11 - ANTIBODY SCREENING AND IDENTIFICATION
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Immune alloantibodies
Naturally occurring alloantibodies
Passively acquired antibodies
Autoantibodies
Unexpected/Irregular Antibodies (4)
Clinically significant alloantibodies
cause decreased survival of RBCs
IgG
37
Clinically significant alloantibodies
typically _ antibodies that react at _°C
Antibody Detection
Detect any potentially clinically significant antibodies in a donor’s or recipient’s sample
patient serum
Antibody Detection
Involves the reaction between _ _ with 2 or 3 reagents phenotyped for multiple antigens
R1R1, R2R2 or R1R1, R2R2, rr
Reagent RBC (2)
Reagent RBC
O cell with: C, c, D, E, e, Fya, Fyb, Jka, Jkb, K, k, Lea, Leb, P1, M, N, S, and s antigens
Homozygous or Heterozygous
Reagent RBC expressions
M, N
M+N+
Antigen present?
Heterozygous
M+N+
Homozygous or heterozygous?
Fya
Fy(a+b-)
Antigen present?
Homozygous
Fy(a+b-)
Homozygous or heterozygous?
Immediate Spin
37C Phase
AHG Phase
3 Phases in Antibody Screening
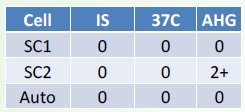
Negative for unexpected antibodies
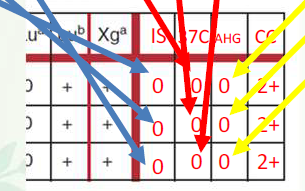
Positive for unexpected antibodies
Cold reacting antibody
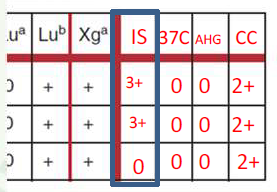
Positive for unexpected antibodies
Warm reacting antibody
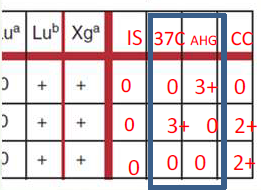
Autologous Control
The patient’s RBCs tested against the patient’s serum in the same manner as the antibody screen
Single antibody
Interpretations
_ _ specificity should be suspected when all screen cells yielding a positive reaction react at the same phase(s) and strength
Multiple antibodies
Interpretations
_ _ are most likely present when screen cells react at different phases or strengths
Autoantibodies
Interpretations
_ should be suspected when the autologous control or DAT is positive and all screen cells tested yield a positive reaction
anti-Lea
anti-Leb
anti-PP1Pk
anti-Vel
Antibodies associated with Hemolysis (in vitro) (4)
anti-Sda
anti-Lu
Antibodies associated with Mixed-Field (Mf) (2)
Rouleaux
Cells have a “stacked coin” appearance when viewed microscopically
Rouleaux
Observed in all tests containing the patient’s serum, including the autologous control and the reverse ABO grouping
washed away
Rouleaux
Does not interfere with the AHG phase of testing in tube method or solid-phase technology because the patient’s serum is _ _ prior to the addition of the AHG reagent
1-3
saline
Rouleaux
Disperses by adding _-_ drops of _ to the test tube when performing tube testing
Single Alloantibody
Probably IgG
Multiple Alloantibodies
Probably IgG
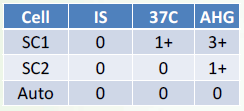
Single or multiple Alloantibody
Probably IgM
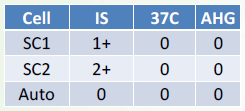
Multiple alloantibodies
Probably IgG or IgM
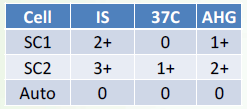
Warm Autoantibody
Probably IgG
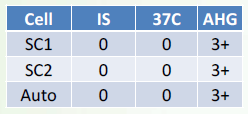
Antibody Identification
Identification of an antibody to red cell antigen(s) requires testing the serum against a panel of selected red cell samples with known antigen composition
Antibody Identification Panel
collection of 11 to 20 group O reagent RBCs
antigen expression should be diverse
Exclusion or “Rule-Outs”
First Step
RBCs that gave a negative reaction in all phases of testing are examined
The antigens on these negatively reacting cells are probably not the antibody’s target
Rule of three
must be met to confirm the presence of the antibody
Positive
Negative
Rule of three
Patient serum MUST be:
_ with 3 cells with the antigen
_ with 3 cells without the antigen
Selected Panel
Enzymes
Neutralization
Adsorption
Additional Techniques for Resolving Antibody Identification (4)
Selected Panel
Additional Techniques for Resolving Antibody Identification
Simplest step
The cells selected for testing should have minimal overlap in the antigens they possess
Enzymes
Additional Techniques for Resolving Antibody Identification
Modify the RBC surface by removing sialic acid residues and by denaturing or removing glycoproteins
Results in the destruction of certain antigens and the enhanced expression of others
Rh
Kidd
Lewis
P1
I
ABO
Additional Techniques for Resolving Antibody Identification
Enzymes
Enhanced (6)
Duffy
MNS
Xga
Additional Techniques for Resolving Antibody Identification
Enzymes
Inactivated (3)
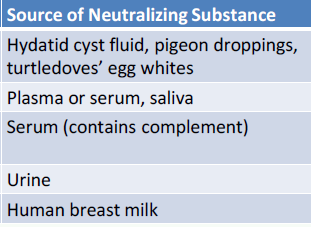
Neutralization
Additional Techniques for Resolving Antibody Identification
Used to neutralize the corresponding RBC antibodies in serum
Anti-P1
Anti-Lewis
Anti-Chido, anti-Rodgers
Anti-Sda
Anti-I
Adsorption
Additional Techniques for Resolving Antibody Identification
Process of removing antibody from the serum
RBC or another antigen-bearing substance
Additional Techniques for Resolving Antibody Identification
Adsorption
Adsorbent
Human platelet concentrate
Additional Techniques for Resolving Antibody Identification
Adsorption
adsorb Bg-like antibodies
Rabbit erythrocyte stroma (RESt)
Additional Techniques for Resolving Antibody Identification
Adsorption
Cold-reacting autoantibodies
two
one
one
20, 3400
Immediate Spin Saline
Procedure
Label four tubes as SC I, SC II, SCIII, and AC.
Add _ drops of serum into each of the tubes.
Add _ drop of the corresponding screening cell to each of the tubes.
Add _ drop of patient’s 5% red cell suspension to the autocontrol tube (AC).
Gently mix then centrifuge for _ seconds at _ rpm.
After centrifugation, gently dislodge the red cells and observe for agglutination or hemolysis.
Grade and record the results as “_ _ _”.
two
37, 15-30
20
37C albumin
Procedure
Add _ drops of bovine serum albumin to each of the four tubes. Mix gently.
Incubate the tubes at _°C for _-_ minutes.
After incubation, centrifuge the tubes for _ seconds.
Repeat step 6.
Grade and record the results as “_ _”.
isotonic saline, 3
two
20
AHG
2
20
CC
Procedure
Wash the serum-cell mixtures with _ _ for _ times.
Add _ drops of antihuman globulin reagent to each of the four tubes.
Gently mix and centrifuge for _ seconds.
Repeat step 6.
Grade and record results as “_”.
Add _ drops of check cells to all negative tubes.
Gently mix then centrifuge for _ seconds.
Repeat step 6.
Grade and record results as “_”.