A&P Part One Exam Study Set
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/75
Last updated 8:42 PM on 11/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
1
New cards
#1
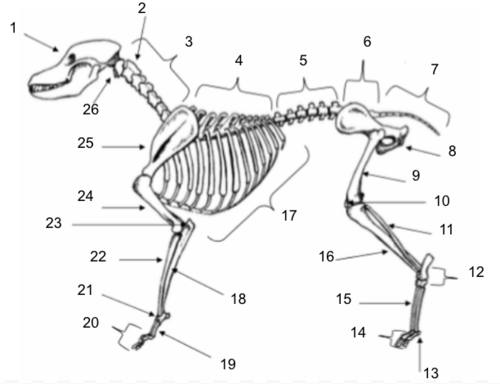
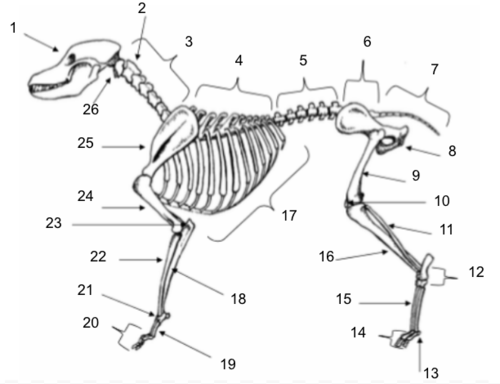
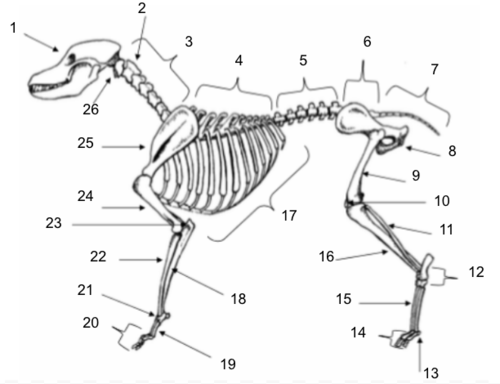
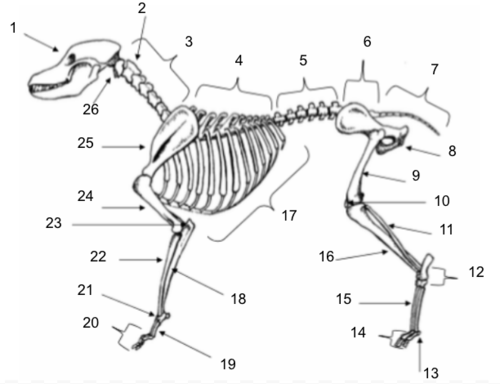
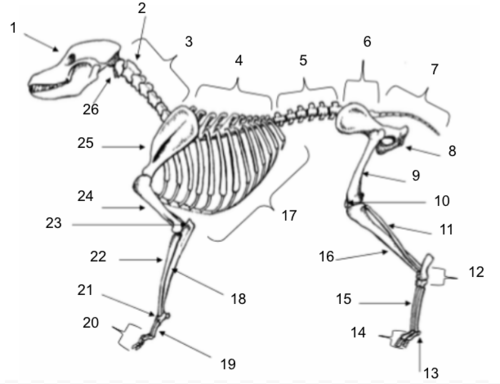
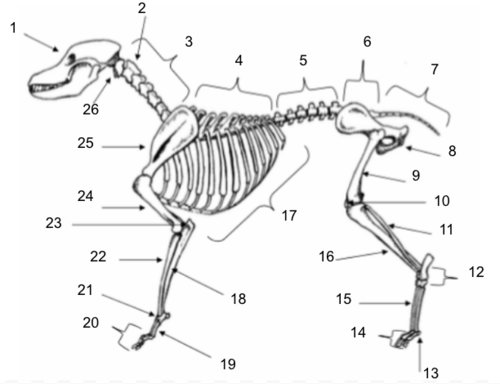
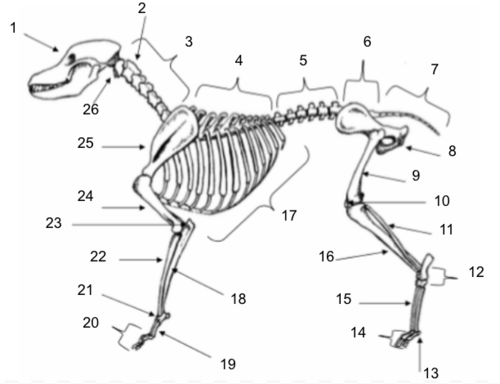
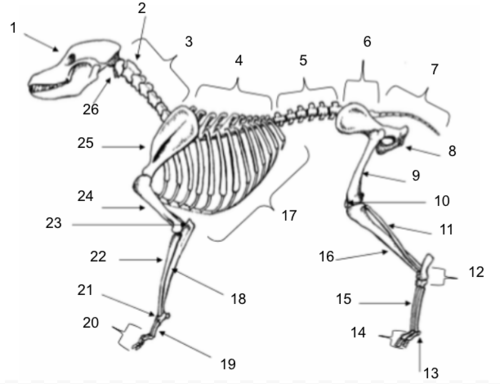
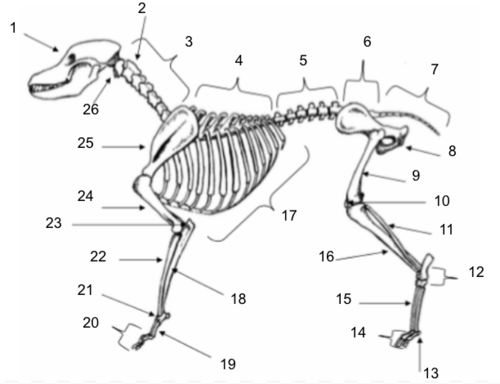
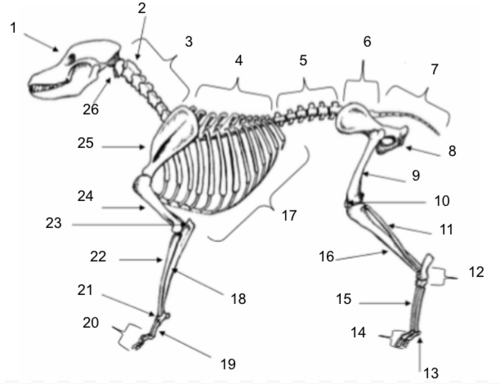
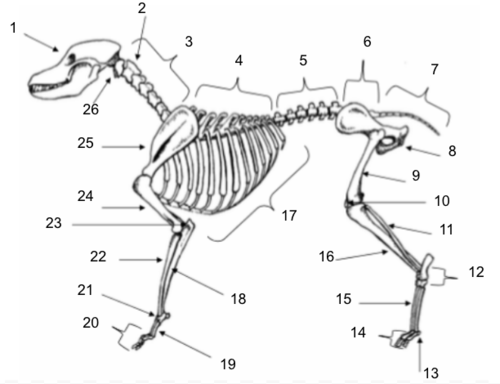
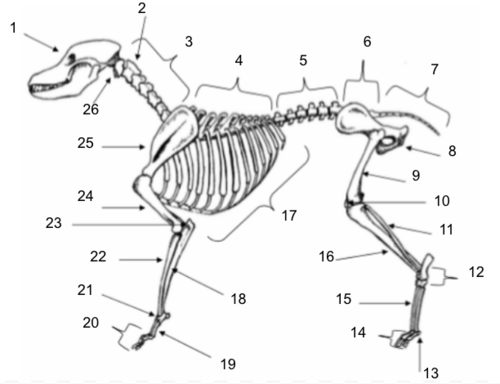
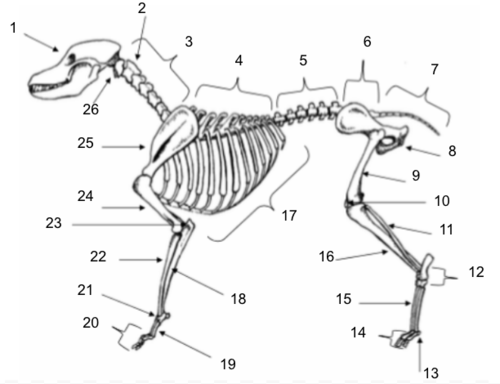
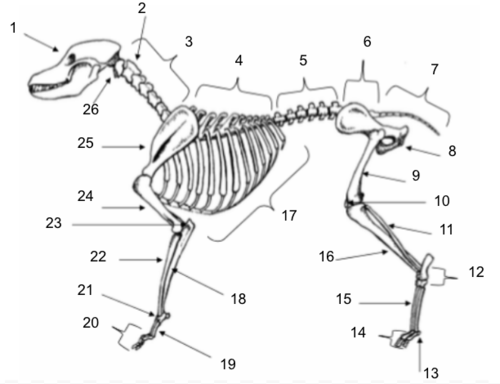
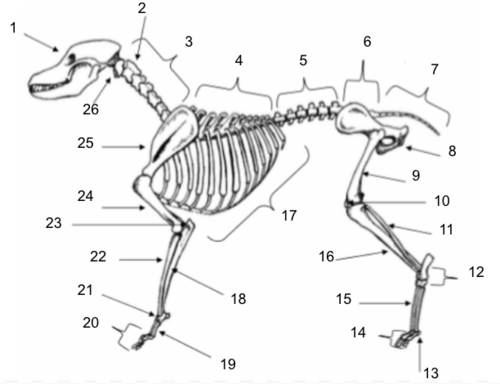
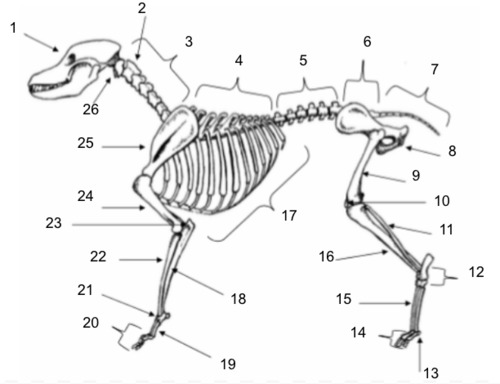
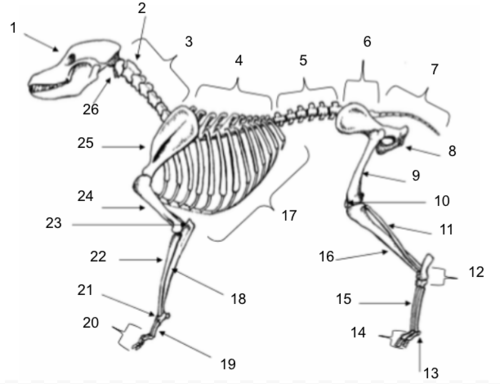
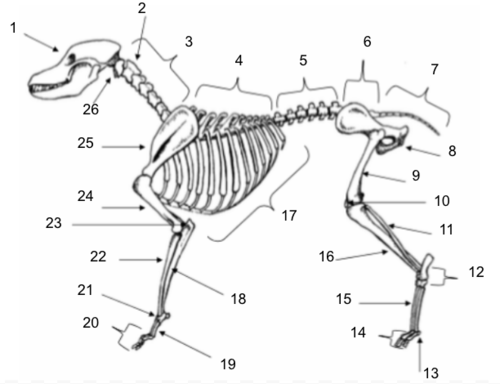
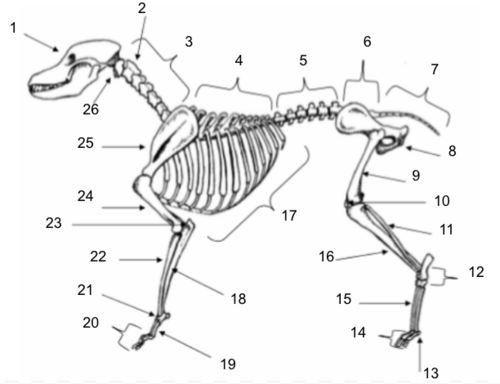
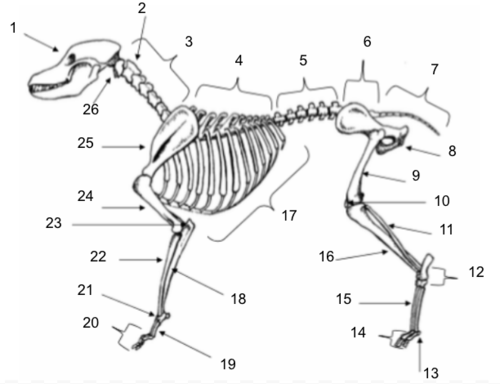
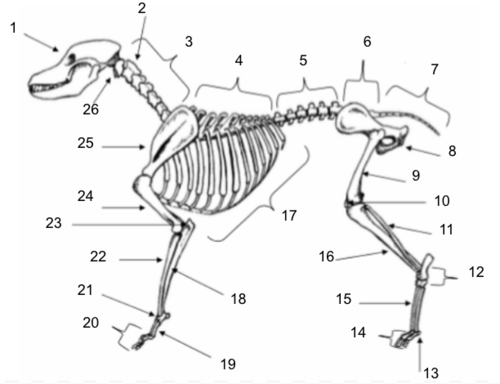
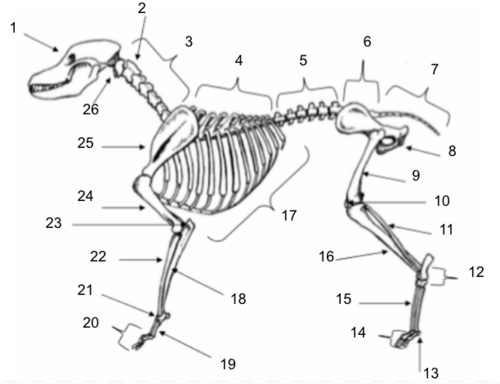
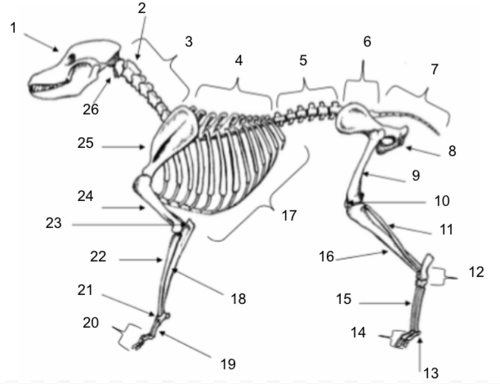
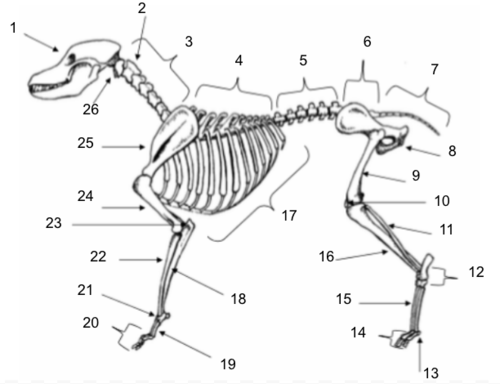
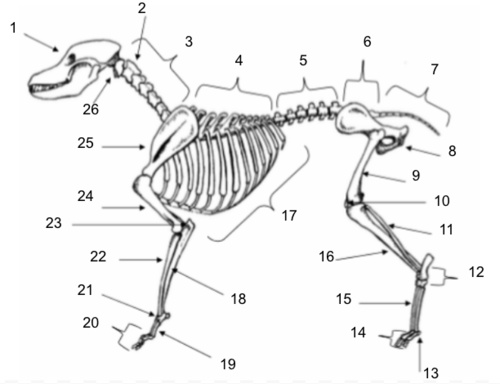
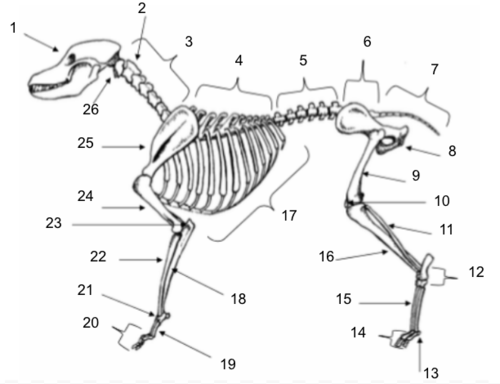
Skull
2
New cards
#2
Axis
3
New cards
#3
Cervical Vertebrae
4
New cards
#4
Thoracic Vertebrae
5
New cards
#5
Lumbar Vertebrae
6
New cards
#6
Sacral Vertebrae
7
New cards
#7
Coccygeal Vertebrae
8
New cards
#8
Pelvis
9
New cards
#9
Femur
10
New cards
#10
Patella
11
New cards
#11
Fibula
12
New cards
#12
Tarsals
13
New cards
#13
Sesamoids
14
New cards
#14
Phalanges
15
New cards
#15
Metatarsals
16
New cards
#16
Tibia
17
New cards
#17
Ribs
18
New cards
#18
Ulna
19
New cards
#19
Metacarpals
20
New cards
#20
Phalanges
21
New cards
#21
Carpals
22
New cards
#22
Radius
23
New cards
#23
Olecranon
24
New cards
#24
Humerus
25
New cards
#25
Scapula
26
New cards
#26
Atlas
27
New cards
#1
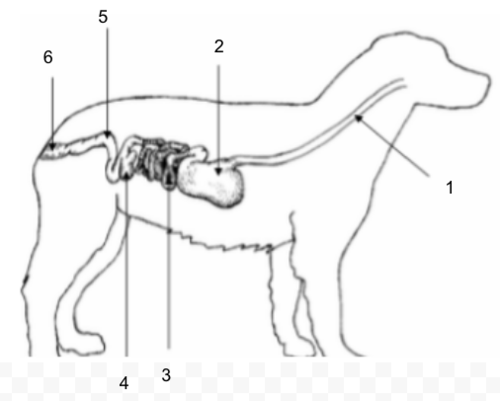
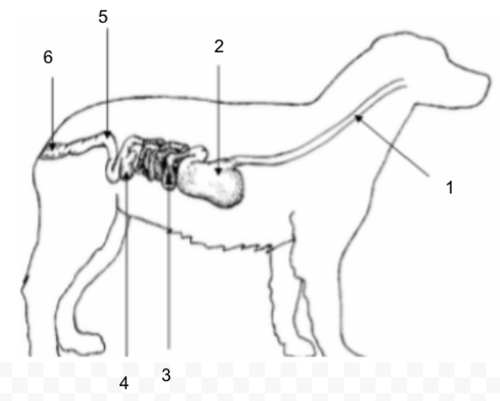
Esophagus
28
New cards
#2
Stomach
29
New cards
#3
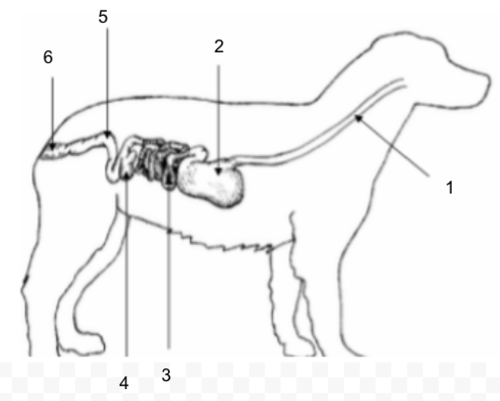
Small Intestine
30
New cards
#4
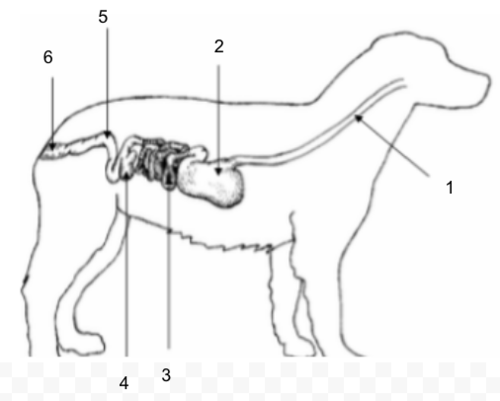
Cecum
31
New cards
#5
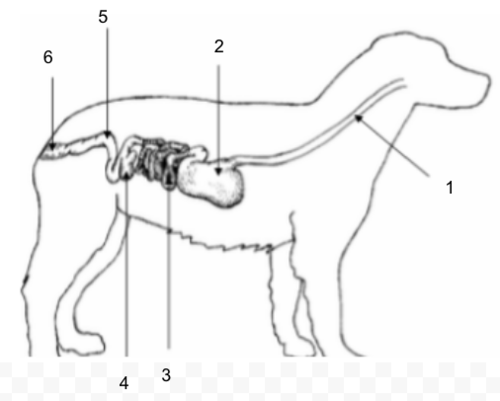
Large Intestine (Colon)
32
New cards
#6
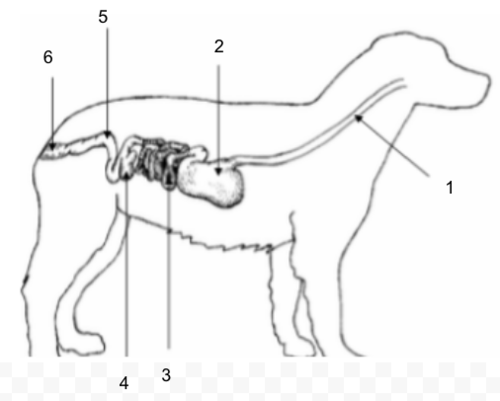
Rectum
33
New cards
#1
Esophagus
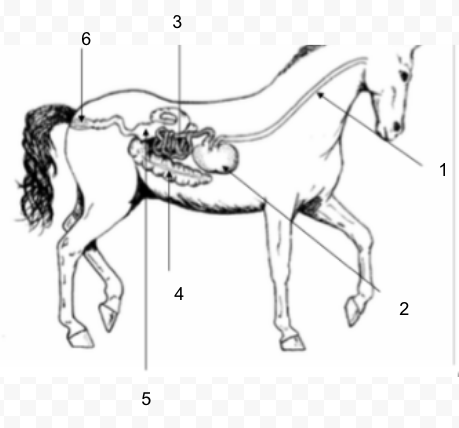
34
New cards
#2
Stomach
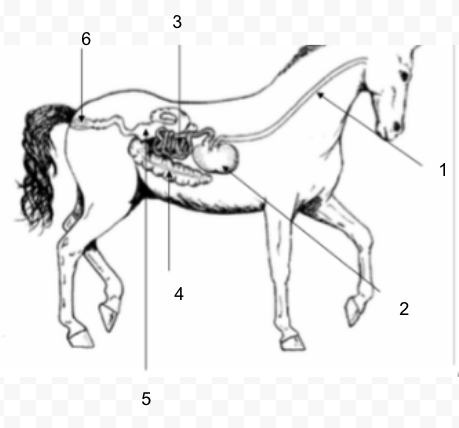
35
New cards
#3
Small Intestine
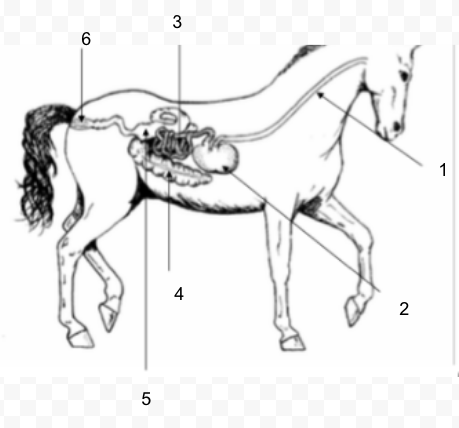
36
New cards
#4
Cecum
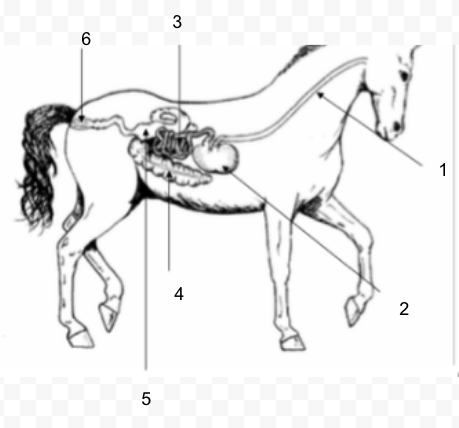
37
New cards
#5
Large Intestine (Colon)
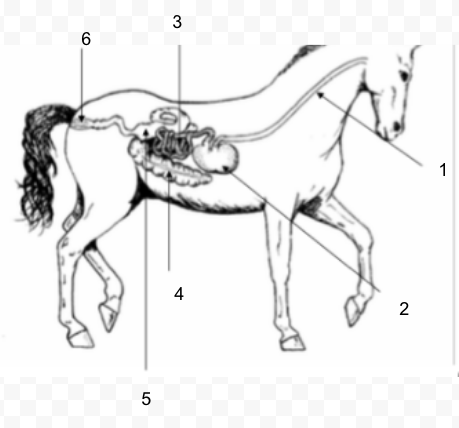
38
New cards
#6
Rectum
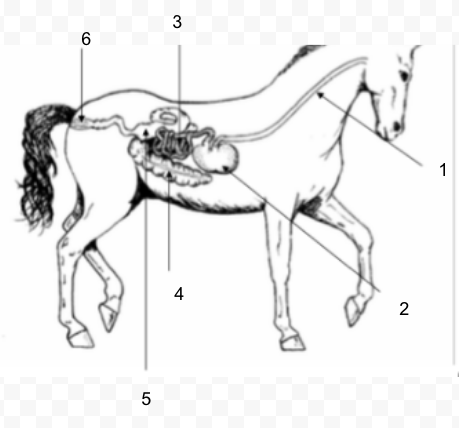
39
New cards
#1
Esophagus
40
New cards
#2
Rumen
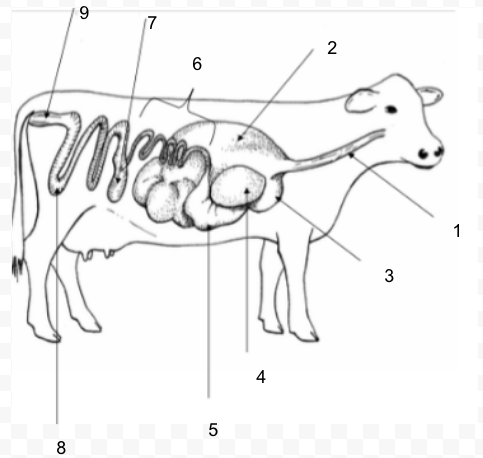
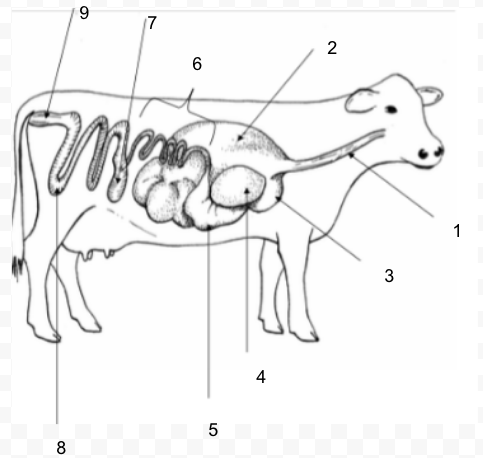
41
New cards
#3
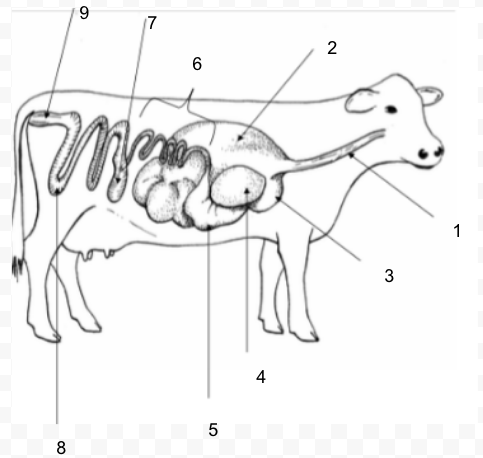
Reticulum
42
New cards
#4
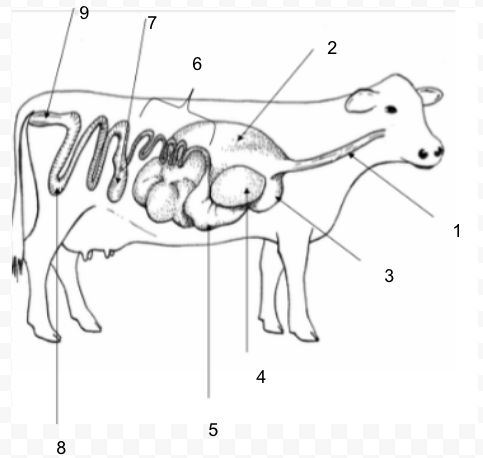
Omasum
43
New cards
#5
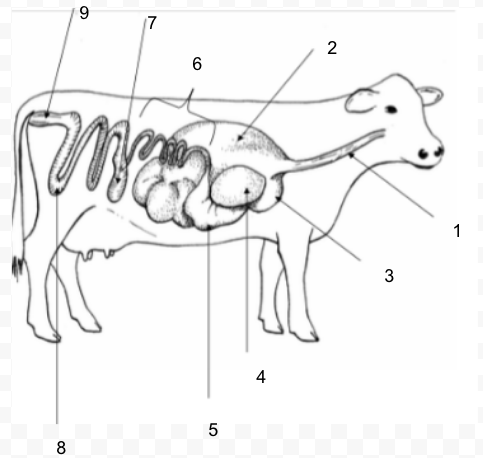
Abomasum
44
New cards
#6
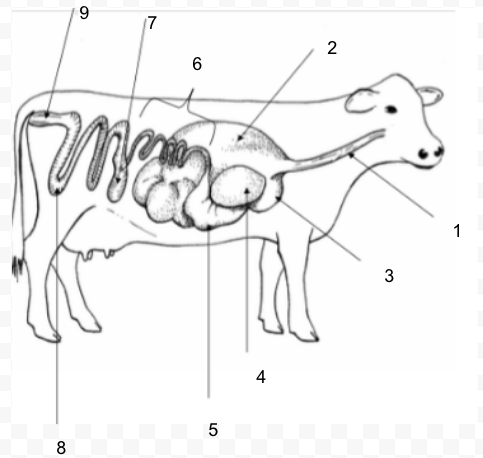
Small Intestine
45
New cards
#7
Cecum
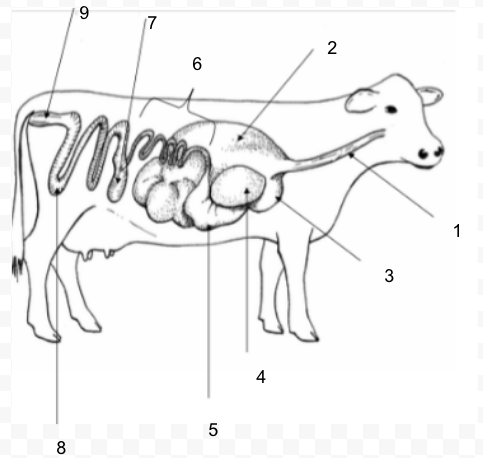
46
New cards
#8
Large Intestine (Colon)
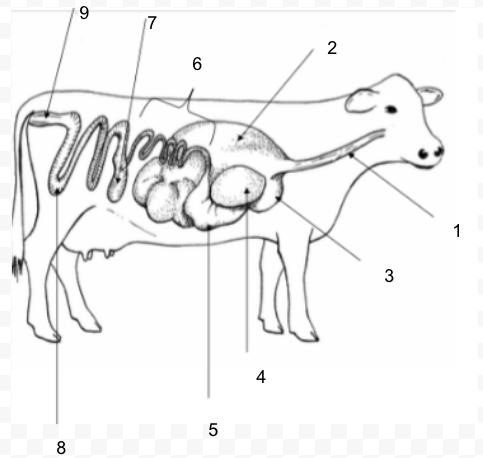
47
New cards
#9
Rectum
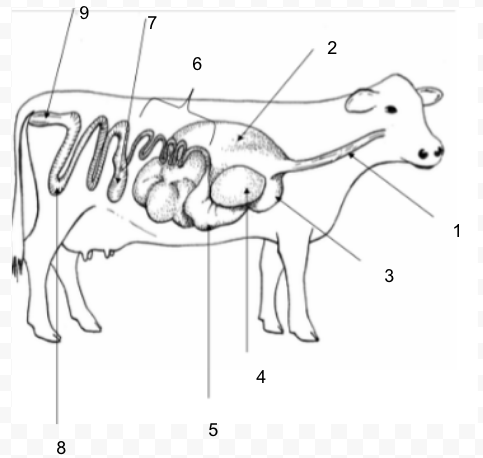
48
New cards
#1
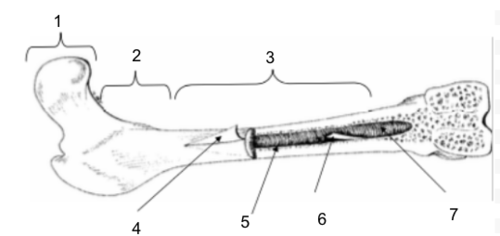
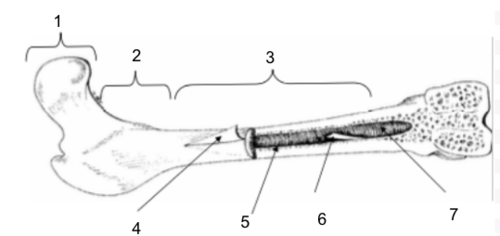
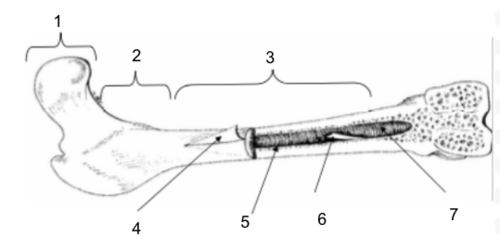
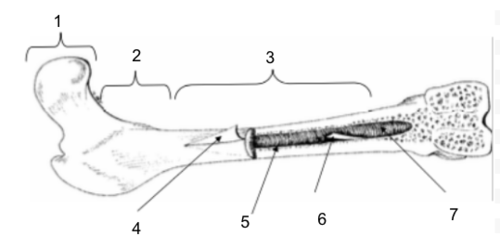
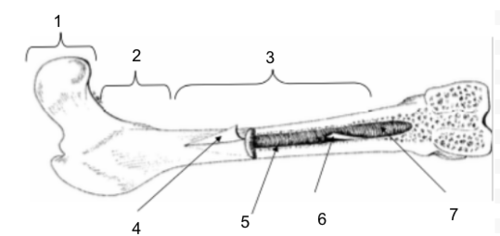
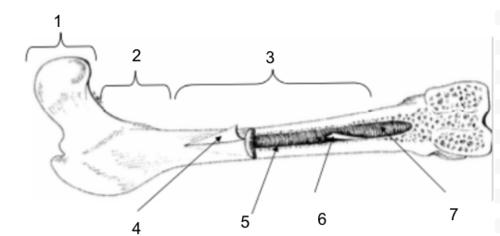
Epiphysis
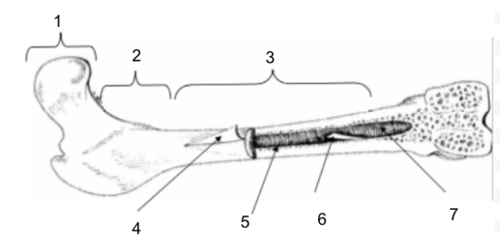
49
New cards
#2
Metaphysis
50
New cards
#3
Diaphysis
51
New cards
#4
Periosteum
52
New cards
#5
Bone Marrow
53
New cards
#6
Endosteum
54
New cards
#7
Medullary Cavity
55
New cards
List and describe the three types of digestive systems.
Ruminant: four compartment stomach: rumen, reticulum, omasum, abomasum - can digest roughages
Monogastric: simple single chambered stomach; cannot digest roughages
Cecal Fermenters: simple single chambered stomach; can digest roughages because of the presence of a cecum.
Monogastric: simple single chambered stomach; cannot digest roughages
Cecal Fermenters: simple single chambered stomach; can digest roughages because of the presence of a cecum.
56
New cards
What are the three parts of the Skeletal System? (I.e. Types of Tissues)
Bones, Cartilage, and Ligaments
57
New cards
What are two functions of the Skeletal System?
Gives structure and support to the body
Protects the internal organs
Makes locomotion and movement possible
Protects the internal organs
Makes locomotion and movement possible
58
New cards
Which two bones or groups of bones are part of the axial skeleton?
Skull and Spine
59
New cards
Which two bones or groups of bones are parts of the appendicular skeleton?
Forelimbs and Hindlimbs
60
New cards
Rumen
fermentation vat; microorganisms break down food
61
New cards
Reticulum
honeycomb; foreign material collects here
62
New cards
Omasum
manyplies; absorbs water and decreases particle size
63
New cards
Abomasum
true stomach; secretes enzymes
64
New cards
Small Intestine
absorption of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins
65
New cards
Large Intestine (Colon)
water absorption; mucus addition
66
New cards
Mechanical Digestion
food is chewed and broken down into smaller pieces
67
New cards
Peristalsis
muscular contractions; move food through system
68
New cards
Chemical Digestion
enzymes and acids reduce particle size
69
New cards
Absorption
nutrients move from digestive tract to bloodstream
70
New cards
Metabolism
removes nutrients from the bloodstream
71
New cards
Comminuted Fracture
bone shatters into many pieces
72
New cards
Compound Fracture
bone breaks through the skin
73
New cards
Fissure Fracture (hairline)
break along the long axis of the bone
74
New cards
Greenstick Fracture
break on one side of the bone; due to bending force
75
New cards
Simple Fracture
bone does not break through the skin
76
New cards
Transverse Fracture
break completely across the bone