ch 1- Electric Charges and Fields
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What happened if glass rod is rubbed with silk?
glass rod attains positive charge and silk attains a negative charge
properties of charge
like charges attract
unlike charges repel
Body which loses electron gets positively charged
Body which gains electron gets negatively charged
additivity of charges
Conservation of charge- total charge of a isolated system remains conserved
quanisation of charge- electric charge is always an integral multiple of e
q=±ne n=1,2,…. e=1.6×10-19 C
Gold Lead Electroscope
detect charge on a body
Coulomb’s law/ Inverse square law
Electrostatic force between two stationary point charges is directly propertional to the product of magnitude of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
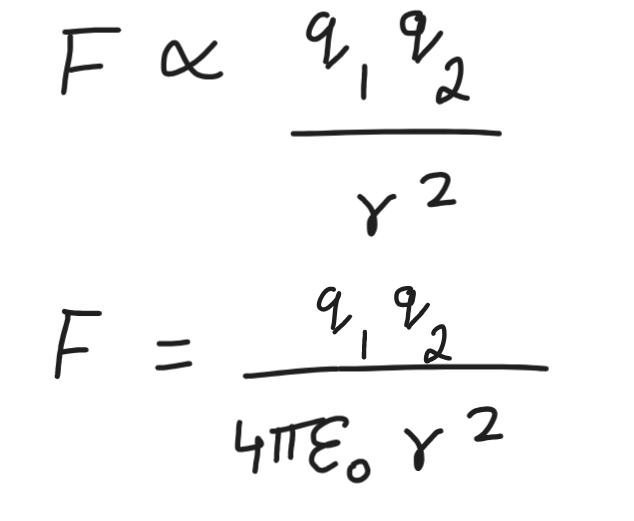
ε0
8.854×10-12 C²N-1m-2
1/(4πε0)
9×109 Nm²C-2
For dielectric constant
ε=ε0×εr
superposition principle
the total force acting on a charge is equal to the vector sum of forces acting on the charge due to individual charges.
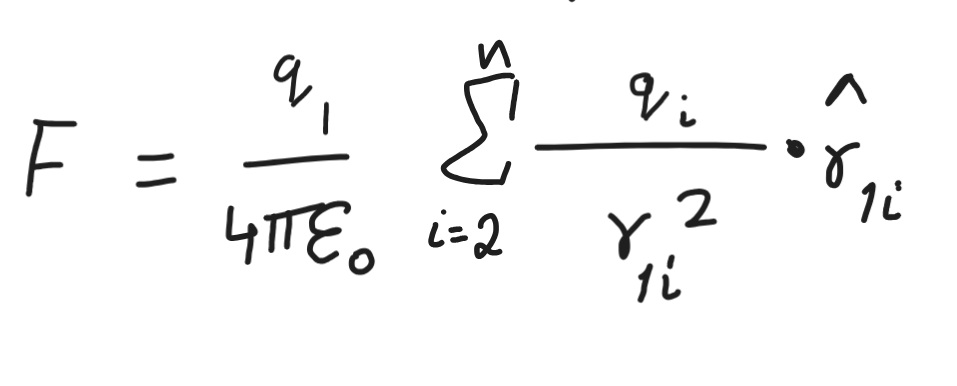
Electric Field
unit- N/C
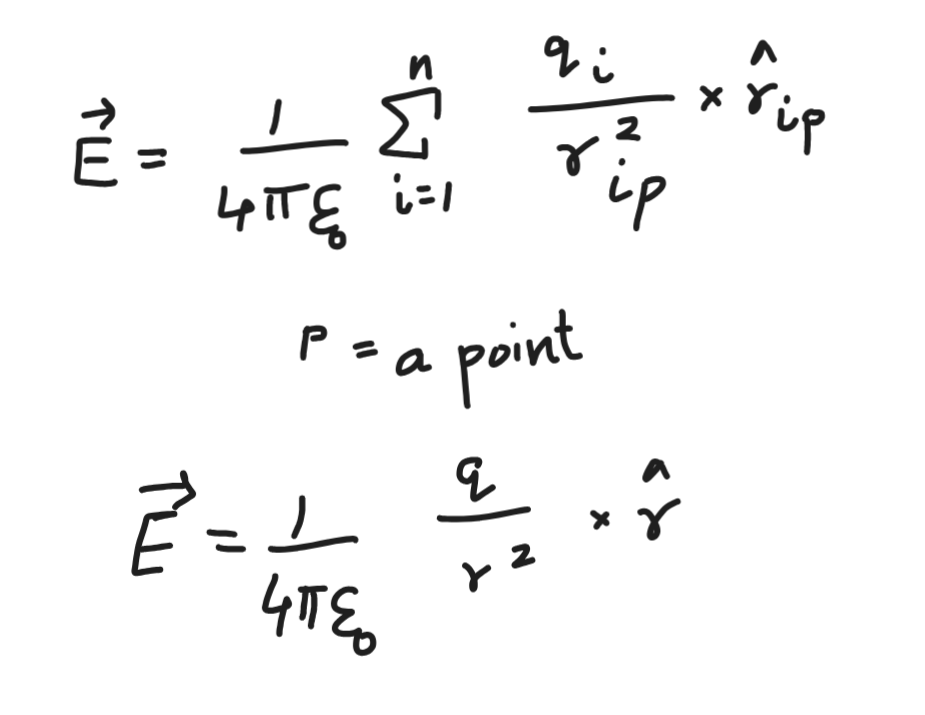
Electric Field Strength/ Electric Field Intensity
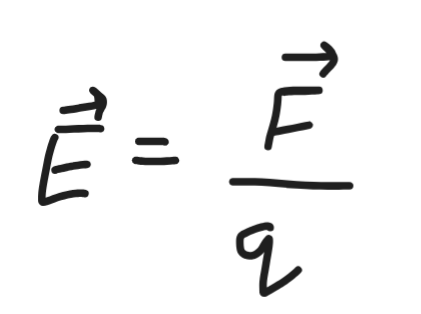
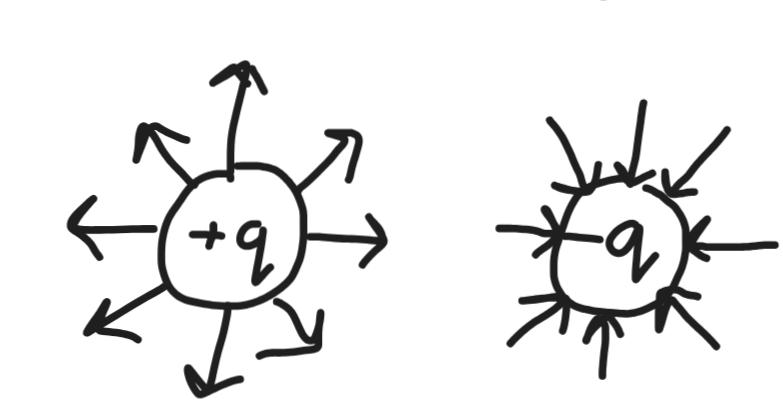
electric field on +ve and -ve charges
Electric Field Lines
is a path straight line or curve through which an imaginary +ve charge moves if free to do so and the tangent to it at each point give the direct of the field at that point.
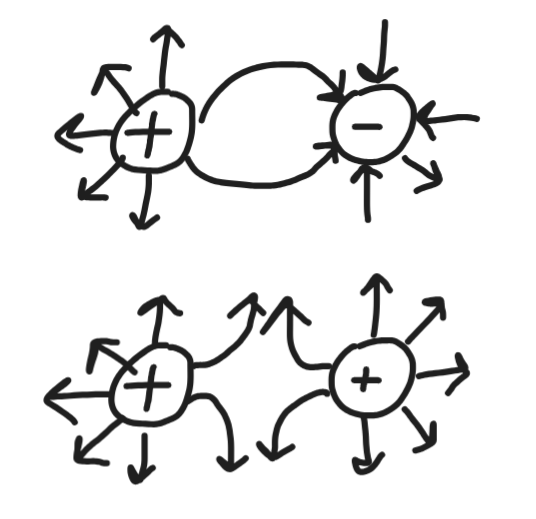
Field lines for unlike charges and like charges
Properties of Electric Field lines
No two field lines never intersect (two directions for electric not possible at the same point)
No. of field lines orginating or terminating increases with increase in magnitude of charge
tangent to the field lines give the direction of the field at that point
for +ve charge field lines are radially outward
for -ve charge field lines are radially inward
field lines originate from +ve charge and terminate at -ve charge
Electric flux
Total no. of electric field lines passing normally through a surface.
unit- Nm²/C or Nm²C-1
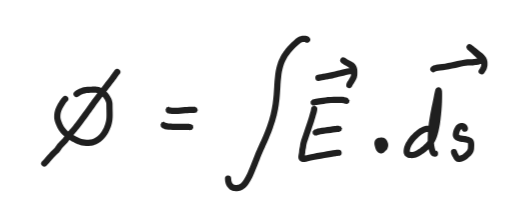
Electric Dipole
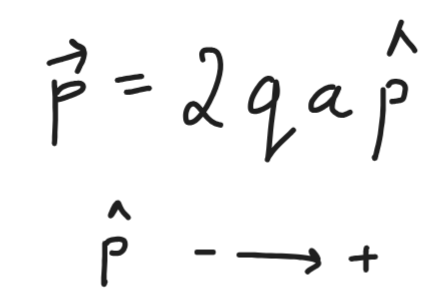
Charge densities
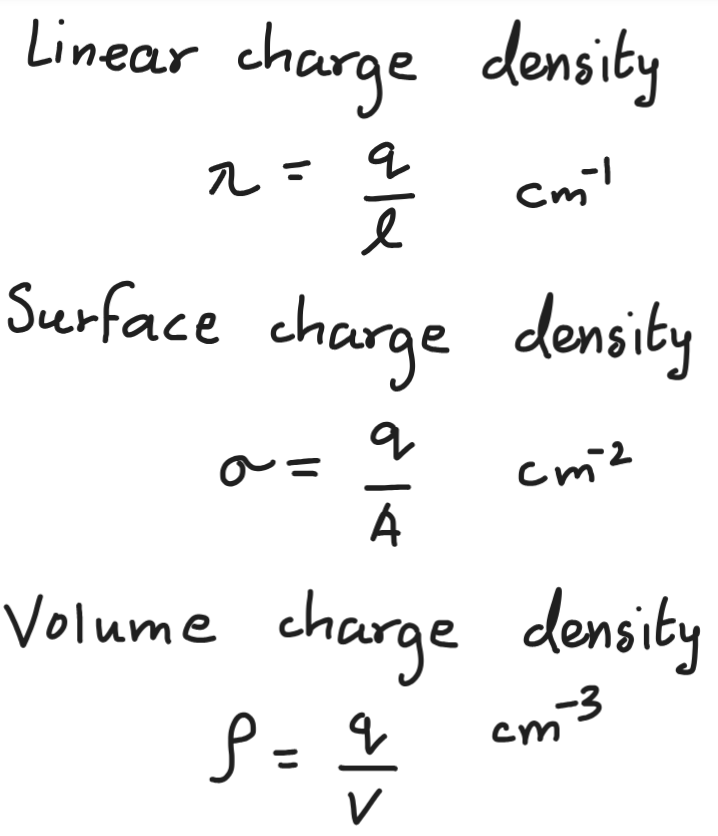
Gauss’s Law
Total electric flux over a closed surface enclosing a charge is equal to,
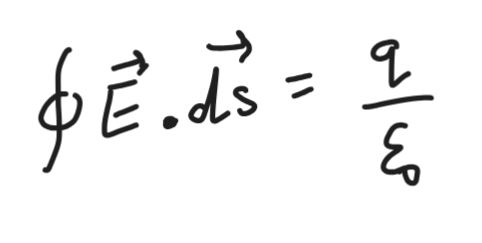
electric dipole axial
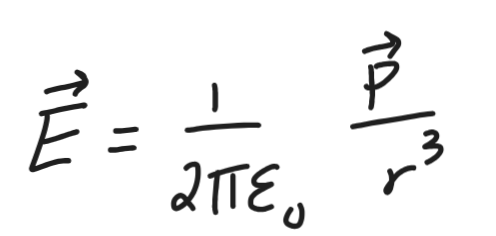
electric dipole equitorial
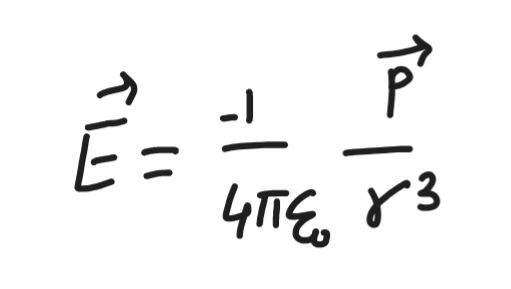
field due to infinitely long wire
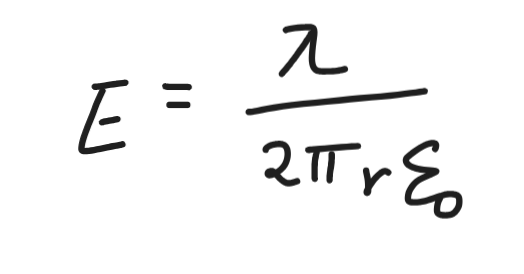
field due to infinitely long plane sheet
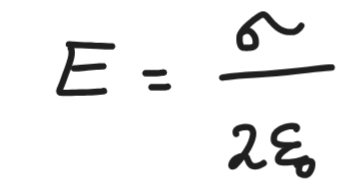
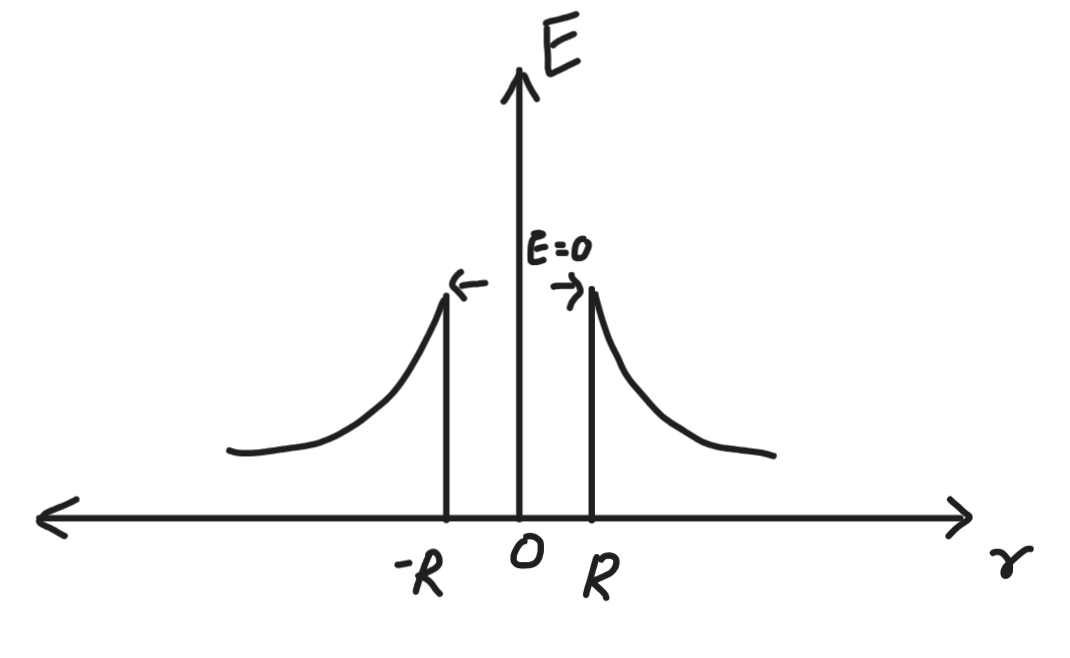
variation of electric field due to uniformly charged shell of radius R with distance r from center of the shell