GEOSCI 110 (UW Madison) Final Exam
1/219
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
220 Terms
What is a scientific hypothesis and theory?
A proposed explanation for an observed phenomenon, must be testable
Neils Stenson (Steno): 3 principles of Stratigraphy
1. Law of Superposition
2. Principle of Original Horizontality
3. Principle of Original Lateral Continutiy
Law of Superposition
One of Steno's 3 Principles of Stratigraphy: strata is arranged in temporal order, oldest layer on the bottom
Principle of Original Horizontality
One of Steno's 3 Principles of Stratigraphy: strata is originally deposited horizontally, departures indicate strata was moved after it formed
Principle of Original Lateral Continuity
One of Steno's 3 Principles of Stratigraphy: strata will be deposited laterally unless interrupted, if layers are interrupted, they were moved after they formed
William "Strata" Smith: Faunal Succession
The order and regularity with which nature has disposed of fossils and assigned each class its own stratum
3 key properties of an Index Fossil
1. easy to identify
2. widespread
3. short-lived species
Georges Cuvier
"proved" extinction, believed in catastrophism
Catastrophism
Catastrophes, that work differently than phenomenon today, explain unconformities (breaks in the rock record)
James Hutton
Father or modern geology, believed in uniformitarianism
Uniformitariansim
Past geological events can be explained by forces today, natural laws were the same throughout time
Rock Cycle
A series of processes on the surface and inside Earth that slowly changes rocks from one kind to another
Plutonism
The formation of intrusive igneous rock by solidification of magma beneath the earth's surface.
Principles of Cross-Cutting and Enclosing Relationships
Molten rock intruding into older pre-existing rock, or fully enclosing it -- relative timing and age of these rocks can be determined by these relationships
Significance of unconformities
It records a period of missing time (and sediment) within the geologic record
Principle of Inclusion
Any rock represented by eroded fragments is older than the rock enclosing it
Chales Darwin - what is the significance of 1859? What were Darwin's 2 claims?
Darwin published the Origin of Species in 1859. Claims:
1. All living things share a common ancestor
2. Species on Earth evolve through a natural process = natural selection
Alfred Russel Wallce - what is the Wallace Line?
an imaginary line that passes between Asiatic and Australian faunas, between Bali and Lombok
Malthus - what did he predict in his Essay on the Principle of Population?
Malthusian theory predicts population size increases in a non-linear geometric rate.
3 requirements for Natural Selection
1. variation
2. inheritance
3. differential reproduction
(4). sometimes overproduction of offspring
3 types of Natural Selection
1. stabilizing
2. directional
3. diversifying
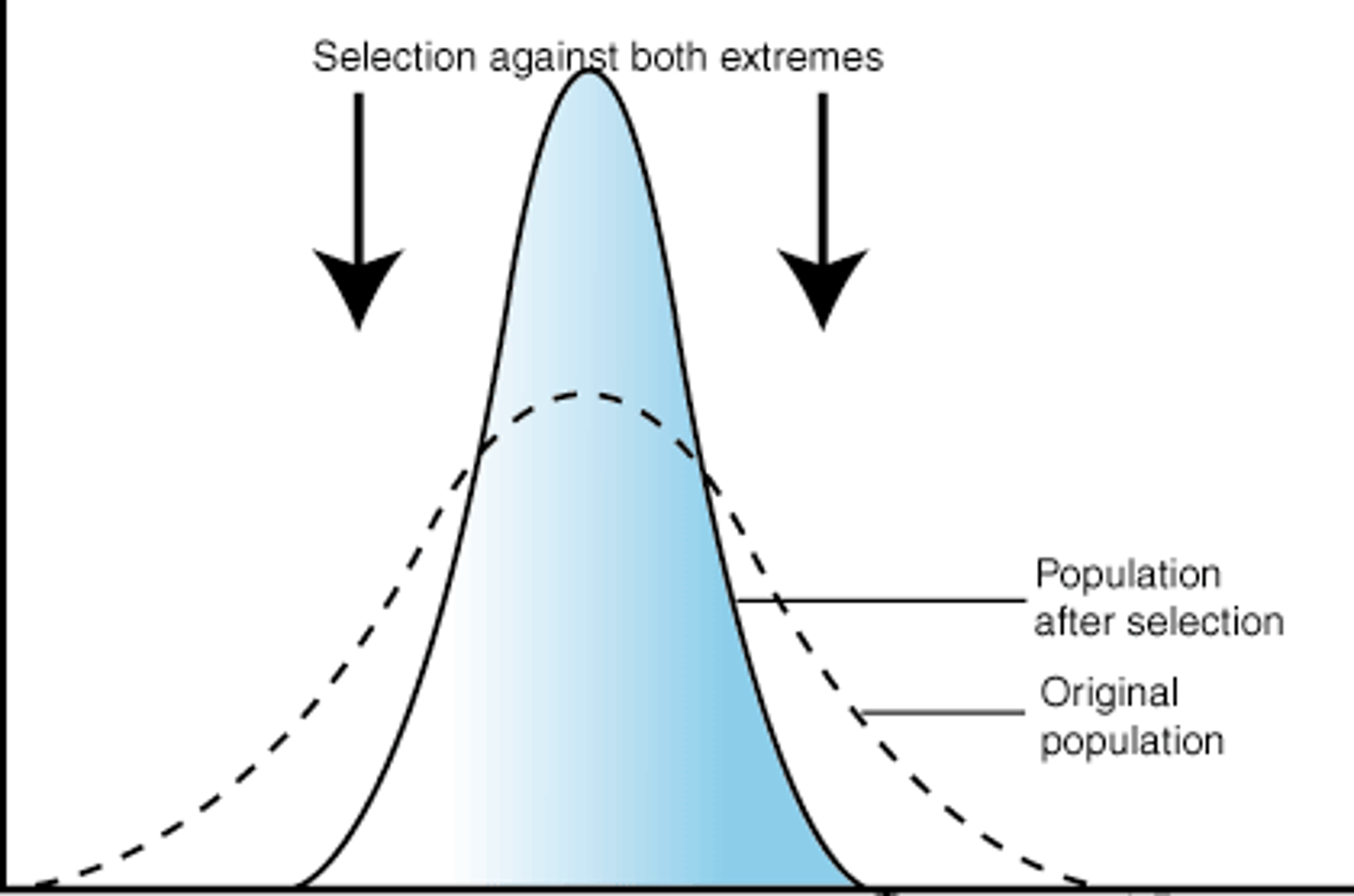
Stabilizing selection
selection against the extremes, maintains status quo
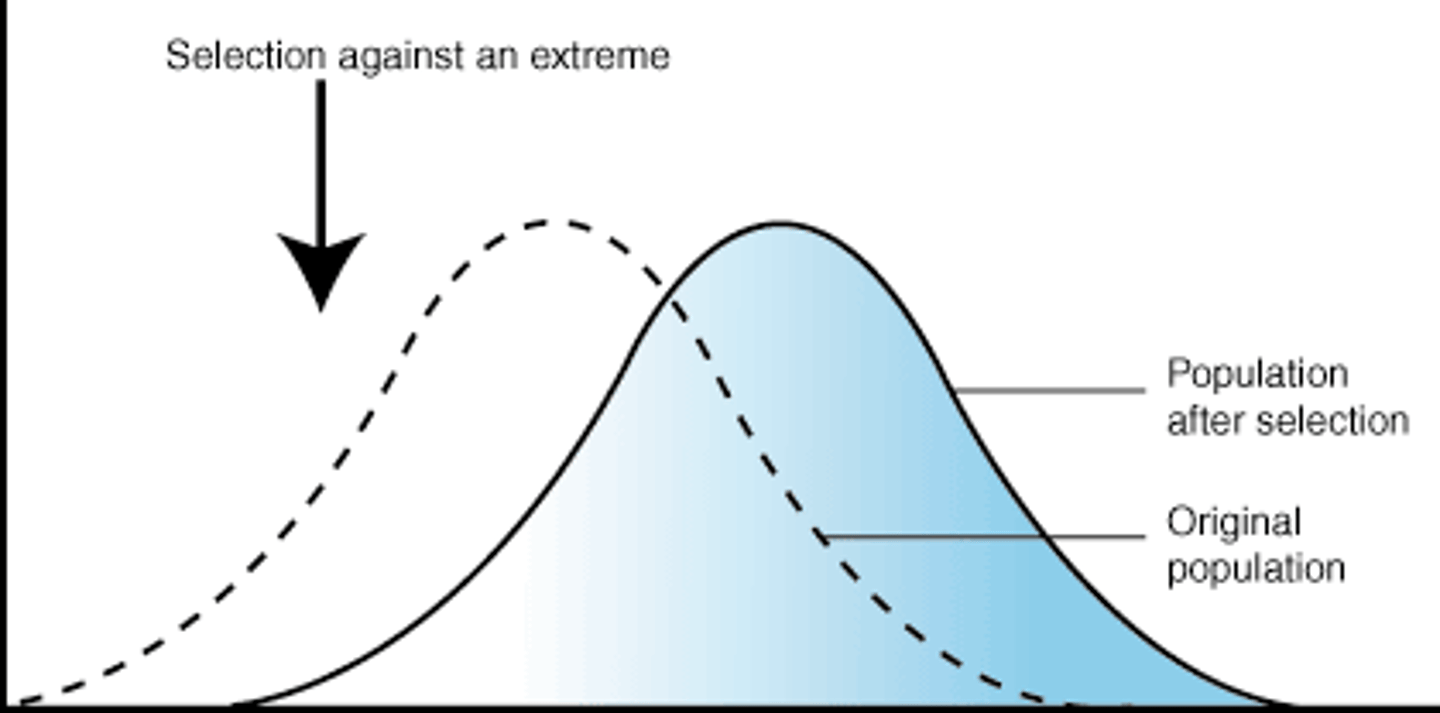
Directional selection
one extreme selected against another
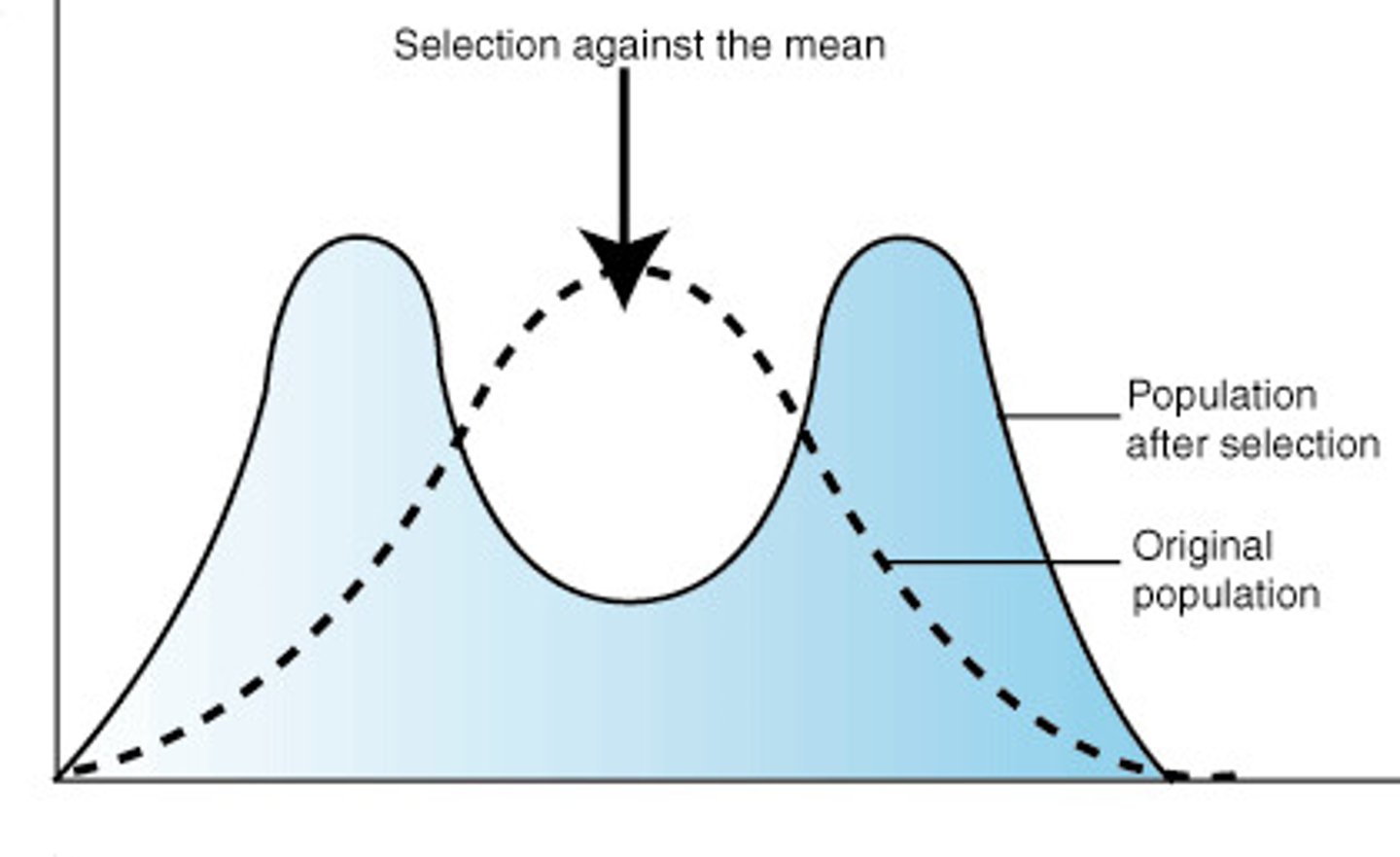
Diversifying selection
selection of extremes
Biological Species Concept
A group of inter-breeding natural populations that re reproductively isolated from other such groups
What does it take for a hybrid to be successful in the wild?
1. capable of reproduction
2. exploits a new niche (hybrids may thrive where parents fear to tread)
"artificial" selection -- what are 3 reasons Darwin focused on artificial selection?
Artificial selection is the process by which a species is modified via human intervention. Dawin used artificial selection as an analogy for natural selection bc:
1. natural selection is too slow to witness in the wild
2. artificial selection results in dramatic changes
3. artificial selection demonstrates inheritance
Gregor Mendel
Mendel applied statistical principles to biology, and proposed discrete units of heredity (aka genes)
allele
alternative forms of the same gene
locus
given sit on a chromosome
homozygous alleles
2 identical alleles
heterozygous alleles
2 different alleles
dominant vs recessive alleles -- when are each expressed?
dominant alleles are expressed even when heterozygous, recessive alleles are only expressed when homozygous
How many chromosomes do humans have? How many pairs?
46 chromosomes, 23 pairs
genotype vs phenotype
genotype refers to alleles and phenotype refers to appearance
What are some commonly observed "non-Mendelian" characteristics of genes or traits?
1. incomplete dominance between alleles
2. codominance of alleles
3. more than 2 alleles for a gene
4. one gene may have multiple effects
5. one trait may result from input of multiple genes
6. genes may influence each other
What are nucleotides?
building blocks of nucleic acids, AT & CG
DNA replication
1. double helix is unzipped by helicase
2. RNA primer that marks starting locus for building new DNA strand, primase, is added
3. DNA polymerase binds to RNA primer and builds new strand by adding nucleotide bases in the 5-3 direction
4. RNA primer on both leading and lagging strands are removed
5. DNA polymerase fills in gaps formed by removal of RNA polymerase
6. both new daughter DNA molecules are sealed by enzyme ligase
direction of DNA synthesis
polymerase writes down 5-3, and reads up 3-5
what does it mean that DNA replication is semi-conservative?
because it produces two copies that each contain one of the original DNA strands and one new strand
"Central Dogma"
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
DNA transcription
step 1 in protein synthesis, occurs in the nucleus.
1. DNA code is transcribed to mRNA
2. genetic code is turned into codons (3 bases)
3. each codon specifies a particular amino acid
How does RNA differ from DNA?
DNA contains thymine (T base), RNA contains uracil (U base)
What is messenger RNA?
Carries copies of the instructions for assembling amino acids from DNA to the rest of the cell.
What does mRNA code for?
proteins
What are mRNA codons?
set of nucleotides that act as a template for protein synthesis; the codons that are actually "read"
mRNA Translation
step 2 in protein synthesis, occurs in ribosomes.
1. ribosomes coordinate the interaction between mRNA and tRNA to make amino acid chains
2. pairing of mRNA blueprint with amino acids (codons?)
What are ribosomes?
"protein factory" of the cell
amino acid structure
amino group, carboxyl group, "R" group
What determines type, structure, and function of proteins?
Amino-acid sequence determines type and structure, 3-D structure of protein determines function
What 3 things are shared by all living organisms?
1. basic DNA structure, including base pairing
2. the genetic code (any particular codon codes for the same amino acid in all organisms)
3. 500 "immortal genes" that are vital to decoding DNA and RNA protein synthesis
What 3 things are different in different organisms?
1. sequence of bases in DNA strand
2. amount of genetic material
3. number of genes and chromosomes
Is genome size (number of nucleobases) a reliable predictor for organism complexity among eukaryotes?
No
Is the number of chromosomes a reliable predictor of organism complexity among eukaryotes?
No
Is the number of conventional, protein-coding genes a reliable predictor for organism complexity among eukaryotes?
No???
Is there a correlation between the amount of non-coding "junk" DNA and organism complexity?
Yes -- more junk DNA = more complex
What percentage of DNA codes for conventional proteins in humans?
1.5%
What is gene regulation?
the ability to turn genes on and off
What is gene expression?
the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis
What are transcription factors?
proteins that regulate expression via transcription
What percentage of our DNA is from viruses ("fossil" virus DNA)?
8.3%
Are viruses living organisms?
no, because they need living cells to be able to reproduce
Where do some scientists think viruses originally came from?
plasmids - genetic structure in cell that can replicate independently of the chromosomes
What are the 2 main sources of variation within a species?
1. mutation
2. recombination (sex)
Because mutations occur randomly, does that mean evolution is random?
No, because of Natural Selection
What are the 3 types of point mutation within a DNA sequence and their consequences?
1. substitution (alters only one codon)
2. insertion (alter all codons "downstream"
3. deletion (^^)
What are the 3 types of mutations within a single chromosome?
1. deletion
2. duplication
3. inversion
What are the 2 types of mutations between two different chromosomes?
Crossover effects
1. insertion
2. translocation (swap)
synonomous mutation (amino acid)
does not change meaning of codon
non-synonomous mutation
results in replacement of one amino acid for another
What happens when there's crossover between chromosomes during meiosis?
it reshuffles allele combinations
What is recombinant chromosomes (sexual reproduction) a source of?
variation
What are Homeobox (HOX) Genes?
The blueprint for skeletal morphology, they code for transcription regulators.
Are HOX genes shared (phylogenetically conserved) by all animals?
yes
vestigial features
rudimentary structures with no useful function, occur in all members of a species
atavistic features
reappearance of a trait lost in evolution, occur only occasionally
What is a psuedogene?
at one time was a gene but no longer codes due to accumulated mutations
How does embryology reflect history by "adding new stuff to old" (recapitulation)?
embryo reflects various stages of evolution as it develops
Linnaen Hierarchical Classification System
KPCOFGS
What are phylogenetic reconstructions based on?
based on degrees of similarity among taxa for homologous traits
homologous vs analogous traits
- homologous trait: trait shared due to common ancestry
- analogous trait: similar traits with independent origins
Carl Woese
Devised a system of classification based on the cellular organization of organisms
What part of the genome (DNA sequence) do geneticists use to construct molecular phylogenies?
rDNA
What are the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes are large and sophisticated by metabolically inflexible, limited to oxygenic photosynthesis and aerobic respiration
What are the 3 domains of life?
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
What is an extremophile?
organisms that are adapted to survive in extreme conditions, microorganisms, especially Archean
Sexual Dimorphism
males and females of the same species have different phenotypes
Why is sexual selection permissive of traits that seem maladaptive in the daily struggle of life?
because they help individuals obtain mates
What are the two processes involved in sexual selection?
1. mate choice (usually female choice)
2. intra-sexual selection (male-male combat)
How does sexual selection perpetuate sexual dimorphism?
The greater the disparity among males in terms of number of females, the greater the levels of aggression and sexual dimorphism
What 2 factors are involved in the evolution of typical sex roles?
1. investment in reproduction is greater for females so they are more choosy
2. reproductive potential is usually greater for males so they are more competitive
Batesian Mimicry
when a palatable species mimics a toxic species to deceive predators, provided Darwin with an example of natural selection in the wild
Why is tinkering, not engineering, the best analogy for natural selection and adaptation?
1. natural selection has no plan, whatever works survives
2. natural selection modifies what already exists
Exaptation
when preexisting traits/structures are adapted to serve a new function
Zygote
fertilized egg
Pre-Zygotic mechanisms for reproductive isolation (6 types)
1. geographic isolation
2. gametic isolation
3. mechanical isolation
4. temporal isolation
5. behavioral isolation
6. ecological preferences and mating isolation
Geographic Isolation (3 types)
1. allopatric speciation = complete separation of populations
2. parapatric speciation = divergence occurs in broadly continuous region
3. sympatric speciation = no spatial separation but isolation occurs
Gametic isolation
occurs when incompatibilities in gametes do not permit viable fertilization
Mechanical isolation
occurs when appendages don't physically match
Temporal isolation
peaks of sexual activity in different populations do not overlap in time