bonding
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Ionic bonding
-electrons are transferred from one atom to another
-the resulting ions ae held together in a crystal lattice by strong electrostatic attraction between opp charged ions
Positive ions
-cations, electrons removed
Negative ions
-anions
-larger than original- electron repulsion in outer shell
-energy released as the nucleus pulls in an electron
-this energy is electron affinity
Electron affinity
The energy change when one mole of gaseous atoms acquires one mole of electrons to form one mole of gaseous negative ions. The greater the effective nucleuar charge, the easier an electron is pulled in
Strength of ionic compounds
-brittle
-if you move a layer of ions you get ions of the same charge net to each other, layers repel each ther and crystal breaks up
How does ion size affect ionic strength
For ions of the same charge, the smaller the size the more energy required to break the bond because the lattice is more tightly packed
Ionic radius
Measure of size of ion
Increase with increase negative charge, decrease with increasing positive charge
Neg ions and ionic radius
Formed by gaining electrons so increases ionic radius
Pos ions and ionic radius
Losing elections so decreases ionic radius
Isoelectronic
Same electron configuration
Ionic radius decreases as number of protons increases as the electrons are attracted more strongly
Covalent bonding- octet
-some dont achieve an octet- not enough electrons
-others only share some as if thy share all they’ll exceed octet
-from 3rd period onwards, they can exceed octet and are nit restricted to 8 in outer shell
Orbital theory
A covalent bond is an overlap of orbitals which can contain a pair of electrons
-the greater thee overlap the stronger the bond
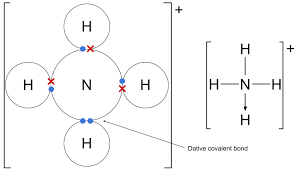
Dative covalent bonding
Both electrons of the shared pair are provided by one species
NH4+
Empty 1s orbital of H+ overlaps with orbital pf N which contains lone pair
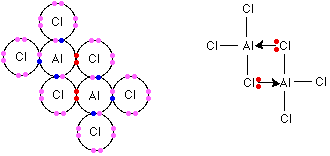
Al2cl6
Lewis base
A lone pair donor
Lewis acid
A lone pair acceptor
Silica
High melting point- many bonds
Strong- each silicon atom joined o 4 oxygens
-non conductor