UC Berkeley Chem 1a Final Flashcards
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
what kind of light will a molecule with a large HOMO-LUMO gap require?
smaller molecules with a larger HOMO LUMO gap will require higher levels of energy (such as UV light) in order to have the electrons knocked off of the highest orbital
smaller HOMO LUMO gaps means:
absorbance of higher or lower energy?
lower
why does Ne2 not exist?
it is a noble gas and will not want to bond; its bonding energy is zero, equal amounts of bonding and antobonding electrons
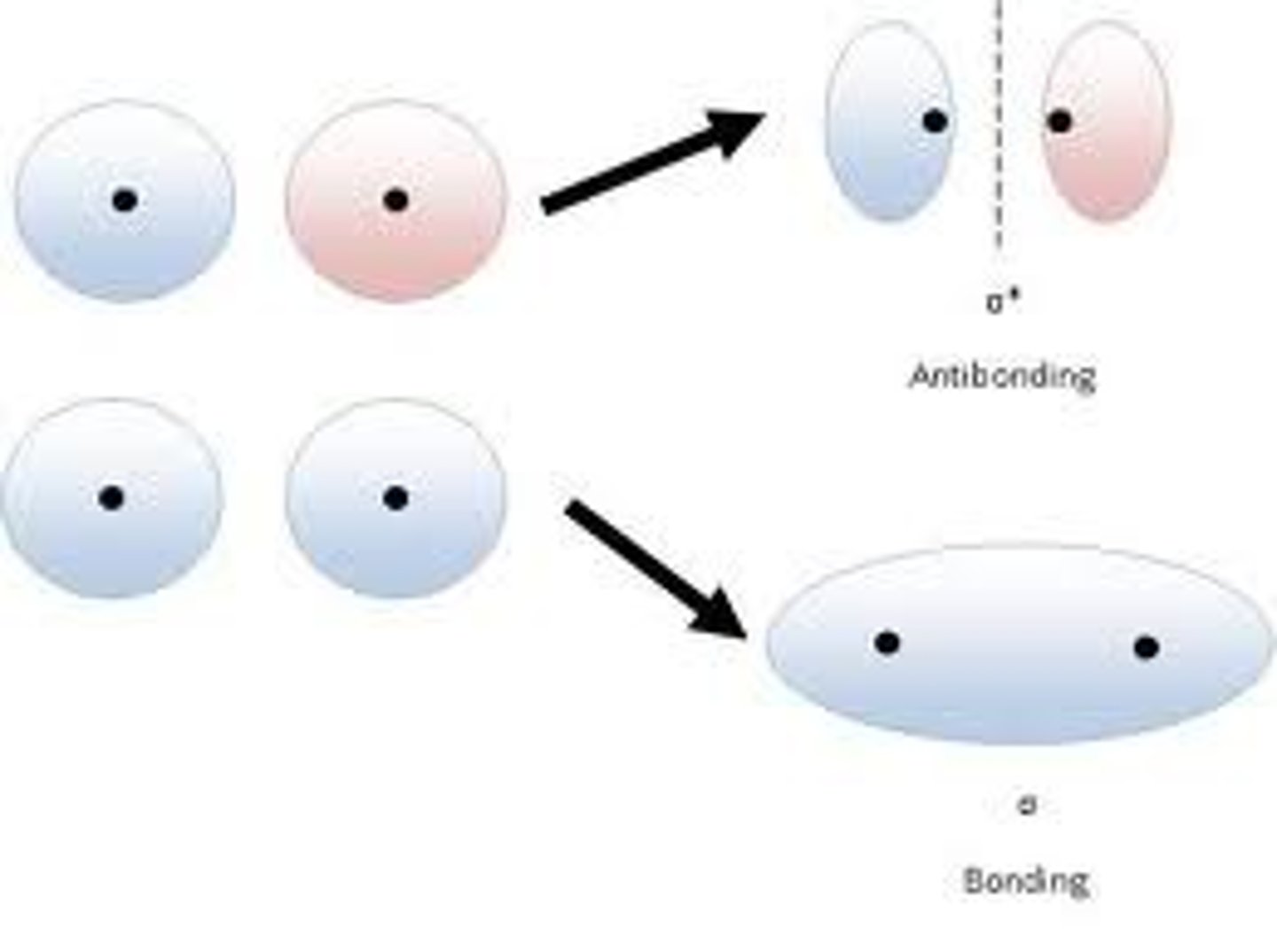
2 AO in......
2 MO out!!!!!
what MO is the electon stabilized in?
bonding MO, the electron is stabilized and the energy is lower
what doe sa double bond indicate?
a pure pi bond, one of th leftovers
sigma 2s orbital
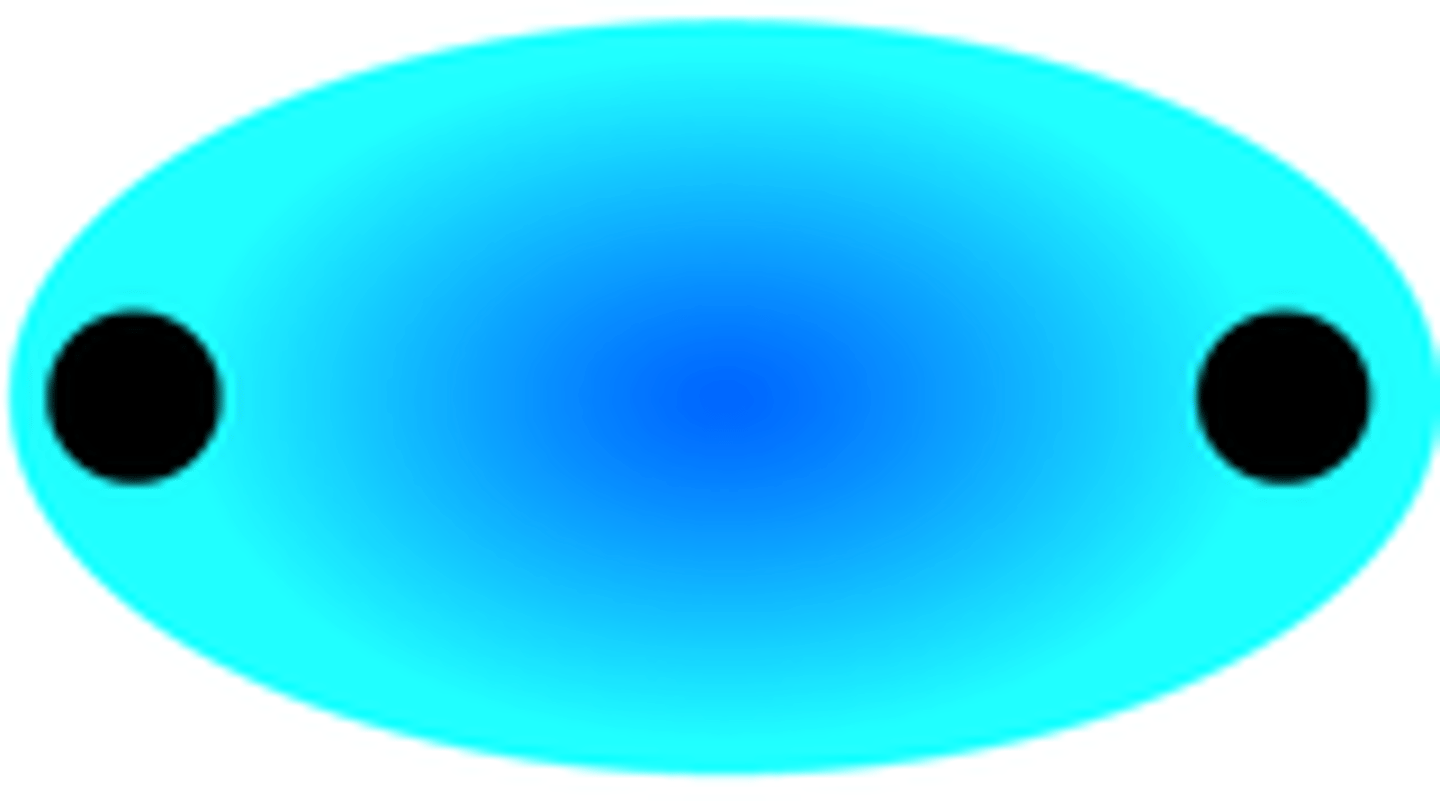
sigma star 2s orbital
one has to be shaded
pi 2p orbital
one has to be shaded
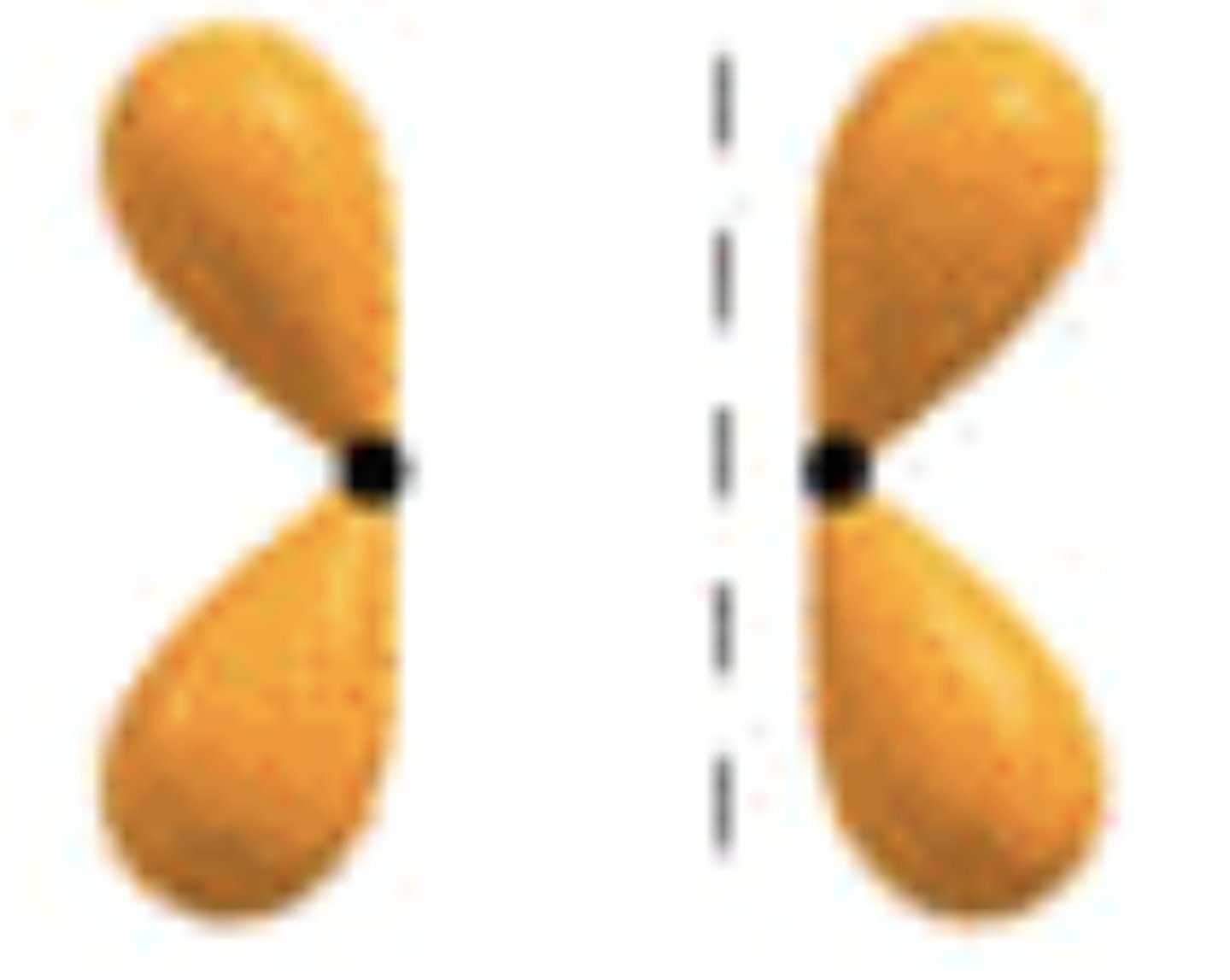
pi star 2p orbital
looks like a four leaf clover , use opposite shading
sigma 2p orbital
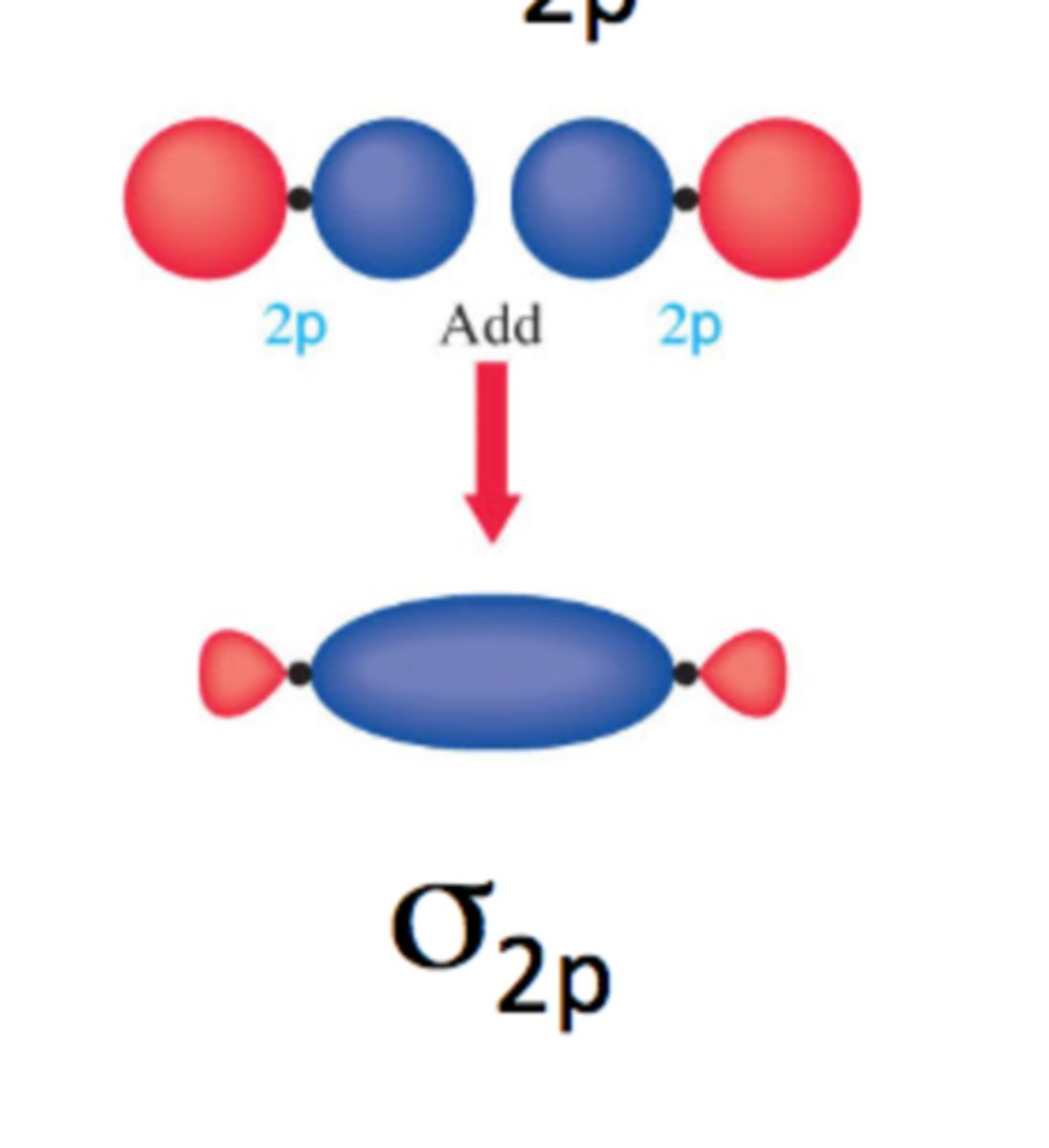
antibonding sigma 2p orbital
four balls all in a line, went in for handshake, got obliterated,
how to determine hybridization of an atom?
number of electrons domains, a double bond counts as one electron domain
general orbital
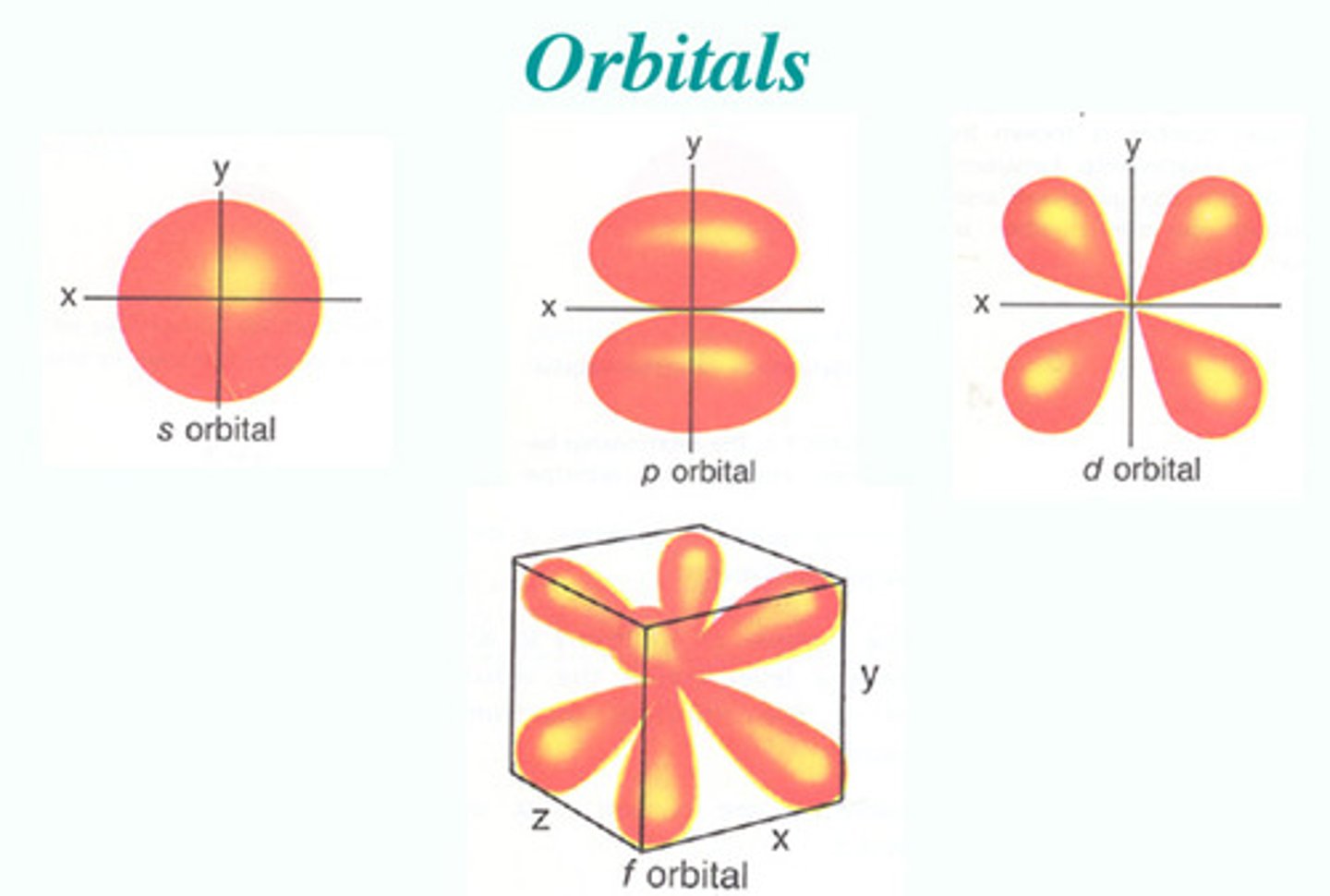
where can orbitals never be?
node
how to determine number of nodes?
highest energy -1
ex: 5f orbital hs 4 nodes
how to determine number of orientations an orbital has?
the highest orbital's letter
ex: 5f will have seven orientations
ex: 4p will have 3 orientations
how many number of electrons in each orbital?
2
ex: 2py:2 , 2px:2, 2pz:2
how many nodes do D orbitals usually have?
4
when is the ryberg constant negative?
when electrons lose energy aka theyre relaxing
how to determine which energies can be absorbed by an atom?
has to reach at least to next energy level
why is the ionization energy trend not perfectly linear towards flourine?
there are dips in energy between beryliuim and boron and then in between nitrogen and oxygen. this is because it is eadier to remove an. electron in boron and oxygen since there 2p box has only one extra electron (4 electrons so one box of three has two while the other 2 only have one) ; this is very unfavorable so it will want to be removed
which delta s is favorable?
positive delta s is favorable.
what does a greater number of unpaired electrons indicate?
stronger attraction to a magnt
what will UV light do to an electeron?
eject it off
why do the inner core electrons have a lower kinetic energy?
due to the high coloumbic attraction to the nucleus, more light energy is required to break off the electron so there is less leftover energy which is kinetic
electron affinity
energy change when a neutral atom attracts an electron and becomes an ion
a weaker bond means less or more energy is required?
less energy is required for a weaker bond
what dies a higher wave number mean
higher energy and higher frequency
higher intensity/ bnrightness of light means...
greater NUMBER of electrons ejected
speed of light (m/s) equals
nu/lambda
when pka sees a very acidic pH..
turns into NEUTRAL acid form
when pka sees a very basic pH...
turns into negatively chrged conjugate base
if pkb sees a very basic pOH...
turns in conjugate acid HB+ (positively charged)
if pkb sees a very acidic pOH...
neutral base
when the pk_ are less than the pOH/pH....
they will be in their charged forms
HCl, H2SO4,
strong acids
NH4, COOH, NH4+
weak acids
Cl-, HSO4-, COO-
weak bases
OH-, CH3NH2, NH3
strong bases