Graphing and Analyzing Radical Functions
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Parent Function
The simplest form of a function that can be transformed to create other functions.
Radical
An expression that includes a root, such as a square root or cube root.
Zeros
The values of x for which a function f(x) equals zero.
Roots
The solutions to the equation f(x) = 0, where the function intersects the x-axis.
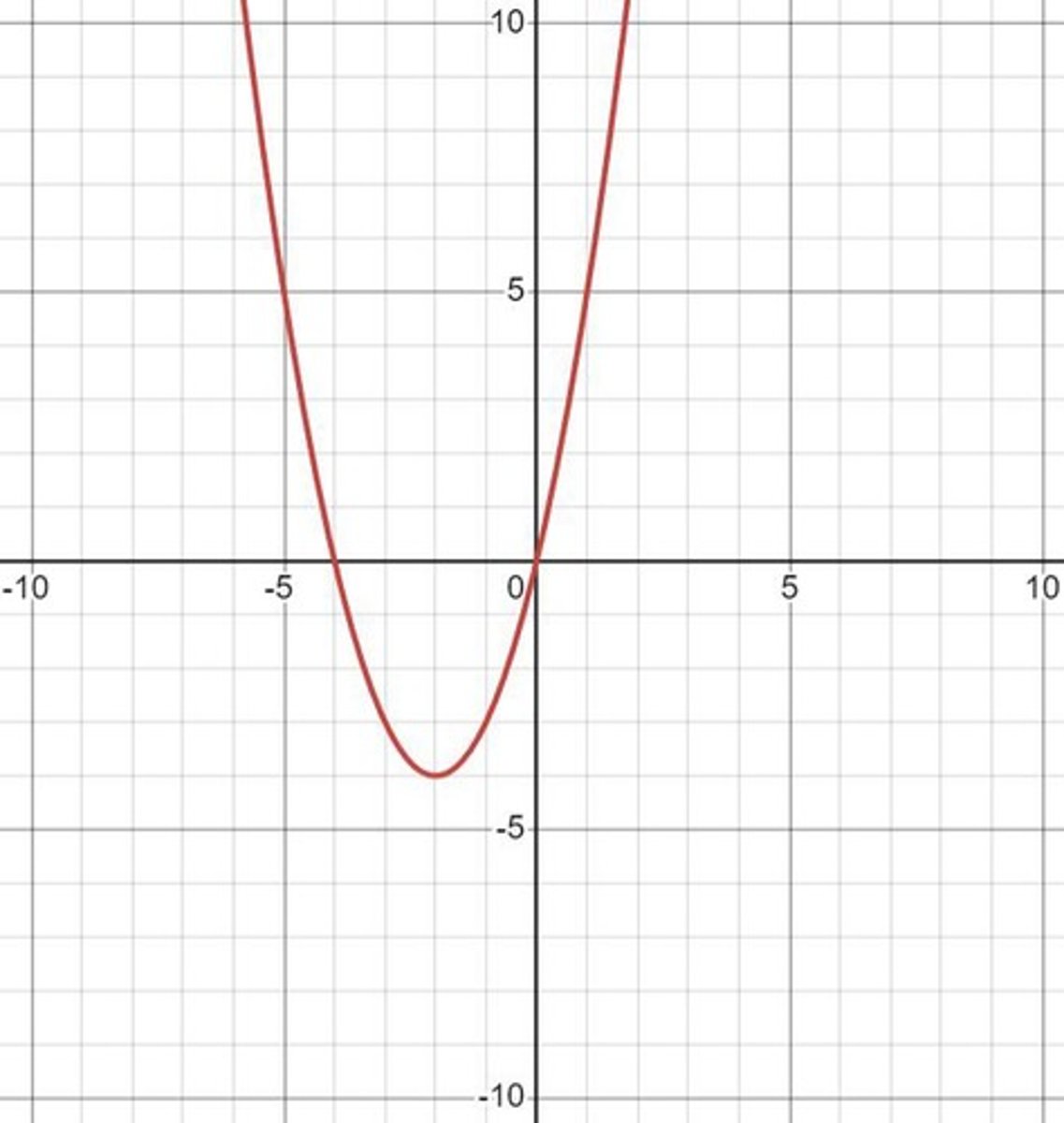
X-intercepts
The points where the graph of a function crosses the x-axis.
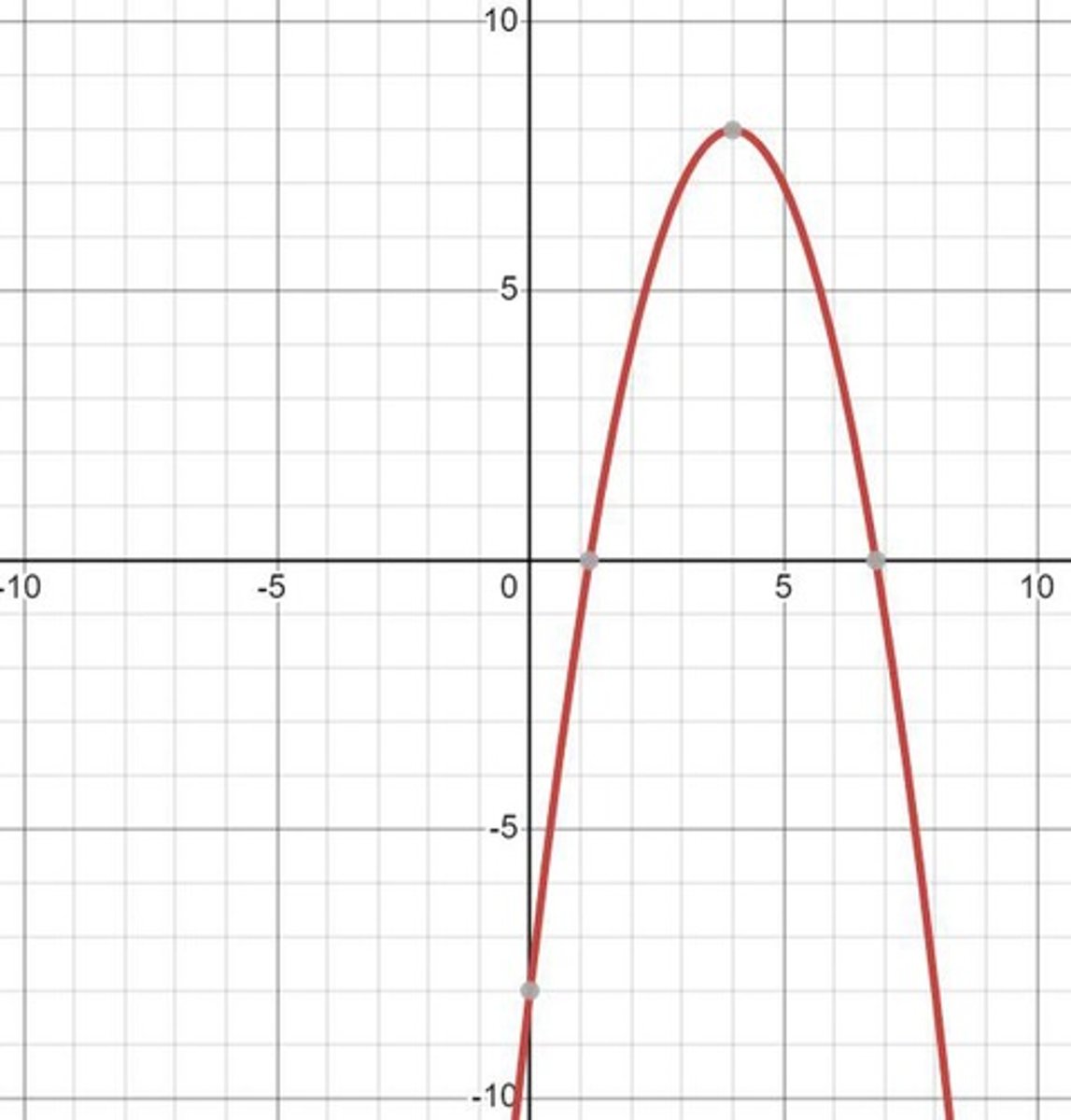
Extraneous root
A solution that emerges from the process of solving an equation but is not a valid solution to the original equation.
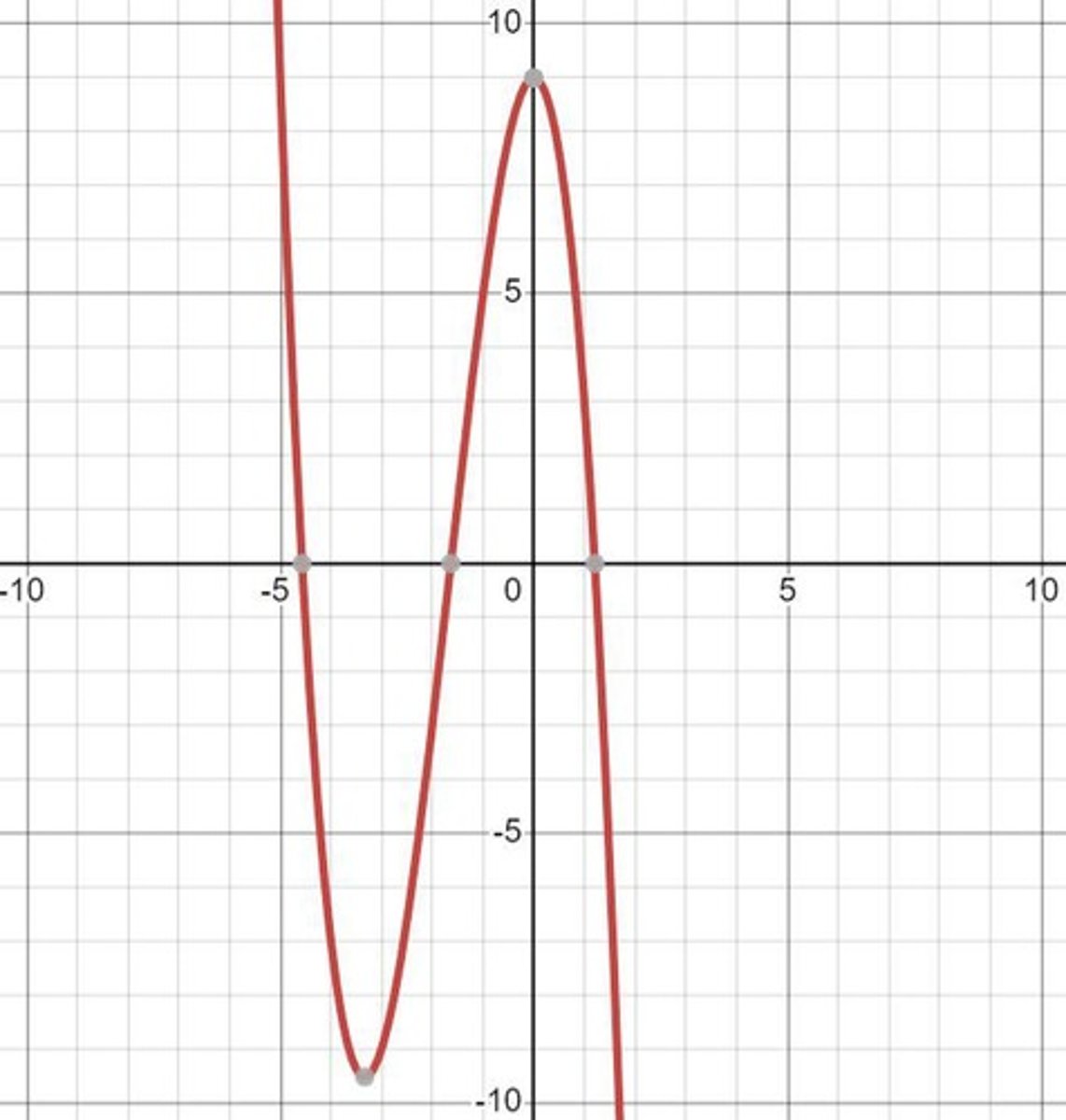
Domain
The set of all possible input values (x-values) for a function.
Range
The set of all possible output values (y-values) for a function.
Invariant points
Points on a graph that remain unchanged under a transformation.
Transformation
A change made to a function that alters its graph, such as shifting, stretching, or reflecting.
Square root function
A function of the form y = √x, which produces the principal square root of x.
Graphical solution
Finding the solution to an equation by analyzing the graph of the function.
Interval notation
A way of writing the domain or range of a function using intervals.
Set notation
A way of expressing the domain or range of a function using curly braces.
Algebraic determination
Finding the roots of an equation using algebraic methods.
Vertical stretch
A transformation that multiplies the y-values of a function by a factor greater than 1.
Horizontal stretch
A transformation that multiplies the x-values of a function by a factor greater than 1.
Reflection
A transformation that flips a function over a line, such as the x-axis or y-axis.
Translation
A transformation that shifts a function horizontally, vertically, or both.
Graphing calculator
A handheld device used to plot graphs, solve equations, and perform calculations.
Table of values
A chart that shows pairs of input and output values for a function.
Function notation
A way to denote functions using symbols like f(x) to represent the output of a function for a given input x.
Trinomials
A polynomial with three terms.
Graphical verification
Confirming algebraic solutions by comparing them to the graph of the function.
Approximate solution
An estimated answer to an equation, often found using graphical methods.
Radical equation
An equation that involves a variable within a radical.
Function f(x)
A general representation of a function in terms of x.
Transformed function
A function that has been altered from its parent function through transformations.
Sketching a function
Drawing the graph of a function based on its characteristics and transformations.
Binomial
A polynomial with two terms.
Linear Factors
Factors of a polynomial that are of degree one.
Polynomial
An expression consisting of variables and coefficients, involving only non-negative integer exponents.
Dividend
The number or expression being divided.
Synthetic Division
A simplified form of polynomial division that uses coefficients.
Remainder
The amount left over after division.
Divisor
The number or expression by which another number or expression is divided.
Integral Zero Theorem
States that the factors of the constant term can be tested in the function using the remainder theorem.
Remainder Theorem
States that the remainder of the division of a polynomial by x - a is equal to the value of the polynomial at x = a.
Factor Theorem
States that x - a is a factor of a polynomial if and only if the polynomial evaluated at a equals zero.
Invariant Points
Points on a graph that remain unchanged after a transformation.
Long Division of Polynomials
A method for dividing a polynomial by another polynomial of lower degree.
Quotient
The result obtained by dividing one quantity by another.
Degree of a Polynomial
The highest power of the variable in the polynomial.
Polynomial of Degree ≤ 5
A polynomial that has a degree of 5 or less.
Graphical Reasoning
Using graphs to understand and solve mathematical problems.
Algebraic Reasoning
Using algebraic methods and principles to solve problems.
Function
A relation that assigns exactly one output for each input.
Transformation
An operation that moves or changes a function in some way.
Coefficient
A numerical factor in a term of an algebraic expression.
Constant Term
A term in a polynomial that does not contain any variables.
Testing Factors
The process of substituting potential factors into a polynomial to find zeros.
Fully Factor
To express a polynomial as a product of its factors completely.
Descending Order
Arranging terms from highest to lowest degree.
Placeholders in Synthetic Division
Using zeros to represent missing terms in the polynomial during synthetic division.
Value of k
A variable used to determine the remainder in polynomial division.
Polynomial Expression
An expression that represents a polynomial.
Test for Zero
The process of evaluating a polynomial at specific values to find roots.
Graphical Solution
Finding the solution of an equation by analyzing its graph.