Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1-Key Area 2: Proteins
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/79
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
1
New cards
What is the proteome?
The entire set of proteins expressed by a genome
2
New cards
Why is the proteome larger than the genome?
More than one protein can be produced from a single gene as a result of alternative RNA splicing
3
New cards
Are all genes expressed as proteins?
No
4
New cards
What are genes that don't code for proteins called?
They are called non coding RNA. They include those that are transcribed to produce tRNA, rRNA and RNA molecules that control the expression of other genes
5
New cards
What can happen to the set of proteins expressed by a given cell type?
They can vary under different conditions
6
New cards
What are some factors affecting the set of proteins expressed?
The metabolic activity of the cell, cellular stress, the response to signalling molecules and diseased versus healthy cells
7
New cards
What do eukaryotic cells have?
A system of internal membranes which increase the total surface area of the cell
8
New cards
What is the advantage of the internal system of membranes?
Because of their size, eukaryotes have a relatively small surface area to volume ratio. The plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells is therefore too small an area to carry out all the vital functions of the cell
9
New cards
Diagram of a cell showing the ER, vesicle, lysosome and golgi apparatus
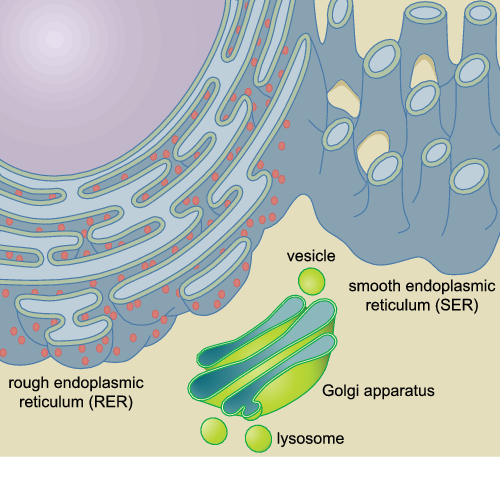
10
New cards
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
It forms a network of membrane tubules continuous with the nuclear membrane
11
New cards
What are the two types of ER?
Smooth and rough
12
New cards
What is the golgi apparatus?
A series of flattened membrane discs
13
New cards
What are lysosomes?
Membrane-bound organelles containing a variety of hydrolysed enzymes that digest proteins, lipids and fats
14
New cards
What are vesicles?
Things that transport materials between membrane compartments
15
New cards
Where are lipids and proteins synthesised?
In the ER
16
New cards
What is the difference between rough ER and smooth ER
Rough ER (RER) has ribosomes on its cytosolic face whereas smooth ER (SER) lacks ribosomes
17
New cards
Where are lipids synthesised?
The smooth ER and they are then inserted into its membrane
18
New cards
Where does the synthesis of all proteins begin?
The cytosolic ribosomes
19
New cards
Where is the synthesis of cytosolic proteins completed?
In the cytosolic ribosomes. The proteins then stay in the cytosol
20
New cards
What do transmembrane proteins do?
Carry a signal sequence, which halts translation and directs the ribosome synthesising the protein to dock with the ER forming RER. Translation continues after docking and the protein is inserted into the membrane of the ER
21
New cards
What is a signal sequence?
A short stretch of amino acids at one end of the polypeptide that determines the eventual location of a protein in a cell
22
New cards
What happens to the proteins when they are in the ER?
They are transported by vesicles that bud off from the ER and fuse with the Golgi apparatus
23
New cards
What do molecules use to move through the Golgi discs?
Vesicles that bud off from one disc and fuse to the next one in the stack. Enzymes catalyse the addition of various sugars in multiple steps to form carbohydrates
24
New cards
What happens to proteins as they move through the Golgi apparatus?
They undergo post-translational modification
25
New cards
What is a major modification?
The addition of carbohydrate groups to proteins
26
New cards
Where do vesicles that leave the Golgi apparatus take proteins?
The plasma membrane and lysosomes
27
New cards
What do vesicles do with microtubules?
Move along them and fuse with them within the cell
28
New cards
What happens to secreted proteins?
They are translated in ribosomes on the RER and enter its lumen
29
New cards
What are some examples of secreted proteins?
Peptide hormones and digestive enzymes
30
New cards
What is the secretory pathway? (simplified)
Rough ER -> Golgi -> secretory vesicles -> cell exterior
31
New cards
What is the secretory pathway (detailed)
Proteins move through the Golgi apparatus and are then packed into secretory vesicles
These vesicles then move to and fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing proteins out of the cell
Many secreted proteins are synthesised as inactive precursors and require proteolytic cleavage to produce active proteins
These vesicles then move to and fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing proteins out of the cell
Many secreted proteins are synthesised as inactive precursors and require proteolytic cleavage to produce active proteins
32
New cards
What is proteolytic cleavage?
Another type of post translational modification
33
New cards
What is one example of secreted proteins that require proteolytic cleavage to become active?
Digestive enzymes
34
New cards
What are proteins?
Polymers of amino acid molecules
35
New cards
How are amino acids linked?
By peptide bonds to form polypeptides
36
New cards
How does the structure of amino acids differ?
Only in the R group present
37
New cards
How can R groups of amino acids vary?
In size, shape, charge, hydrogen bonding capacity and chemical reactivity
38
New cards
What is the basic structure of an amino acid?
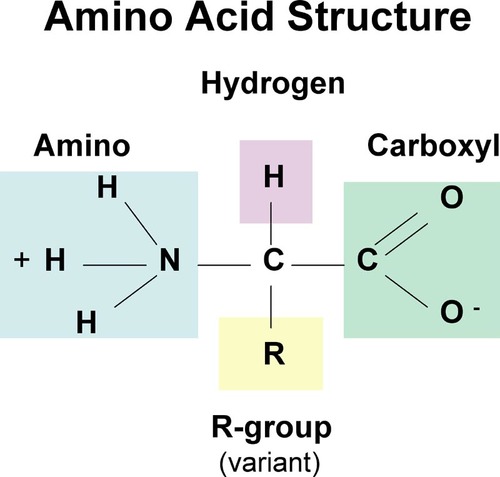
39
New cards
How can the different types of amino acids be classified?
According to their R groups
40
New cards
What are the different groups of amino acids?
· Basic (positively charged)
· Acidic (negatively charged)
· Polar
· Hydrophobic
· Acidic (negatively charged)
· Polar
· Hydrophobic
41
New cards
What does the wide range of functions carried out by proteins result from?
The diversity of R groups
42
New cards
What is the primary structure of a protein determined by?
The sequence in which amino acids are synthesised into the polypeptide
43
New cards
How is the secondary structure of a protein determined?
Hydrogen bonding along the backbone of the protein strand results in regions of secondary structure. The hydrogen bonding occurs between the N-H and C=O sections of an amino acid molecule. The different types of secondary structure are alpha helices, parallel or antiparallel beta sheets and turns.
44
New cards
How is the tertiary structure determined?
The polypeptide folds into a tertiary structure. This confirmation is stabled by interactions between R groups. These interactions include:
· Hydrophobic interactions
· Ionic bonds
· London dispersion force
· Hydrogen bonding
· Disulfide bridges
· Hydrophobic interactions
· Ionic bonds
· London dispersion force
· Hydrogen bonding
· Disulfide bridges
45
New cards
What are hydrophobic interactions?
Interactions between two non-polar molecules
46
New cards
What are ionic bonds?
Interactions between positive and negative groups on the amino acids
47
New cards
What are london dispersion forces?
Weak forces of attraction between covalently bonded molecules
48
New cards
What is hydrogen bonding?
Intermolecular forces that occur when hydrogen atoms are bonded to highly electronegative elements like nitrogen or oxygen
49
New cards
What are disulfide bridges?
Covalent bonds between R groups containing sulfur
50
New cards
When does quaternary structure exist?
In proteins with two or more connected polypeptide subunits. Quaternary structure describes the spatial arrangement of the subunits
51
New cards
What is a prosthetic group?
A non-protein unit tightly bound to a protein and necessary for its function
52
New cards
What is an example of a protein with a prosthetic group?
Haemoglobin. The ability of haemoglobin to bind to oxygen is dependent upon the non-protein haem (iron) group
53
New cards
What can interactions between R groups be influenced by?
Temperature and pH
54
New cards
How does increasing temperature affect protein shape?
It disrupts the interactions that hold the protein in shape. The protein begins to unfold and eventually becomes denatured
55
New cards
How does pH affect protein shape?
It affects the charges on acidic and basic R groups. As pH increases or decreases from the optimum, the normal ionic interactions between charged groups are lost, which gradually changed the conformation of the protein until it becomes denatured
56
New cards
What is the name of a substance that binds to a protein?
A ligand
57
New cards
What are involved in ligand binding?
R groups not involved in protein folding
58
New cards
What will binding sites have?
Complementary shape and chemistry to the ligand
59
New cards
What happens when a ligand binds to a protein binding site?
The conformation of the protein changes. This change in conformation causes a functional change in the protein
60
New cards
What are allosteric interactions?
Interactions that occur between spatially distant sites. The binding site of an allosteric enzyme increases the affinity of the other active sites for binding of subsequent substrate molecules
61
New cards
What is the biological importance of allosteric interactions?
The activity of allosteric enzymes can vary greatly with small changes in substrate concentration
62
New cards
What do many allosteric proteins consist of?
Multiple subunits (they have a quaternary structure)
63
New cards
What do allosteric proteins with multiple subunits show?
Cooperativity in binding in which changing in binding at one subunit alter the affinity of the remaining subunits
64
New cards
What do allosteric enzymes contain?
A second type of site called an allosteric site
65
New cards
What is an allosteric site?
A site on the enzyme other than the active site
66
New cards
What do modulators do?
They regulate the activity of an enzyme when they bind to the allosteric site
67
New cards
What occurs after binding of a modulator?
The conformation of the enzyme changes and this alters the affinity of the active site for the substrate
68
New cards
What do positive modulators do?
Increase the enzyme's affinity for the substrate
69
New cards
What do negative modulators do?
Reduce the enzyme's affinity for the substrate
70
New cards
What shows an example of cooperativity?
The binding and relays of oxygen in haemoglobin. Changes in binding of oxygen at one subunit alters the affinity for the remaining subunits of oxygen
71
New cards
What can influence the binding of oxygen?
Temperature and pH
72
New cards
How does a decrease in pH or an increase in temperature affect haemoglobin?
It lowers the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen, so the binding of oxygen is reduced. Reduced pH and increased temperature in actively respiring tissue will reduce the binding of oxygen to haemoglobin promoting increased oxygen delivery to tissue
73
New cards
What is the effect of the addition or removal of a phosphate on a protein?
It causes a reversible conformational change in the protein
74
New cards
What is the addition or removal of phosphates?
A common form of post translational modification
75
New cards
What do protein kinases do?
Catalyse the transfer of a phosphate group to other proteins. The terminal phosphate of ATP is transferred to specific R groups
76
New cards
What do protein phosphatases do?
Catalyse the reverse reaction (the removal of phosphate groups)
77
New cards
What does phosphorylation do?
Brings about a conformational change which can affect a protein's activity
78
New cards
What is the activity of cellular proteins like enzymes regulated by?
Phosphorylation
79
New cards
What two effects can phosphorylation have on a protein?
Some proteins are activated while others are inhibited
80
New cards
What does adding a new phosphate group do?
Adds a negative charge. Ionic interactions in the unphosphorylated protein can be disrupted and new ones created