Economics exam 3
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
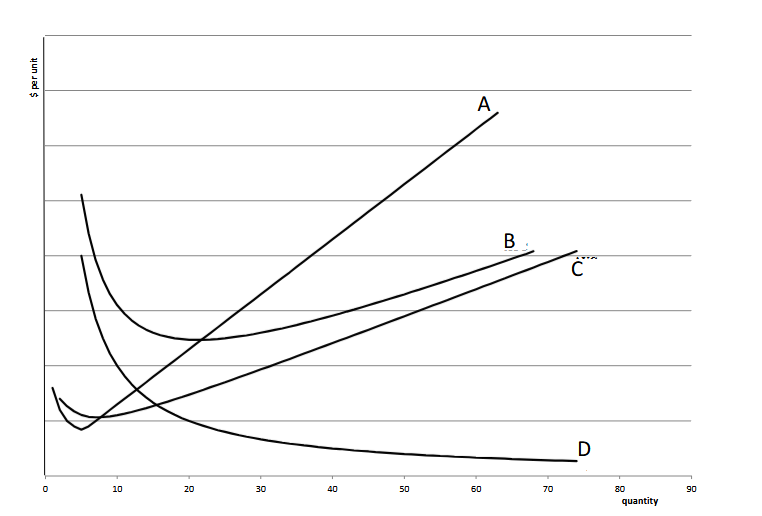
Which is the average fixed cost?
D
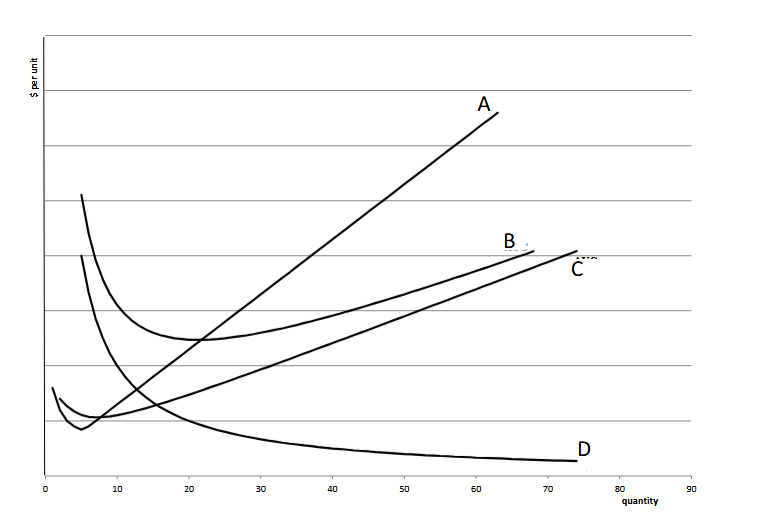
What is the MC?
A
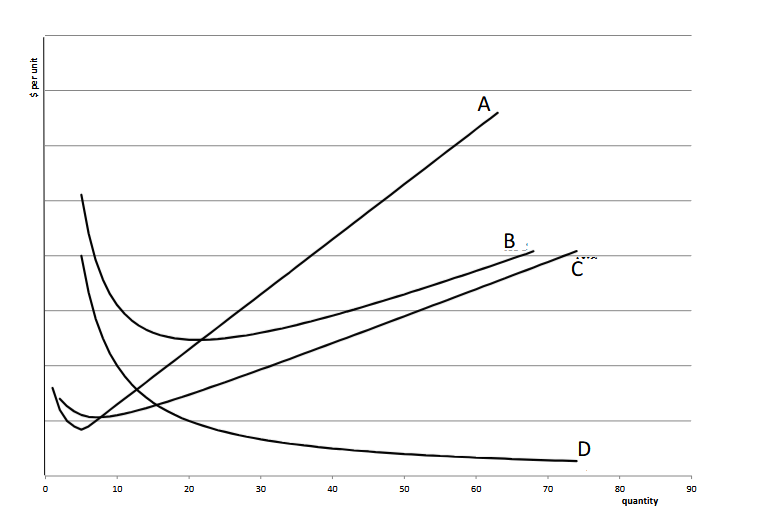
What is the Average Total cost?
B
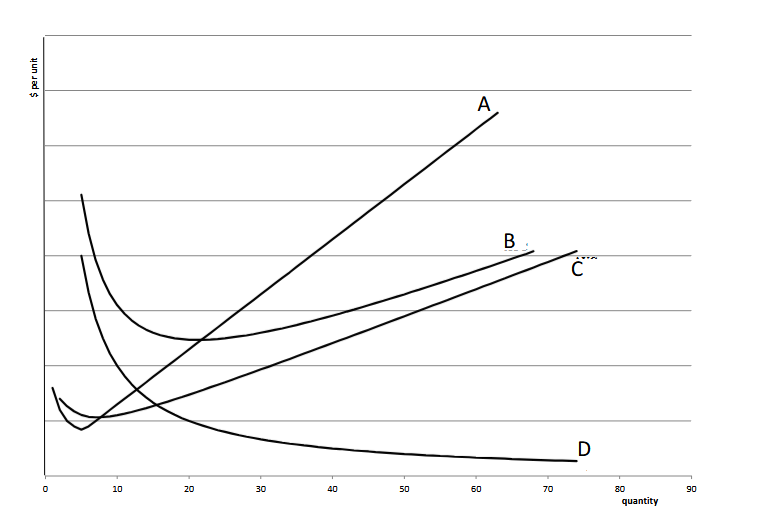
What is the AFC
D
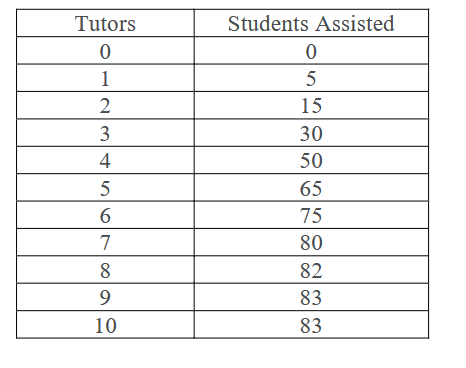
When does this table experience the diminishing marginal product?
With the 5th tutor as it starts to decline
What cost curve is a firms supply curve?
MC (it is the info we pull to know quantity)
Expansion, occuring in long run atc decreased from 3 per pound to 2.50 per pound.
Economies of Scale
Apple charges Chase a fee every time a customer downloads one of his games. If apple increases the fee, what curve will increase
Average total cost, average variable cost and Marginal cost
Charlie sells kittens mittens on etsy. He advertises on tv. If advertising charges go up. What cost curve will increase?
Average Total cost and Average fixed cost only.
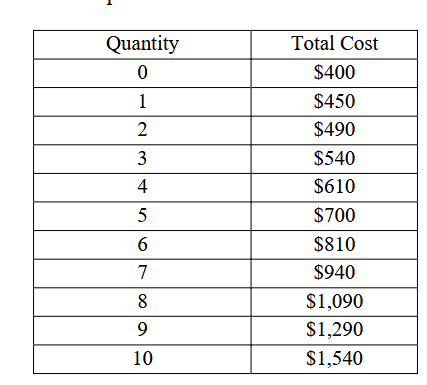
If the firm is in competitive market and market price is 90, will the firms output be?
5 (match MC=MR)
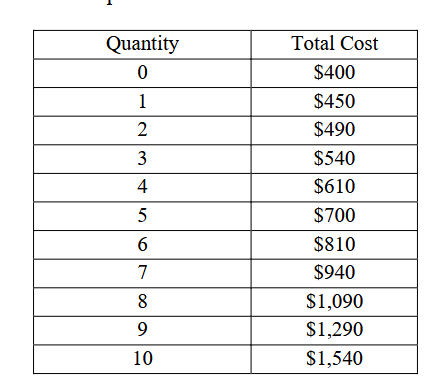
What will be the profit at market price 90
-250 (Profit = Price * Quantity - Total cost)
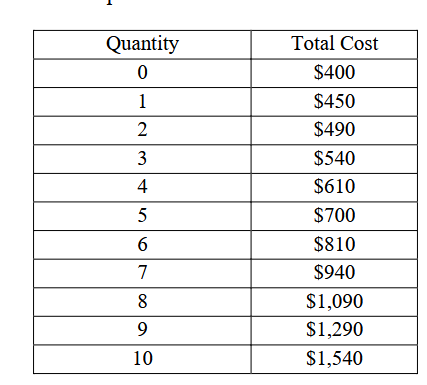
What is the firms profit at 90$
-250 (Profit = Price * Quantity - Total cost)
What is primary difference between monopolistic competitive markets and monopoly markets?
Monopoly markets have one firm and barriers to entry, while monopolistically competitive markets have many firms and easy entry

Which market is firms objective to maximize profit?
All of them are

which market is economic profit driven to zero in the long run?
Perfect compitition and monopolistic competition

Which markets is economic efficiency achieved?
Perfect Competition
Which market results in the greatest quantity?
Perfect Competition
Firms that are price takers cannot earn economic profits
Price takers can earn economic profits.
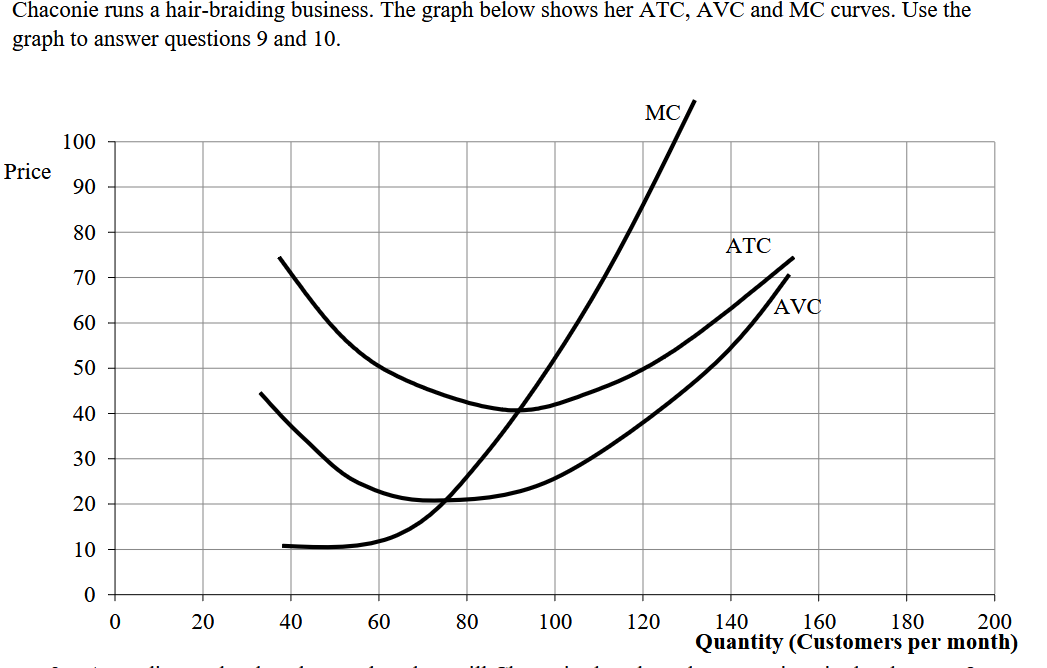
When will chaconie shut down operations in the short run?
Shutdown will apply if price falls down below 20 per customer
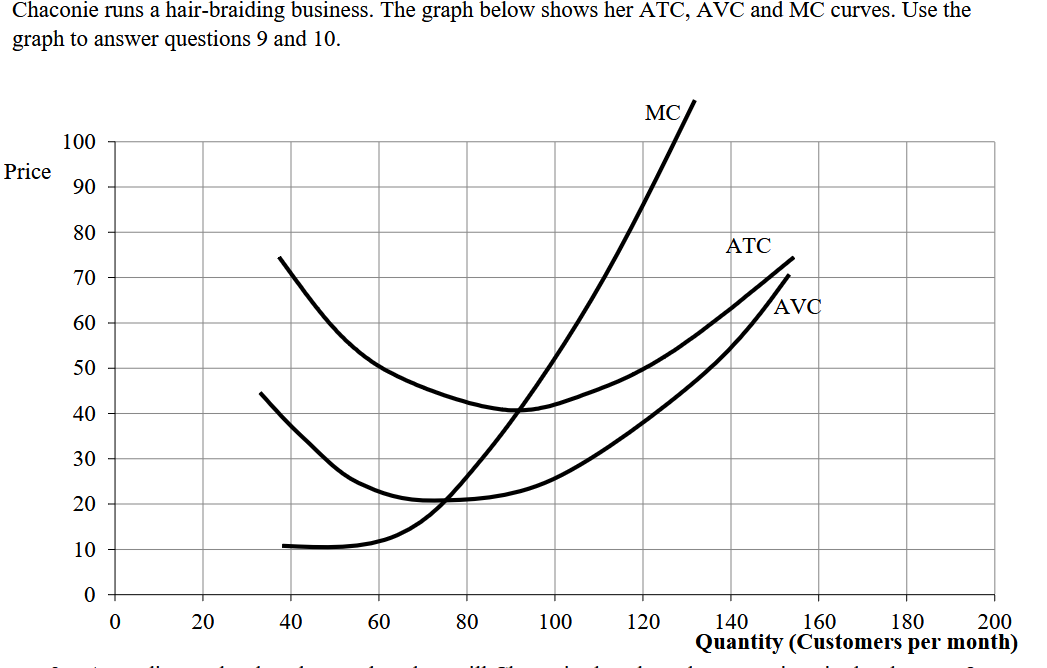
Suppose perfect competitive market with easy entry. What long run supply curve look like?
It will be a horizontal line at price of 40.
In perfectly Comp markets we assume firms have no control over price. If firms have no control over price, how are prices determines in these markets?
Market forces push prices to the point where quanity demanded equlas quantity supplied in the market
If firms in perfect comp market are earning economic profits, which of the following would we expect to occur in the market?
New firms entering the market will increase supply and economic profits will get smaller
There are 300k farmers of corn. Which type of market is the US corn market?
Perfect competition
What long run adjustments would we expect to take place in the following monopolistic comp market.
New firms will enter, firm demand will decrease, and economic profits will get smaller
If a apartment (monopolistically competive) decidees to include washer and dryer hookups i the apartments. It will increase costs by 40$. Objective is to maximize profit, apartment should not include it since it will cause profits to decrease.
false since differeting is profitable
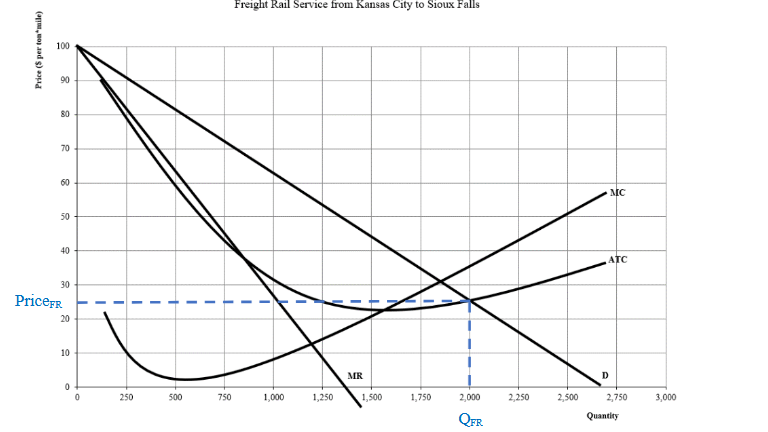
If goverment decided to regulate the price of rail service doing the fair return pricing rule, what price would be set?
26 dollars since atc = D price
List the four barries to entry
Goverment barrier to entry
Firm has control of raw material
Network externality
Natural Monopoly
Select the firm demand and marginal revenue curves given the market price of 60 dollars
There would be a line where 60 labeled as D = MR
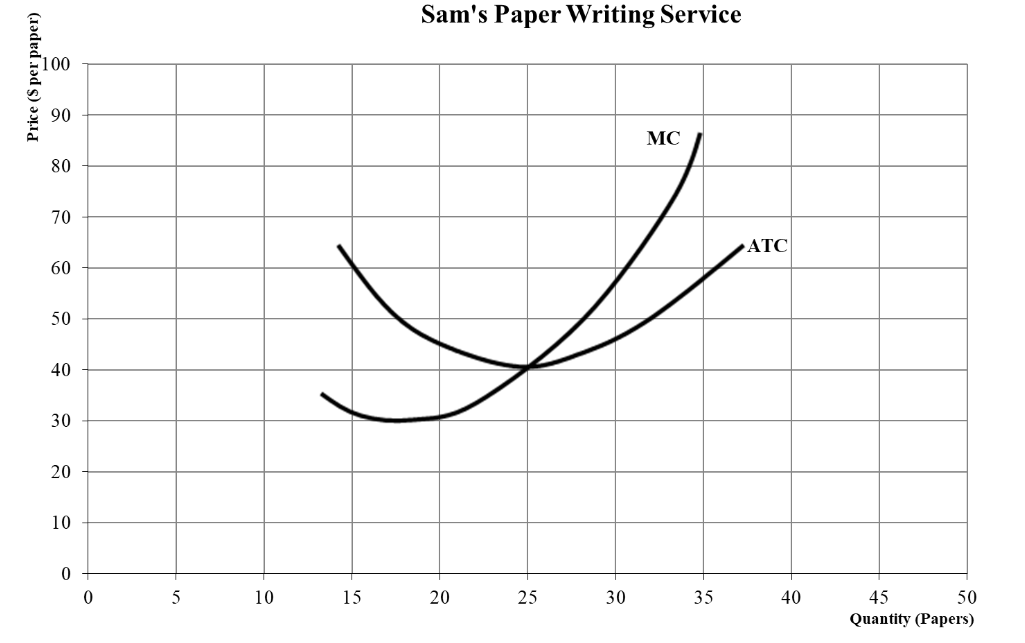
What is the Q*
It would be 32 since MR=MC
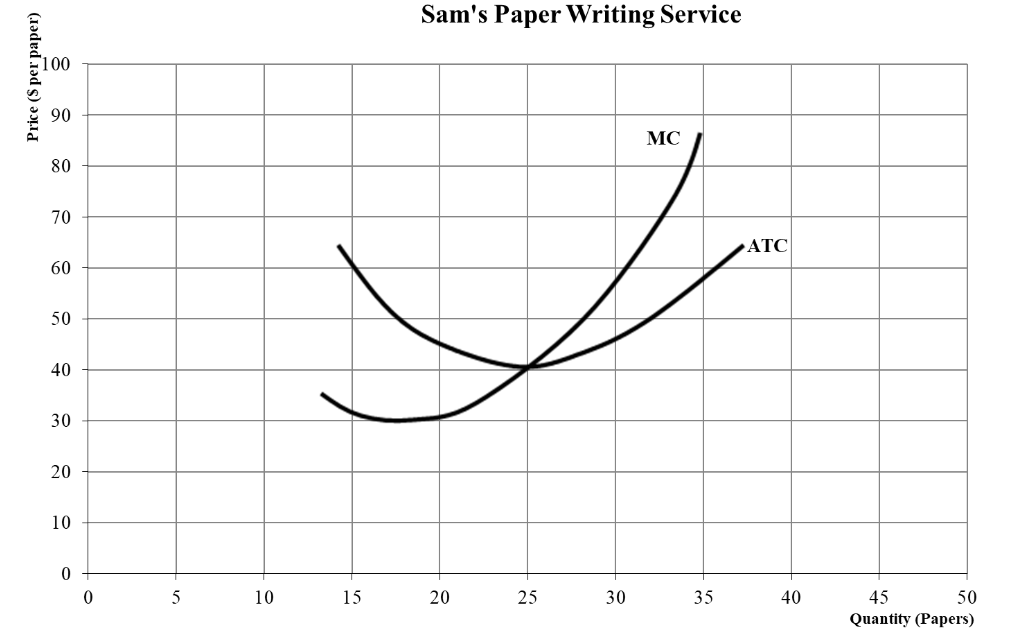
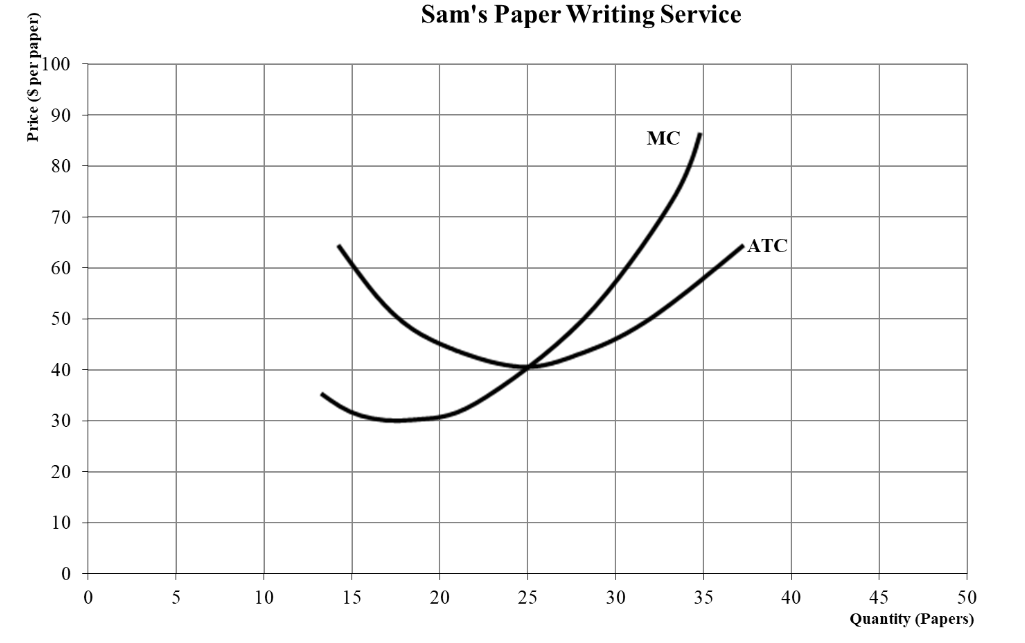
What would be Sams profit?
465 (price-ATC) * quanity
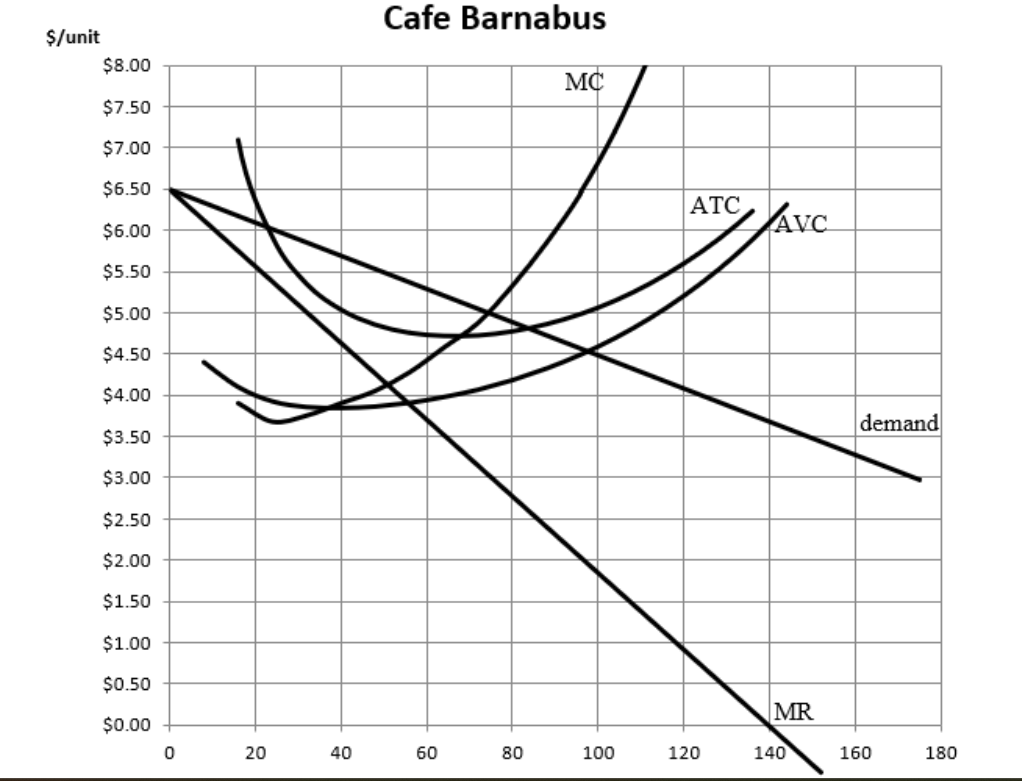
What is profit max quanity and profit
50 for quanity and 5.50 for price. Go up to demand for price and quantity where MR=MC
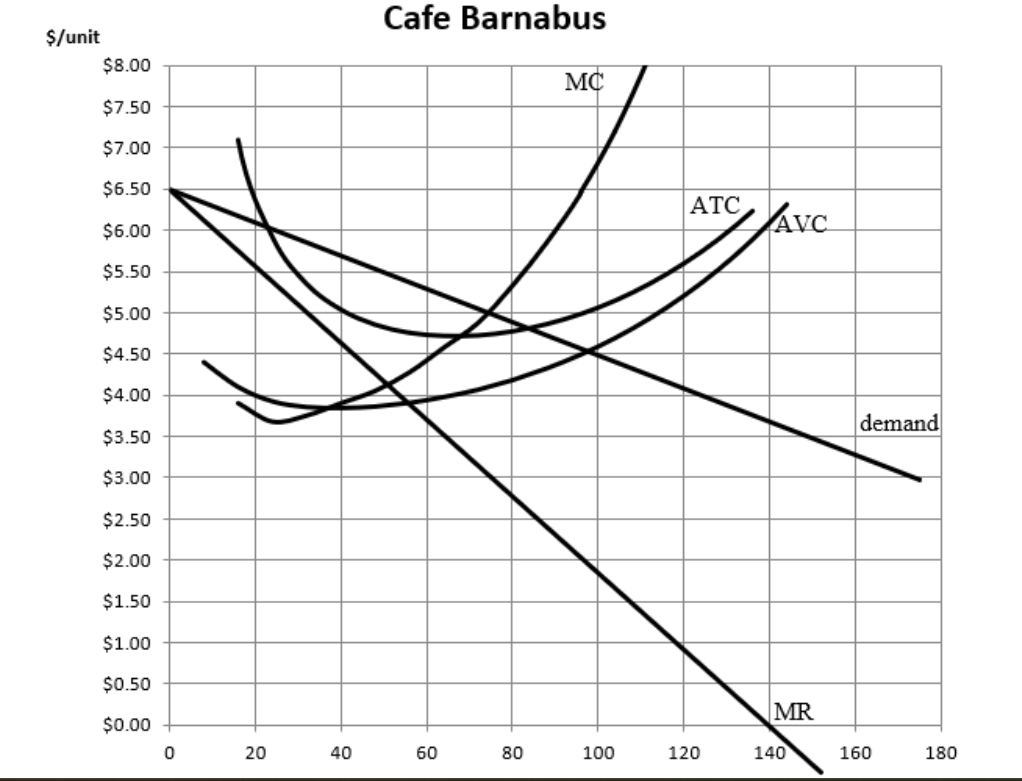
what is the profit
(5.50 - 4.80) times 50 = 30
Washbrun decieded to increase rent for cafe barn. How would this impact cafe barn profit maximizing price and profits
The price they charge will stay the same, profits will decrease
Accounting profit
Revenue - explicit costs
Economic profit
Revenue - explicit costs - implicit costs
Short run economics
time period firms inputs are fixed, number of firms in market are fixed. L
Long run economics
Time period which all firms inputs are variable, firms can exit and enter then market
Marginal product
additional output that can be produced by adding one more unit, holds other inputs fixed
Law of diminishing marginal product
Adding more of a variable input to the same amount of a fixed input will cause the MP input to decline
When MP increase…
MC decreases
When MP decreases
MC Increases
Marginal cost
Change total cost as result of reproducing an additonal unit of output
Average Total cost
Total cost/ quantity
Average variable cost
variable cost / quantity
Average Fixed Cost
Fixed Cost/ quantity
Changes in price of labor, materials, transportation costs, energy costs for manufacuring firm, tax changes in variable cost changes…
Marginal cost, average variable cost, average total cost
cost do not vary with output: price of rent, borrowing costs, licenses changes in a fixed cost.
changes fixed costs = ATC and AFC. Does not affect MC or AVC
Economies of scale
Firms long run ATC descreases as it increases output by technology of production or purchasing inputs at lower prices
Constant returns to scale
Firms long run atc remians unchanged as it increases output
Diseconimeies of scale
firms long run atc increases as it increases output
Which market results in economic efficeincy
Perfect Competition
which markets end up with zero economic profits in the long run?
perfect and monopolistic competitive markets