Deck 2: Trigeminal Nerve
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
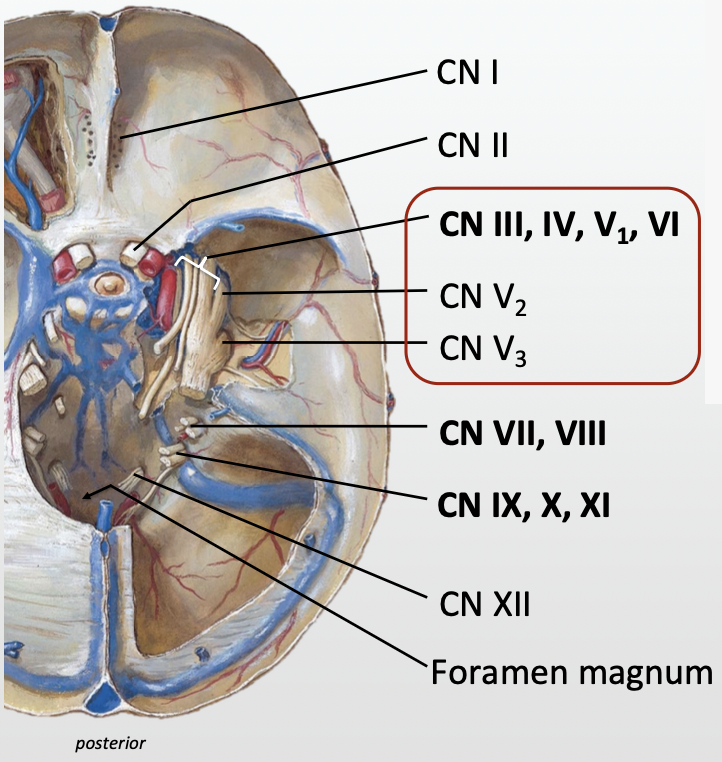
Which cranial nerves attach to the forebrain?
CN 1 (Olfactory)
CN 2 (Optic)
Which cranial nerves attach to the brainstem?
CN 3 to 10
CN 12
Describe the course of CN 11 (Spinal accessory) nerve.
Emerges from the cervical spinal cord
Ascends through foramen magnum
Exits via the jugular foramen
Which cranial nerve is the only one to emerge from the dorsal surface of the brainstem?
CN 4 (Trochlear)
What cranial nerves does the CN 5 (Trigeminal nerve) travel in close proximity to?
CN 3, 4 & 6
What type of innervation does the Trigeminal nerve have? Sensory, motor or both?
Both!
Somatic sensory nerve - for the face
Somatic motor nerve - for the muscles of mastication + other small muscles
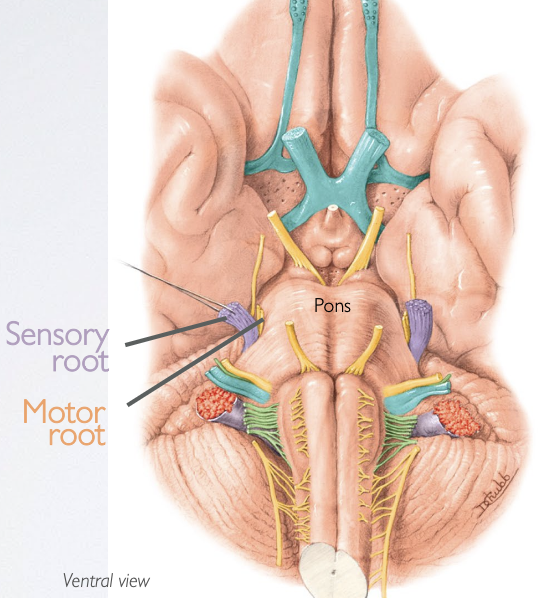
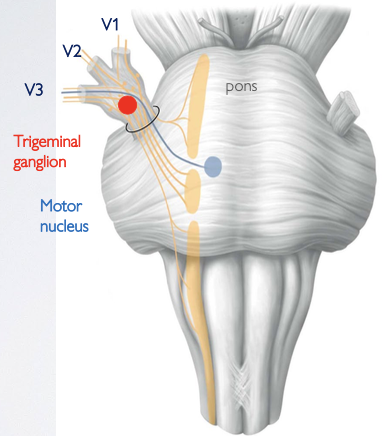
Where does the trigeminal nerve (CN V) emerge, and what are the two roots?
→ emerges from the lateral surface of the pons of the midbrain via 2 roots
Large sensory root
Small motor root
How are the branches of the trigeminal nerve (V1, V2, V3) formed?
Sensory and motor root fuse → trigeminal ganglion (Gasserian ganglion, semilunar ganglion) → V1 (Ophthalmic) + V2 (Maxillary) + V3 (Mandibular) arise
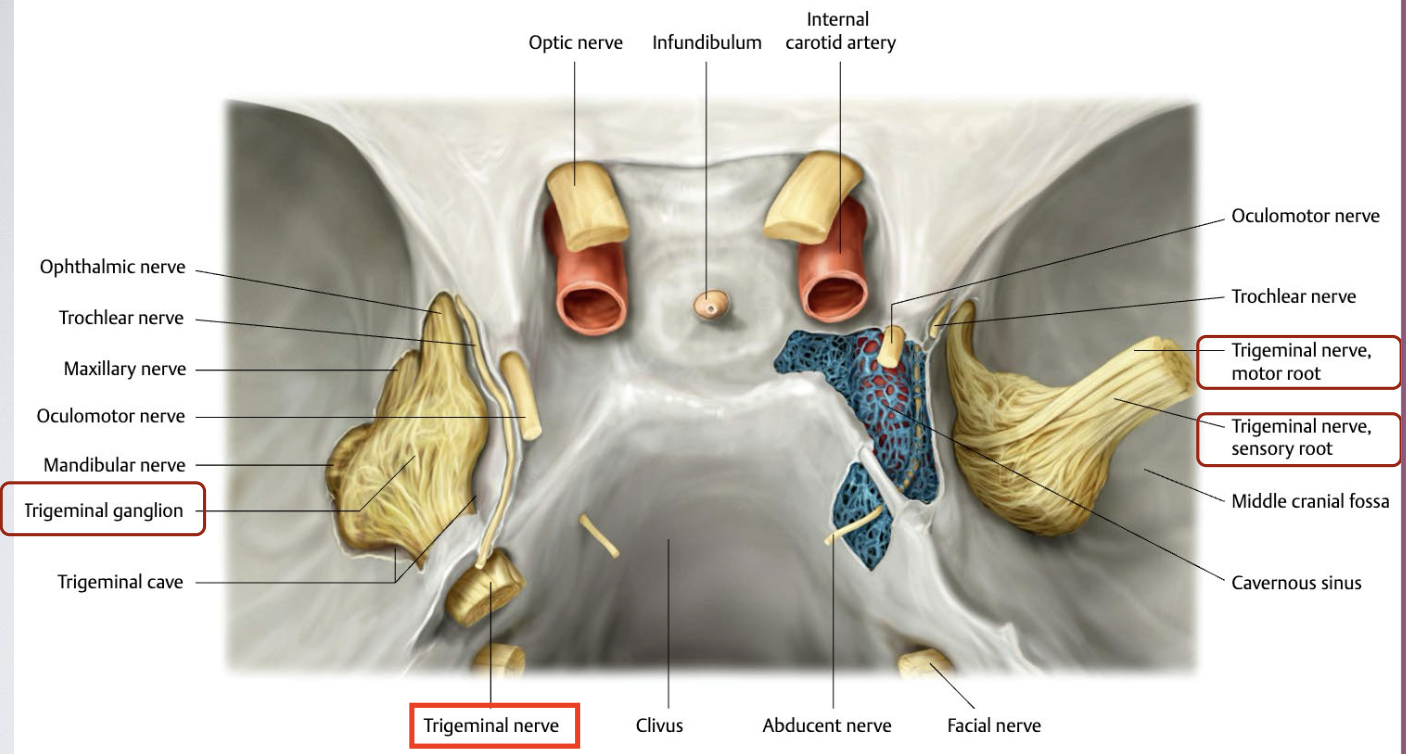
Do the sensory and motor roots synapse on the trigeminal ganglion?
No it does NOT synapse at the ganglion
What does the trigeminal ganglion contain?
has cell bodies of somatic sensory neurons
What type of innervation does V1, V2 and V3 have?
V1 and V2 - only sensory
V3 - sensory and motor
Trace the path of V1, V2 and V3.
V1 → cavernous sinus → superior orbital fissure → orbit
V2 → cavernous sinus → foramen rotundum → pterygopalatine fossa
V3 → foramen ovale → infratemporal fossa
Does V3 pass through the cavernous sinus?
No, only V1 and V2
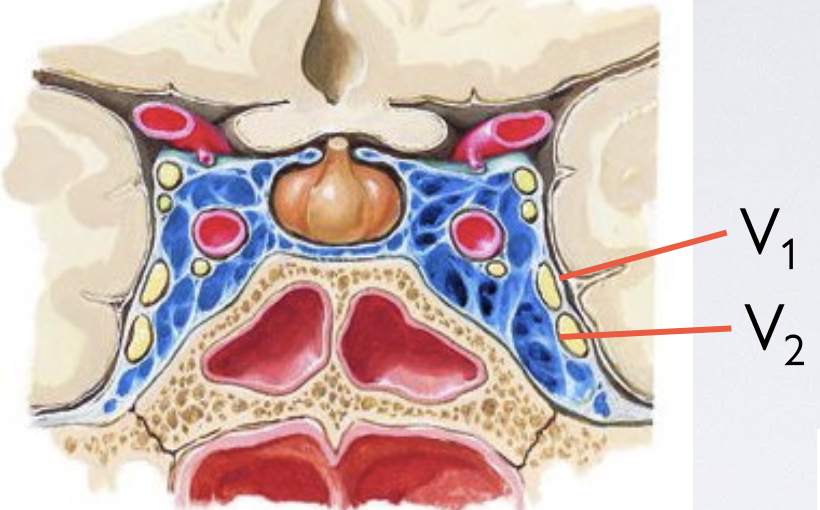
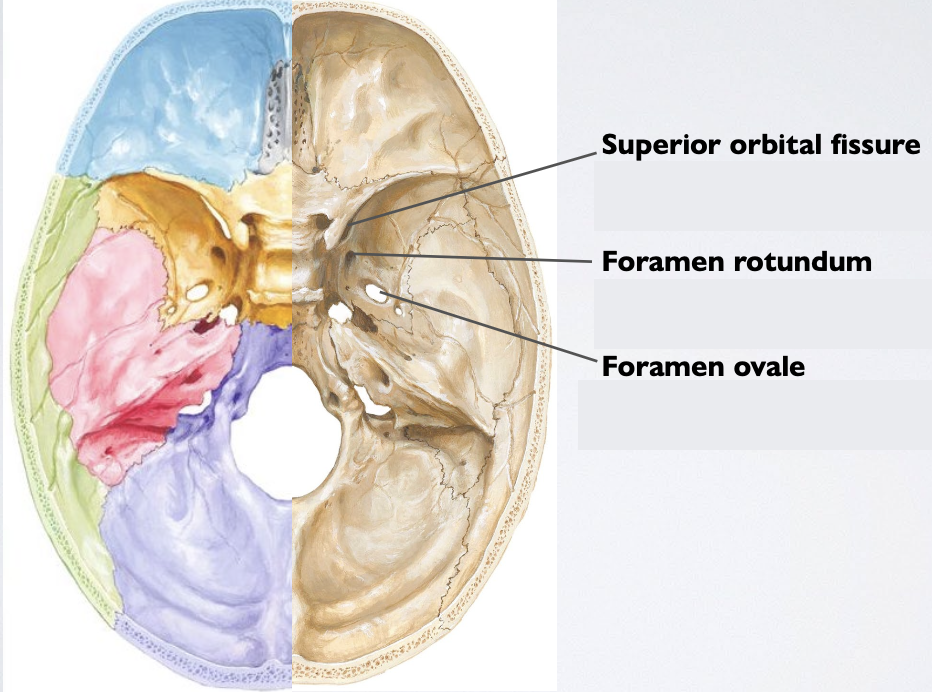
Which cranial openings do V1, V2, V3 travel through?
V1 (and CN III, IV, VI) → Superior orbital fissure
V2 → Foramen rotundum
V3 → Foramen ovale
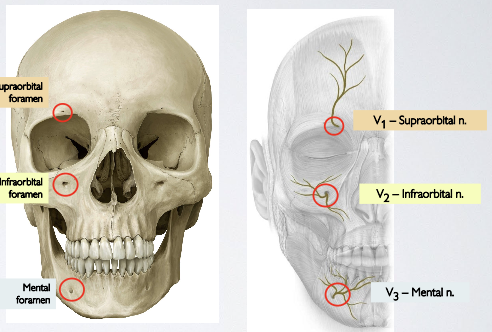
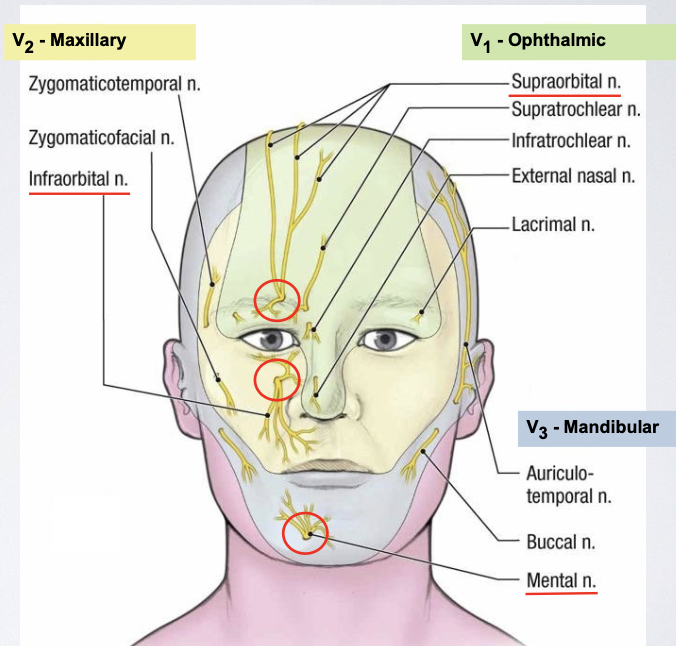
What sensory nerve branches of the trigeminal nerve (CN 5) emerge onto the face, and from which skull foramina do they exit?
V₁ → Supraorbital nerve → exits through the supraorbital foramen/notch
V₂ → Infraorbital nerve → exits through the infraorbital foramen
V₃ → Mental nerve → exits through the mental foramen
Which nerves provide sensory innervation to the posterior scalp and neck?
spinal nerves (C2 & C3)
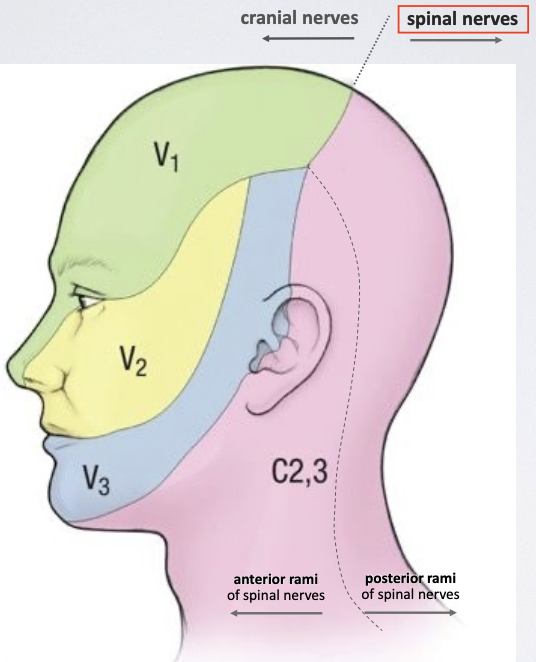
Why is C1 not shown providing sensory innervation to the scalp or face? What happened to C1?

C1 does not provide sensory innervation to the face or scalp
What is the main sensory nerve of the face and anterolateral scalp?
CN 5 (trigeminal) = main sensory nerve of the face and anterolateral scalp
What areas does the ophthalmic division (V1) innervate?
Skin of the:
anterior forehead
upper eyelids
anterior nose
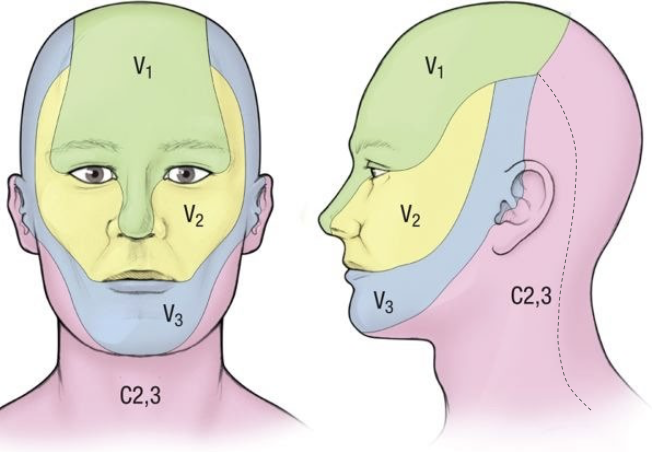
What areas does the maxillary division (V2) innervate?
Skin of the:
lower eyelid
cheek
lateral nose
upper lip

What areas does the mandibular division (V3) innervate?
Skin of the:
lower lip
lower face along the mandible
lateral forehead near the temples
part of the ear

How are cutaneous nerve branch names determined?
descriptive of their location (foramen) and the skin area/region they innervate
All 3 divisions (V1, V2 & V3) are associated with ____________ ganglia and help distribute _______________ fibers to their targets.
All 3 divisions (V1, V2 & V3) are associated with parasympathetic ganglia and help distribute parasympathetic fibers to their targets.
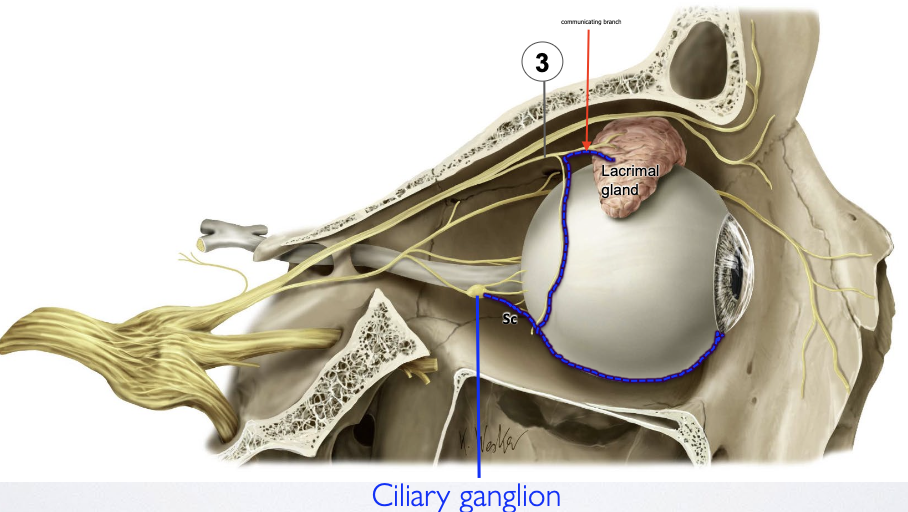
List 4 parasympathetic ganglia. Name where this ganglia is located and which CNV division is associated with it.
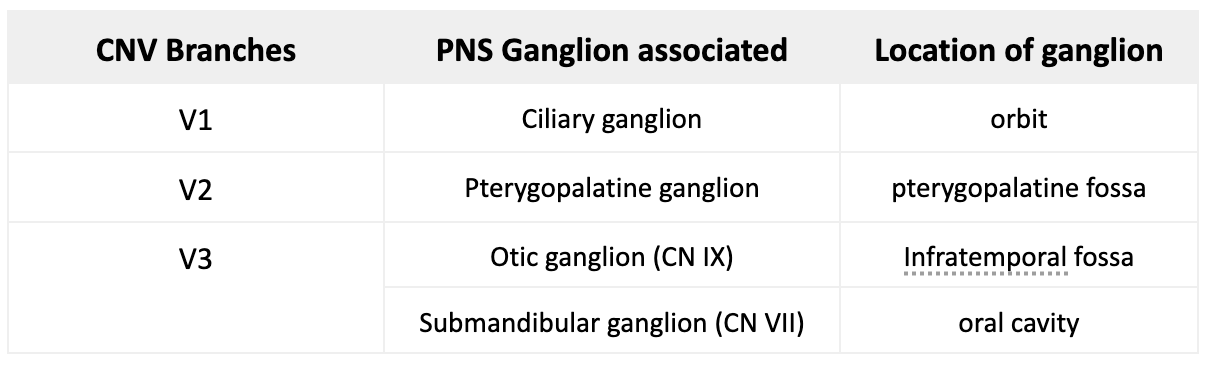
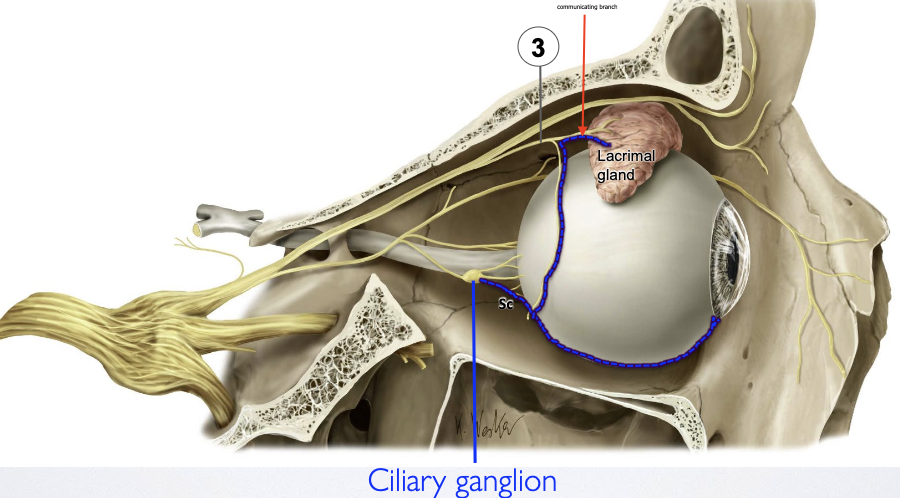
Describe the synapse that occurs at the Ciliary ganglion.
Preganglionic PNS fibers from CN 3 synapse onto ciliary ganglion
Postganglionic PNS fibers are conveyed via short ciliary nerves to pupillary sphincter & ciliary muscles
Describe the synapse that occurs at the Pterygopalatine ganglion.
Preganglionic PNS fibers from CN 7 synapse onto pterygopalatine ganglion
involved with innervating the lacrimal gland & mucous glands of the nose and palate
Describe the synapse that occurs at the Otic ganglion.
Preganglionic PNS fibers from CN 9 synapse
involved with innervating the parotid gland
Describe the synapse that occurs at the Submandibular ganglion.
Preganglionic PNS fibers from CN 12 synapse
involved with innervating the sublingual and submandibular glands
List all the regions the CN V1 provides sensory innervation to.
Skin - anterior scalp & forehead, upper eyelid & anterior nose
Orbit, cornea, superior palpebral & bulbar conjunctiva
Mucous membranes - anterior nasal cavity & paranasal sinuses (frontal, ethmoid & sphenoid)
Dura of anterior cranial fossa
What is the role of CN V1 in the corneal reflex?
CN V1 is the sensory limb of the corneal reflex
this is a key brainstem reflex used clinically to test the integrity of this division
After the passing superior orbital fissure, the V1 divides into 3 branches. What are they?
1) Frontal nerve
Runs superior
2) Nasociliary nerve
Runs medially towards the nose
3. Lacrimal nerve
Runs laterally
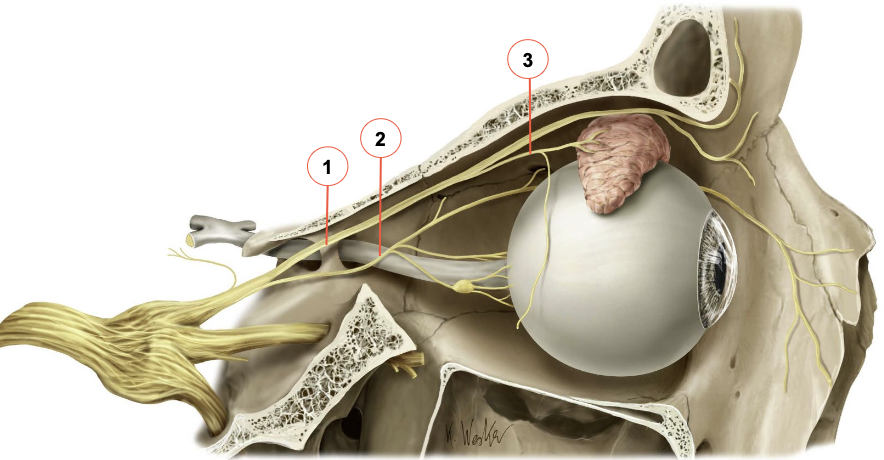
What does the frontal nerve divide into? What do these nerves supply?
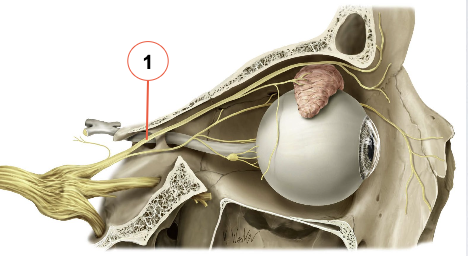
1) Supra-orbital
2) Supratrochlear
→ supply the superior eyelid, scalp & forehead
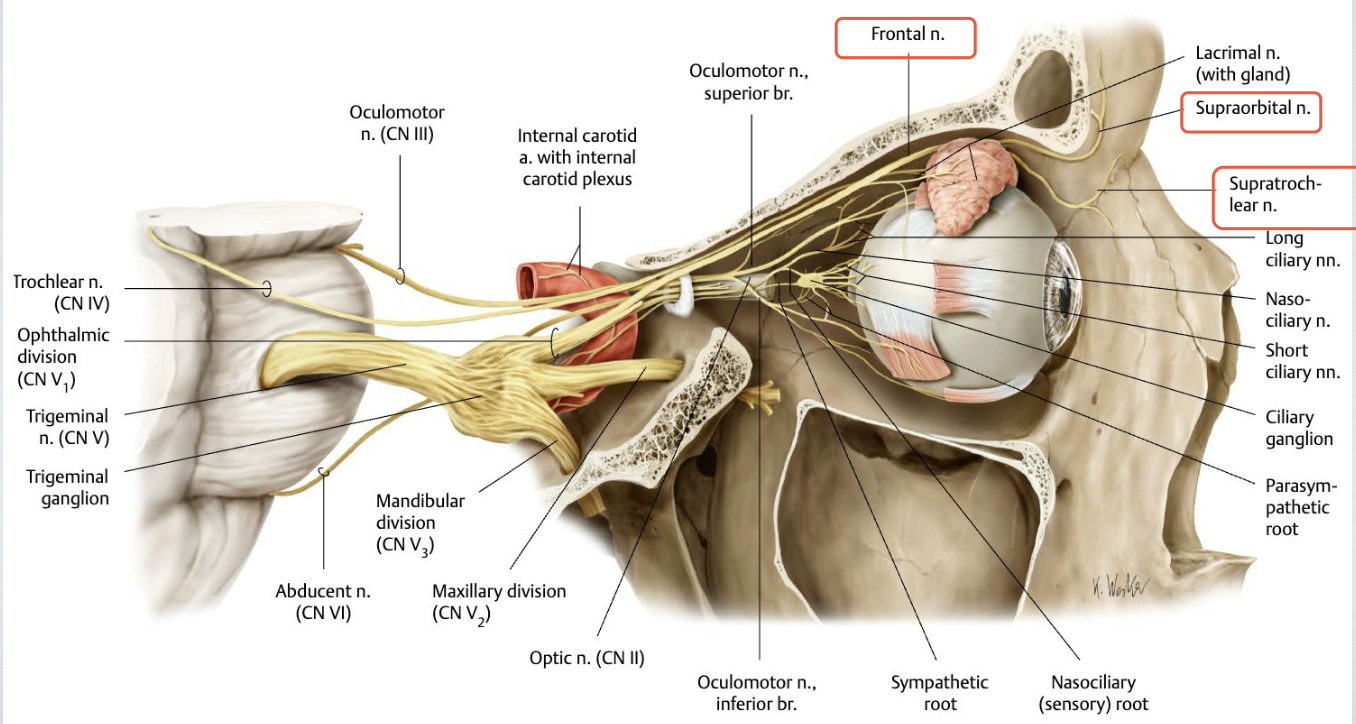
What is the nasociliary nerve? What does it supply?
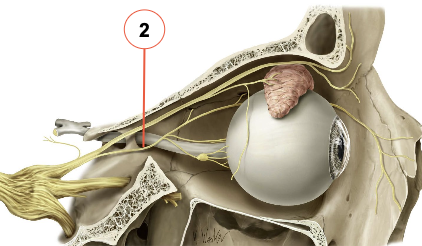
→ sensory nerve to the eyeball
also supplies several branches to the orbit, paranasal sinuses, nasal cavity & dura mater of anterior cranial fossa
What does the nasociliary nerve divide into? What do these nerves supply?

1) Infratrochlear nerve
supplies the eyelids, conjunctiva, skin of the nose & lacrimal sac
2) Anterior 3) Posterior ethmoidal nerves
supply the mucous membranes of the sphenoidal and ethmoidal sinuses, nasal cavities & dura mater of the anterior cranial fossa
4) Long ciliary nerve
supplies the iris and cornea
conveys postsynaptic SNS fibers to the dilator pupillae
What’s the significance of the postsynaptic SNS fibers to the dilator pupillae?
these post-synaptic SNS fibers → sensory limb of corneal reflex
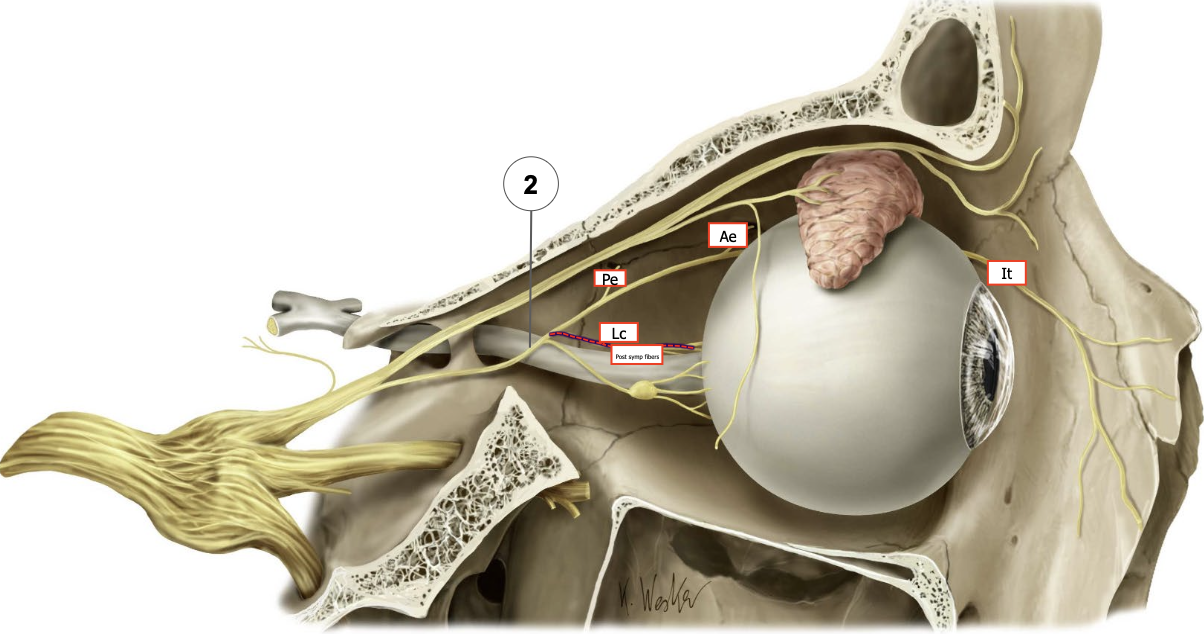
Describe the course of the lacrimal nerve. What does it supply?
→ courses superolaterally to the lacrimal gland
supplies the conjunctiva & skin of upper eyelid
its distal part carries secretomotor fibers conveyed to it from ‘hitchhiking’ on the zygomatic nerve (CN V2) via a communicating branch
What are the characteristics of the Corneal reflex?
→ refers to the contraction of the o.oculi in response to light touch of the cornea
direct & consensual response
present at infancy (works on anyone — whether you’re disabled or in coma)
reflex may be slowed or absent in many disorders affecting the BOT (brain stem nuclei, ophthalmic nerve, or trigeminal ganglion)
What are the afferent and efferent limbs of the corneal reflex?

Afferent - nasociliary branch of V1 → detecting the stimuli
Efferent - Facial nerve (CN 7) → closure of eye
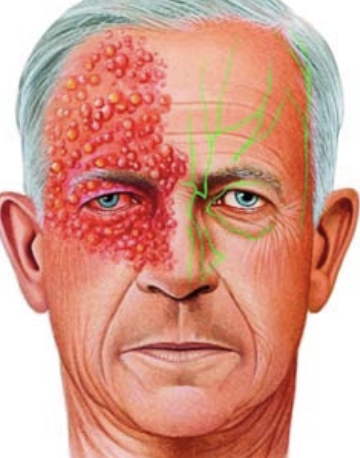
What is Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus (HZO)?
→ viral disease causing a unilateral, painful skin rash
occurs when the virus travels through trigeminal nerve dermatomes including areas shared by the eye and ocular adnexa
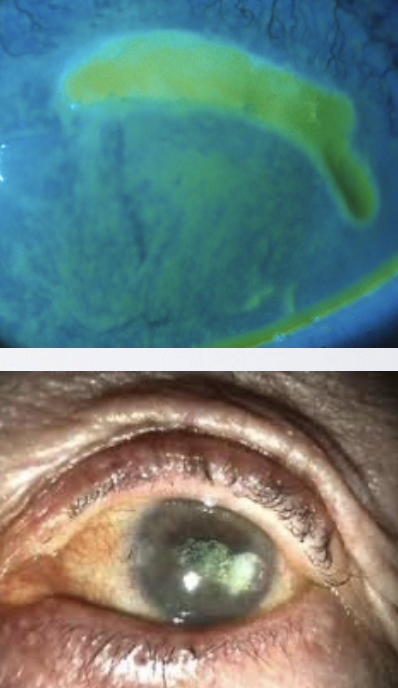
What is Zoster Keratitis/Keratouveitis? Why is it an ocular emergency?
occurs in ~50% of HZO cases
Ocular findings include conjunctivitis, uveitis, episcleritis, keratitis, and retinitis
it’s an ophthalmologic emergency b/c delayed treatment → vision loss
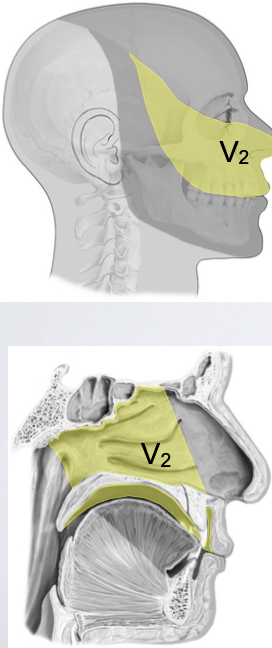
List all the regions the CN V2 provides sensory innervation to.
Skin of midface: lower eyelid, cheek, lateral nose, upper lip
Mucous membranes of the postero-inferior nasal cavity, maxillary sinus, hard and soft palate, superior oral vestibule
Maxillary teeth
Dura of middle cranial fossa
What is the MAJOR sensory nerve of the maxillary region & mid face?
V2
Maxillary nerve (CN V2) divides into 6 major branches. What are they?
Zygomatic
Infraorbital
Superior alveolar
Greater palatine
Lesser palatine
Nasopalatine
Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
What does the Zygomatic (zygomaticofacial and zygomaticotempora) nerves supply?
skin of the prominence of the cheek and anterior part of temporal fossa
sends communicating branch to lacrimal nerve to distribute postganglionic parasympathetic motor fibers to lacrimal gland & mucous glands of the nose & palate
Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
What does the Infraorbital nerve supply?
skin and conjunctiva of the lower eyelid, cheek, lateral nose, and upper lip
ends in the infraorbital foramen to supply the dermatomes of the face
mucosa of the superior oral vestibule and antero-inferior nasal septum
Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
What does the Superior alveolar nerve supply?
maxillary sinus
maxillary teeth
Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
What does the Greater Palantine nerve supply?
mucosa & glands of the hard palate
Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
What does the Lesser Palantine nerve supply?
mucosa & glands of the soft palate
Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
What does the Nasopalatine nerve supply?
mucosa of the anterior part of the hard palate & nasal septum
Of all the nerve branches of the Maxillary nerve (V2), which ones distribute postganglionic parasympathetic fibers from the Pterygopalatine ganglion?
Zygomatic
Greater palatine
Less palantine
Nasopalantine
List all the regions the CN V3 provides sensory innervation to.
Skin of the lower face along the mandible, lower lip, lateral forehead near the temples, part of auricle
Mucous membranes of floor of mouth, inferior oral vestibule, anterior 2/3 tongue
Mandibular teeth
TMJ
Dura of middle cranial fossa
List all the regions the CN V3 provides motor innervation to.
4 Muscles of mastication
2 oral floor muscles
1 tensor muscle of the middle ear
1 tensor muscle of the palate
Mandibular nerve (CN V3) divides into 5 major sensory branches. What are they?
Auriculotemporal
Inferior Alveolar
Mental
Lingual
Buccal
Of all the nerve branches of the Mandibular nerve (V3), which ones distribute postganglionic parasympathetic fibers from the Otic & Submandibular ganglion?
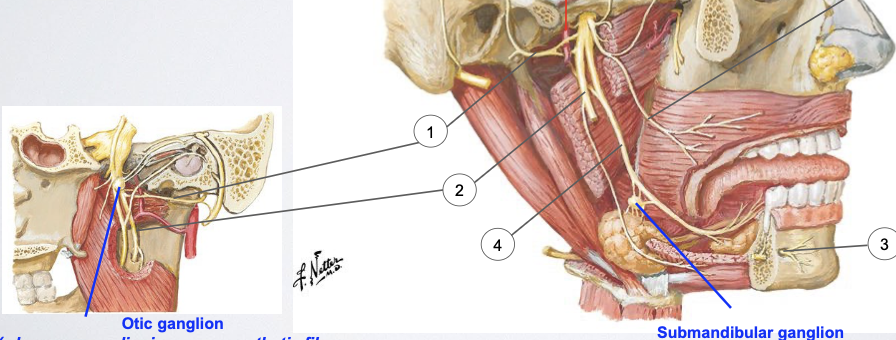
Auriculotemporal
Lingual
Of all the nerve branches of the Mandibular nerve (V3), which ones distribute postganglionic taste fibers from the Otic & Submandibular ganglion?
Lingual
Mandibular nerve (CN V3) divides into 4 major motor branches that supply the muscles of mastication. What are they?
Masseter
Temporalis
Medial pterygoid
Lateral pterygoid
(each is the “nerve to ___ muscle”)
Mandibular nerve (CN V3) divides into 2 major motor branches that supply the 2 oral muscles. What are they?
mylohyoid
anterior belly of the digastric
Mandibular nerve (CN V3)
What nerve supplies the mylohyoid & anterior belly of the diagastric?
mylohyoid nerve
Mandibular nerve (CN V3)
Mandibular nerve (CN V3) divides into 2 major motor branches that supply the 2 tensors. What are they?
Tensor tympani (middle ear)
Tensor veli palatini (palate)
Where are many of the motor branches of V3 located?
infratemporal fossa
What is trigeminal neuralgia and what are its key features?
Most common disorder of CN 5
Usually affects V2 or V3 (less often V1)
occurs due to vascular compression (abnormal blood vessel) of the sensory root near the brainstem
Causes recurring, severe, electric-shock–like stabbing pain in trigeminal nerve distributions
Triggers = eating, talking, shaving, or light touch