SHPEP A&P - chemical properties (lecture 2)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Molecule
Particle formed when TWO OR MORE of the SAME atoms chemically combine (ex: O2)
Compound
Partcle formed when TWO OR MORE atoms of DIFFERENT elements chemcially combine (ex: CO2)
Molecular formulas
Depict the elements present and the number of each atom present in the molecule (ex: H2, C6H12O6, H2O)
When do bonds form?
when atoms share or transfer valence electrons (atoms combining with other atoms)
Electron shells
Electrons of an atom occupy this space which circles the nucleus
How many electrons can the first shell hold?
2 electrons
How many electrons can the second and third shells hold?
8
Ion
An atom that gains or loses electrons to become stable. Electrically charged atom.
Cation
A positively charged ion. Formed when an atom loses electrons.
Anion
A negatively charged ion. Formed when an atom gains electrons.
Ionic bonds
An attraction between a cation and an anion. Formed when electrons are TRANSFERRED from one atom to another atom.
Covalent bonds
Bonds created by SHARING ELECTRONS with other atoms
What bonds does Hydrogen form?
Single bonds
What bond does Oxygen form?
it forms two bonds (double)
What bond does Nitrogen form?
Nitrogen forms three bonds (triple)
What bond does carbon form?
Carbon forms FOUR bonds
What is a polar molecule?
A molecule in which the charges are unevenly distributed (electrons are not shared equally in covalent bonds). Molecules have a slightly negative end and a slightly positive end.
What is an important polar molecule?
WATER
hydrogen bonds
A very WEAK attraction between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule.
Formed between water molecules.
Important for PROTEIN and NUCLEIC ACID structure.
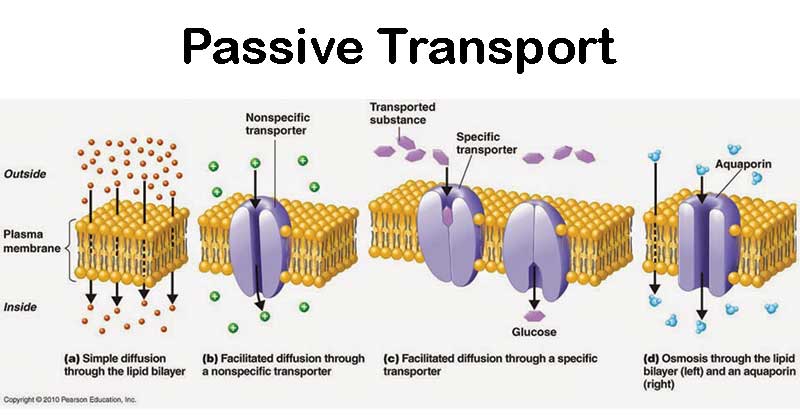
Passive (physical) transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane WITHOUT the use of energy by the cell
Passive transport examples
Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, filtration
Active (physical) transport
ENERGY-REQUIRING process that moves material across a cell membrane against the concentration gradient.
Moves molecules, atoms, ions, etc. from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration.
active transport examples
Active transport, endocytosis, exocytosis, transcytosis
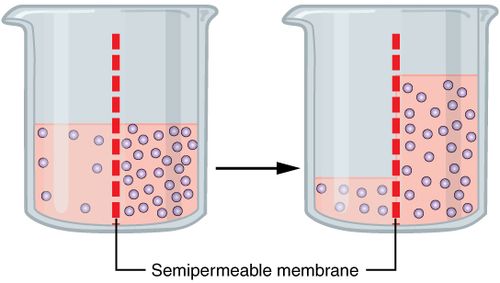
Osmosis
movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration.
T/F: in osmosis, water moves toward a higher concentration of solutes.
True! In osmosis, water moves toward a higher concentration of solutes
Osmotic pressure
Ability of osmosis to generate enough pressure to move a volume of water
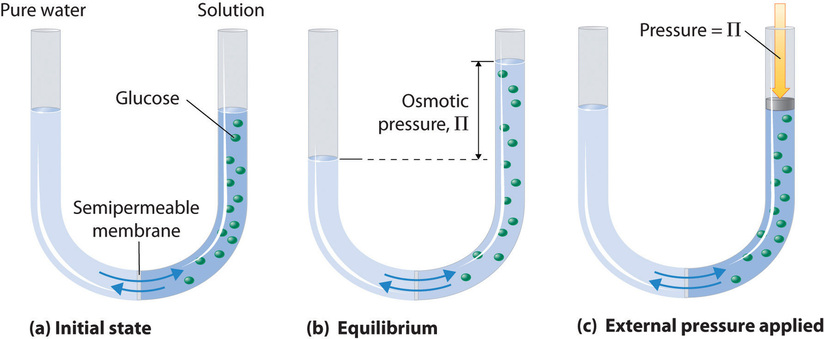
T/F: osmotic pressure increases as the concentration of non permeable solutes increases
True! Osmotic pressure increases as the concentration of non permeable solutes increases
Isotonic
when the concentration (osmotic pressure) of two solutions is the same
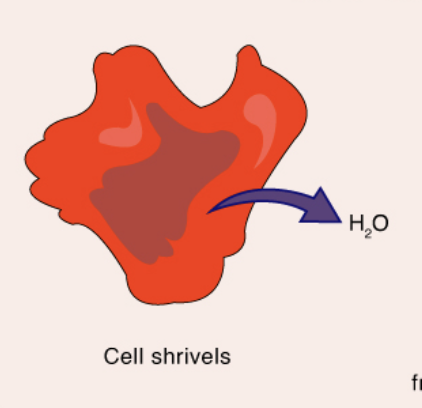
Hypertonic
when comparing two solutions, the solution with the greater concentration of solutes (higher osmotic pressure = water loss)
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution (Lower osmotic pressure = water gain)
Filtration
A process that separates materials based on the size of their particles. Smaller molecules are forced through porous membranes.
Sugars, amino acids, sodium/potassium ions require what kind of transportation?
They require ACTIVE transport with carrier molecules that transport these substances across a membrane from regions of low concentration to high concentration.
Oxygen, CO2, and lipid soluble molecules require what kind of transport?
Just simple diffusion!
T/F: glucose and amino acids required facilitated diffusion to get into a cell.
True, glucose/amino acids require the help of a channel or carrier molecule (facilitated diffusion) to enter a cell.
Sodium potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell (salt gets OUT and bananas go IN…just think which is healthier yk)
How does the sodium potassium pump create balance?
It does so by "pumping" 3 sodium (Na+) ions OUT and 2 potassium (K+) INTO the cell
(3:2 ratio), maintaining the essential electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane
sodium out, potassium in
Endocytosis
Cell engulfs a substance by forming a vesicle around the substance
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes (SUBSTANCE = MOSTLY WATER)
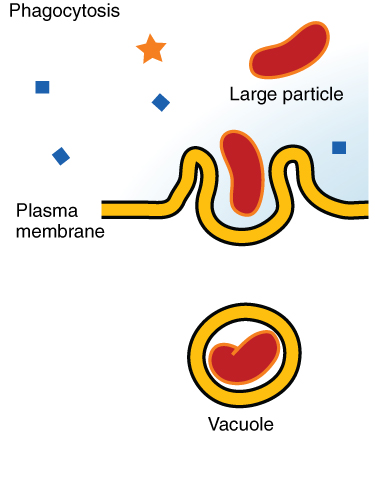
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells (SUBSTANCE = SOLID)
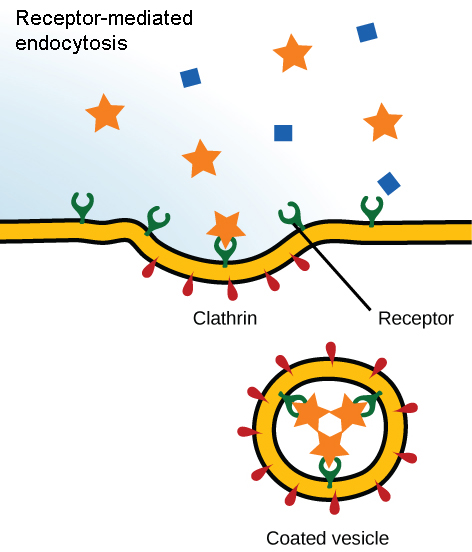
receptor-mediated endocytosis
substances bind to membrane bound receptor, which stimulates the formation of an invagination and ultimately a vesicle is internalized
Exocytosis
Substances in a vesicle fuse with cell membrane, contents released outside the cell
ex: release of neurotransmitters from nerve cells