Occlusal Problems in the Mixed Dentition
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what is dilaceration
abrupt chnage in axial inclination between the crown and root
caused by trauma or idiopathic development - sometimes developmental syndromes
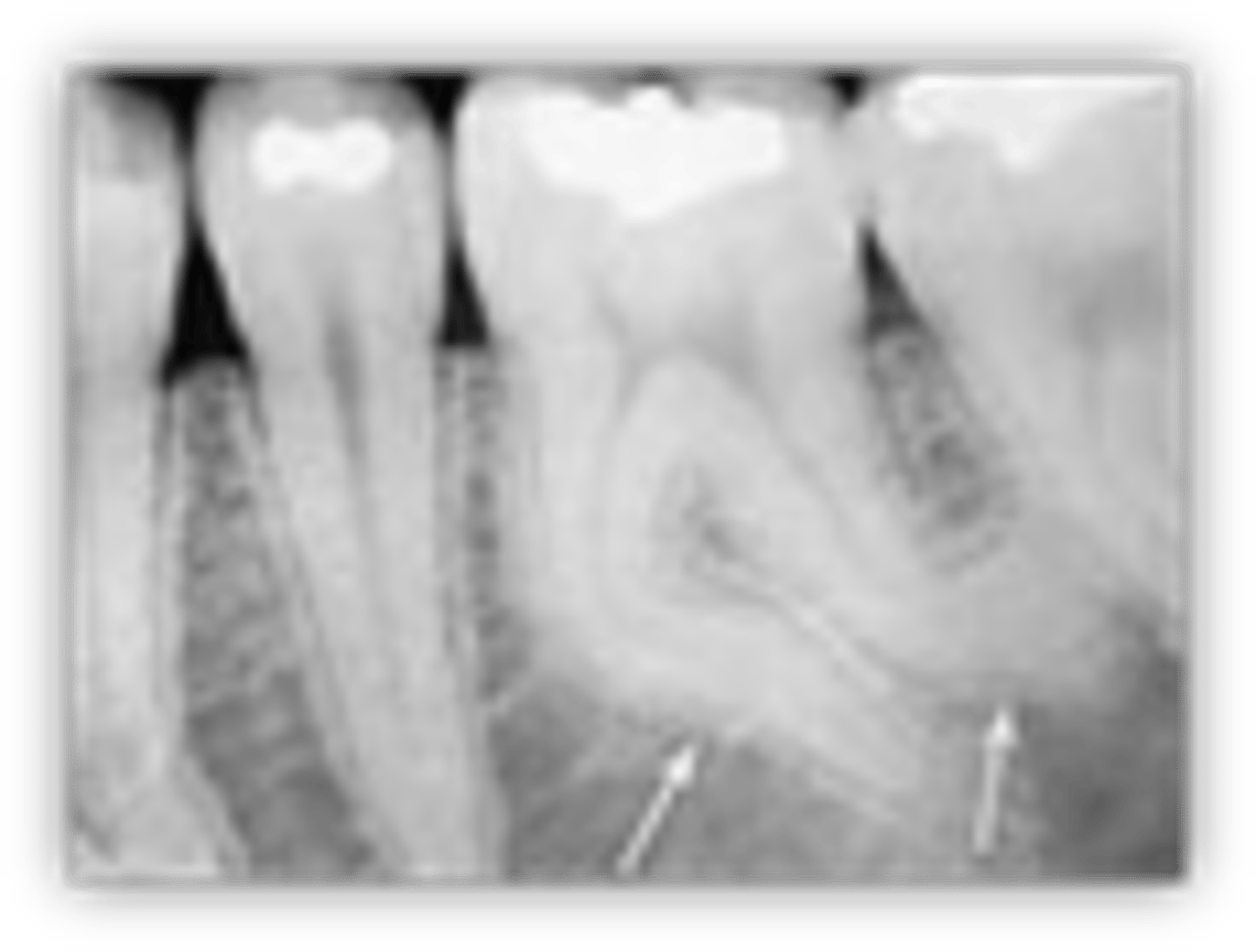
how do we manage dilaceration
fairly common - 3%
half are impacted
depends on factors and inidvidual
if unerupted, have closed exposure and ortho alignment or removal
if erupted removal and pontic based on severity
what is peg lateral
associated with hypodontia - one peg on one side, the other side is likely missing
also has a risk of ectopic canine so always check canines
what types of supernumary teeth are there
supplemental - exact replica of another tooth, suually teeth at the end of the series
odontome - mass of tooth tissue that can cause distrupted eruption
conical - like a peg lateral but extra
tuberculate - kind of looks like premolar but not but extra and can impede central incisors
most common in premaxilla, if in midline call mesiodens
how do we manage supernumaries
depends on whole malocclusion
usually extract but can leave if unerupted
if they sit behind central incisors, if needing orth tx most likely need taken out to avoid damaging the roots
what is hypodontia
abscence of 1 or more teeth noy including the 8s
often hereditary
most commonly affects upper lateral incisors and lower second premolars and also 8s
more common in perm, if they have missing primary it means missing perm
be suspicious of delayed exfoliation or late eruption
what is infraocclusion
Teeth are depressed below the line of occlusion
because it doesnt keep up with growth of alveolar bone
due to ankylosing of the decidoius tooth
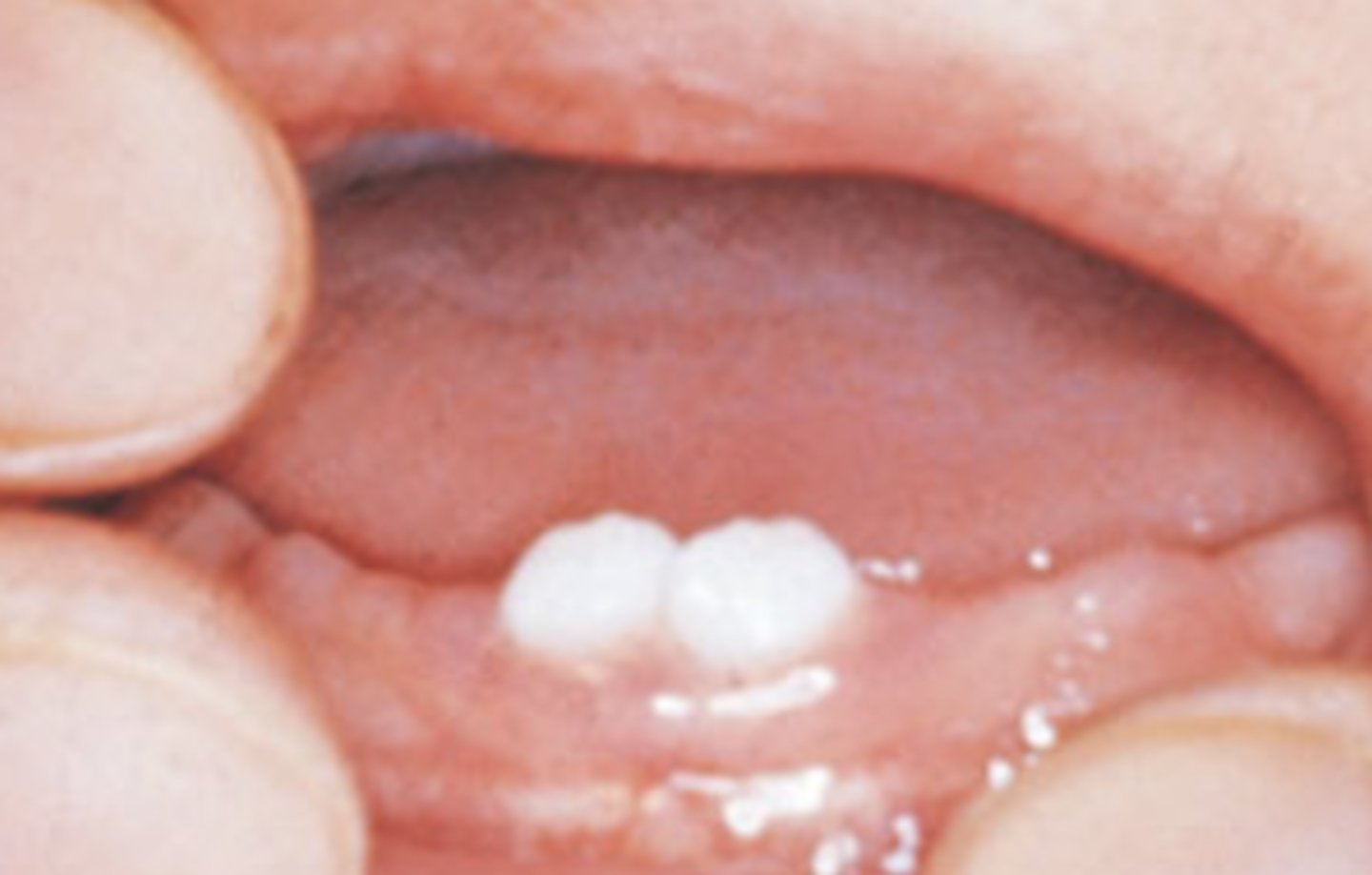
what are neonatal teeth
any tooth present at birth
can cause feeding problems
if mobile, consider extraction
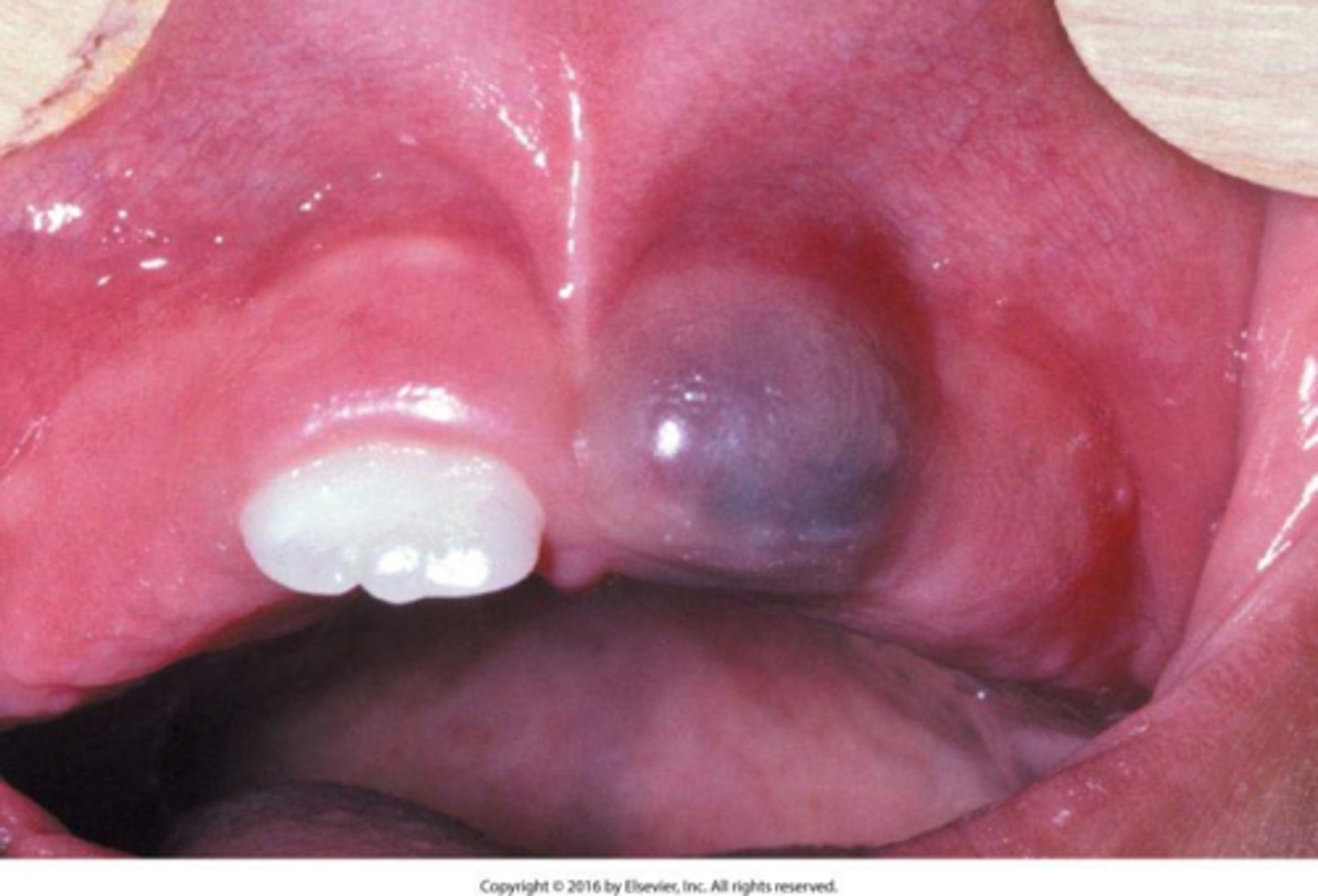
what is eruption cyst
appears as blue mucosa
most common over Es and 6s
usually asymptomatic unless traumatising witht he occlusion
as soon as the tooth erupts, it will dissapear
what are impavcted teeth
tooth not erupted
due to lack of space at alveolar ridge, ectopic teeth or obstruction
often first permanent molars and canines
what are retained deciduous teeth
perm tooth maybe missing or ankylosed and dont exfoliate in a normal manner
need extracted if ankylosed as they can displace permanent successor
what causes premature loss of deciduous teeth
caries - see mesial drifting of first perm molars and can see crowding
trauma - can result in centreline shift and delayed eruption due to fibrous mucosa
balancing extractions
compensating extractions
why is trauma bad for deciduous teeth
why is caries bad for deciduous teeth
what are balancing extractions
try to maintain midline by removing teeth
consider when extracting C and Ds not rlly Es
what is a compensating extraction
if a tooth is out on one arch u take it out of the other
mostly for FPMS
theoretical risk of overeruption of the occlusing tooth and can cause issues in future
what are serial extractions
aim to relive incisor crowding in mixed dentition
to try avoid ortho tx
extract all 4 Cs and all Ds and then all premolars when erupt to improve the spacing of the permanent teeth
what happens in early loss of FPMS
not ideal for ortho
often due to caries or MIH
ideally have all perm teeth and check with DPT
optimum age is 9-10 but based on development of unerupted second molars
delay if necessary
what is ankylosis
tooth is fused to the bone and loses PDL so it cannot erupt
this is why it appears to sink
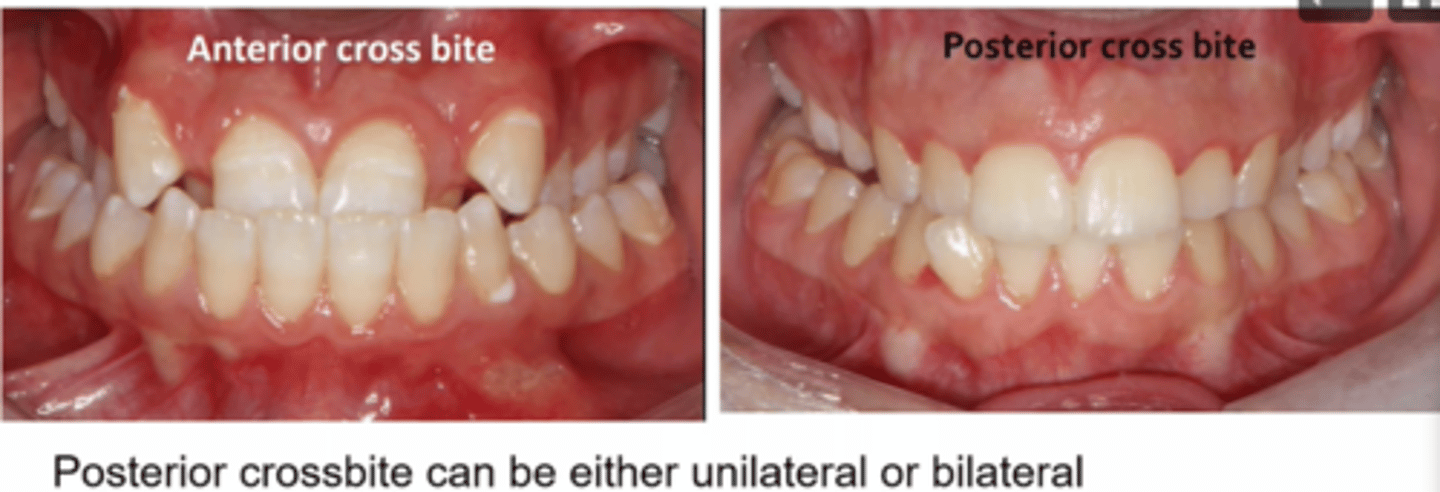
what are cross bites
affect any tooth or teeth
commonly incisors or molars
can result in mandibular displacement tooth wear and gingival recession
can correct in the mixed dentition if causing problems
how do we correct crossbites
if mixed, a removeable applicance is best
RME - rapid maxillary expansion
2 x 4 fixed applance
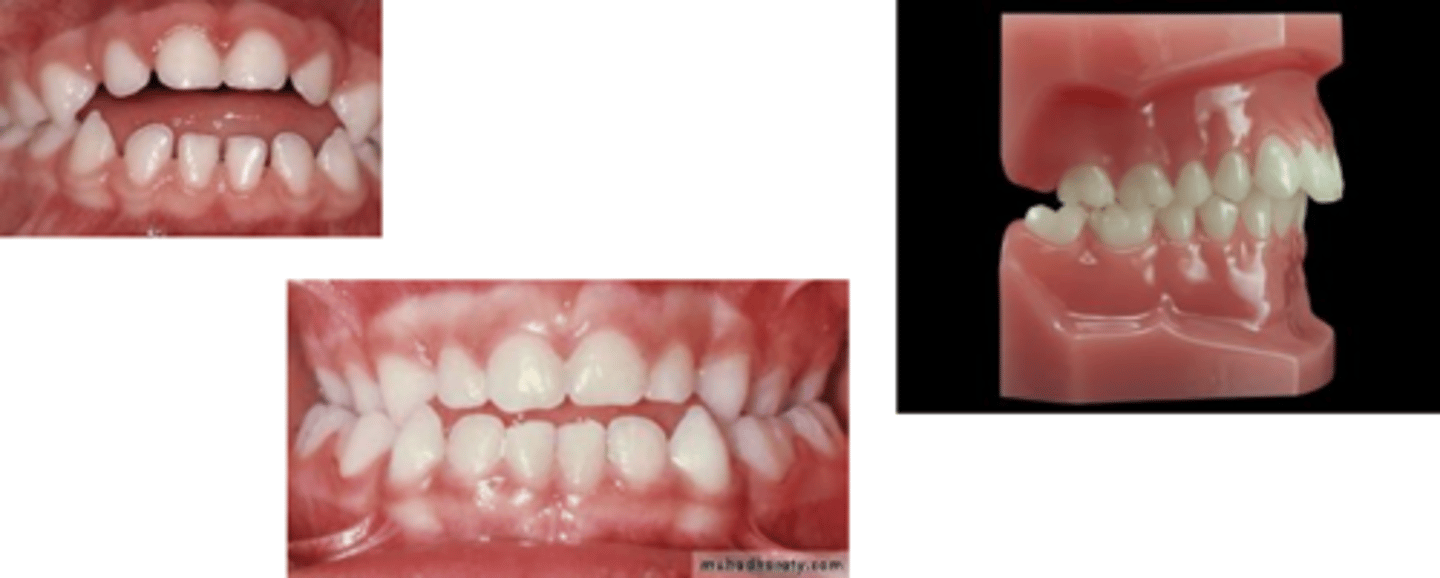
what are non nutritive sucking habits
dummy or thymb
results in proclined maxillary incisors
retroclined mandibular incisors
anterior open bite
posterior buccal crossbites - pressure pushinf the max teeth in and makes a narrow maxilla
depends on intensity and duration
how do we manage non nutritive sucking habits
positive reinforcement
non invasive methods such as glove, nail varnish, plasters
if unsuccessful try fixed or removeable habit breaker appliance
can get spotnaneous resolving when younger but older needs ortho which is difficult to fix
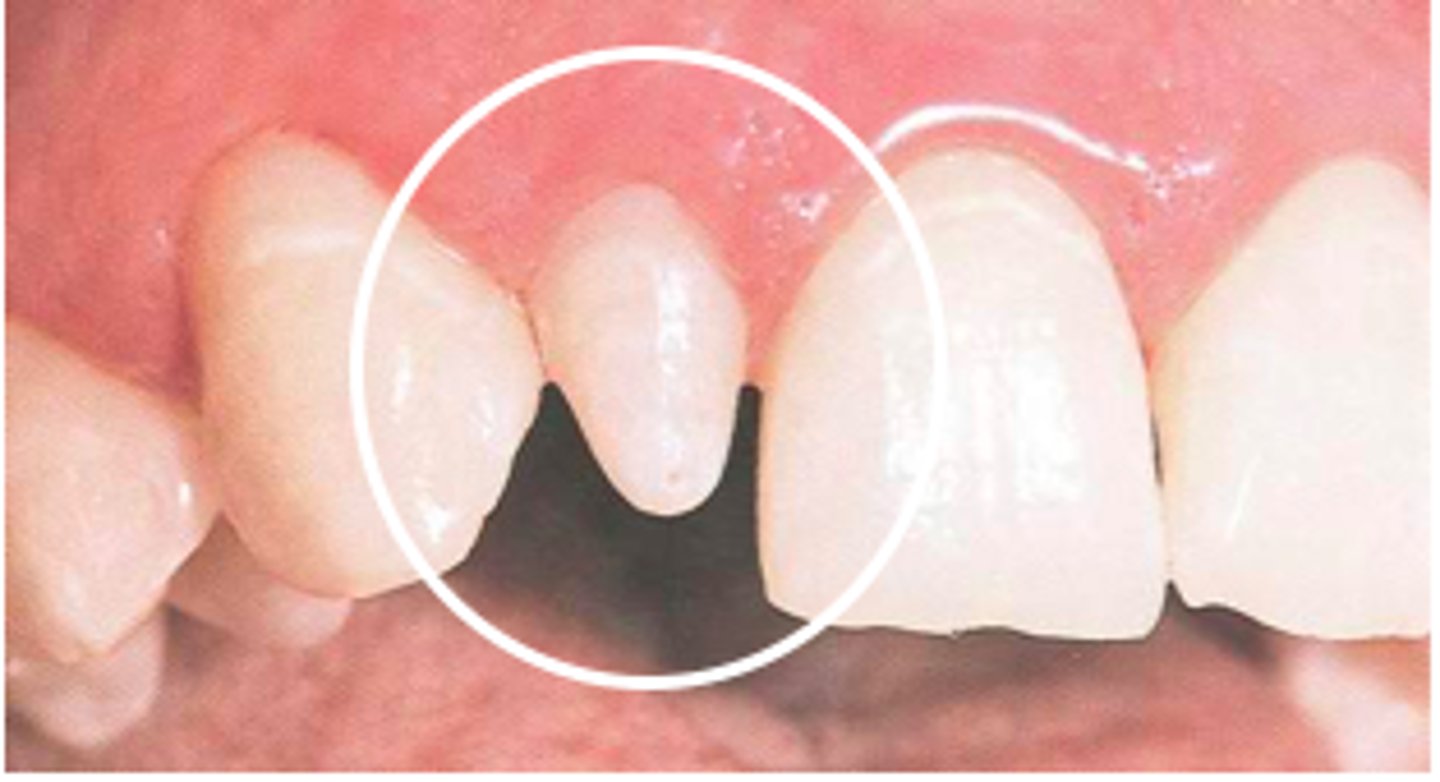
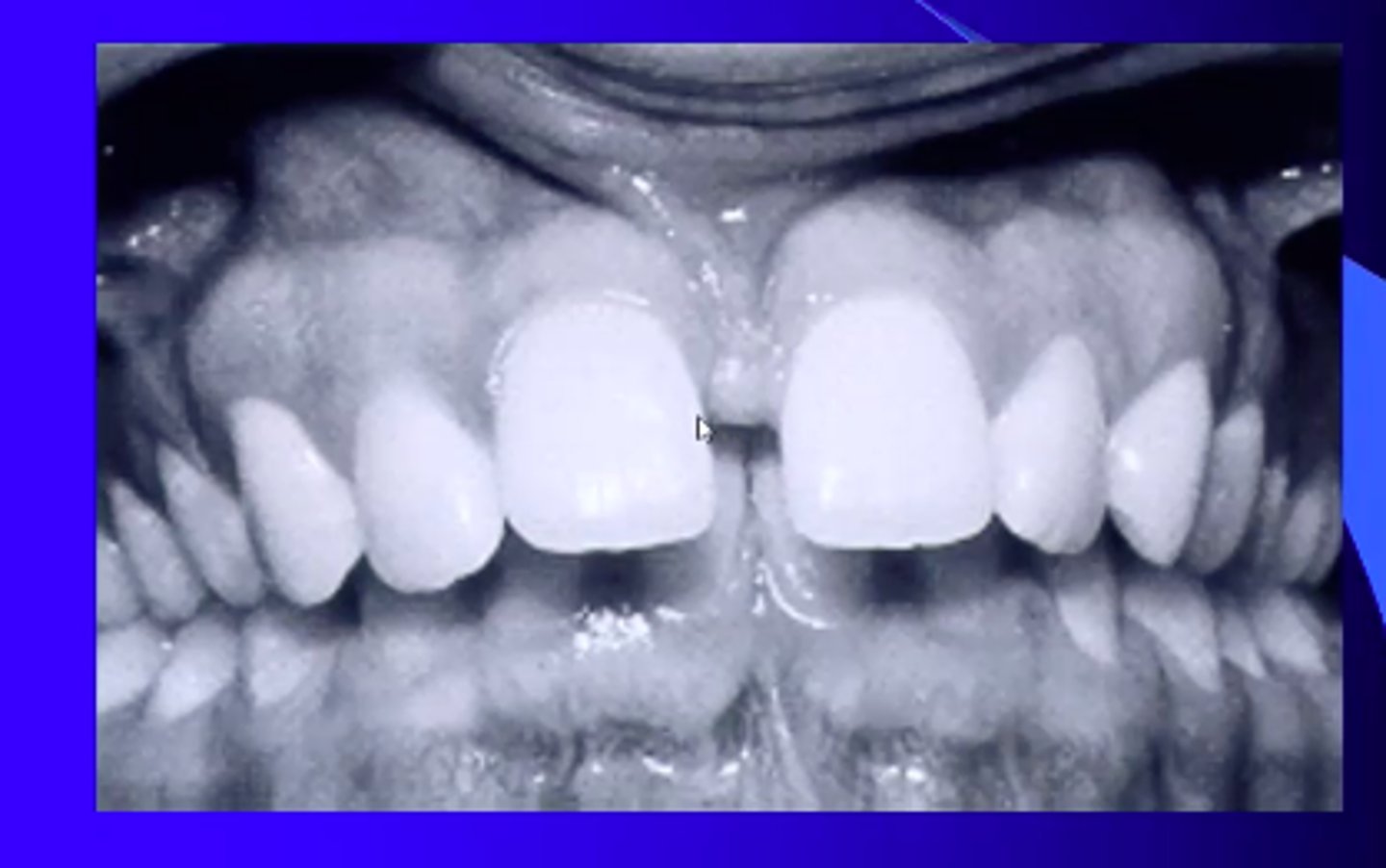
what is midline diastema
developmental stage of space between central incisors
is normal but sometimes an indication of hypodontia and supernumaries and large frenum
manage with eruption of permanent teeth but might need ortho when older usually a fixed applinace
sometimes need frenulectomy
what do impacted Es impact on
impavct on distal of Ds and difficulty in OH
consider monitoring a seperator or extraction
what do impacted FPMs impact on
not commmon and usually due to crowding
mnitioring extraction or separator
what do impacted second premolars impact on
due to crowding following early loss of deciduous molars
common
what do impacted central incisors impact on
caused by supernumary, dilaceration, trauma, premature loss of deciduous
be suspicious of if eruption sequence id distruptrd by > 6 months since contralateral tooth
remove obstruction if present, create space and dependant on age either await eruption or surgical exposure and gold chain
what do impacted canines impact on
always palpate 8-10 year olds to check and then take xrays
early intervention - extract Cs and review
if it fails to erupt then either leave it and monitor if not resorbing roots, surgical exposure and ortho alignment or extraction
majority are palatal