Charpentier Biology T5-S2-4Q
1/178
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Half of the information on this was only covered in honors. Some images you need to enlarge to see what section the question is referring to.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
RBC Lifespan and Function
120 Days; Transport
Neutrophil Lifespan and Function
7hrs; Immune Defense
Eosinophil Lifespan and Function
?; Defense Against Parasites
Basophil Lifespan and Function
?; Inflammation Response
Monocytes Lifespan and Function
3 days; Immune Surveillance
B-Cell Lifespan and Function
?; Make antibodies
T-Cell Lifespan and Function
?; Cellular Immune Response
Platelet Lifespan and Function
7-8 days; Blood Clotting
3 Functions of Blood
metabolites, salts + ions, and proteins
Functions of the circulatory system 1
Transportation
a) Respiration - O2 attaches to the hemoglobin in red blood cells to get transported to the tissues and CO2 then gets carried and eliminated
b) Nutritional - the digestive system breaks down food so nutrients can be absorbed into circulation
c) Excretory - metabolic waste/ H2O and Ions
Functions of the circulatory system 2
Regulation - blood vessels just under epidermis maintain body temp by circulating warm blood
Functions of the circulatory system 3
Protection
a) Immune System - White blood cells in blood attack foreign cells/ diseases
b) Clotting - blots clots to protect against blood loss
Hemoglobin
the molecule needed to move oxygen; contains Fe2+ (x4); When the concentration of O2 is high oxygen binds to the heme group but when CO2 is high it changes the shape of the hemoglobin in order to bind to it
Circulatory System
O2 and nutrients are transported from the environment and digestive cavity to the body cells by an internal fluid
Open Circulatory System
no distinction between the circulatory fluid (hemolymph) and the extracellular fluid of the body; arthropods; hemolymph returns to circulatory system via pores in the heart
Closed Circulatory System
the circulatory fluid (blood) is always enclosed by blood vessels that transport blood to and from the heart
Counter Current Heat Exchange
warm blood going out of the heart warms the cold blood going in
Major Ions transported in blood
Na+, Cl-, HCO2-
Minor Ions transported in blood
k+, Zn+, Ca2+, Mg2+
Carries Blood to the heart
Vein
Carries blood from the heart
Artery
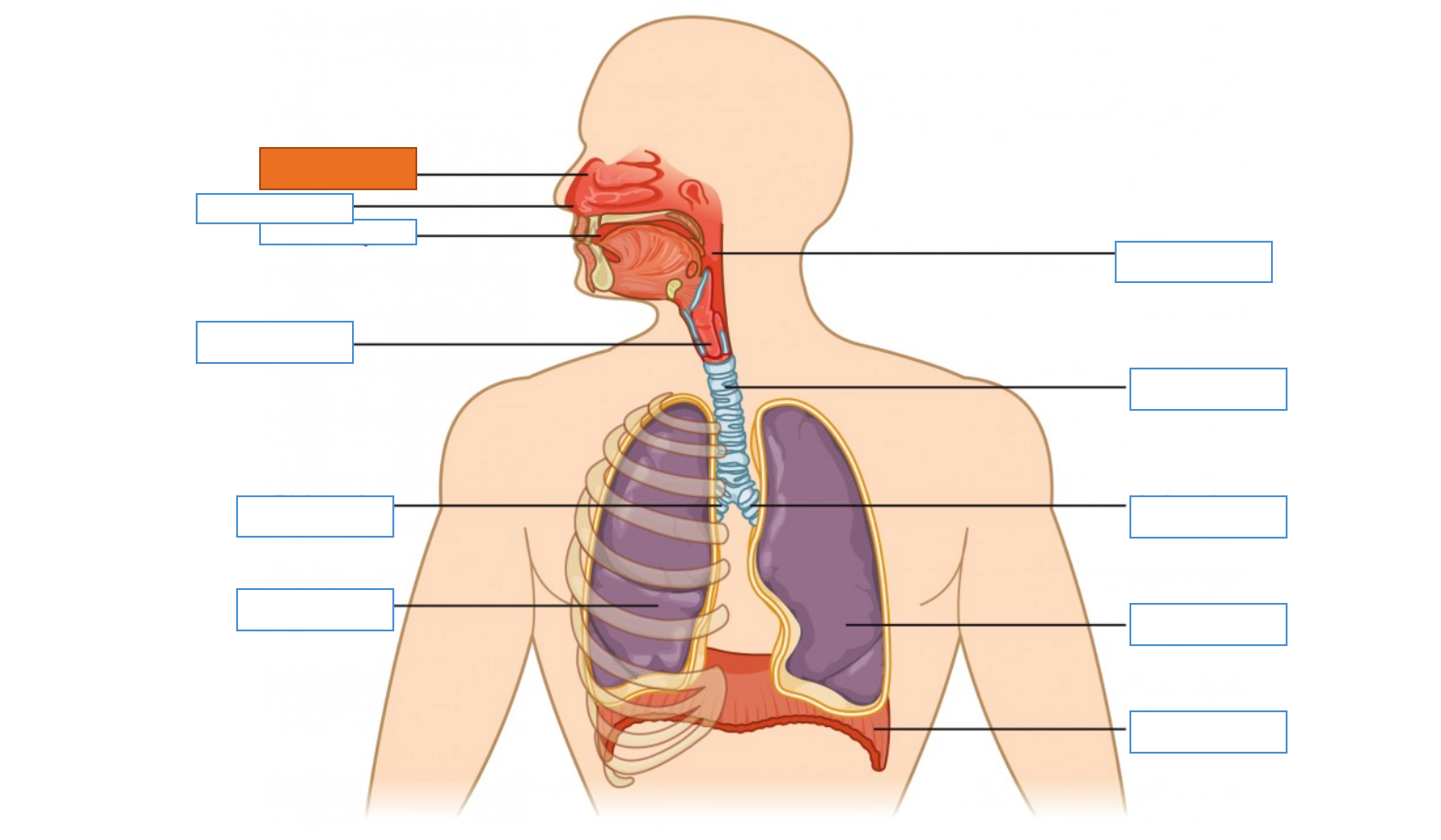
What is this identifying?
Nasal Cavity
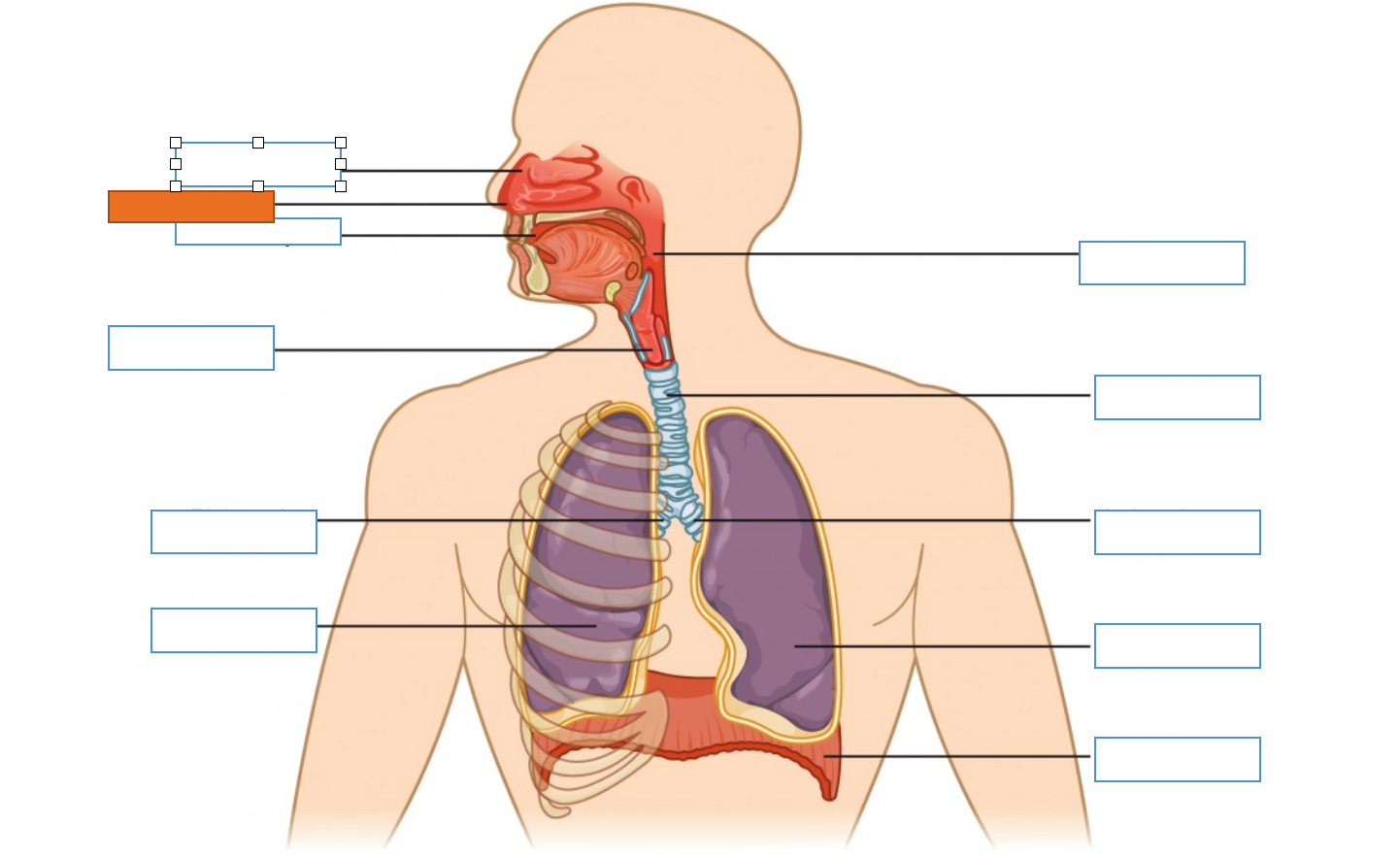
What is this identifying?
Nostril
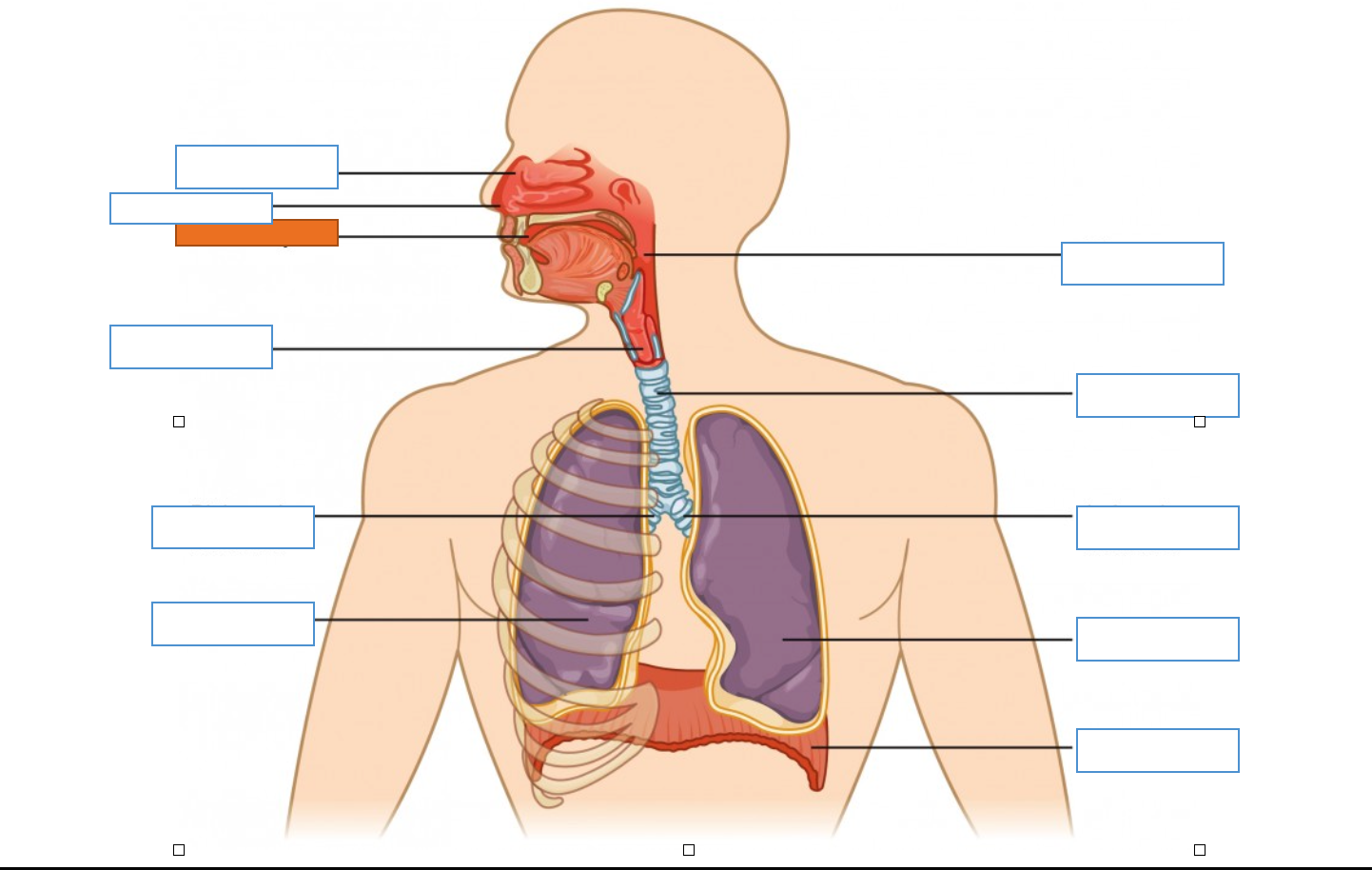
What is this identifying?
Oral Cavity
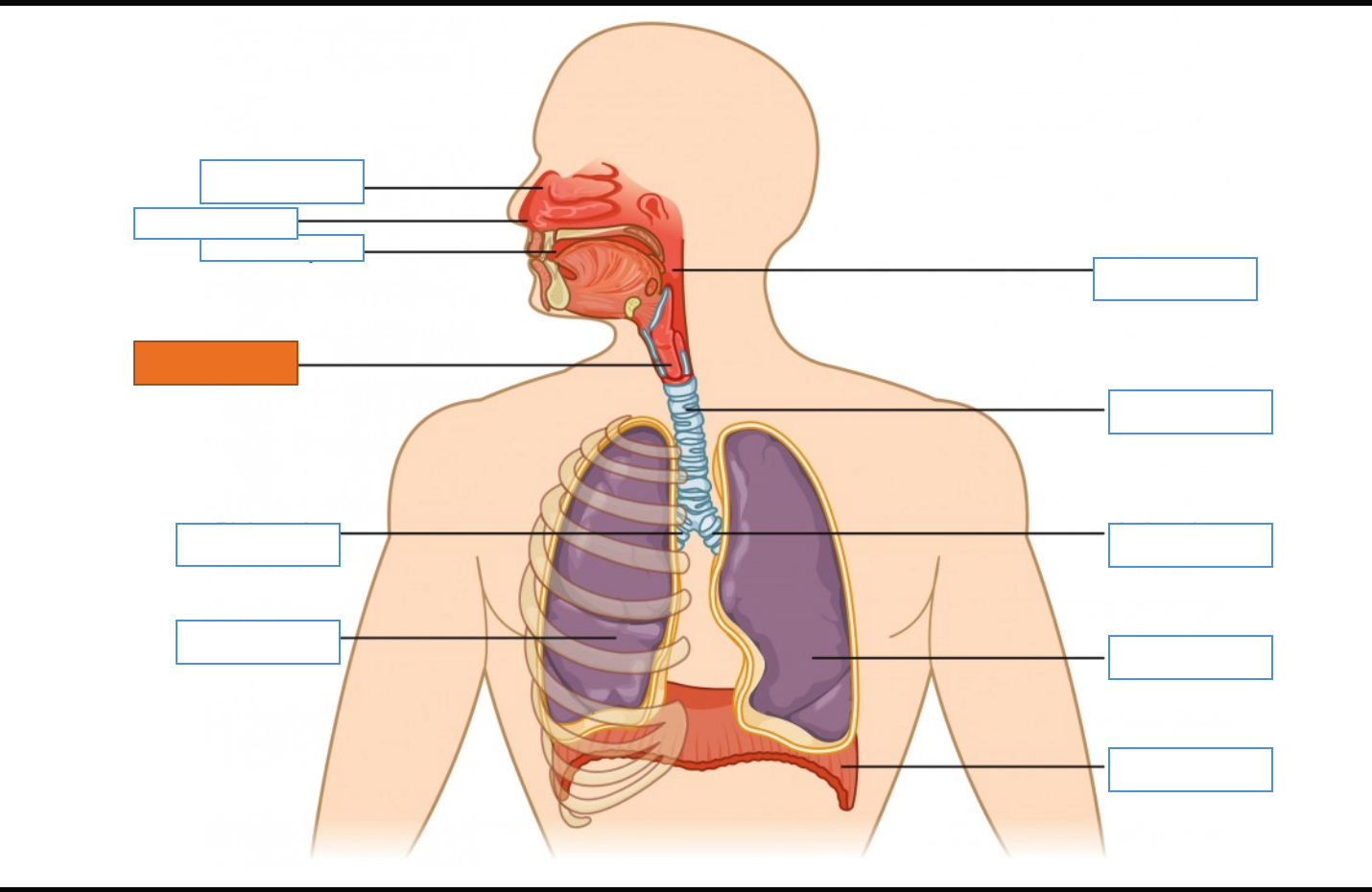
What is this identifying?
Larynx
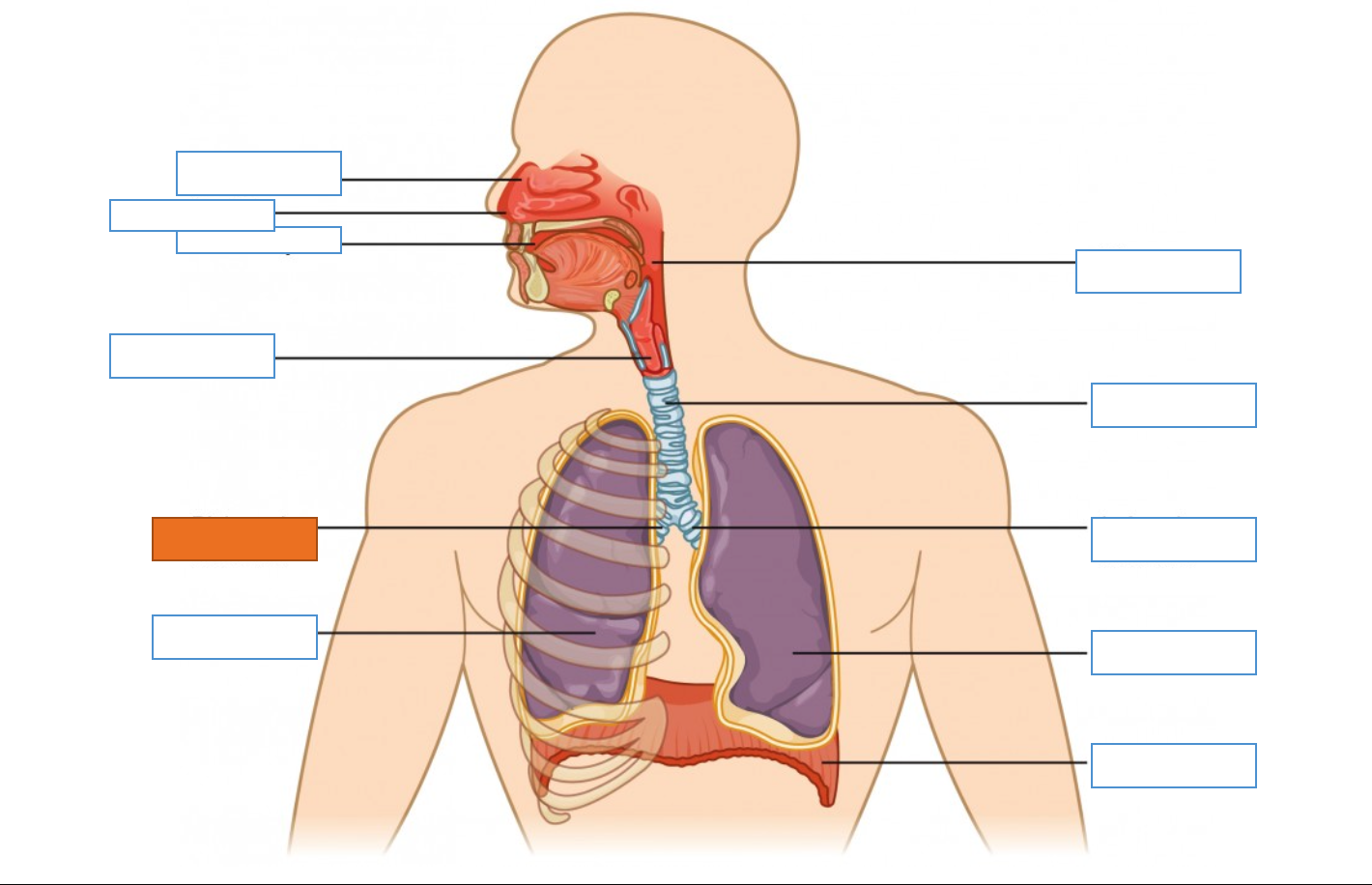
What is this identifying?
Right Main Bronchus
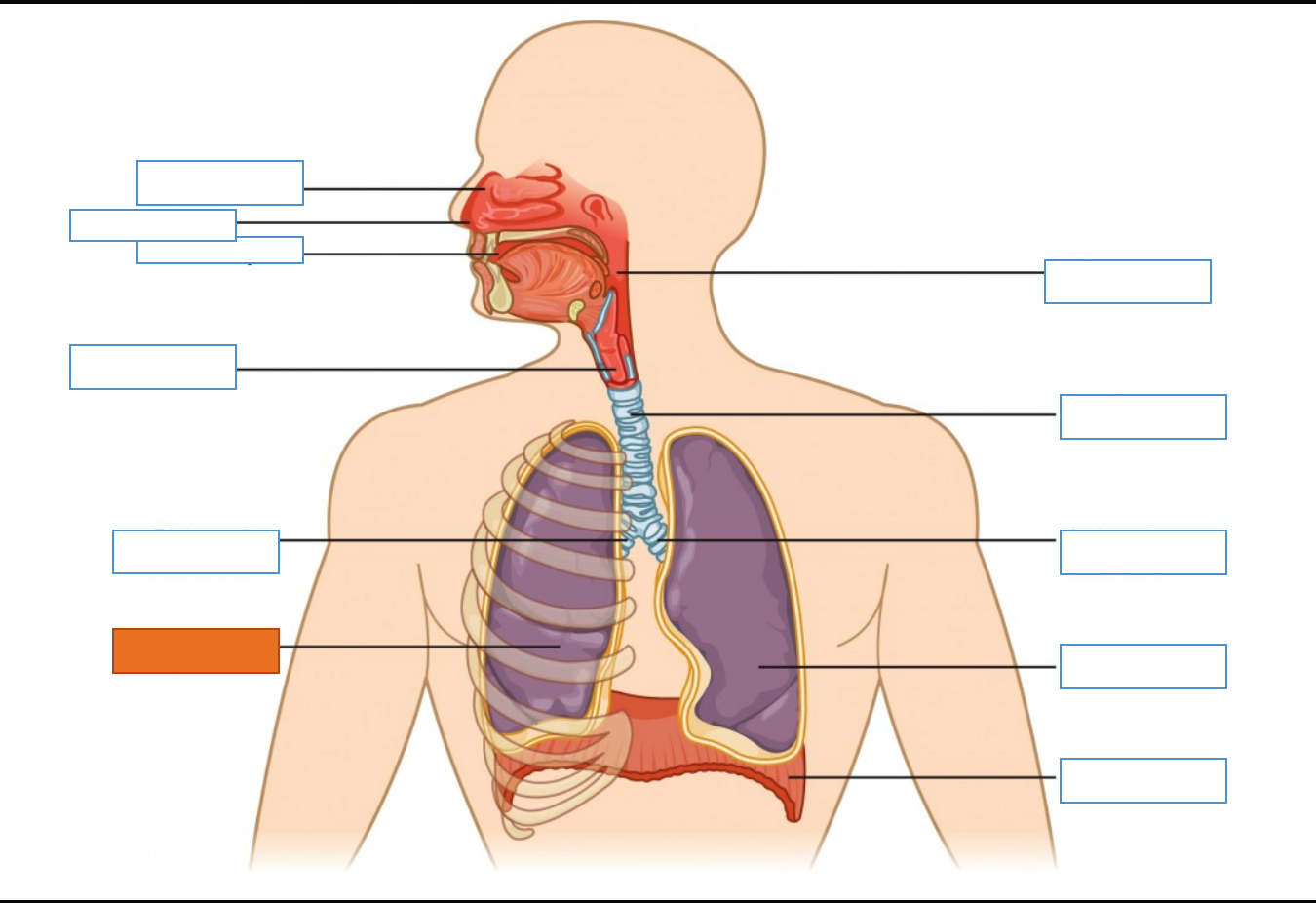
What is this identifying?
Right Lung
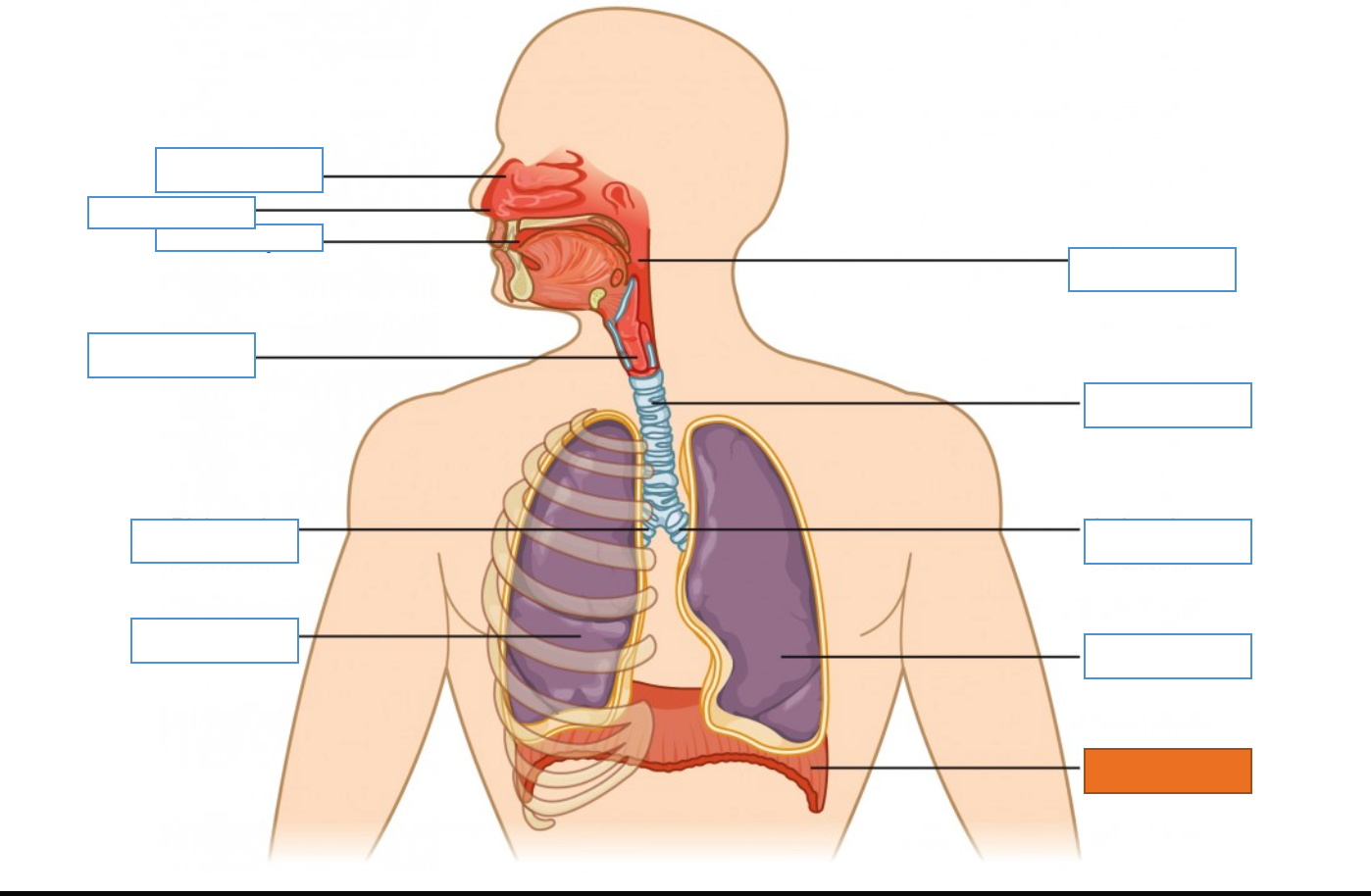
What is this identifying?
Diaphragm
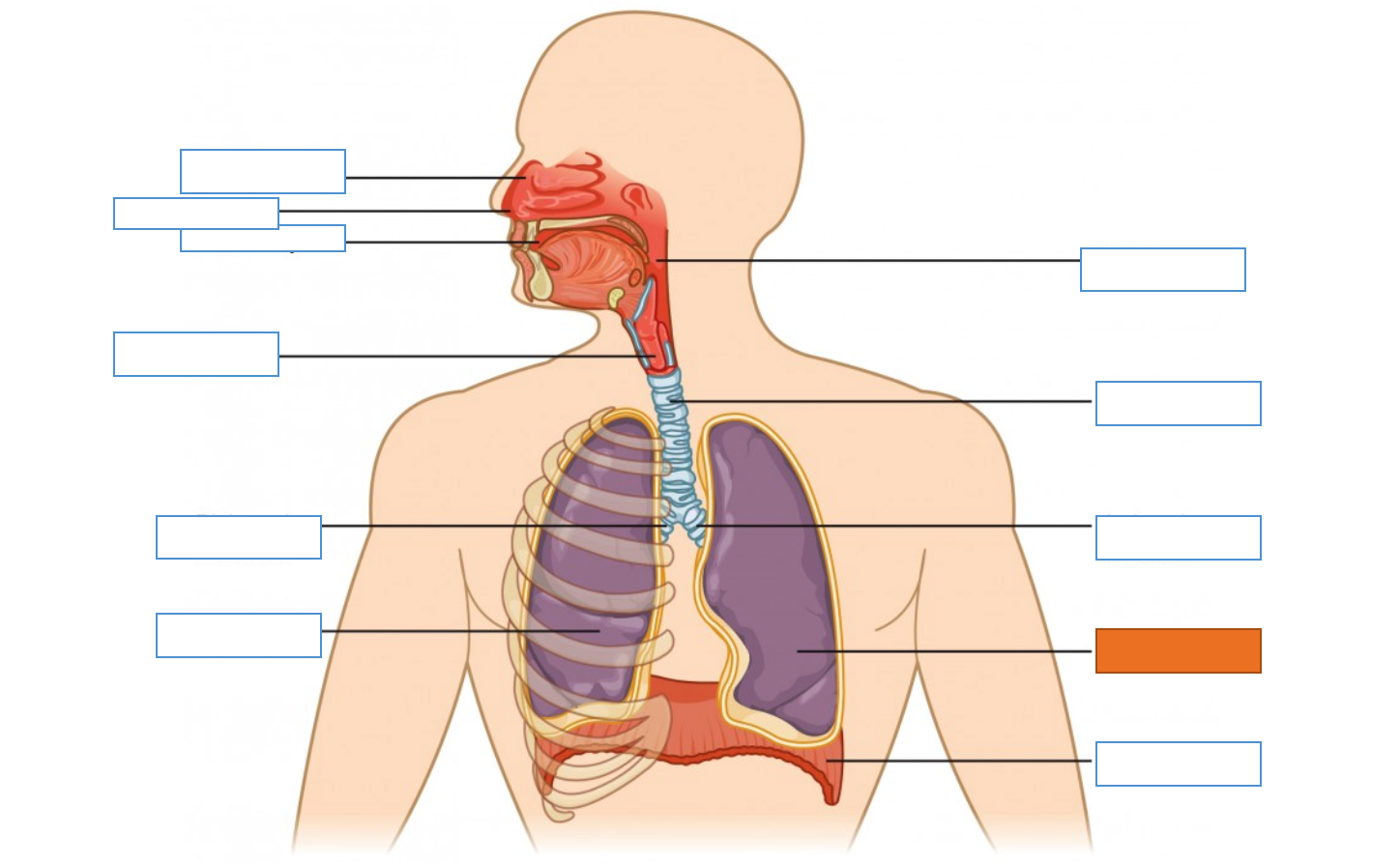
What is this identifying?
Left Lung
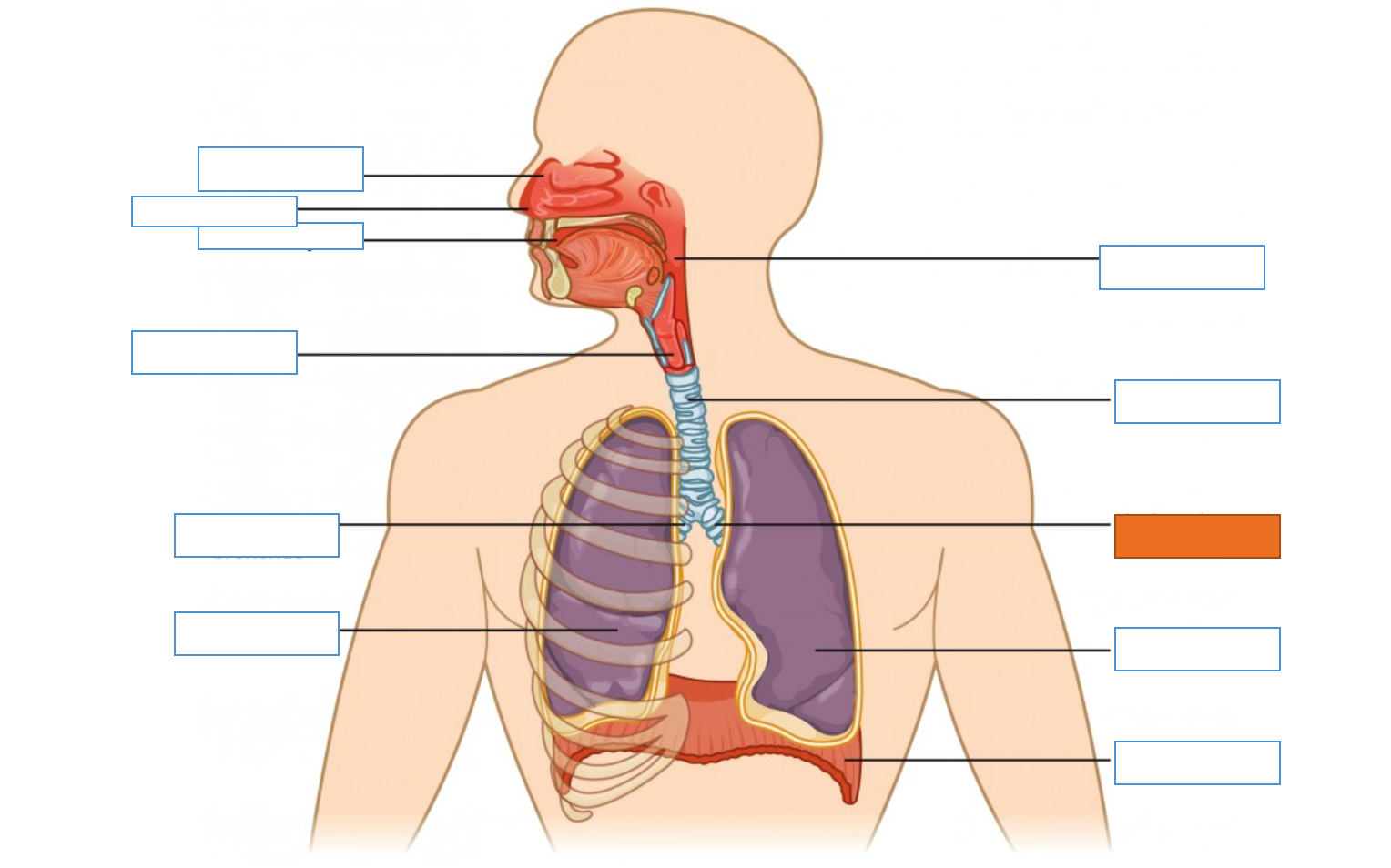
What is this identifying?
Left Main Bronchus
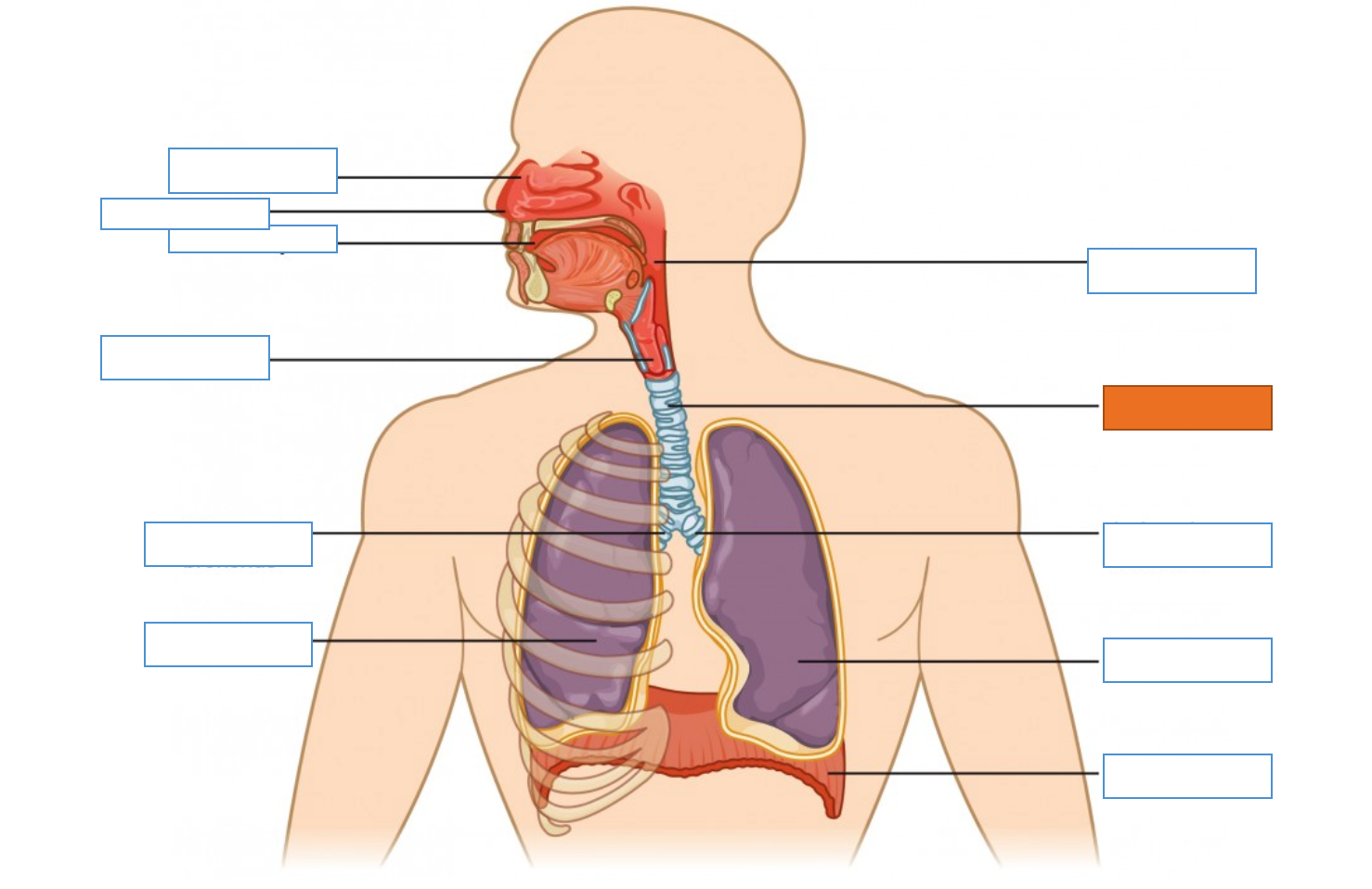
What is this identifying?
Trachea
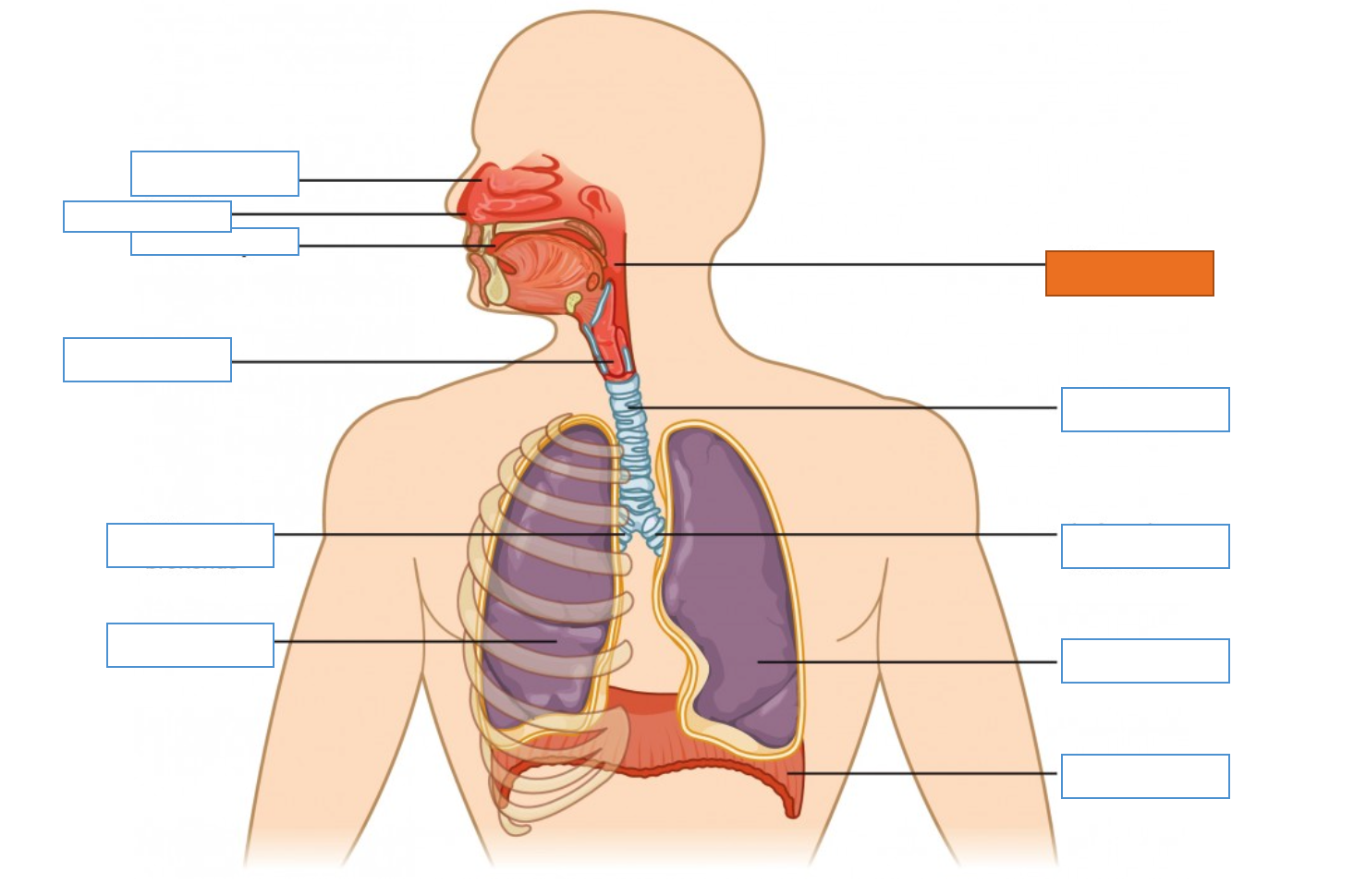
What is this identifying?
Pharynx
What is the function of the diaphragm when breathing?
When Inhaling, the chest expands and the diaphragm contracts and when exhaling the chest contracts and the diaphragm relaxes
Whats the difference between the anatomy of a vein and the anatomy of an artery?
There is higher pressure in arteries so they maintain a more cylindrical shape whereas vein appear slightly “squished down”; veins have thinner smooth muscle and arteries have thicker smooth muscle
Do veins carry deoxygenated blood or oxygenated?
deoxygenated
Do arteries carry oxygenated blood or deoxygenated blood?
oxygenated
What is the “breathing formula”/ the gas law?
PV=nRT
When we’re breathing in what happens to P in relation to V?
P increase and V decreases
When we’re breathing out what happens to P in relation to V?
P decreases and V increases
What is true of nRT?
It is constant
Diaphragm
a muscle attached to the bottom of the lungs use to breathe
What does the heart-beat sound like?
Lub-dub
Path of an Electrical Signal Throughout the Heart
SA (Sino Atrial) Node —> AV (atrial ventricular) node —> Bundle of HIS —> Purkinje Fibers
Path of Blood Flow
Right Atrium —> Right Ventricle —> Lungs (via pulmonary artery) —> Left Atrium (via pulmonary veins) —> Left Ventricle —> Aorta —> Capillaries —> Vena Cava
How does the blood pumping process work?
Atriums squeeze blood on the first beat to the ventricles and ventricles squeeze blood out to the rest of the body on the second beat
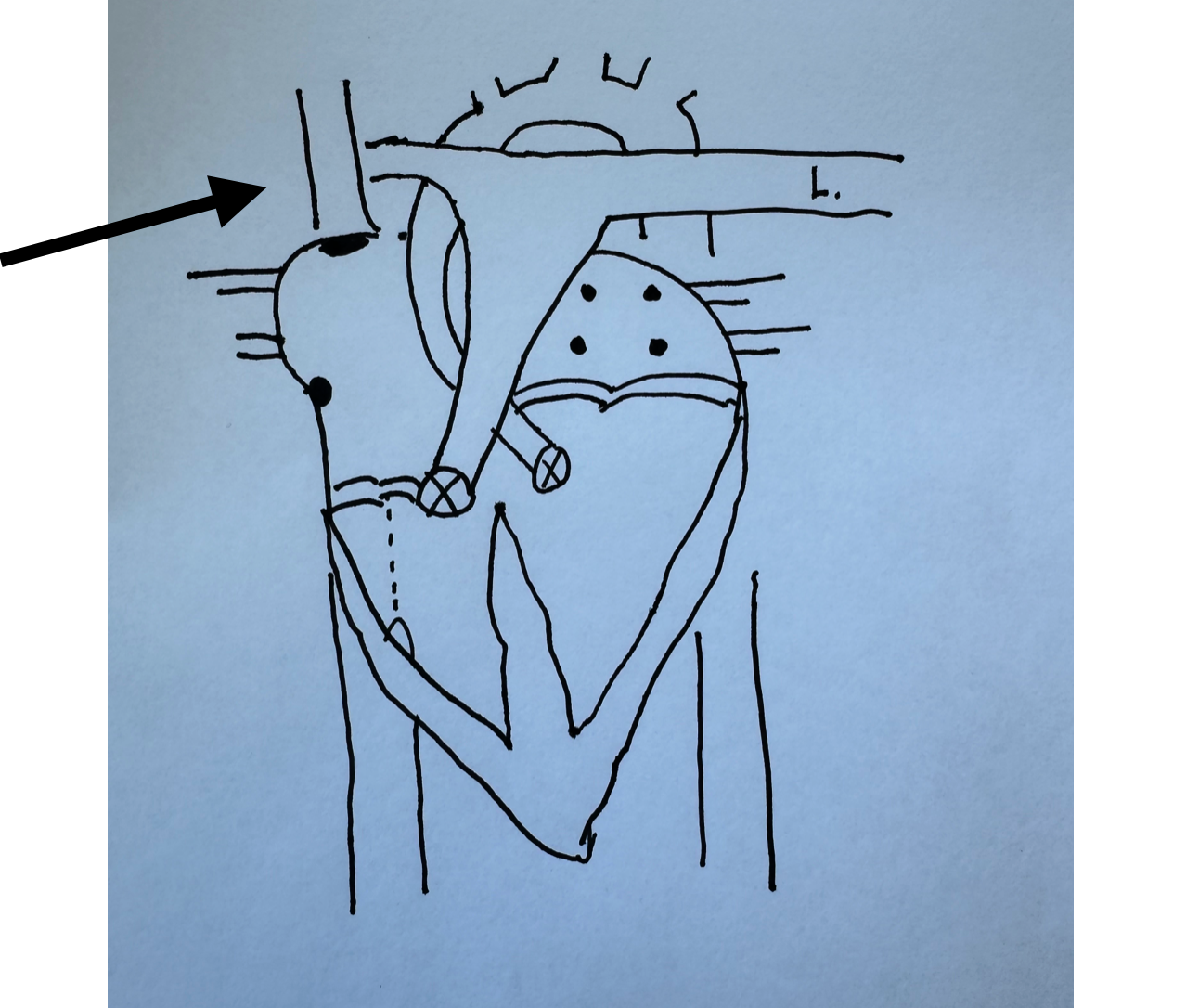
What is this identifying?
Superior Vena Cava
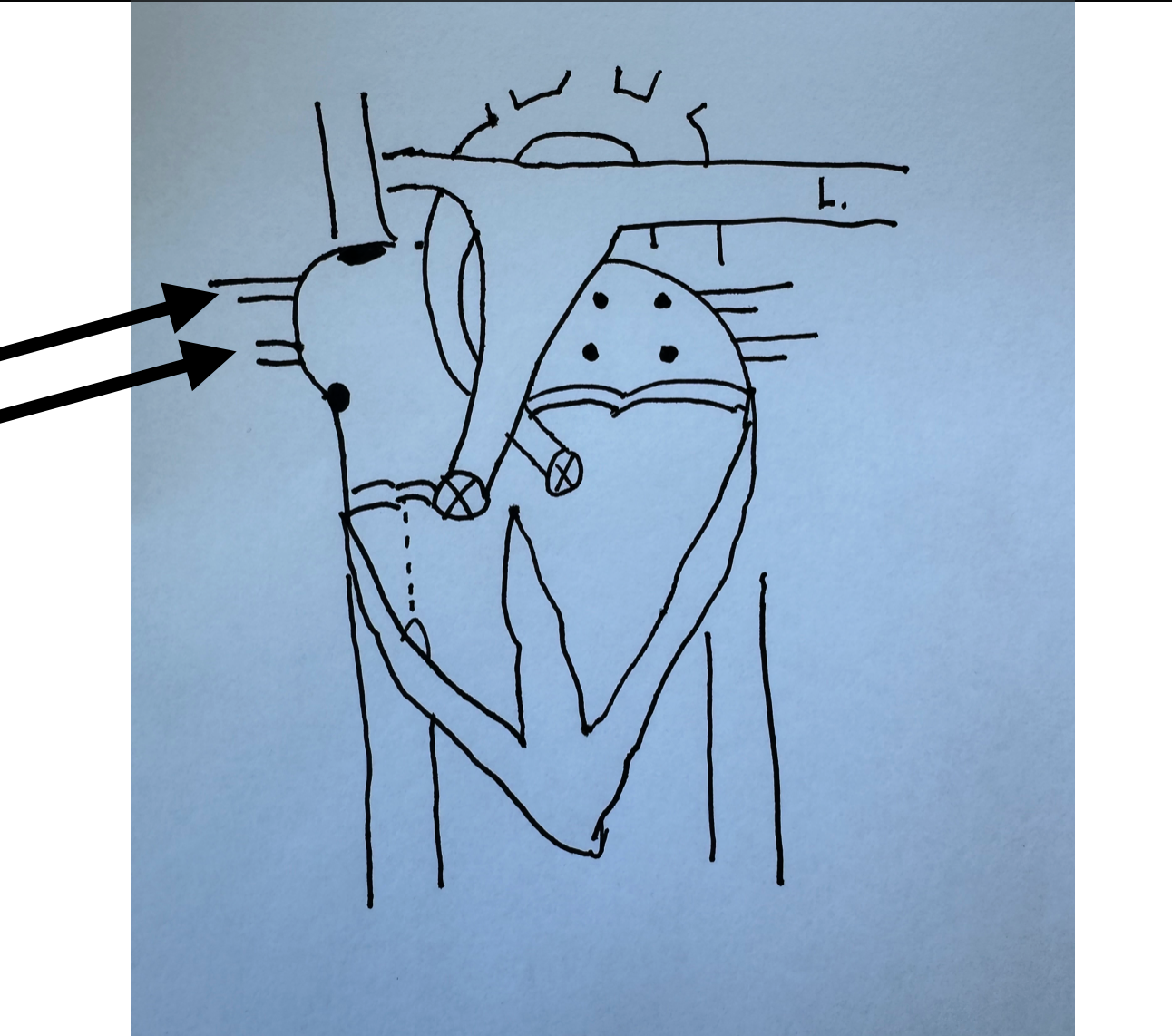
What is this identifying?
Right Pulmonary Veins
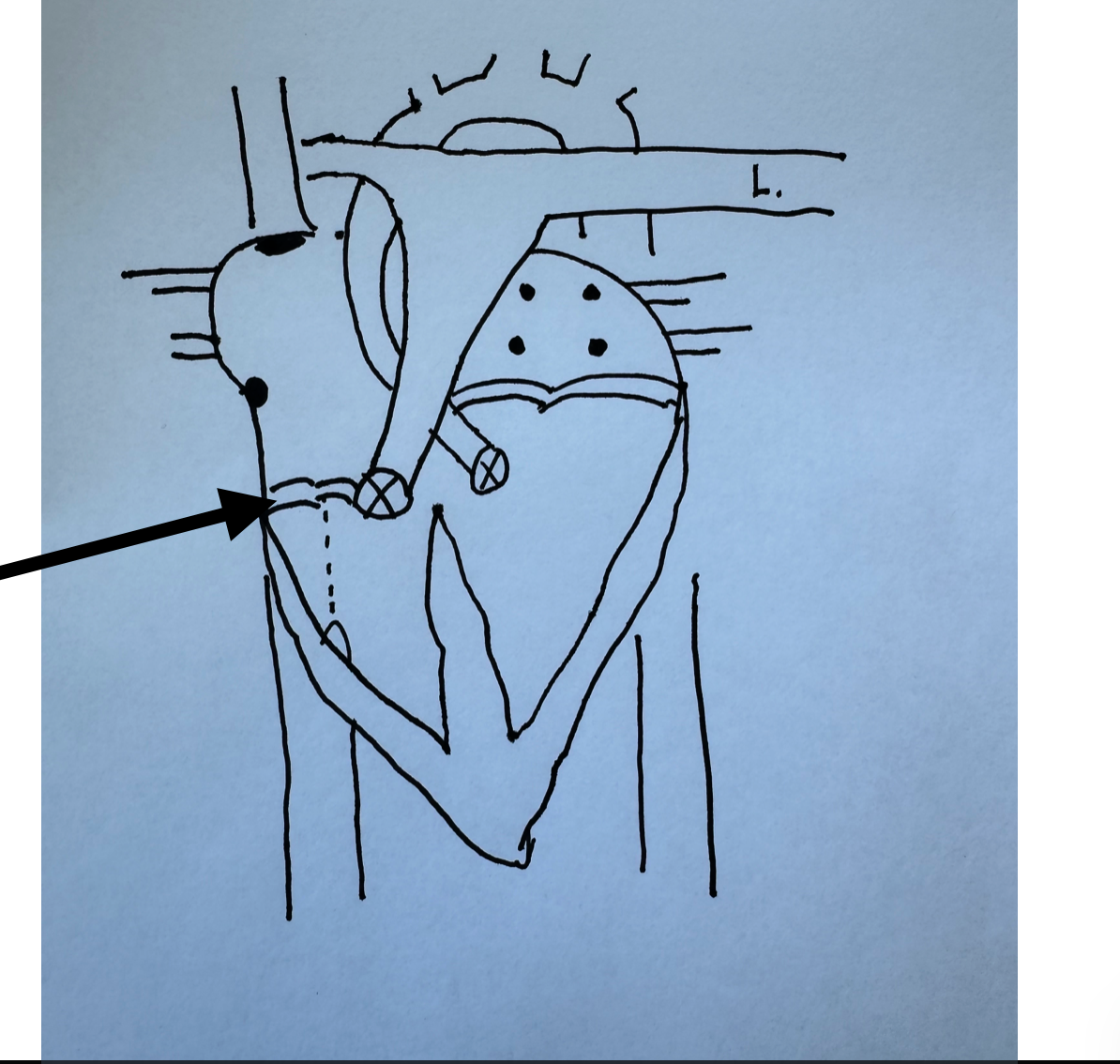
What is this identifying?
Tricuspid Valve
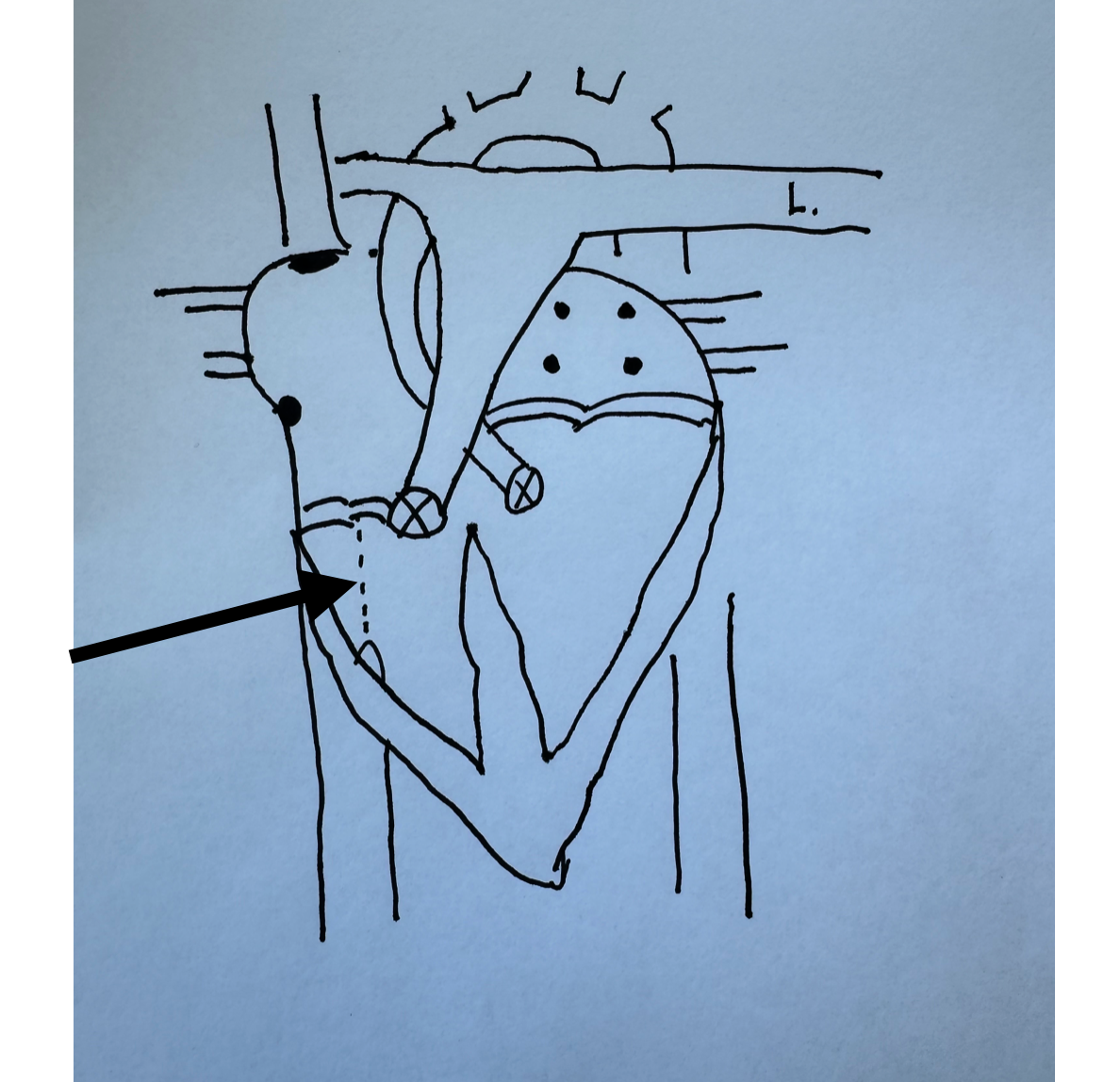
What is this identifying?
Chordae Tendineae
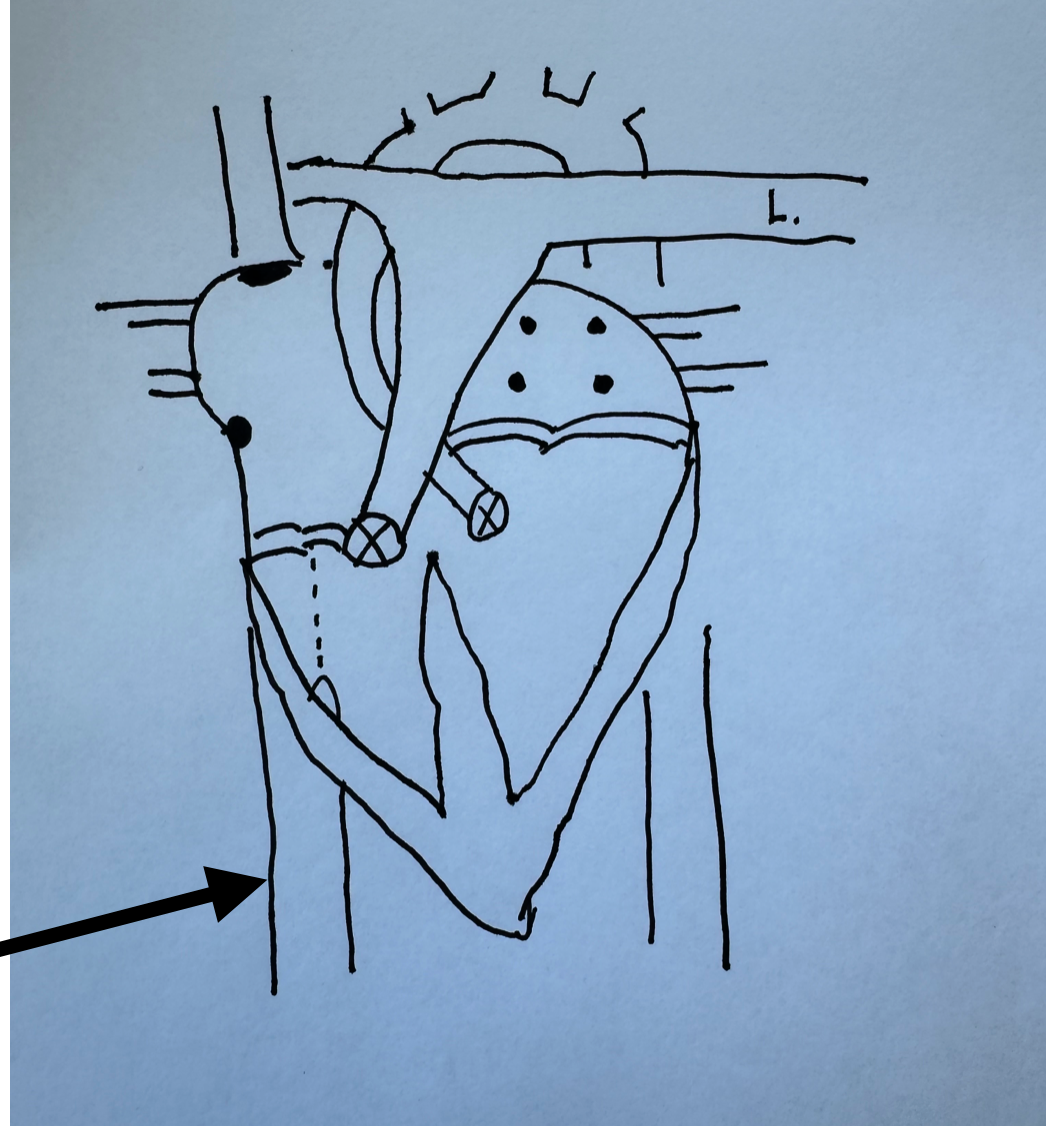
What is this identifying?
Inferior Vena Cava
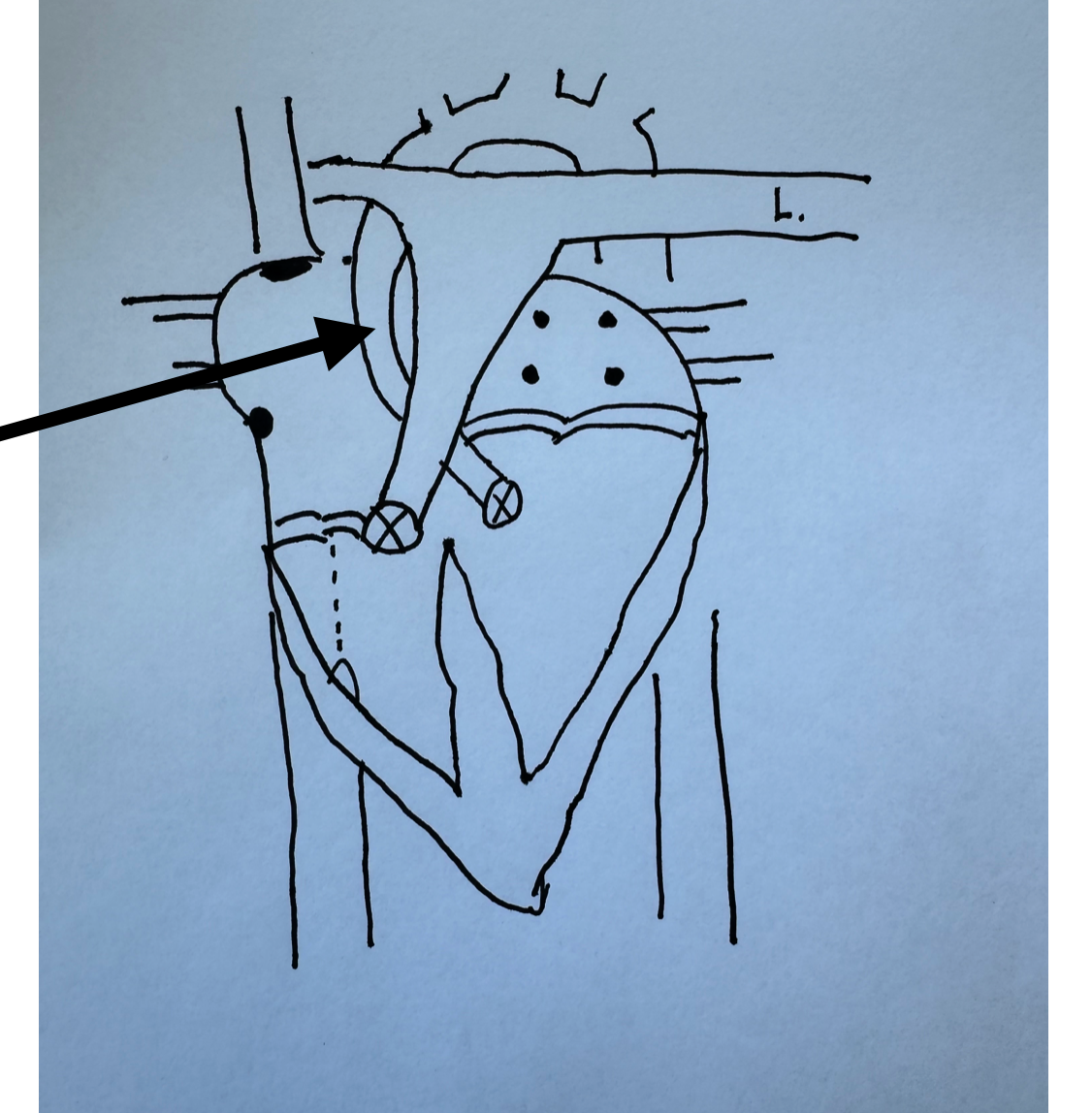
What is this identifying?
Aorta
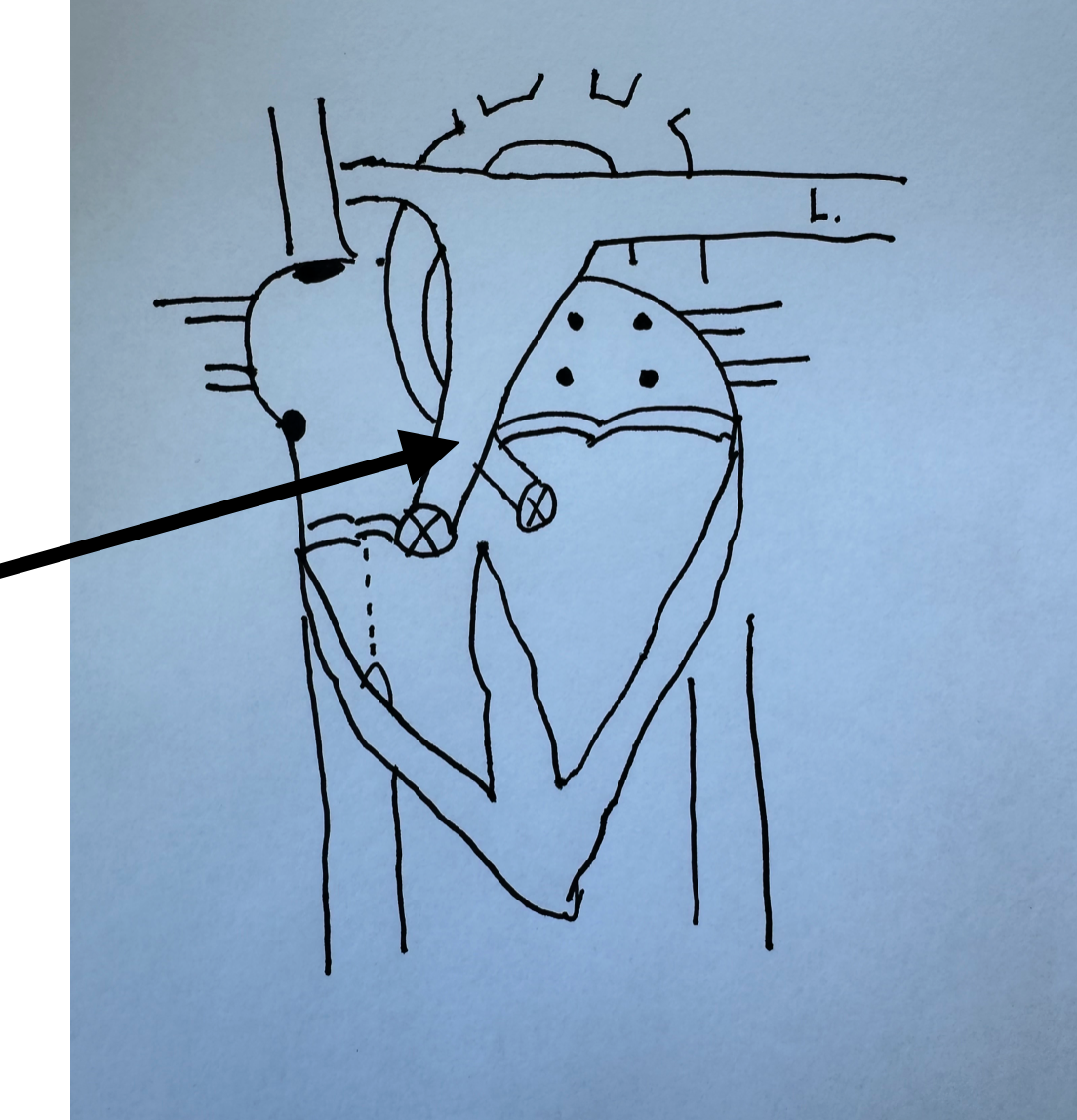
What is this identifying?
Pulmonary Artery
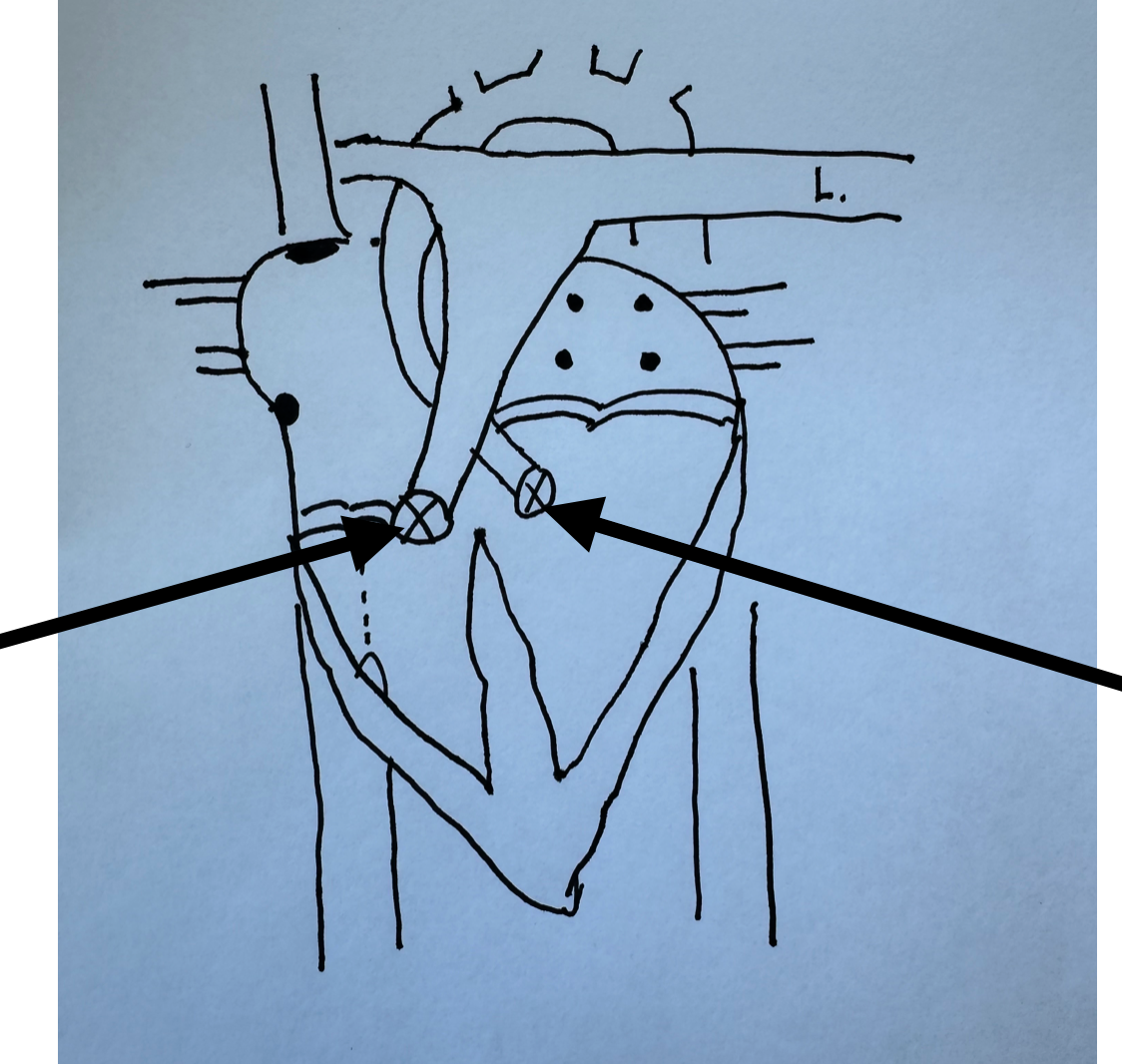
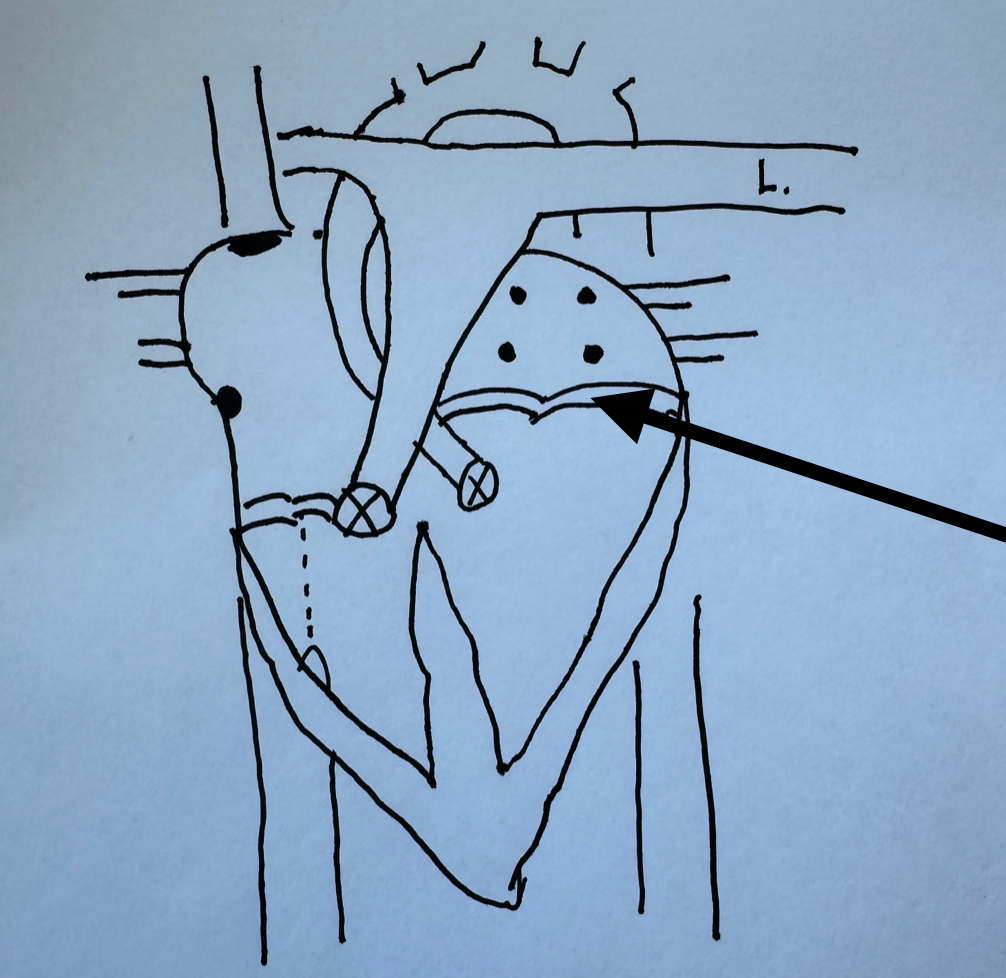
What is this identifying?
Semi-lunar Valves
What is this identifying?
Bicuspid Valve
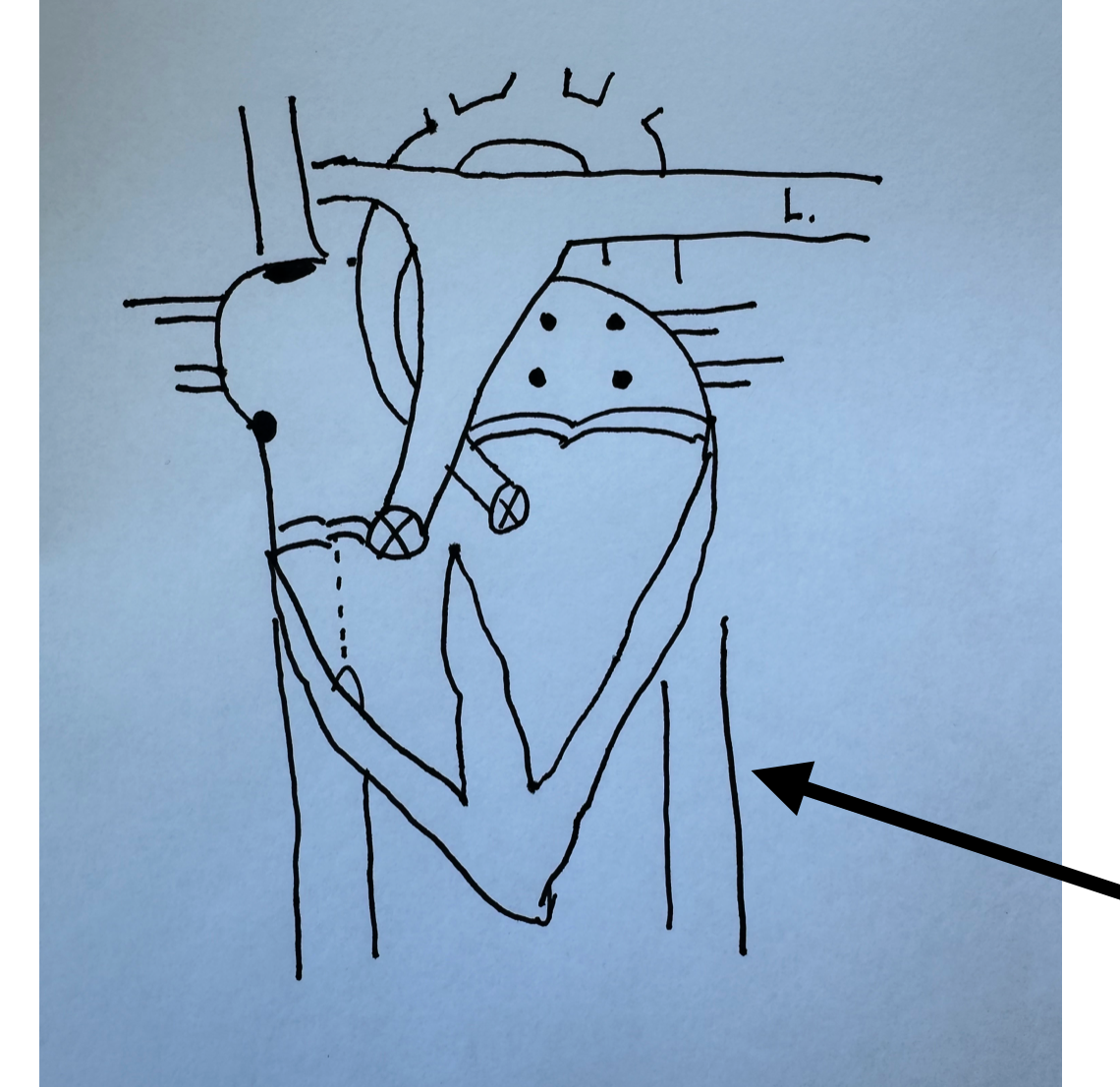
What is this identifying?
Descending Aorta
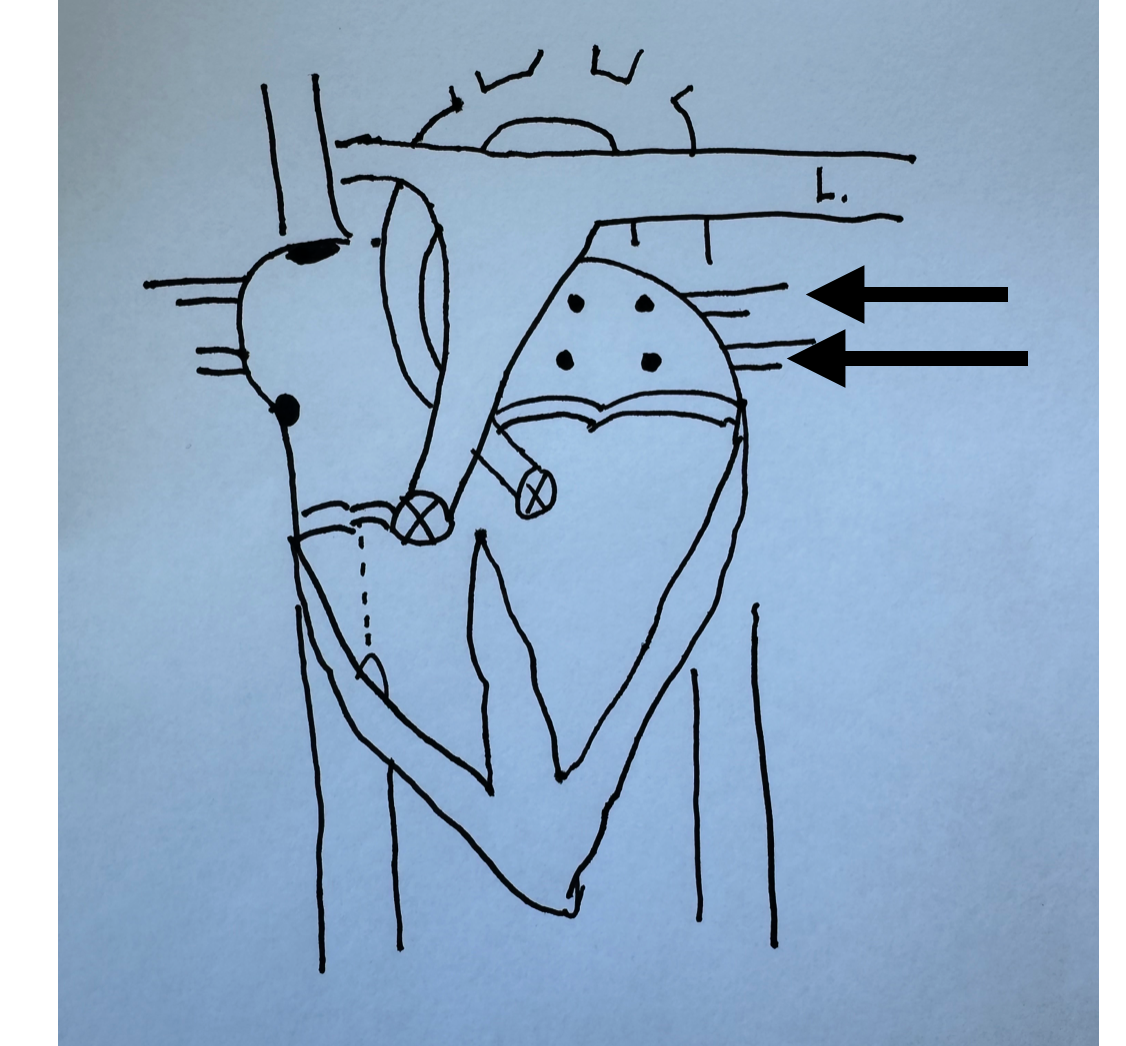
What is this identifying?
Left Pulmonary Veins
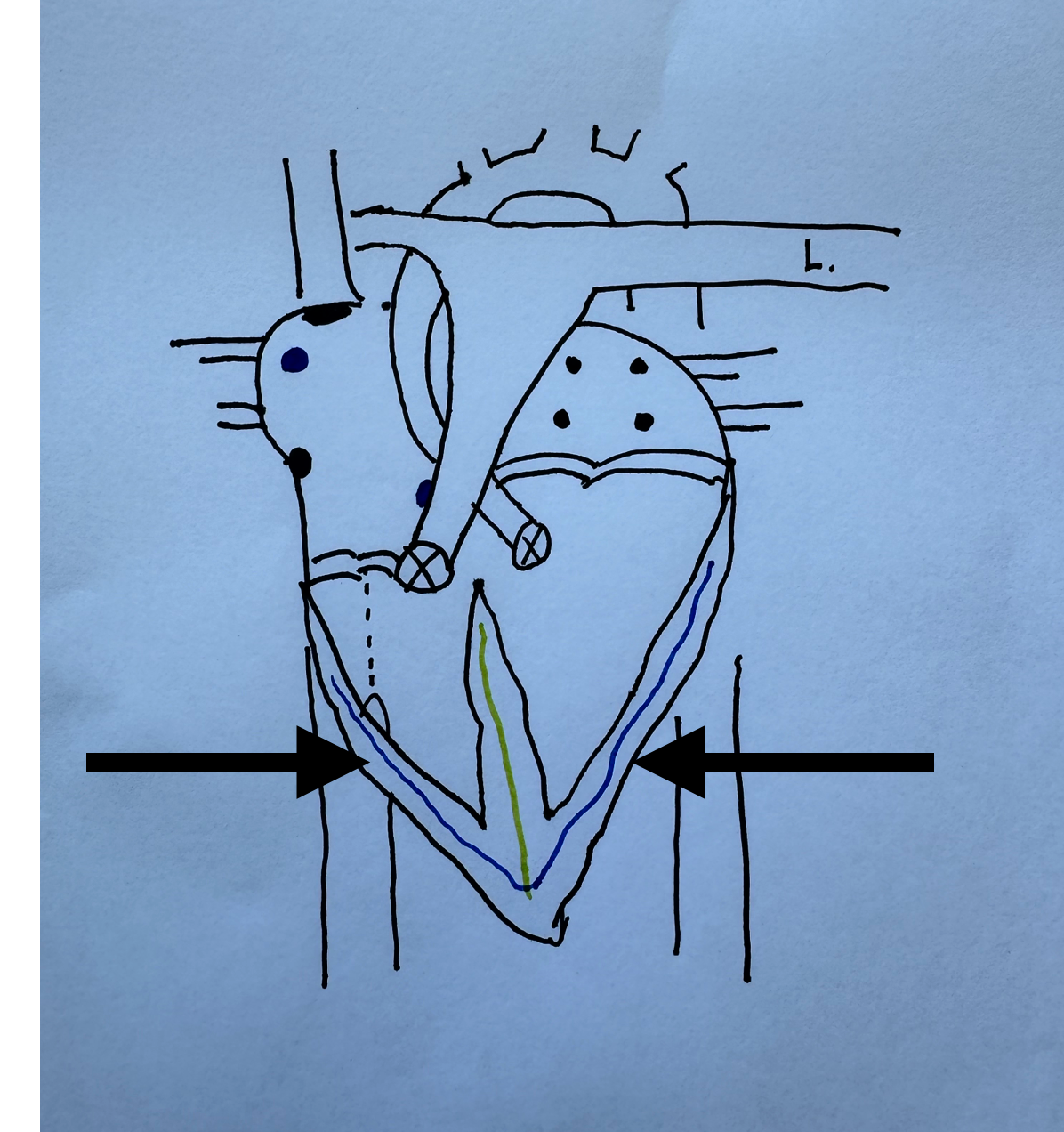
What is this identifying?
Purkinje Fibers
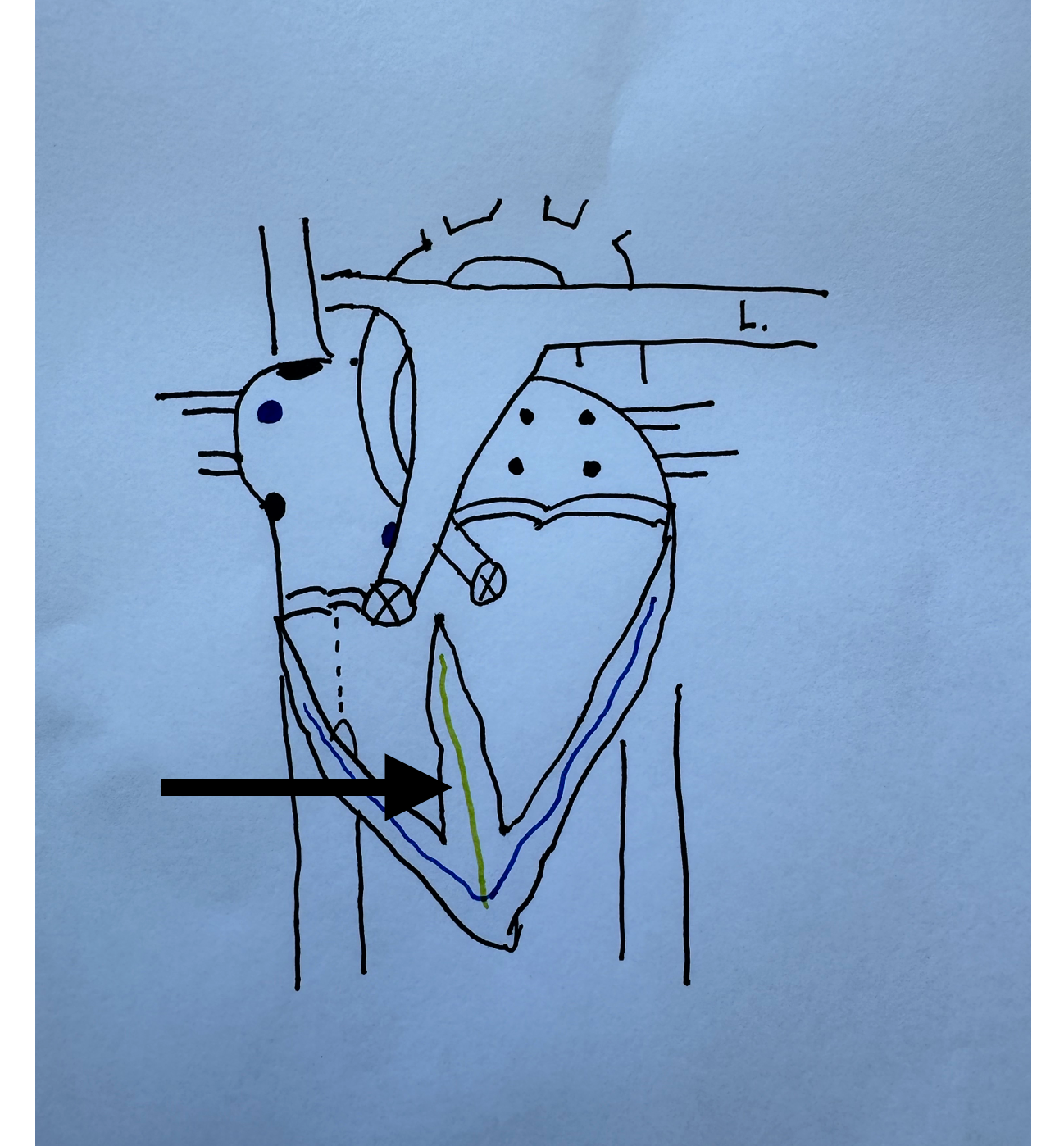
What is this identifying?
Bundle of HIS
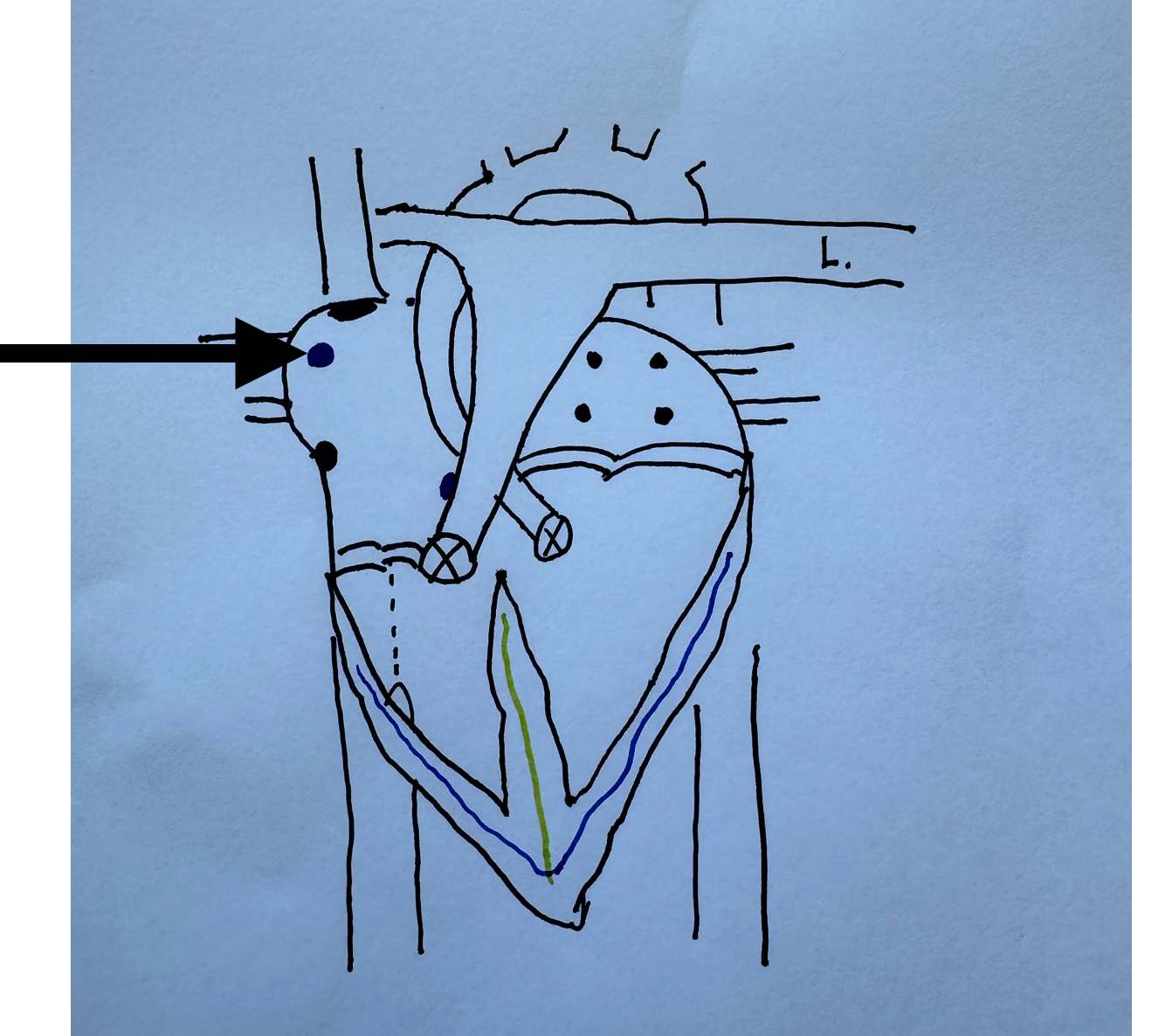
What is this identifying?
Sino Atrial Node
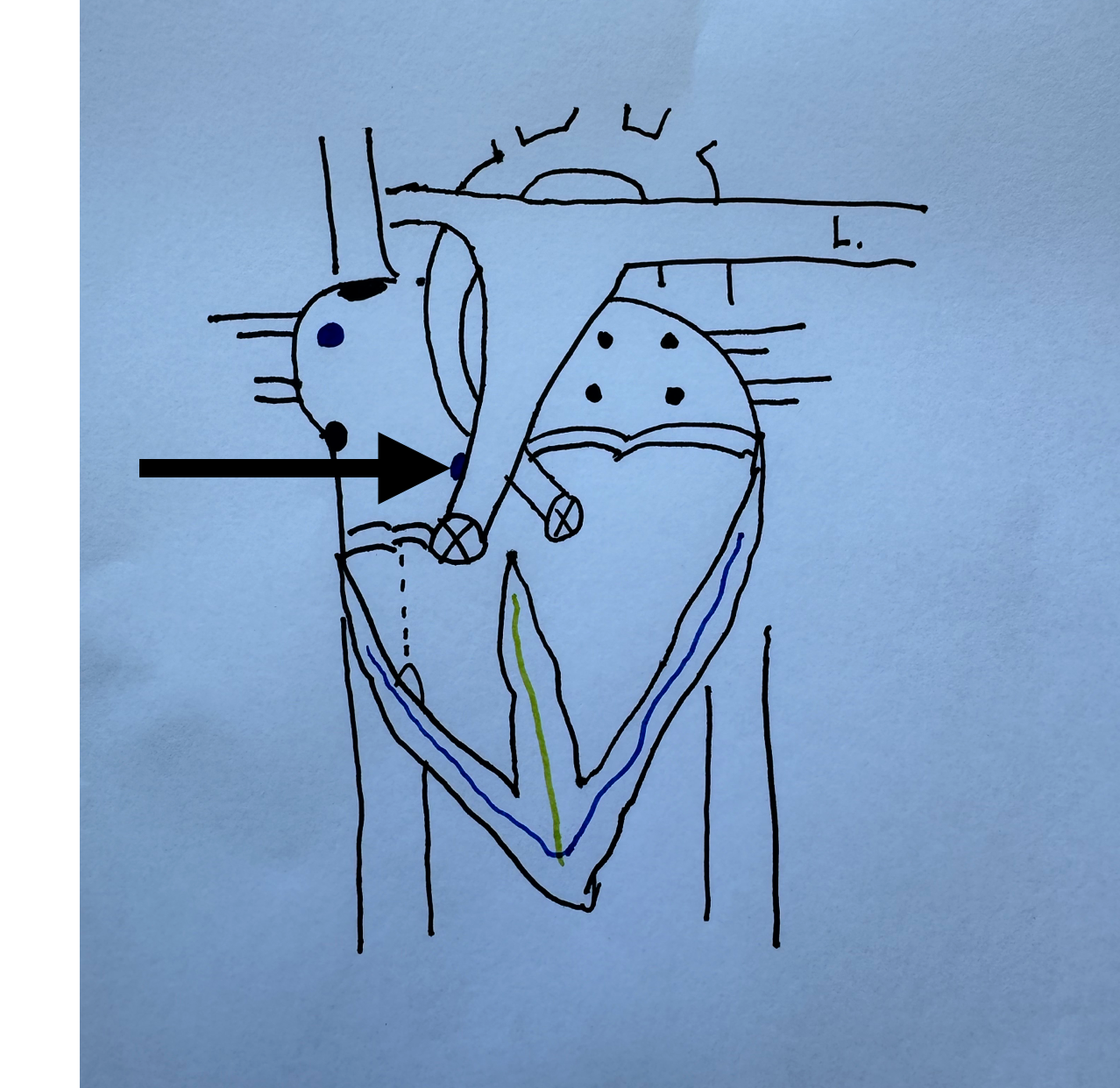
What is this identifying?
Atrial Ventricular Node (lies underneath the pulm. artery and aorta)
Diastolic Pressure
measures pressure in arteries when heart is at rest
Systolic Pressure
measures pressure in arteries when the heart is beating; large
What is the blood pressure fraction?
Systolic/Diastolic; measured in mmHg (millimeters of mercury)
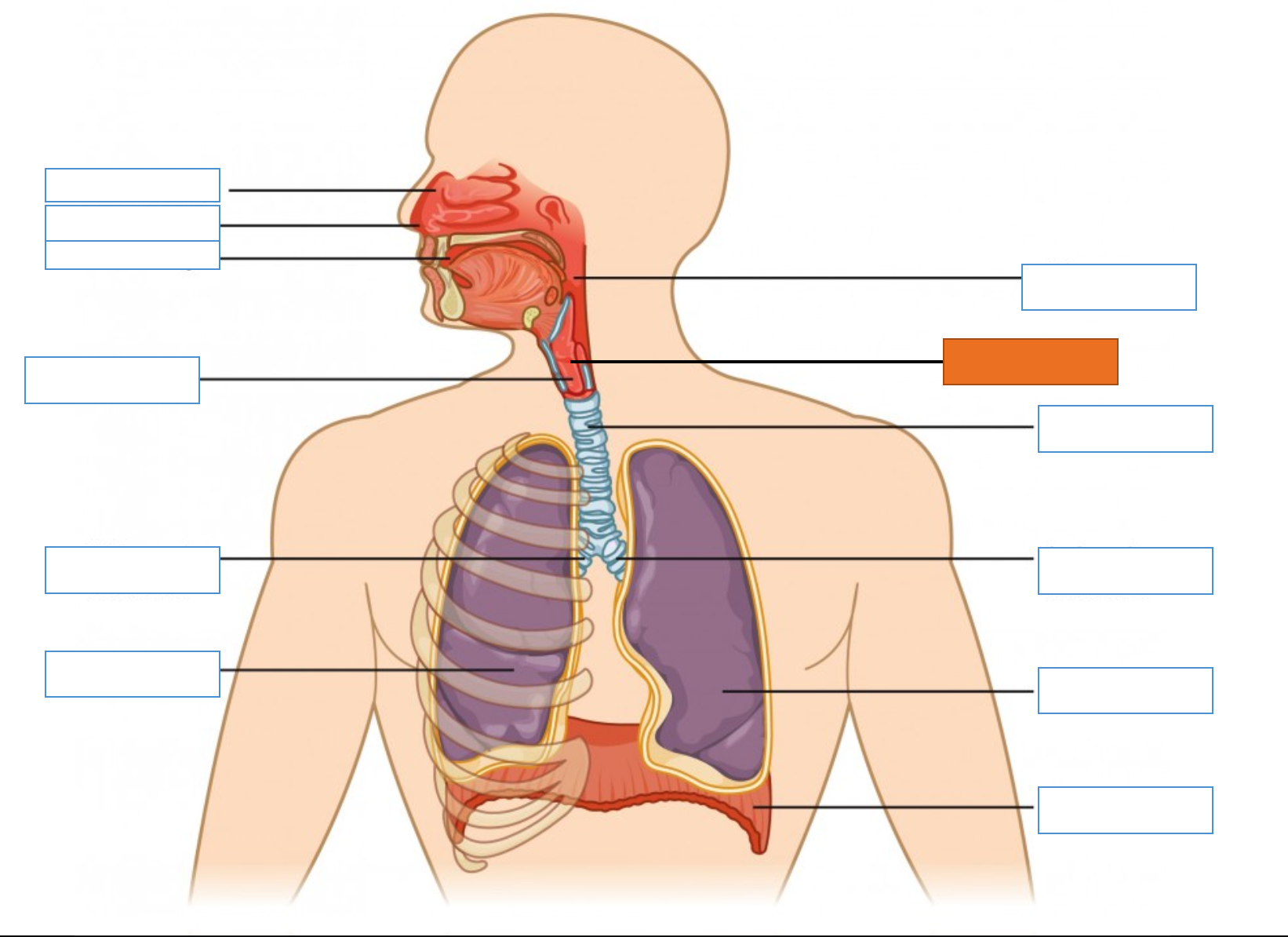
What is this identifying?
Glottis
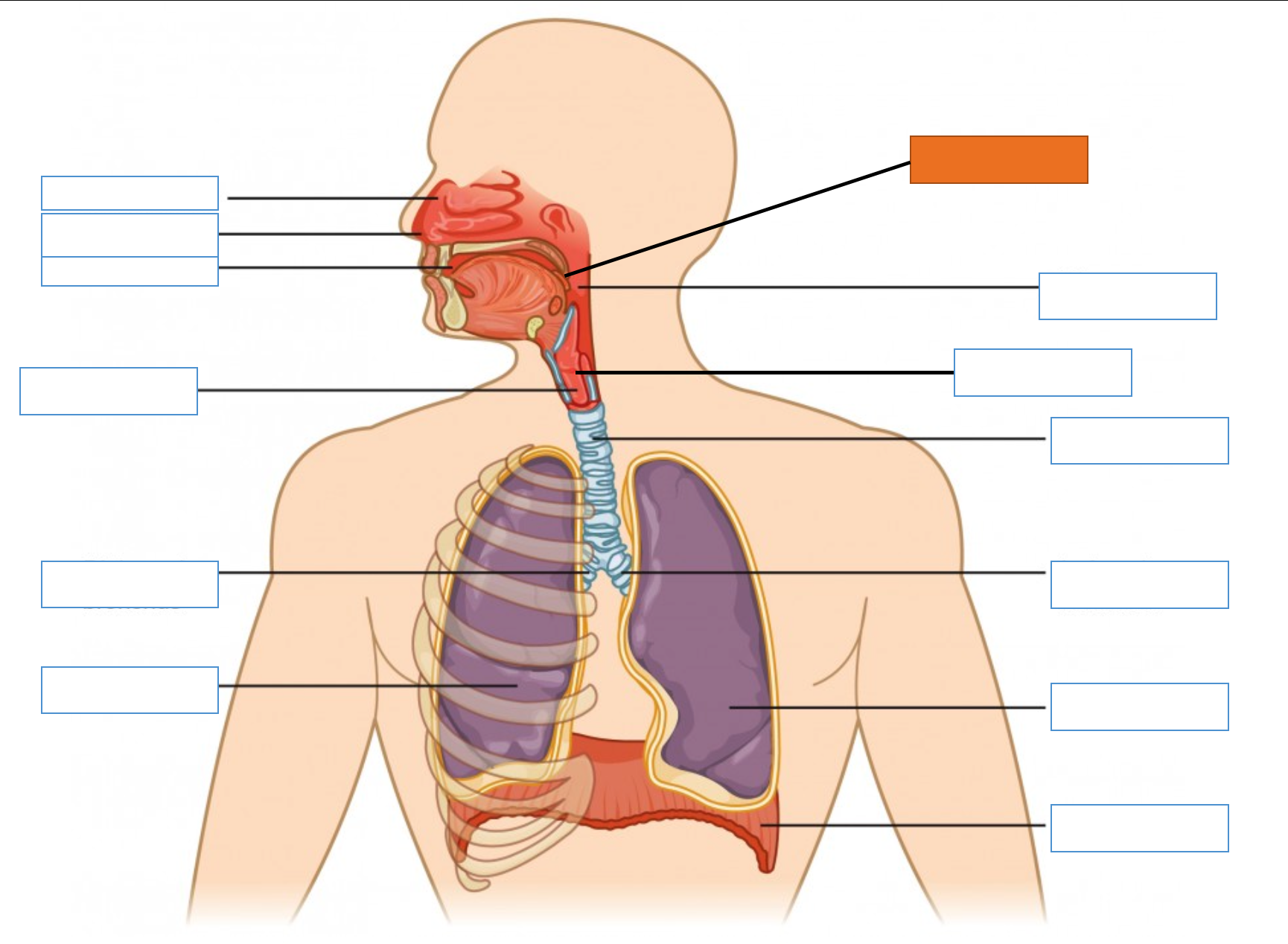
What is this identifying?
Epiglottis
pulmonary system
parts that work together to bring oxygen into your body when you inhale and get rid of carbon dioxide when you exhale
coronary artery
supplies high pressure blood to the heart, it is directly off the aorta
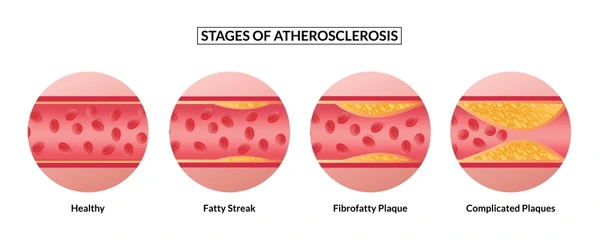
Atherosclerosis
the build-up of cholesterol plaques on the coronary artery walls
Symptoms of Atherosclerosis in men
Tend to have chest pain but can also have these symptoms: chest tightness/pressure/discomfort/shortness of breath/pain in neck, jaw, throat, upper belly or back, pain/numbness/coldness of arms + legs
Symptoms of Atherosclerosis in women
Tend to have shortness of breath, nausea, extreme fatigue, w/ chest pain
Arrythmaias
hearts beats too fast, too slow, or irregularly
Symptoms of Arrythmaias
chest pain/discomfort, dizziness, fainting, fluttering chest, light headedness, racing heart, shortness of breath
Heart Murmur
a blowing/whooshing/rasping sound during a heartbeat; caused by turbulent blood flow
Fix for Atherosclerosis?
Bypass Surgery
Bypass Surgery
when a coronary artery is blocked, a bypass made of harvested tissue can be added to go around the blockage and create a new pathway for the blood to flow
Amount of bypasses that can be added?
One, two, or three
Fix for Irregular Heartbeat?
Pacemaker
Pacemaker
the SA node is the natural pacemaker but when it doesn’t function properly an artificial pacemaker can be added to control the heartbeat
What determines the characteristics of one’s teeth?
Diet
Why are human teeth the way they are?
Humans are omnivores and have teeth adapted for eating plants + animals
Where does digestion start?
Mouth
Salivary Amylase
breaks down starch; secretion is triggered by neuronal stimulation like smell or taste; other learned stimulations can trigger secretion too like the sight of food
function of the pharynx in the digestive system
in order for food to go down the esophagus the epiglottis moves to cover the trachea and direct food down the right pipe
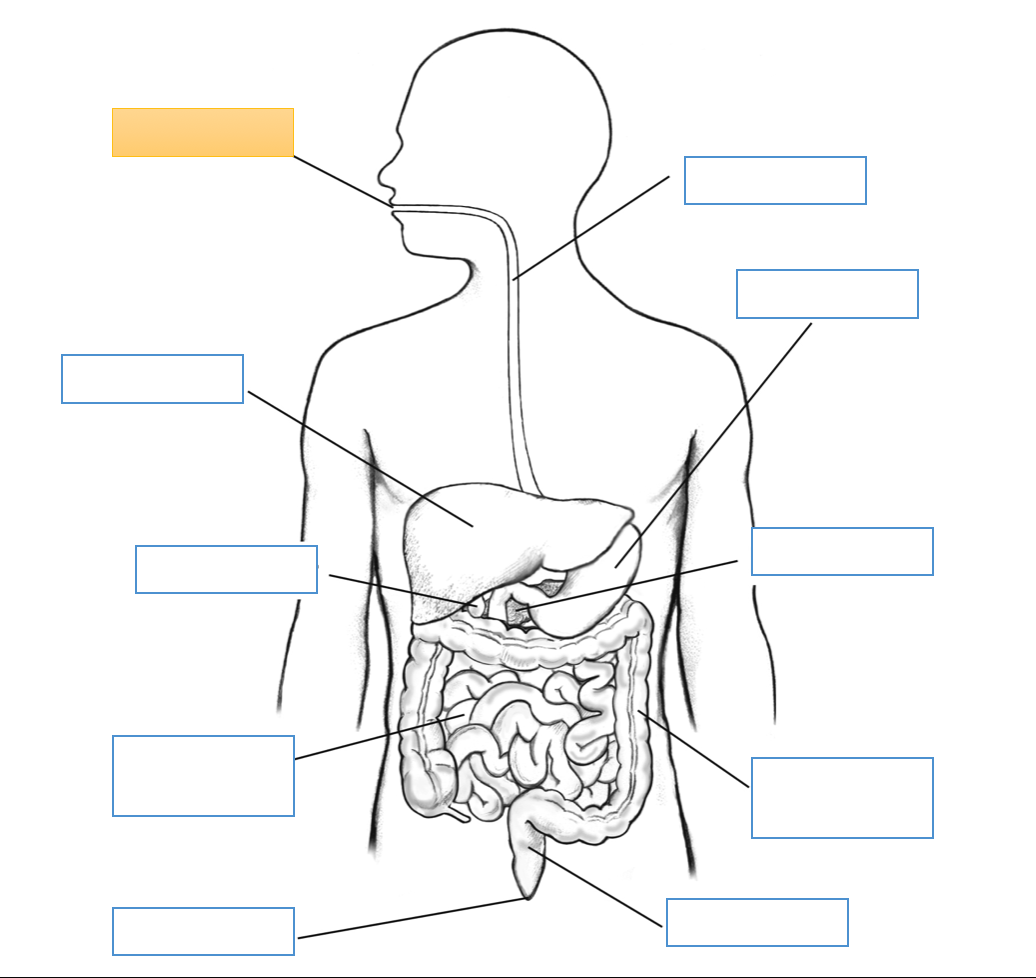
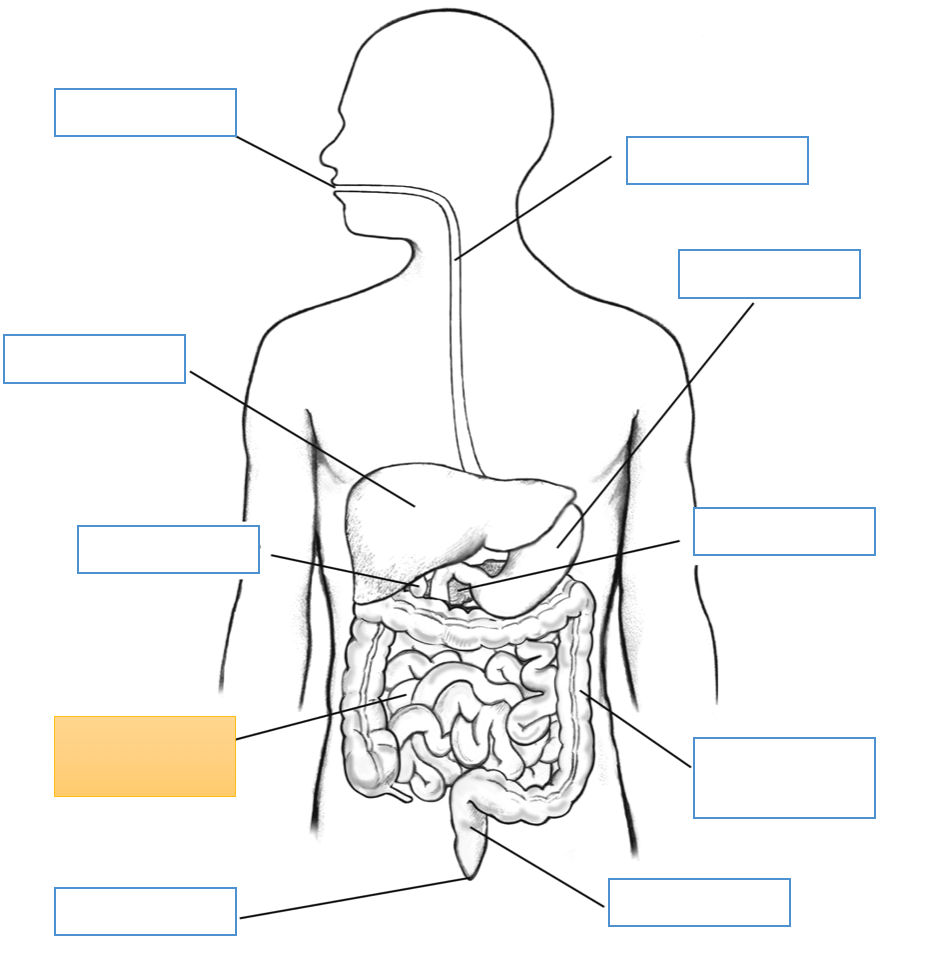
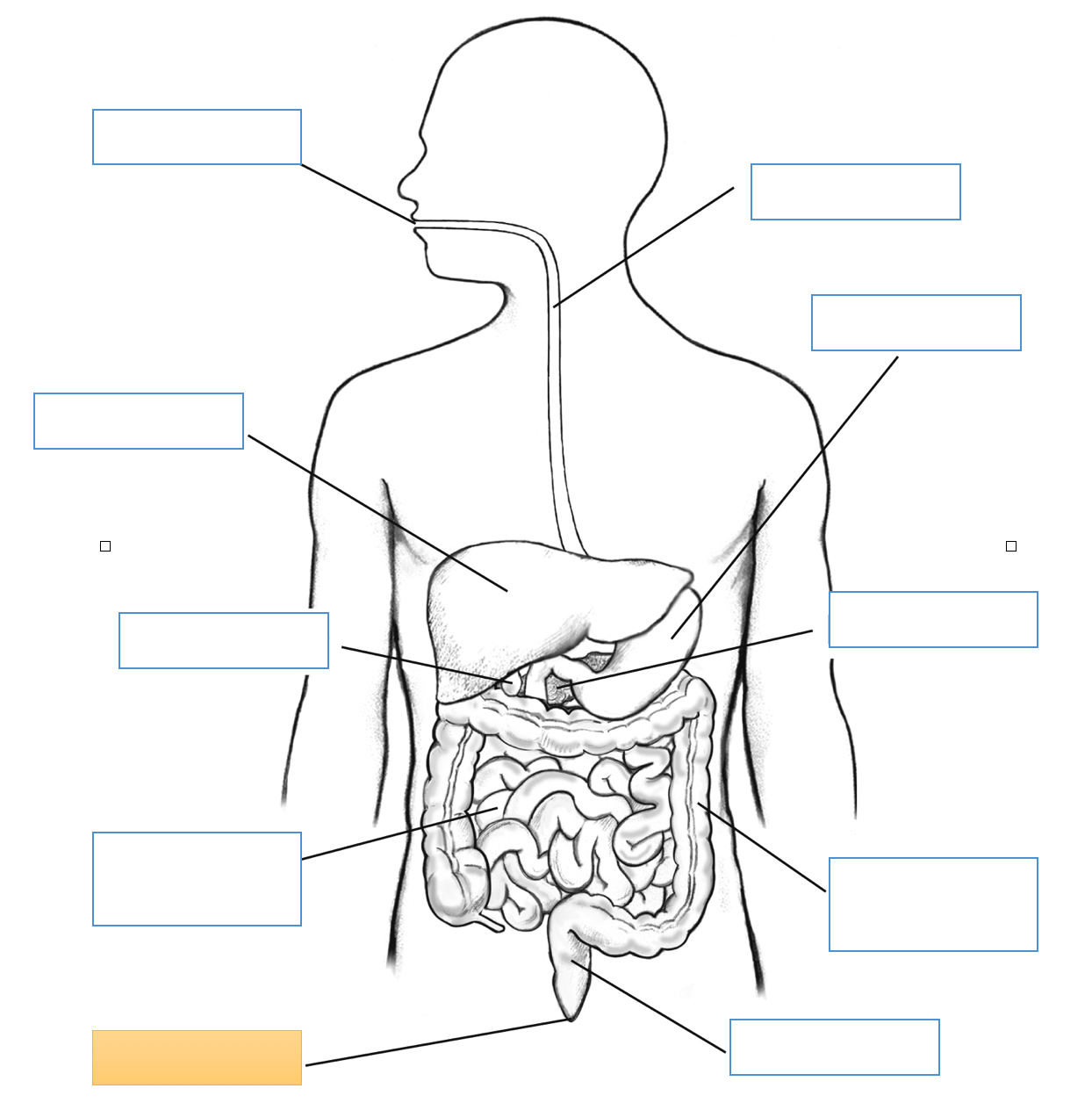
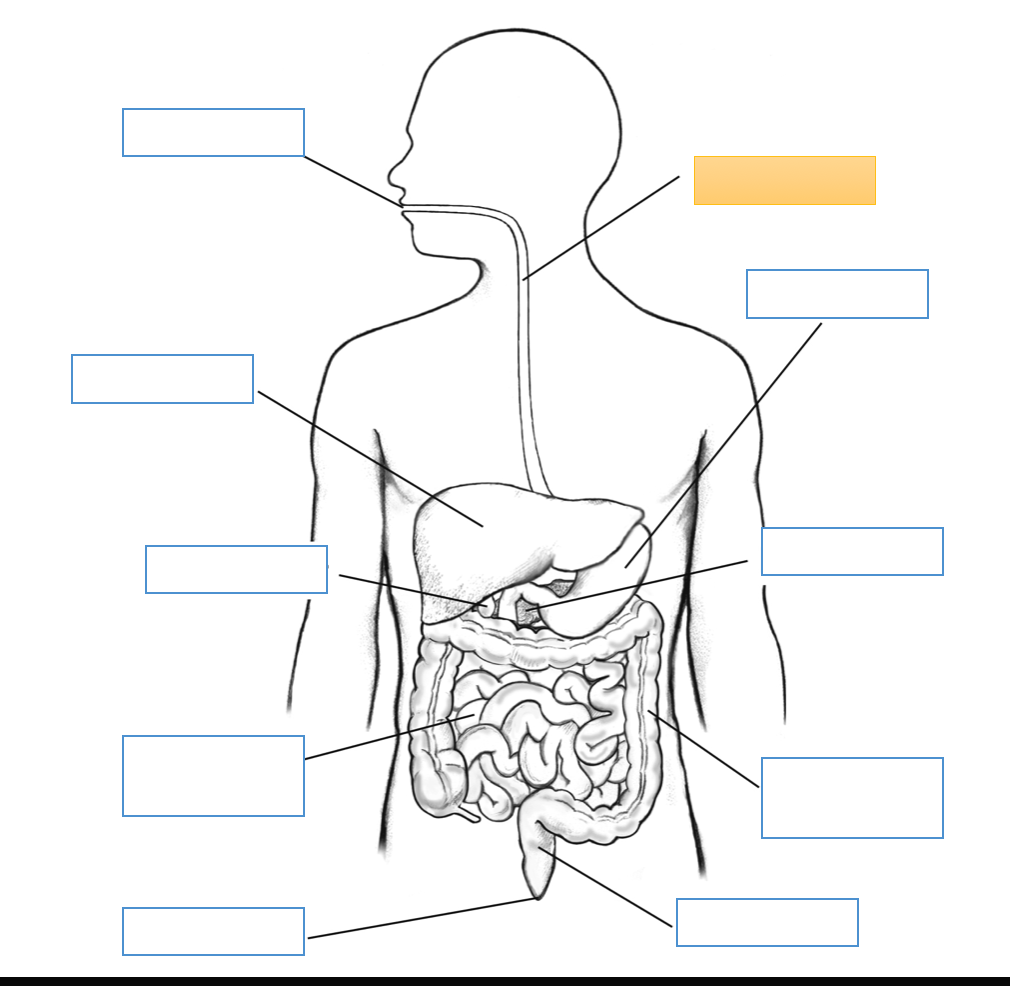
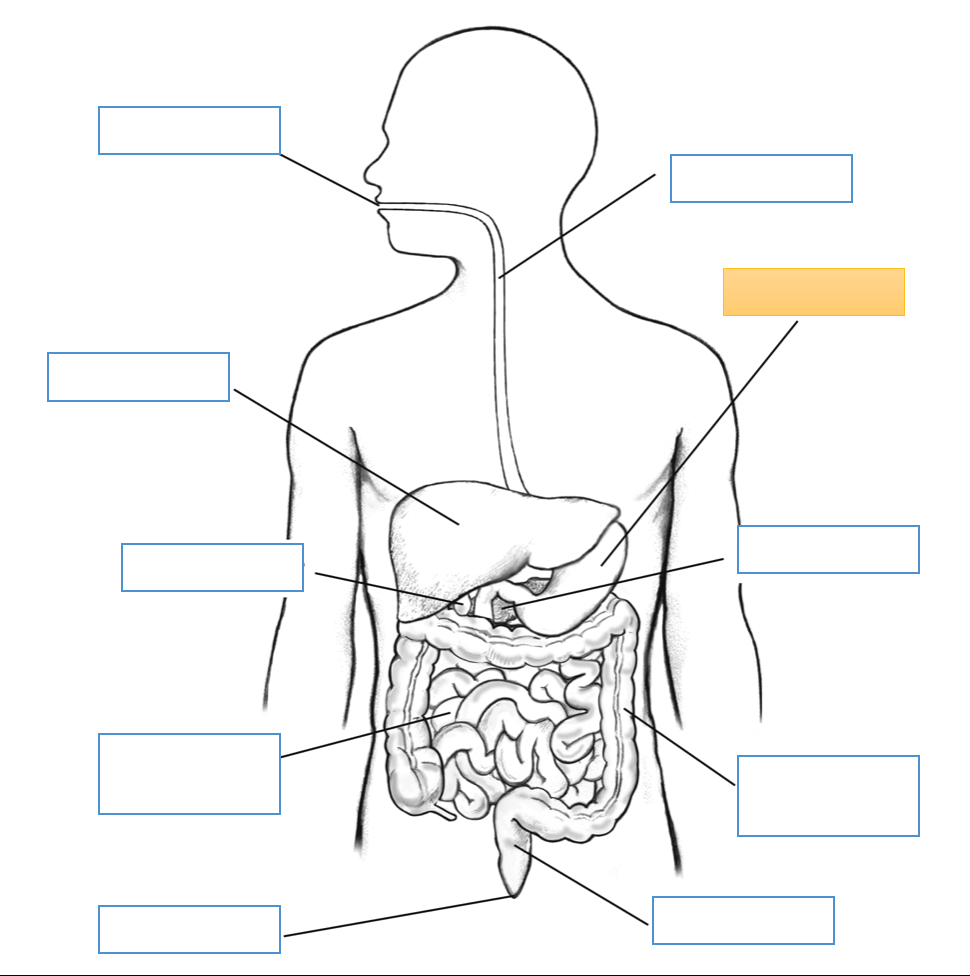
What is this identifying?
Mouth
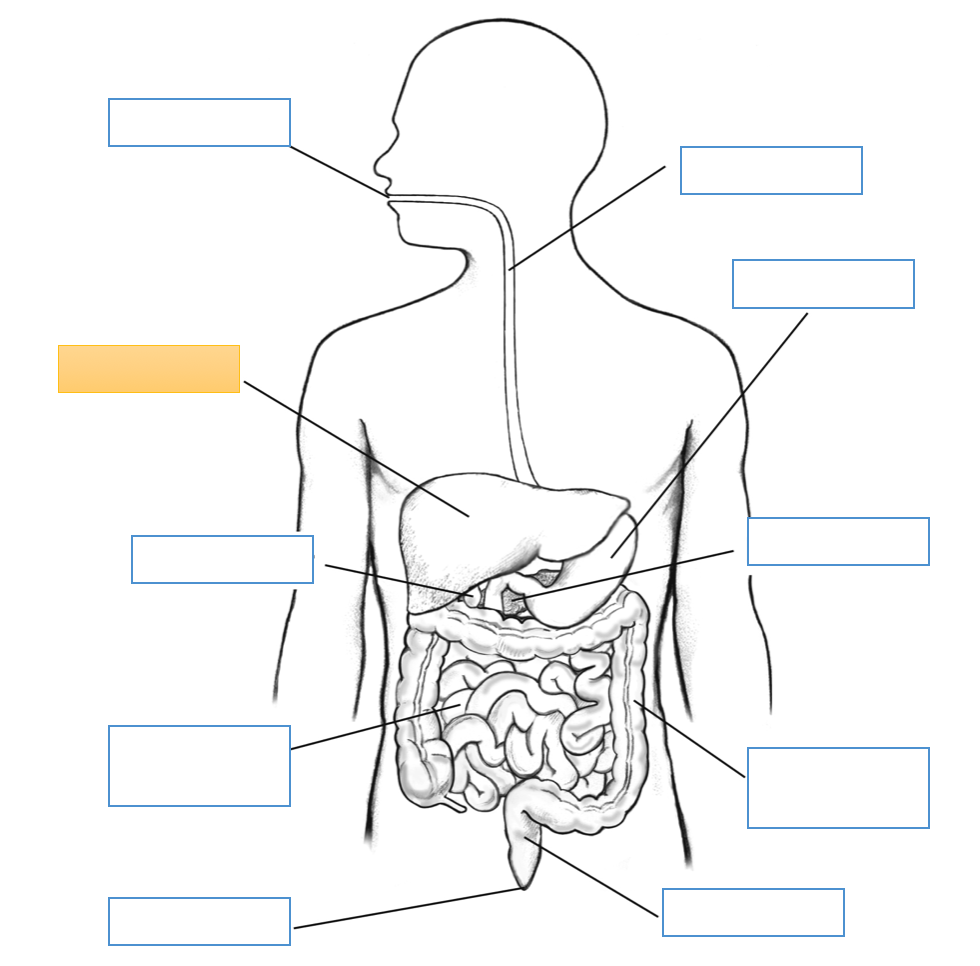
What is this identifying?
Liver
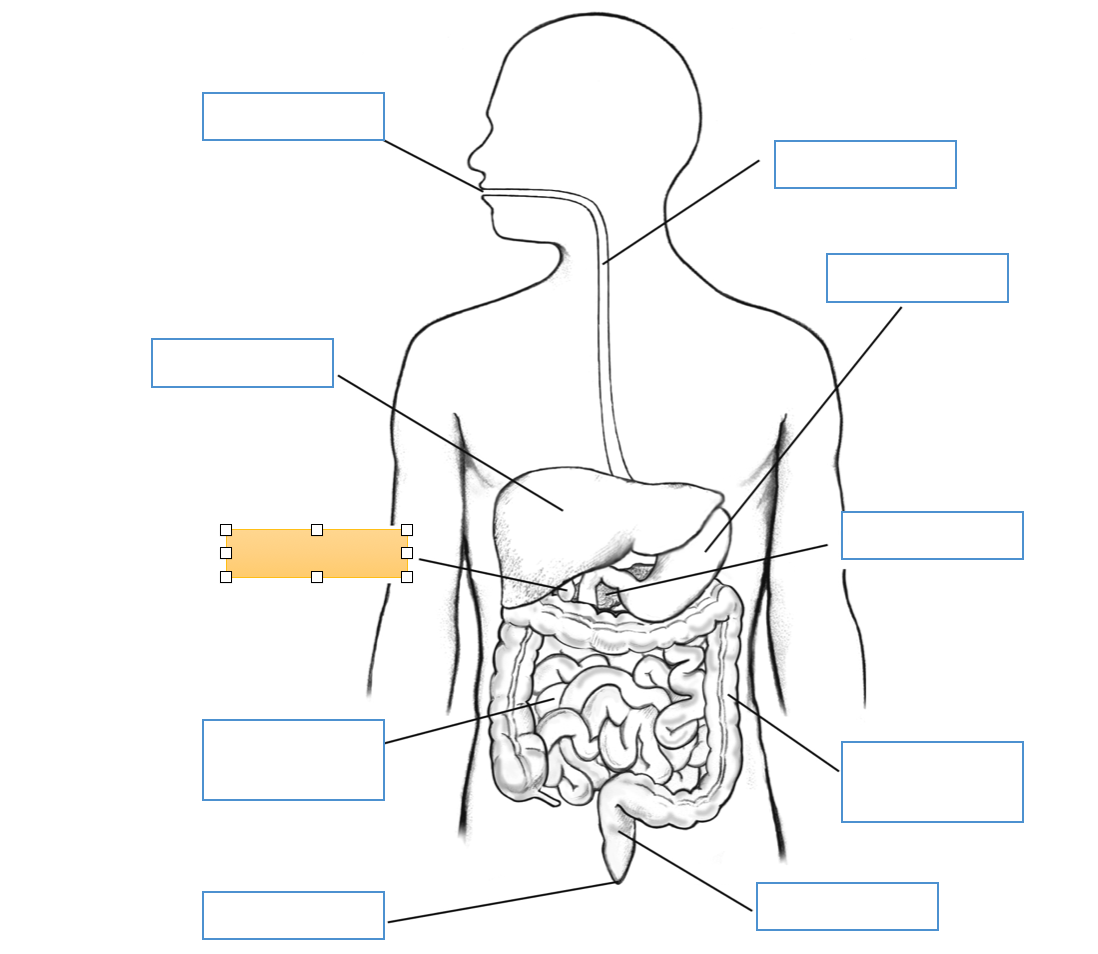
What is this identifying?
Gallbladder
What is this identifying?
Small Intestine
What is this identifying?
Anus
What is this identifying?
Esophagus
What is this identifying?
Stomach
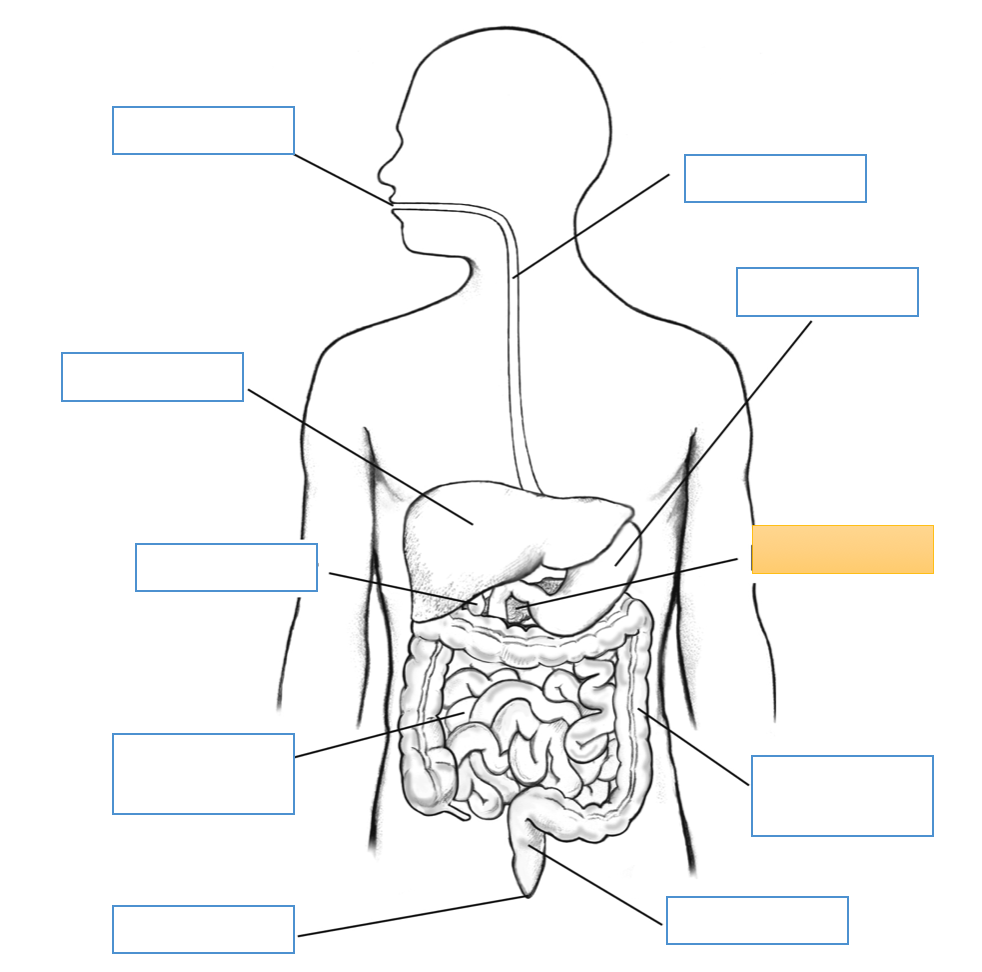
What is this identifying?
Pancreas
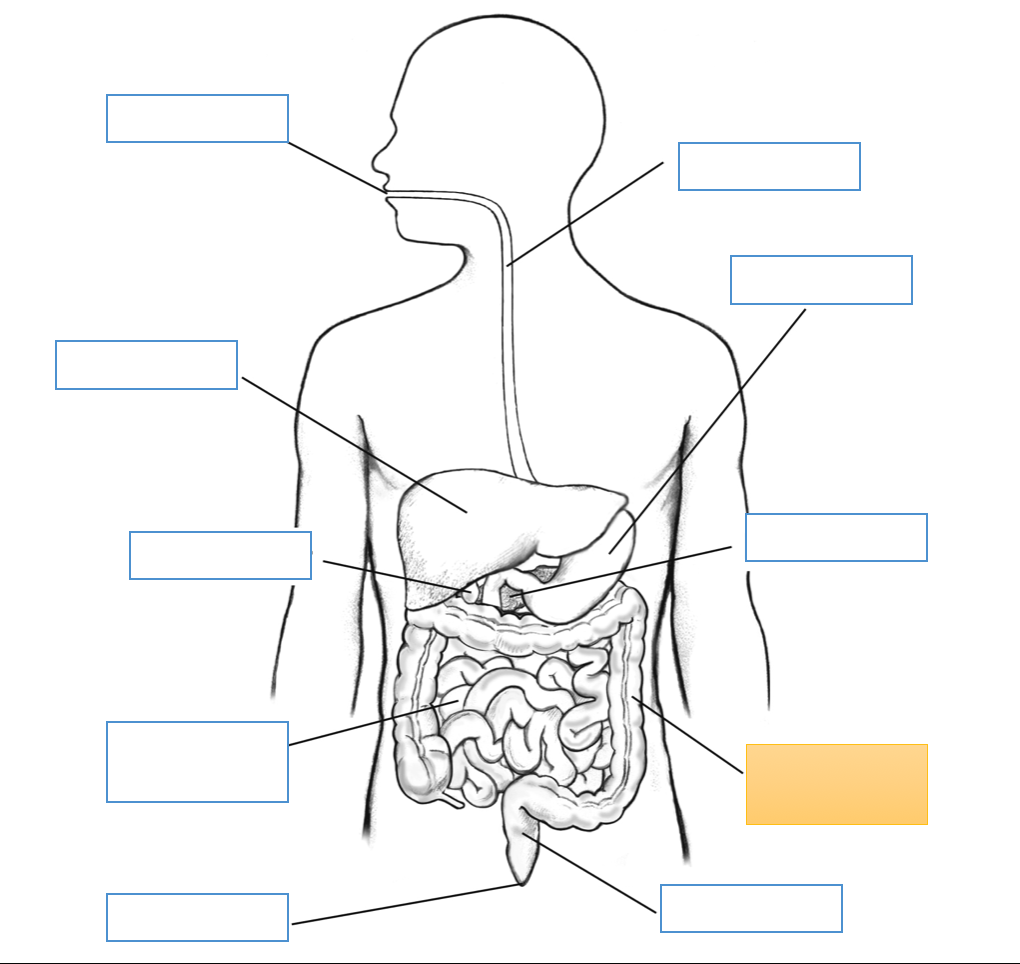
What is this identifying?
Large Intestine
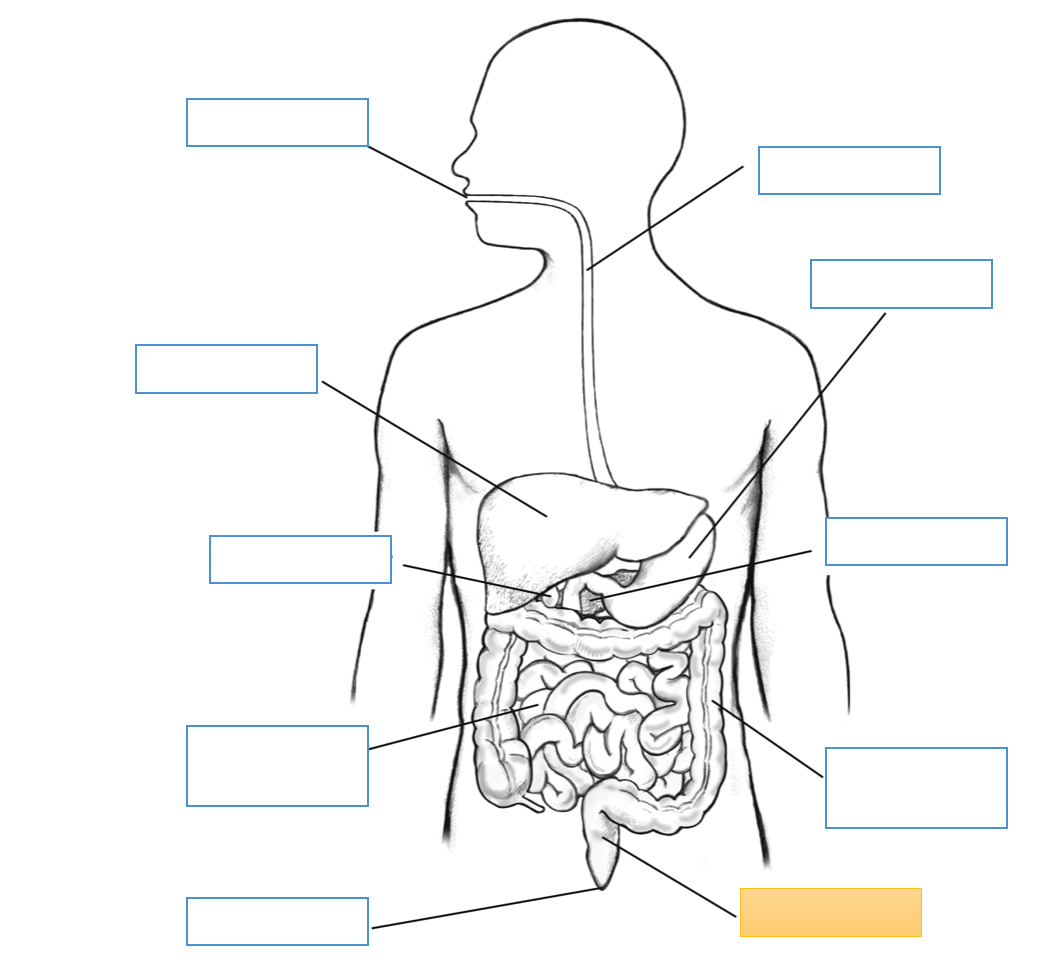
What is this identifying?
Rectum
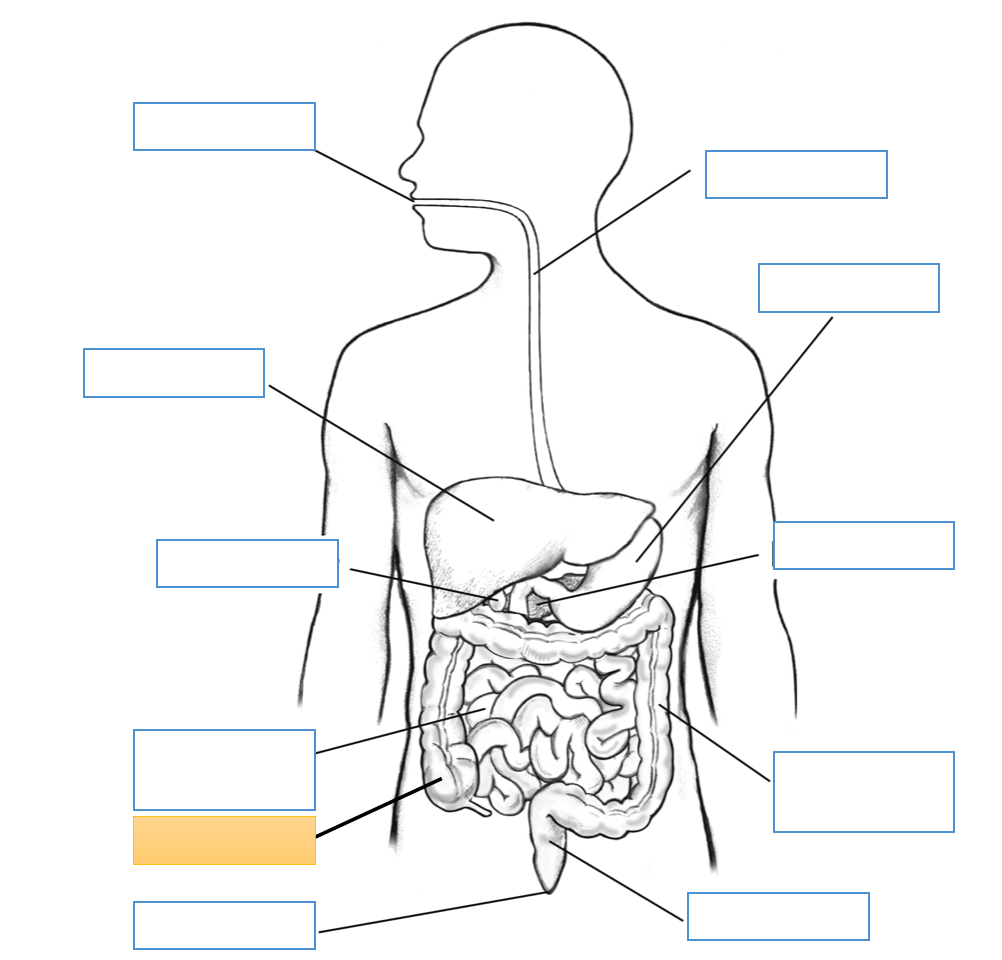
What is this identifying?
Cecum
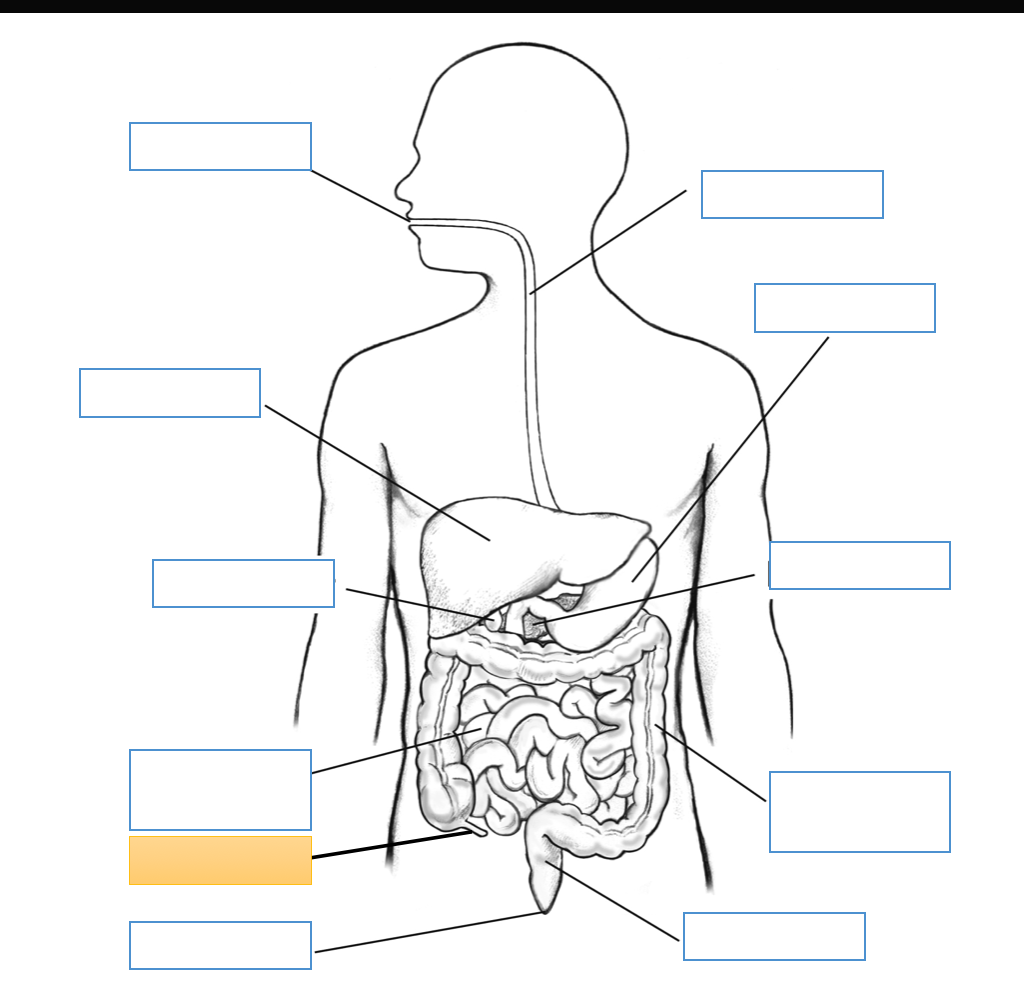
What is this identifying?
Appendix
pancreatic juice
neutralizes stomach acid
sphincter
ring of smooth muscles that divide the digestive system into compartments
feature specific to the anus?
as we age skeletal muscles develop on it that are voluntary and allow us to “hold it”
Large intestines absorb what?
Water
Bile
a bitter greenish-brown alkaline fluid that aids digestion and is secreted by the liver and stored in the gallbladder