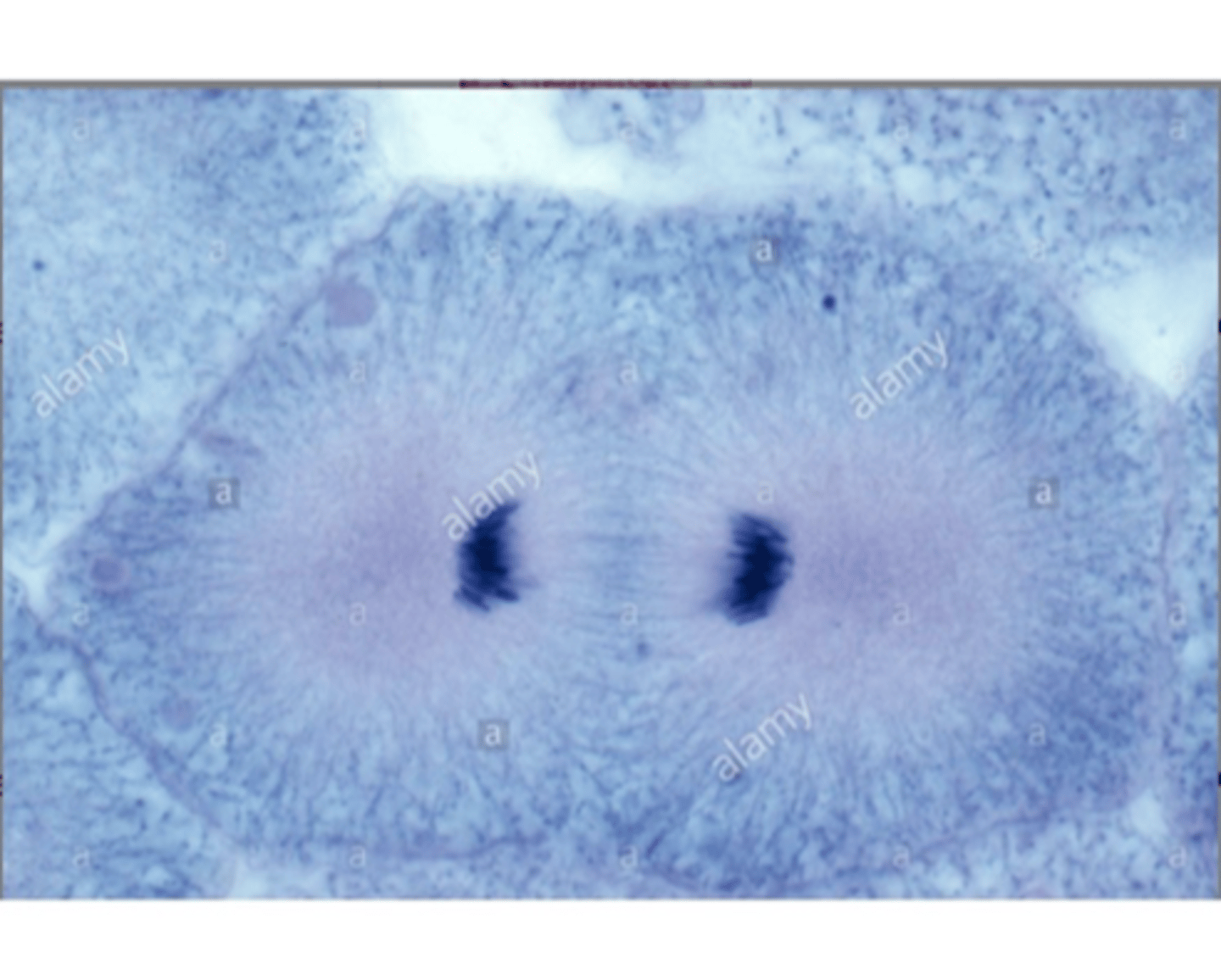
Telophase
Light microscopy
Technique for viewing cells and tissues at low/high power.
Lumen
Interior space of a tubular structure.
Plasma Membrane
Microtubules