ECON 3330 Test 3
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bowes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
With direct finance, high transaction costs occur mainly because
Savers and borrowers have to take the time and effort to find each other
The asymmetric information issue between savers to borrowers
Means that borrowers have better information than savers
If Dave buys stock from Carnival Cruise Lines Company, which uses the funds to build new cruise ships, then in macroeconomic terms
Carnival is investing (I), and Dave is saving
In one year you will receive a $100 bill. If the interest rate today rises from 5% times 10%, the $100 bill. You will receive one year from now becomes worth
less today (lower present value)
Based on the BOnd Market model, interst rates will rise during an economic expansion because
The supply of bonds increases more than the demand for bonds
Which has NOT been observed about interest rates?
Longer maturity interest rates are always higher than shorter maturity rates
During a recession
Firms have fewer investment opportunities, so the supply of bonds decreases
Today’s interest rate for an Aaa-rated bond is 4.35%, while a Baa rated of the same maturity pays a rate of 5.03%. The difference in these two rates
occurs because the Aaa rated bond is less risky
Why was the Federal Reserve created?
To provide the nation with a more stable and flexible financial system
The Federal Reserve System is overseen by a governing board based in Washington, D.C. What is the official name of this board?
The Board of Governors
Who controls the Federal Reserve?
The Board of Governors, which acts as an independent government agency
What is the Fed’s primary Monetary policy-making body?
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
The Fed has a dual mandate. What are its two primary goals?
Achieve maximum employment and maintain price stability
Who owns Federal Reserve Banks?
They are privately held by their member commercial banks.
Which of the following is the most frequently used tool of U.S. monetary policy by the Fed?
Conducting Open Market Operations (buying and selling government securities)
If the Fed wants to slow down the economy and fight inflation, it will typically do what?
Raise the target range for the Federal Funds Rate
What is the term for the interest rate that commercial banks charge each other for overnight loans?
The Federal Funds Rate
What is one of the key services the Federal Reserve Banks provide to commercial banks?
Acting as a lender of last resort
If the Required Reserve Ratio= 20%, what is the Deposit Multiplier?
1/0.2= 5
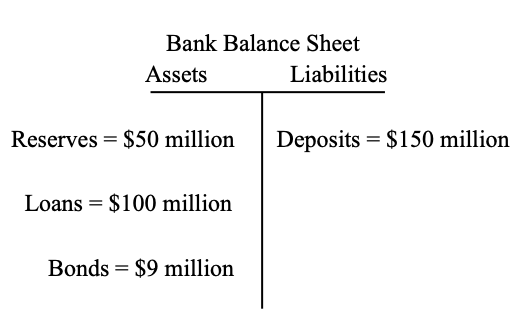
Given the bank balance sheet below, if the Required Reserve Ratio is 20%, calculate the amount of new loans that the bank can create.
Max. Deposits= Reserves x Deposit Multiplier = $50M x 5 = $250M
New Loans= Max. Deposits – Current Deposits = 250M – 150M= 100M
If the required reserve ratio is 25%, and the Fed buys $2 million in bonds from a bank, what will be the change in the money supply?
Deposit Multiplier: 1 0.25=4
Change in Money Supply: $2M x 4 = $8M increase
Fed policy tools
Required Reserve Ratio
Open Market Operations
Discount Rate & Target Federal Funds Rate
How would the Fed use its policy tools to increase the Money Supply?
Reserve ratio: lower it
Open Market: buy securities
Discount/TFFR: lower them
How would the Fed use its policy tools to decrease the Money Supply?
Reserve ratio: raise it
Open Market: sell securities
Discount/TFFR: raise them
Primary goals of Monetary Policy
Economic Growth (reduce unemployment)
Price Stability (reduce inflation)
Why is it impossible to pursue both goals of monetary policy at the same time?
They have a negative relationship. The goals require policies that move in different directions (Phillips curve)
Expansionary policy
Increase money supply and growth in GDP
lowers borrowing costs & encourages Investment and Consumption, increcreases GDP, and creates growth in output and employment
Contractionary policy
Decreases the money supply and reduces inflation
intended to raise borrowing costs, discourage investment and consumption, slow down growth of GDP and reduce inflation
Reserve ratio determines the deposit multiplier
Multiplier is less effective when banks hold more excess reserves and/or people hold more currency
Ex. reserve ratio at 25% (multiplier= 4) If fed buys $2 Mil in securities, money supply increases by
$8 Million (4×2)
Open Market changes _______ and creates ______
Reserves; new loans
Change in reserve ratio
Changes multiplier
Ex, Change from 25% to 20%, multiplier goes from 4 to 5
Discount/Federal Funds rate change
Either encourages or discourages bank lending
Fed is responsible for Monetary Policy = changing the money supply
M1= currency in circulation + demand deposits
Fed does not directly control M1
The Fed controls the relationship between Bank Reserves and Demand Deposits
Fed Reserve Bank
Central bank for the U.S.
Created by the Federal Reserve Act in 1913
The Fed is responsible for
Bank supervision,
Monetary Policy,
Services to Banks and the Government
Fed Reserve Bank Structure and Organization
12 regional banks (decentralized & flexible)
Regional banks headed by Presidents chosen by private board
Governor (headed by chairperson) chosen by President of U.S. and Senate
Federal Open Market Committee
Policy making group
12 members (Board of Governors, President of NY Fed, 4 others)
Fed is independent
Controls their own budget & pays for their operations
Regional presidents chosen by private citizens
Governors chosen for 14-year terms, non-renewable or removable (not subject to political threats/favors
Good things about Fed’s independence
Avoid political business cycle,
able to focus on long term
those controlling money supply are different from those that spend money
Fed policy strictly economic (bankers and economists not lawyers)
Bad things about Fed’s independence
policy-makers are un-elected and unnaccountable
may pursue policies that benefir their own business (banking)
economic policy affects everyone
The Fed is not completely unaccountable
Congress can change laws and take over budget
Characteristics of a good central bank
Accountability
Transparency of policy decisions
Decisions by committee,
Independence,
Good policy framework
Fractional Reserve System
Banking system in US
Reserve ratio
Fraction of deposits set aside
How do banks create money?
By making loans which create new deposits
Only a fraction of each new deposit must be set aside as required reserves
That lending is repeated until all reserves are held as required reserves
Total amount of lending found by using
Using Deposit mulitiplier= 1/reserve ratio
Maximum total deposits
Total reserves x deposit multiplier
T/F: The independence of the Fed leaves it completely unaccountable for its actions
False, not completely. Congress can change/eliminate if necessary
Why was the Fed set up with Reserve banks rather than a single central bank?
To avoid too much central authority
Flexibility with regional issues
What is the difference between Monetary Policy and Fiscal Policy?
Monetary policy: implemented by a central bank, allows Fed to change the volume of money and credit and their priceinterest rates, and has a goal to influence inflation, employment, and output.
Fiscal policy: conducted by the national government, involves changes in taxes and government spending, and its goals are to influence economic activity through taxation and public budgets
Which type of policy, Fiscal or Monetary, takes effect more quickly?
The fiscal policy
Given that the Federal Open Market Committee meets and makes a policy decision in 2 days, which policy is most likely implemented more quickly
The Monetary policy