BIOL 108 Topic 13: Evolution of land plants
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
How long did Earth's terrestrial surface remain devoid of life for?
over 3 billion years
When are cyanobacteria estimated to have begun occupying land?
Cyanobacteria are estimated to have begun occupying land around 1.2 bya
When did small plants, fungi, and animals emerge on land?
around 500 mya
What happened to pants overtime?
Over time, plants evolved various
adaptations to terrestrial life, gradually increasing in height to compete for sunlight
by ~385 mya.
Since their colonization of land, what has happened to plants?
Since their colonization of land, plants
have diversified into approximately 250000 living species
What do plants do/their role?
Plants supply atmospheric oxygen and
are the primary source of food for land animals
Where do most plants live?
Most plants live in terrestrial
environments, including deserts, grasslands, and forests
What have some plant species done?
ome species have returned to aquatic
environments, although their ancestors were terrestrial; most in freshwater,
a few in marine waters (e.g. ~60 spp. of seagrasses)
What are many characteristics found in land plants also present in?
Many characteristics found in land plants are also present in various
protist clades, primarily in algae.
Are plants uni or multi cellular?
Plants are multicellular, photosynthetic (photoautotrophic) eukaryotes.
Many photosynthetic protists (algae) also fit this description.
Do plants possess cell walls?
Plants possess cell walls composed of cellulose.
This feature is shared among red, green, and brown algae, as well as some dinoflagellates.
Do plants have chloroplasts?
Plants have chloroplasts with chlorophyll a and b.
Chloroplasts containing chlorophyll a and b are another common trait shared by plants and certain
protists such as green algae, euglenids, and a few dinoflagellates.
The presence of chloroplasts is considered a shared, ancestral trait for land plants.
What do plants store sugar as?
Plants store photosynthetic sugars as starch in plastids, a characteristic also
observed in green algae and land plants.
Do land plants have life cycles?
Land plants have life cycles featuring alternation of generations, a phenomenon
seen in both land plants and some algae, e.g. brown algae (Stramenopile protist).
The evolution of alternation of generations occurred independently in these lineages.
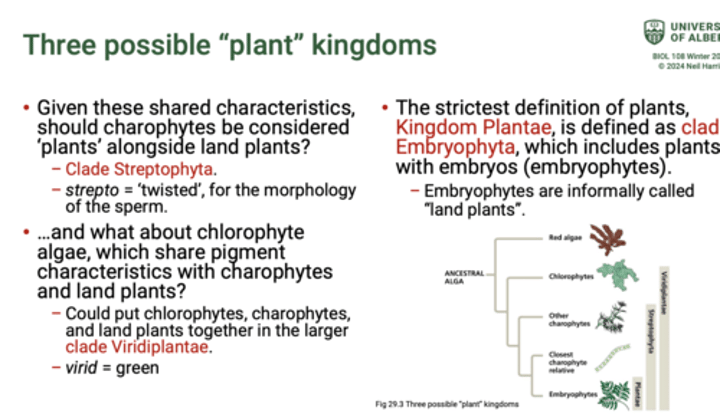
What are the closest living relatives of land plants?
Comparisons of nuclear and chloroplast DNA identify charophytes
(freshwater green algae) as the closest living relatives of land plants.
What is the closest charophyte relatives of land plants?
Zygnema and related taxa are the closest charophyte relatives of land plants.
Land plants are not descended from living charophytes but share
a common ancestor with living charophytes.
What are extant charophytes? (two things)
Extant charophytes are multicellular and morphologically complex.
e.g. species of Chara and Zygnema are common charophytes in Alberta lakes.
What do many charophyte algae inhabit?
Many charophyte algae inhabit shallow freshwater habitats subject
to occasional drying.
Natural selection favours individuals that can survive
periods when not submerged in water.
What did charophytes and land plants share?
Charophytes and land plants
shared several traits that originated
in the common ancestor of clade
Streptophyta.
− Clade Streptophyta includes
charophytes and land plants.
What are three shared, derived traits of clade Streptophyta?
1. Rings of cellulose-synthesizing
proteins anchored in the plasma
membrane.
2. Homologous structure of
flagellated sperm.
3. Phragmoplast formation during
cell division (mitosis).
Explain: Rings of cellulose-synthesizing
proteins anchored in the plasma
membrane.
-Synthesize cellulose microfibrils
(glucose polymers) that provide
structural rigidity to the cell wall.
cf. cellulose-synthesizing proteins are
linearly arranged in non-charophyte algae.
− Cellulose deposition in cell walls is
very similar in charophytes and land
plants.
Explain: Homologous structure of
flagellated sperm.
The sperm of basal land plants
closely resemble those of
charophytes, although not all plant
sperm possess flagella (lost in seed
plants).
Explain: Phragmoplast formation during
cell division (mitosis).
This process aids in constructing a
cell wall plate that merges with the
existing cell wall, separating the two
daughter cells.
What is the strictest definition of plants, Kingdom Plantar, defined as?
The strictest definition of plants,
Kingdom Plantae, is defined as clade
Embryophyta, which includes plants with embryos (embryophytes).
− Embryophytes are informally called
"land plants".
What were the advantages of movement of charophyte ancestors onto land?
-Decreased competition: Land provided spacious habitat with reduced competition
-Increased photosynthesis: plants benefited from bright sunlight unfiltered by water and phytoplankton algae, enhancing photosynthetic activity.
-Abundant CO2: the atmosphere on land contained plentiful carbon dioxide, supporting plant growth
-Rich soil: Land offered soils rich in mineral nutrients, aiding plant development
-Few herbivores of pathogens: initially there were relatively few herbivores or pathogens posing threats to early land plants
What are two challenges of living on land?
-scarcity of water: Desiccation was a major challenge due to scarcity of water on land
-lack of structural support: Early plants lacked the structural support necessary for upright growth.
What did plants do to overcome these challenges?
To overcome these challenges, early
plants evolved adaptations that enhanced their survival out of water , allowing them to successfully colonize the land.
What is sporopellenin?
Sporopollenins are complex, highly cross-
linked polymers composed of C, H, and O
that are resistant to degradation by enzymes
and inorganic chemicals.
• Sporopollenin has been identified intact
in sedimentary rocks dating back 500
million years.
What do charophyte zygotes secrete?
Charophyte zygotes secrete sporopollenin, Ań incredibly durable polymer in the cell wall.
What does sporopollenin protect? charophyte zygotes
from desiccation, UV light, and physical
stresses.
charophyte zygotes
from desiccation, UV light, and physical
stresses.
-many charophytes live in ephemeral ponds that dry up
Where is sporopollenin found?
Sporopollenin is also found in the cell
walls of spores and pollen of plants.
Increases resistance of these structures
to desiccation and physical stresses.
What are the adaptations facilitating land colonization?
1. Sporopollenin
2. Adaptations for water conservation
3. Lignified vascular tissue for internal transport
4. Functional compartmentalization in terrestrial
plants.
What are the adaptations for water conservation?
-The waxy cuticle acts as a protective layer
covering the epidermis, mitigating
desiccation and microbial attacks.
− Stomata (singular: stoma), tiny pores in the
epidermis of leaves and other
photosynthetic organs, facilitate gas
exchange and serve as sites for water
evaporation.
What do tomato do to minimize water loss during dry conditions?
Stomata can close to minimize water loss during
dry conditions.
when did waxy cuticles and stomata likely evolve?
Waxy cuticles and stomata likely evolved
early in the history of land plants.
What is lignified vascular tissue for internal transport?
Xylem and phloem
What is xylem?
Xylem transports water and minerals from
roots to shoots/leaves via microscopic
conduits formed by dead, lignified cells.
What is lignin?
Lignin, a complex polymer, strengthens and
waterproofs xylem cell walls.
What his phloem?
Phloem are living cells that distribute soluble
organic compounds produced during
photosynthesis.
What does vascular tissue provide?
Rigidity for vertical (tall) growth (supported by
lignified xylem).
Water transport, enabling plants to grow in
desiccating environments, i.e. air.
What is functional compartmentalization in terrestrial plants?
Most plants exhibit structural and functional
specialization, with roots exploring underground for
water and minerals, and shoots seeking light and
gases aboveground.
− Elongation and branching optimize root and shoot
exposure to environmental resources, promoting
growth toward resource-rich areas.
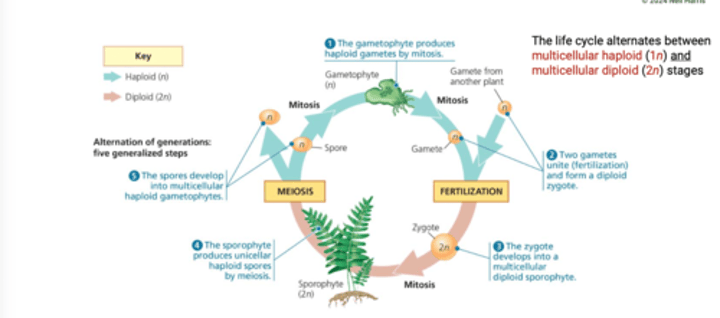
What distinctive characteristics do land plants possesss? (shared derived traits of land plants)
1. Alternation of generations
2. multicellular, dependent embryos
3. Walled spores are produced in sporangia
4. multicellular gametangia
5. Apical meristems
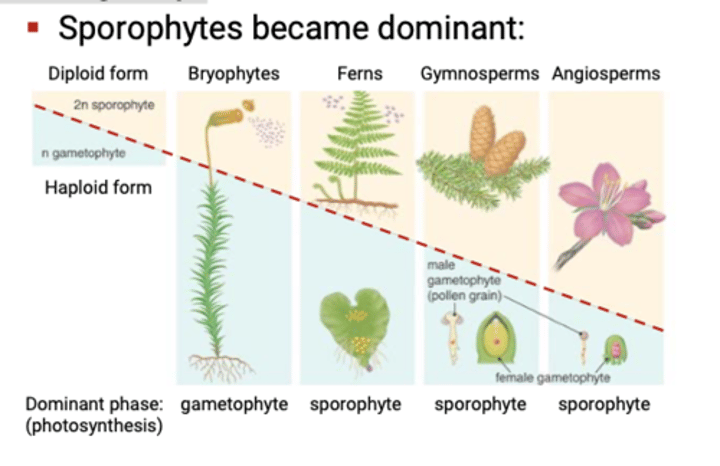
How did alternation of generations evolve in land plants?
Alternation of generations evolved in
land plants by the addition of a
multicellular diploid generation, the
sporophyte.
Altenration of generations provides what?
Alternation of generations provides a
reproductive advantage, allowing for spore
dispersal through the air.
What is the effect of dispersal of desiccation-resistant spores?
Dispersal of desiccation-resistant
spores provides a reproductive fitness
advantage, i.e. disperse to
new areas free of
competition
or pathogens.
What does the relative body size of sporophytes and gametophytes depend on?
he relative body size of sporophytes
and gametophytes depends on the
plant group.
What do land plants retain?
Land plants retain multicellular, diploid
embryos within the tissues of the
female gametophyte.
Where are multicellular, diploids embryos retained?
Multicellular, diploid embryo retained
within the tissues of the female
gametophyte.
What are land plants called?
Land plants are called embryophytes
because of embryo dependency on the
gametophyte.
How does nutrient transfer occur?
Through specialized placental transfer cells
What are spores?
Spores are produced by the
sporophyte within structures called
sporangia.
What are sporocytes?
Diploid cells called sporocytes
undergo meiosis to yield haploid
spores.
What do spore walls contain?
Spore walls, containing sporopollenin,
confer resistance to harsh
environments, particularly
desiccation.
How do gametophytes produce gametes?
Gametophytes produce gametes by
mitosis within multicellular structures
known as gametangia.
Do flowering plants have gametangia?
Note: flowering plants (angiosperms) do
not have gametangia, but still produce
gametes by mitosis.
What is archegonia?
Archegonia, the female gametangia,
house eggs and serve as sites for
fertilization.
What is antheridia?
Antheridia, the male gametangia,
produce and release sperm.
What do plants exhibit structural specialization in?
Plants exhibit structural specialization in roots
and shoots, sustained by apical meristems.
What are apical meristems?
Apical meristems are regions of cell division at
the shoot and root tips that enable continual
growth.
How do plants move?
Plants "move" by growing, i.e. apical meristems
sustain continual growth of roots and shoots.
What happens to meristem produced cells?
Meristem-produced cells differentiate into various
tissues, including the epidermis and internal
structures.
MEMORISE THIS AND KNOW EVERTGHIG IN DIAGRAM
What do additional derived traits in most plant groups include?
Specialized epidermal cells, such as the
cuticle and stomata, for water
conservation.
The cuticle, a waxy layer, minimizes water loss
and shields against microbial threats.
Guard cells regulate water loss by controlling
stomatal opening and closing.
− Mycorrhizae, symbiotic associations
between fungi and plant roots, assist in
nutrient acquisition, particularly in early
land plants lacking true roots.
How did plant evolution begin?
Terrestrial photosynthetic cyanobacteria emerged
~1.2 bya.
What happened second in plant evolution?
Fossil evidence suggests plants inhabited land at
least 470 mya.
Fossilized spores and tissues date back 450 million years
and larger structures like sporangia appear around 425
mya.
What happens third in plant evolution?
"Molecular clock" estimates place the origin of
land plants between 425 to 490 mya.
What did ancestral plant species diversify into?
Ancestral plant species diversified into various extant
plant taxa.
What are land pants informally classified based on?
Land plants are informally classified based on the presence
or absence of vascular tissue, with most possessing vascular
tissues (vascular plants) and others lacking them
(nonvascular plants).
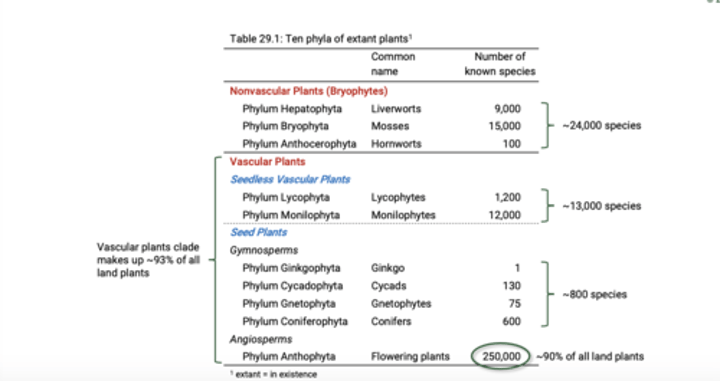
What are nonvascular plants commonly called?
Nonvascular plants are commonly
called bryophytes, which includes
liverworts, mosses, and hornworts.
-However, their relationships with each
other and vascular plants remain
unresolved.
Are bryophytes a monophyletic group?
Bryophytes are not a monophyletic group.
What do seedless vascular plants consist of?
two clades
What two clades do seedless vascular plants consist of?
-Lycophytes (club mosses and their relatives)
− Monilophytes (ferns and their relatives; also known as pteridophytes)
Are seedless vascular plants paraphyletic?
Seedless vascular plants are paraphyletic.
What do seed plants characterized by seeds containing an embryo and nutrients enclosed in a protective coat represent?
Seed plants, characterized by seeds containing an
embryo and nutrients enclosed in a protective coat,
represent the third clade of vascular plants.
What two clades do seed plants consist of?
-Gymnosperms (e.g. conifers)
− Angiosperms (flowering plants), which are the most
diverse and dominant plant group.
What is the current diversity of Plantae?