Mark 201 Chpt. 10: Marketing Channels and Supply Chains
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Importance of Marketing Channels
Reaching potential buyers (manufacturer to consumer) is an essential part of successful marketing (need to get the right product, at the right price, to the right place, at the right time)
Buyers benefit from well-structured and efficient distribution systems – - Can be direct and indirect
Marketing Channels
sets of interdependent organizations that participate to make offerings available for consumers
sometimes called partners, in creating value value for the consumer
large organizations figured out a long time ago how to make all of the logistics work
the organizations/partners have ‘super-ordinant’ goals: big goal that everyone has (it is to provide VALUE to the consumer)
Channel decisions require considerations of two (2) elements
cost
level of service: ↓ level of service = ↓ cost = but not serving very many people, ↑ level of service = ↑ cost = but serving more people
ex. Mark’s is selling blue jeans
how many different styles should they stock?
how many different price points?
how many different sizes?
they have lots of all of these, they provide a very high level of service; anyone who comes in the store will find something
What must every channel member/partner provide?
VALUE
not providing value = get rid of it/them
value is created by …
intermediaries
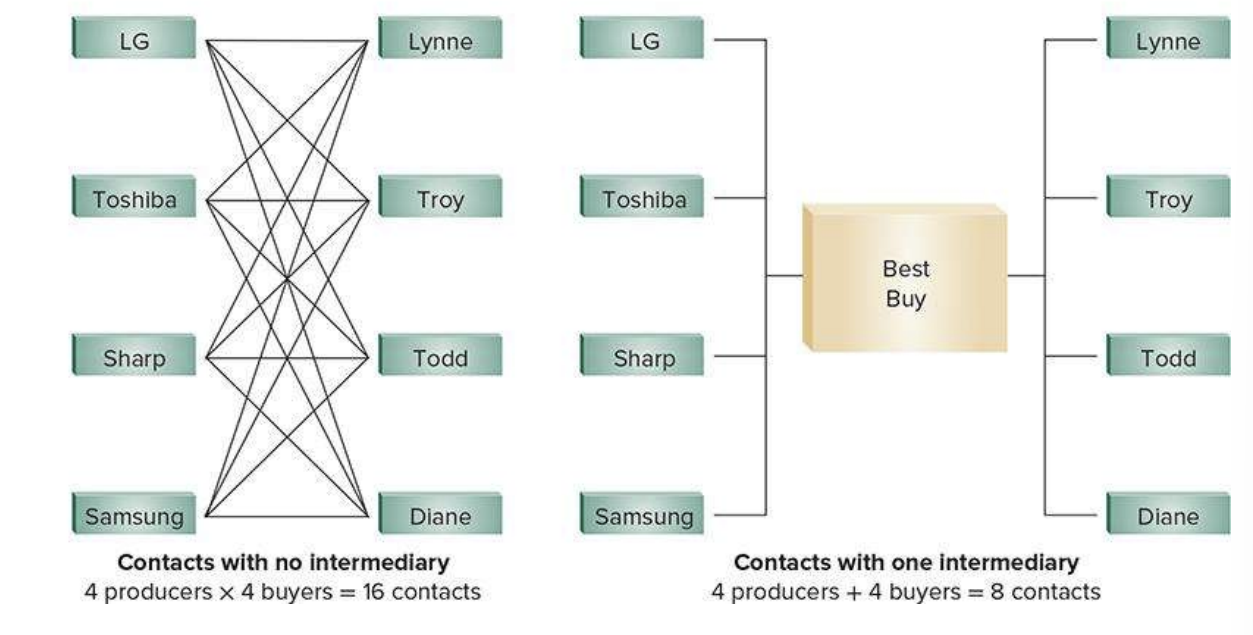
Intermediary
a business or individual that acts as a link between producers and consumers, helping to move goods and services to the final user
Marketing channel functions performed by intermediaries…
AKA what do intermediaries do?? (3)
transactional function
logistical function
facilitating function
Acitivity of transactional function (3)
buying: purchasing products for resale
selling: contacting potential customers, promoting products, and seeking orders
⭐ risk-taking: : assuming business risks in the ownership of inventory; risk in return (↑ risk = ↑ return), risk in inventory not selling; ex. wholesaler buys jeans from a company to sell
Acitivity of logistical function (4)
selection: : putting together a selection of products from several different sources
storing: assembling and protecting products at a convenient location
sorting: purchasing in large quantities and dividing into smaller amounts
transporting: physically moving a product to customers
ex. Dorito’s by Pepisco insists on stocking shelves at grocery stores themselves, so they can carefully arrange them how they want; in their mind, it’s worth the extra expense for their product to look good on the sehlf
Activity of facilitating function (2)
financing: : extending credit to customers
marketing information and research: providing information to customers and suppliers, including competitive conditions and trends; what’s selling well and what’s not selling well, what are people commenting on?, etc.
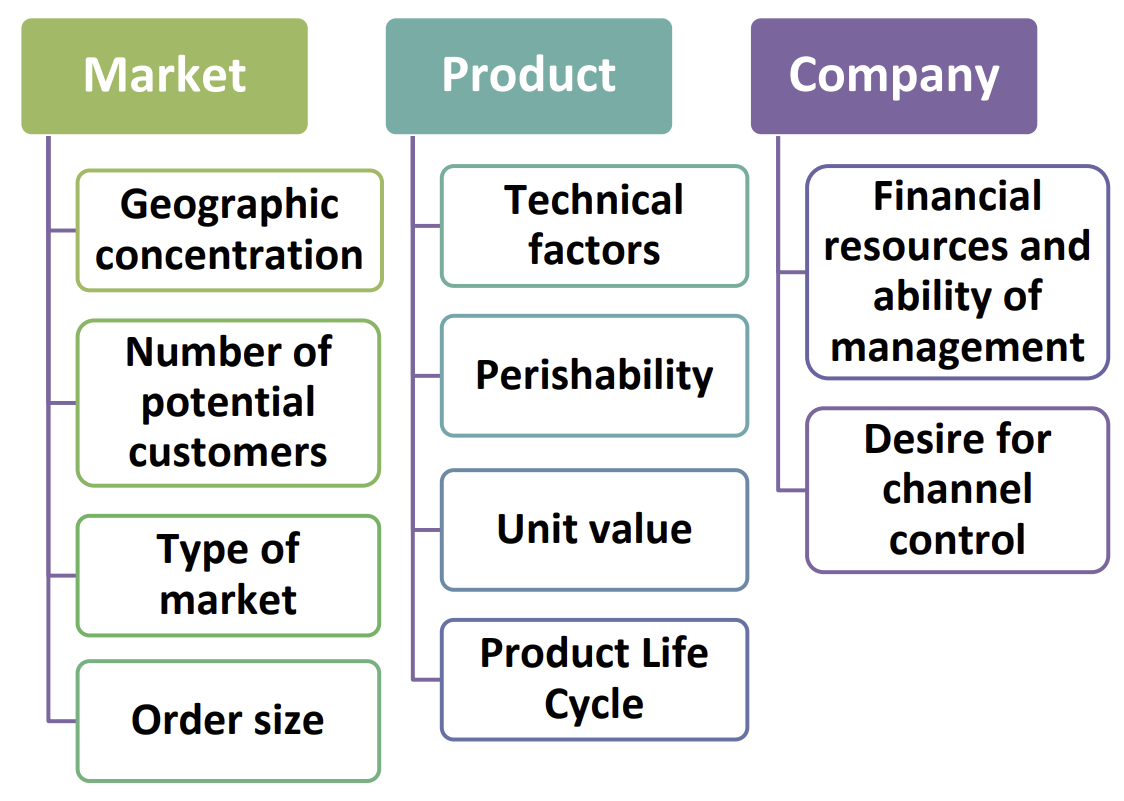
Factors affecting channel choice (3) - diagram
market (challenging in Canada b/c we are a huge country)
product
company
Channel design considerations (3)
Target market coverage – Intensive, exclusive (ex. one store in Edmonton has them), or selective distribution
Satisfying buyer requirements – Information, convenience, variety, and preand/or post-sale services ex. offering delivery? (how important is that to the consumer? adds value but costs money, worth it?)
Profitability – Distribution, advertising, and selling expenses
Motivating channel members- power
power relationships do happen ex. giant grocery chain and smaller supplier (power imbalance); marketers want people focused on ‘superoridinant’ goals; each channel member wants to create value but also have their own goals (can cause conflict); ex. big brand like Canadian Tire or Superstore with a smaller private label (potential for conflict with lots of other peoples, ex. sales)
coercive (relating to or using force or threats)
reward
legitimate
others
ultimatley, conflicts are possible!
ex. Tide laundry detergent is a market leader, if people walk in looking for it and don’t see it, they will leave; “walk-away factor”; this means Tide has power in the market (people will search multiple places for the product)
Evaluating channel members
evaulation is formal and ongoing; channel members are trying to reach the same goals (generally create value)
sales (selling enough product? making enough sales on your behalf?)
inventory levels (do people have enough choice when buying?)
treatment of damaged/lost goods
others; customer delivery times (↑ reliability = ↑ satisfaction), cooperation in promotional programs (↑ sales of manufacturer)
Ecommerce trends
what do these channels do for the marketer?? (think WHY are companies using these channels)
Top categories of online buying: fashion, electronics
Use of AI (personalization), AR, VR; enhances customer interaction ex. can look at a piece of furniture in your house using AI before you buy it (augmented reality; lowers risk of buying, increases convenience)
CRM, customer support is important
Hybrid commerce; part of “omnichannel” experience, people engage across multiple channels ex. in-store, online, order and pick-up, delivery, etc.; this is very important in terms of convenience but also people who interact amongst multiple channels spend more money
Multiple payment options including buy now, pay later (which is popular in some stores (take it home now and pay later); have digital payments, crypto (digital wallets), credit cards, etc. (allows consumer choice and freedom with how to consumer)
Voice activations ex. Alexa (convienent shopping)
Social selling (live product demonstrations/promotions, influencers (create impulse buys) ex. chocolate bars at the checkout at grocery stores) - part of the plan to engage consumers
Data privacy
Sustainability
Fast, free delivery (standard expectation now, but also a critical factor in purchase decisions for majority of people; people want purchases delivered very quickly otherwise they will look/go elsewhere)
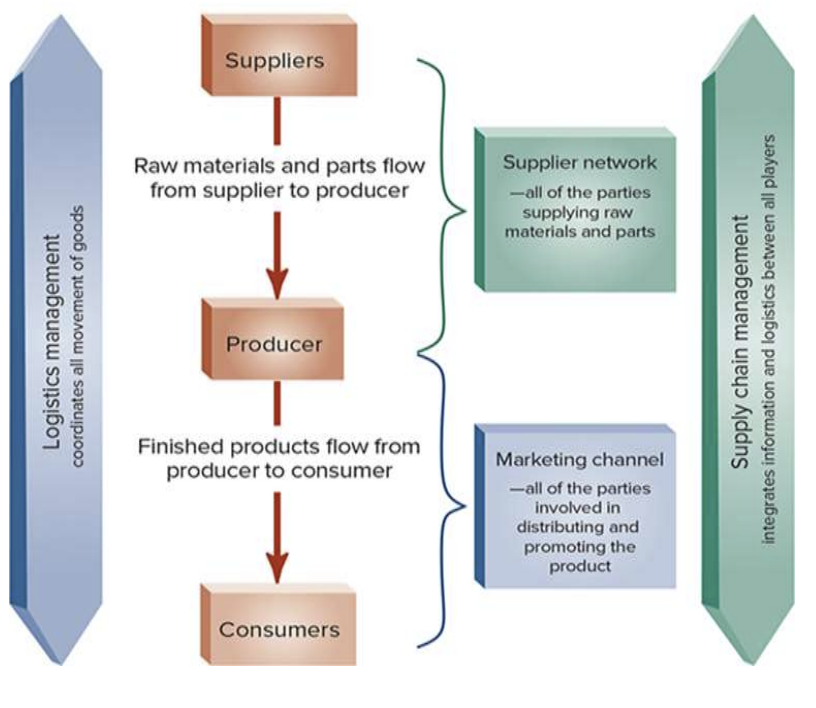
Logistics
activities that focus on getting the right amount of the right products to the right place at the right time at the lowest possible price (on trucks we don’t see “Webb Trucking”, we see “Webb Logistics”)
Expected level of customer service
(*important) Collaboration, coordination, and information sharing among manufacturers, suppliers, and distributions → seamless
Supply Chain vs Marketing Channels - diagram
*all are trying to achieve the same goal!
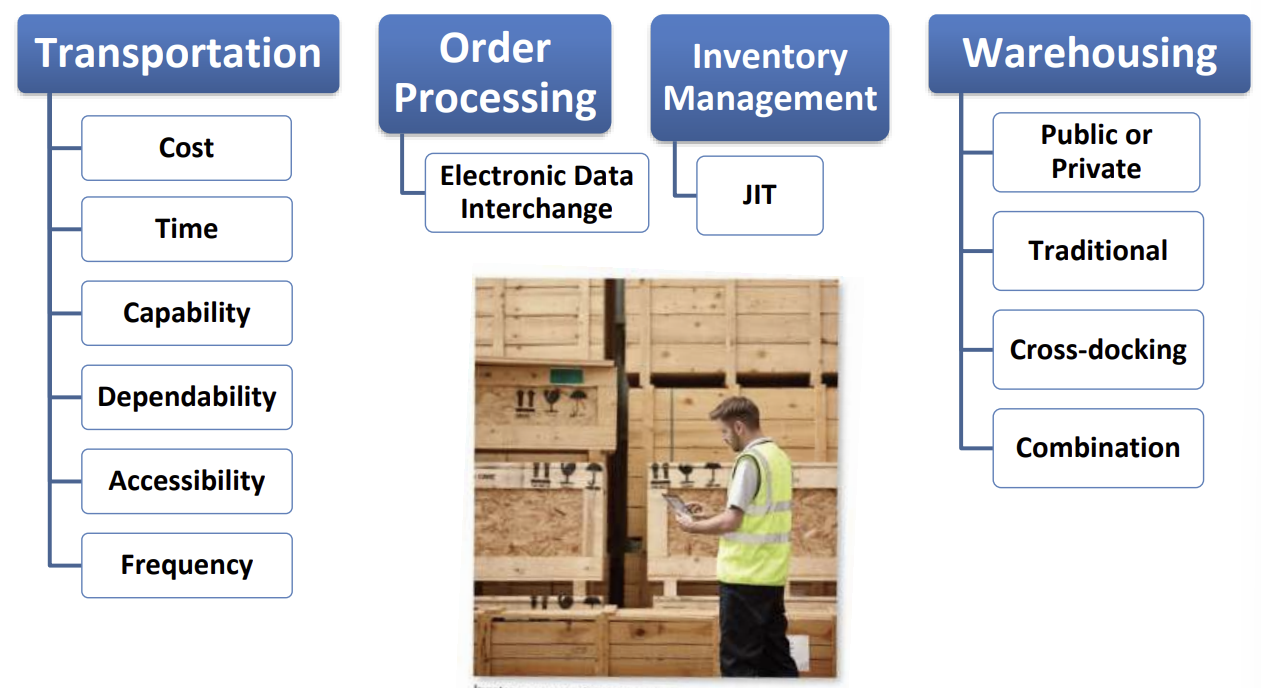
Key logistics functions in a supply chain - diagram
*important considerations
transportation - cost, time, capability, dependability, accessibility, frequency
order processing - electronic data interchange
*inventory management - JIT (just-in-time): a strategy where businesses receive materials and produce goods only as they are needed, minimizing waste and storage costs by aligning inventory with demand
warehousing - public or priavte, traditional, cross-docking, combination