Topic 9 - Plant Diversity II
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What are the key adaptations of seed plants for terrestrial life?
Seeds, reduced gametophyte, heterospory, ovules, and pollen.
What is the main advantage of seeds over spores?
Seeds provide protection, a nutrient supply, and extended lifespan through dormancy.
What are the two major groups of seed plants?
Gymnosperms (naked seeds) and Angiosperms (seeds enclosed in fruit).
How is the gametophyte stage different in seed plants compared to non-seed plants?
It is microscopic, dependent on the sporophyte, and housed within sporangia for protection.
What is heterospory, and why is it important?
It is the production of two types of spores: microspores (male) and megaspores (female), allowing for specialized reproductive roles.
What is an ovule?
A structure that contains the megasporangium and houses the developing female gametophyte.
What is pollen, and why is it an important adaptation?
Pollen is the male gametophyte, enabling fertilization without water through pollination.
How do gymnosperms differ from angiosperms?
Gymnosperms have 'naked seeds' on cones, while angiosperms enclose seeds in fruit.
What is the main reproductive structure of gymnosperms?
Cones (strobili), with male cones producing pollen and female cones housing ovules.
Describe the fertilization process in gymnosperms.
Pollen lands on female cones, forms a pollen tube, and delivers sperm to fertilize the egg inside the ovule.
What are the four major phyla of gymnosperms?
Ginkgophyta, Cycadophyta, Gnetophyta, and Coniferophyta.
What are the two major reproductive structures of angiosperms?
Flowers (for pollination) and fruits (for seed protection and dispersal).
What is the function of flowers in angiosperms?
They contain reproductive organs (stamens and carpels) and attract pollinators.
What is the significance of fruit in angiosperms?
Fruits protect seeds and aid in their dispersal.
What is double fertilization in angiosperms?
One sperm fertilizes the egg (zygote), and another fuses with the central cell (endosperm formation).
What does the triploid endosperm in angiosperms do?
It provides nutrients to the developing embryo.
How does pollination work in angiosperms?
Pollen lands on a flower’s carpel, a pollen tube forms, and sperm cells travel to the ovary for fertilization.
What is the only phylum of angiosperms?
Anthophyta.
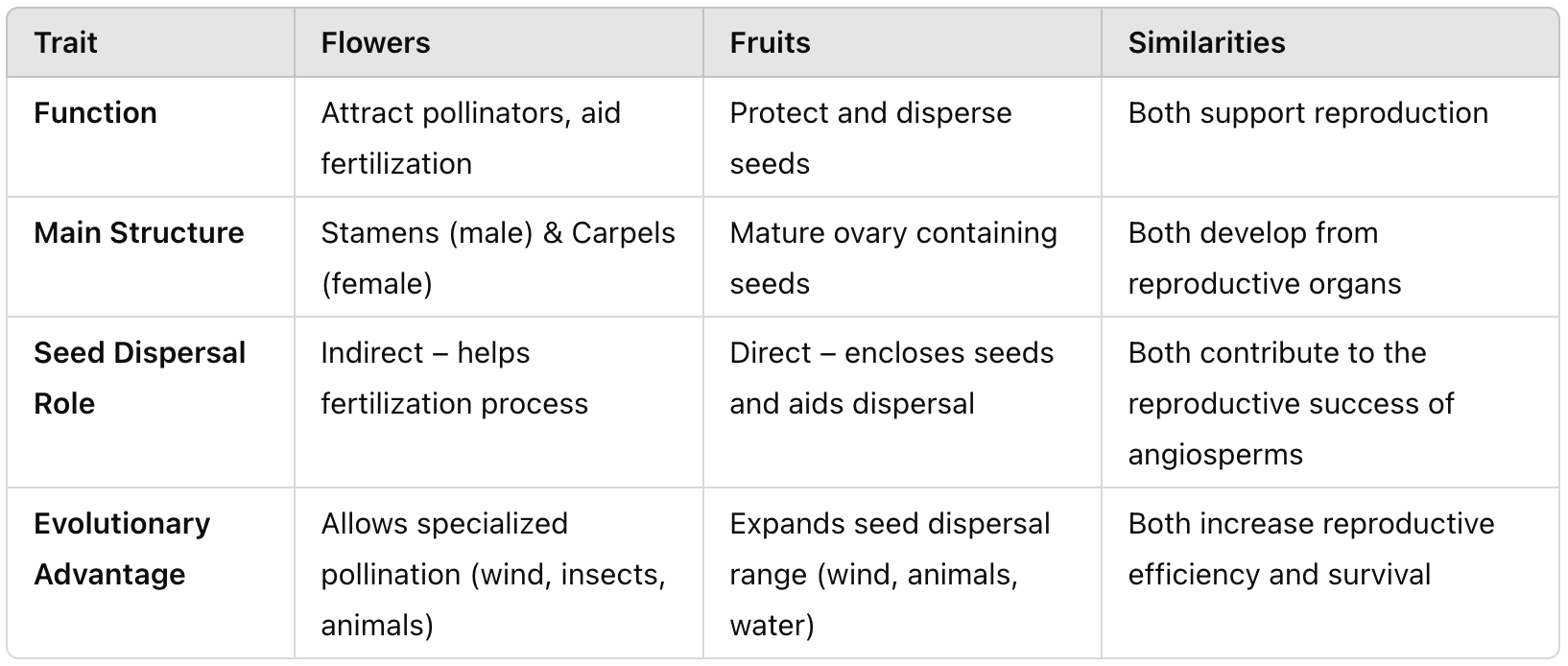
Compare gymnosperms and angiosperms in terms of reproductive structures.
Gymnosperms use cones; angiosperms use flowers and fruits.
Compare gymnosperms and angiosperms in terms of fertilization.
Gymnosperms use direct pollen transfer; angiosperms undergo double fertilization.
Compare gymnosperms and angiosperms in terms of seed dispersal.
Gymnosperms rely on wind; angiosperms use fruit for seed dispersal.
Compare gymnosperms and angiosperms in terms of diversity.
Angiosperms are far more diverse and widespread than gymnosperms.
Compare and contrast derived traits of seed plants in terms of seed protection, reproductive structure, pollination, fertilization, seed dispersal, and diversity.
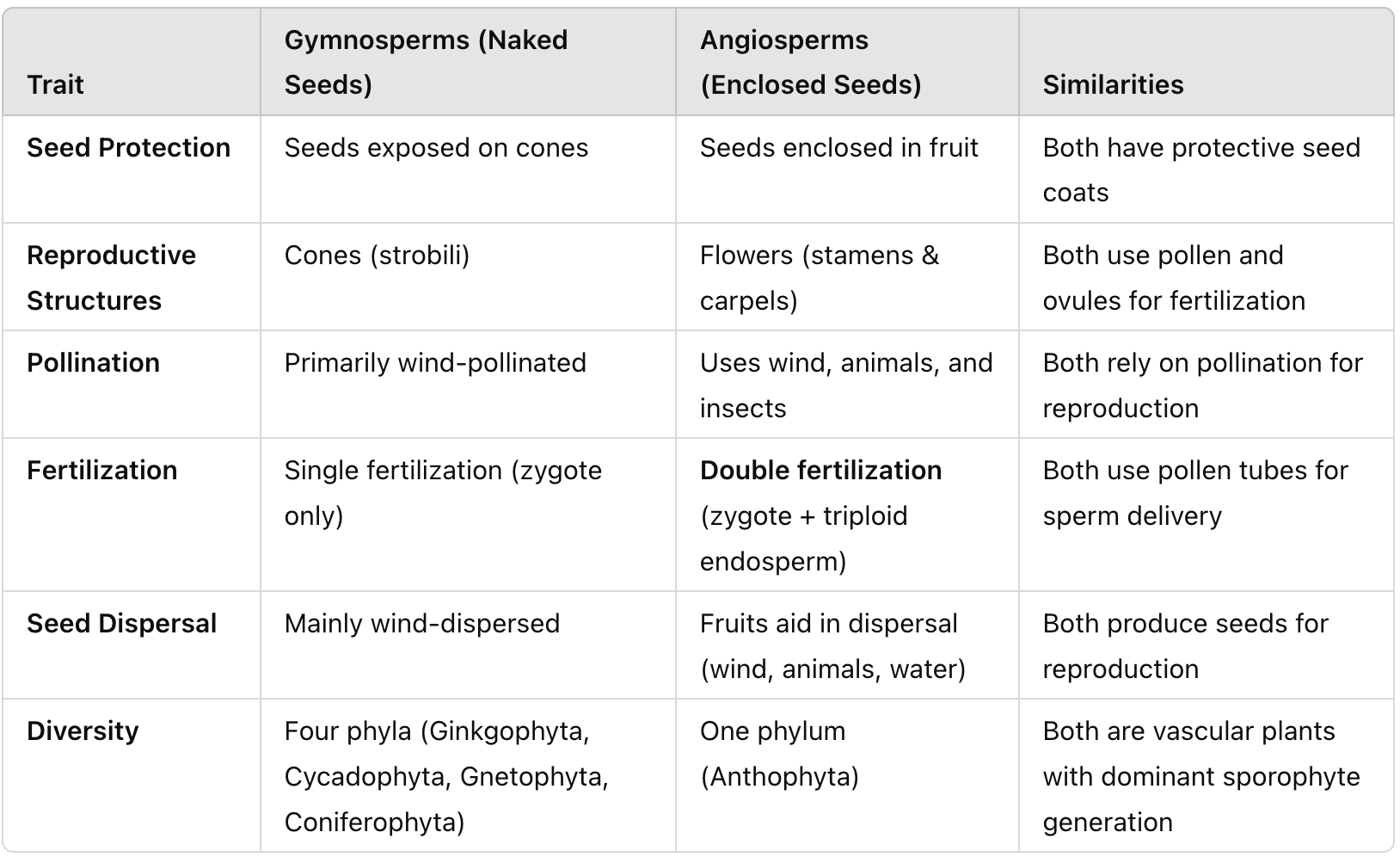
Compare and contrast derived traits in different types of angiosperms in terms of their function, main structure, seed dispersal role, and evolutionary advantage.