AP Psychology Social Psychology
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Altruistic Behavior
helping behavior that is not linked to personal gain; recognition and reward are not expected
Attribution Theory
theory that addresses the question of how people make judgments about the causes of behavior; theorist Heider argued that a given behavior is attributed to either internal or external causes, but not both
Authoritarian Personality
source of prejudice; bigoted personality or persons who are rigidly conventional, tradition abiding, and exhibit hostility towards those who defy norms
Cognitive Misers
Susan Fiske and Shelley Taylor; idea that human thinkers are stingy with our mental efforts; Example: we keep our first impressions of despite evidence to the contrary
Foot-in-the-Door Effect
technique to ensure conformity; strategy that states once a person grants a small request, they are more likely to comply with a larger one; Example: once a sales pitch begins the odds of the sale increase because the individual is listening to the request

Lowball Procedure
technique to ensure conformity; strategy to induce a person to agree to something by enticing the individual with a low 'cost' and then add-on to the original product; Example: buy a car with no options, but when you add-on the options you have paid more money

Door-in-the-Face Effect
technique to ensure conformity; strategy where the individual feels guilty because the first request was refused and therefore, agrees to the second request; Example: Mom can I have a thousand dollars? No, then can I have $20?
Conformity
voluntarily yielding to social norms, even at the expense of one's own preferences; necessary for social groups to function effectively; studies by Solomon Asch
Contingency Theory
Fiedler; personal characteristics are important to the success of a leader: task-oriented, relationship-oriented
Cultural Truism
belief that most members of society accept as true; "normal" or "right ways" to behave; typically learned through modeling, imitation, and conditioning; Example: norms, folkways, mores, and laws
Defensive Attribution
tendency to attribute our successes to our own efforts or qualities and our failures to external factors; motivation to present ourselves well; Example: self-serving bias or just-world hypothesis
Deindividuation
loss of personal sense of reasonability of a group; the more anonymous a person feels in a group, the less responsible s/he feels as an individual; used to explain mob behavior; can be influenced by the snowball effect
Exchange
factor that shows how closely linked people are; concept that relationships are based on trading rewards with another person; part of the reward theory of attraction
Frustration-Aggression Theory
a source of prejudice; result of the frustrations experienced by the prejudiced group; people who exploited and oppressed often cannot vent their anger against an identifiable or proper target so they displace their hostility onto persons lower on the social scale than themselves
Fundamental Attribution Error
tendency to attribute the behavior of others to causes within themselves; overemphasizes personal causes for other people's behaviors and to underemphasize personal causes for their own behavior; part of the actor-observer effect
Great Person Theory
are leaders extraordinary people who assume positions of influence and then shape the events around them or do the event produce great leaders?
Hawthorne Effect
principle that people will alter their behavior because of researchers' attention and not necessarily because of manipulations of the setting; study of the relationship between productivity and working conditions at an electric plant, productivity increased because of the researchers presence and not because of the change in lighting effects
Industrial/Organization Psychology
field that is concerned with the application of principles to the problems of human organizations, especially at work
Just-World Hypothesis
an attribution error; based on the assumption that bad things happen to bad people and good things happen to good people; jumping to conclusions than give full weight to the situational factors that may have been responsible
Polarization
phenomena where individuals become more extreme in their attitudes as a result of group discussion; Example: jury
Prejudice
an attitude; intolerant, unfavorable, and rigid view of a group of people; assumption that all members of a group share certain negative qualities; unable to see members of a group as individuals; ignore information that disproves beliefs; theories such as frustration-aggression theory and racism often account for prejudice; expression of suspicious, mistrusting approach to life
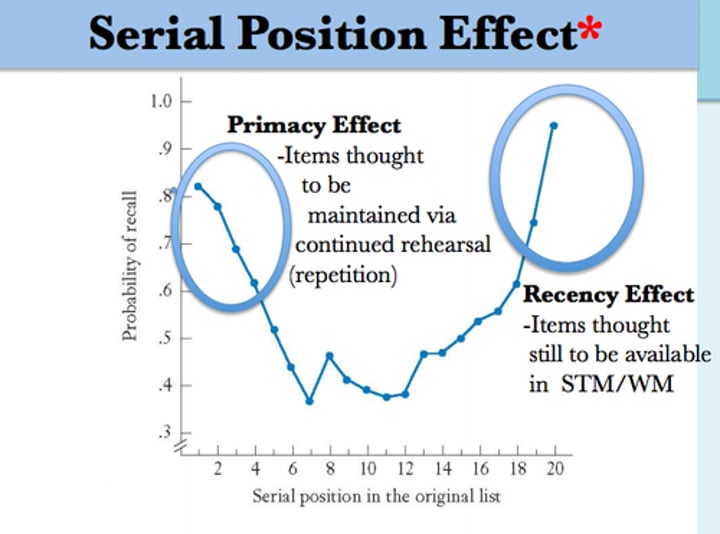
Primacy Effect
Theory that early information about someone weighs more heavily than later information in influencing one's impression of that person;
Racism
belief that members of certain racial or ethnic groups are innately inferior; belief that intelligence, industry, morality, and other valued traits are biologically determined and therefore cannot be change; when prejudice and discrimination are directed at a particular racial or ethnic group
Risky Shift
phenomenon where a group will take larger risks than if an individual was making the decision
Schema
(plural: schemata) a set of beliefs or expectations about something based on past experience; mental representation of an event, object, situation, person, process, or relationship stored in memory that leads one to expect an experience to be a certain way; Example: if you are in a room with a chalkboard and desks, schema leads you to believe that you are in a classroom of a school
Similarity
factor that shows how closely linked people are; complementary traits of attitudes, interests, values, backgrounds, and beliefs; part of the reward theory of attraction
Social Influence
process by which others (individually or collectively) affect our perceptions, attitudes, and actions; includes cultural influence, cultural assimilators, conformity, compliance, and obedience
Social Loafing
phenomena where people exert less effort when working in groups than they would if working individually because they assume that other group members will do the work

Stereotype
A set of characteristics believed to be shared by all members of that social category; stereotype is a special type of schema; inference based on social category and ignores facts about the individual's traits
Attitude
relatively stable organization of beliefs, feelings, and behavior tendencies directed toward something or someone—the attitude object; can include facts, opinions, and general knowledge about the object
Bystander Effect
situational variable; as the number of passive bystanders increases, the likelihood that any one of them will help someone in trouble decreases; used to explain the death of Kitty Genovese
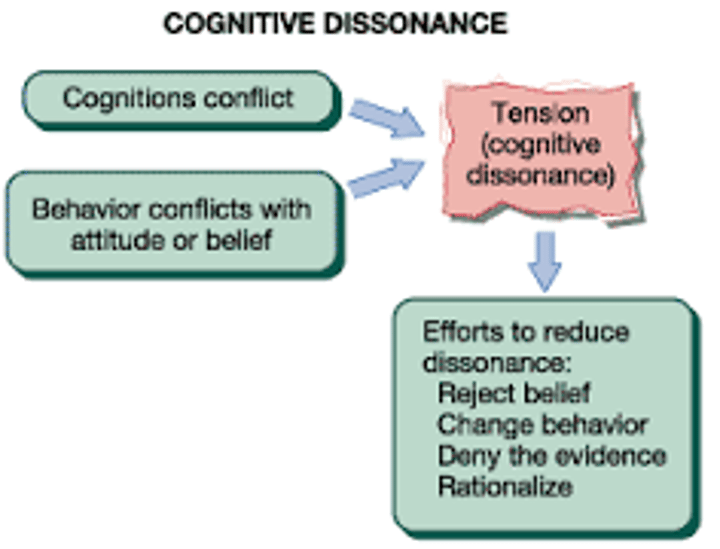
Cognitive Dissonance
perceived inconsistency between two thoughts; when a person has 2 contradictory or opposite thoughts at the same time;
Compliance
change of behavior in response to an explicit request from another person or group; techniques to ensure include foot-in-the-door effect, lowball procedure, door-in-the-face effect
Cultural Norm
shared idea or expectation on how to behave; strengthened by habit; folkways-social norms that are acceptable by society (covering mouth when you cough), mores-norms taught by family and community with a religious or moral basis (obey your mother and father, do not kill), and laws-enforced by government (speeding, murder)
Culture
tangible goods and the values, attitudes, behaviors, and beliefs that are passed from one generation to another
Discrimination
a behavior; an act or series of acts that denies opportunities and social esteem to an entire group of people or individual members of a group; to treat a group as less than equal
In-group bias
members see themselves not just as different but also as superior to members of out-groups
Intimacy
factor that shows how closely linked people are; the quality of genuine closeness and trust achieved in communication with another person; part of the reward theory of attraction

Obedience
compliance with a demand, especially when it comes from an authority figure; Study by Milgram-shock experiment
Proximity
factor that shows how closely linked people are; how close two people live to each other
Self-fulfilling Prophecy
process in which a person's expectation about another elicits behavior from the second person that confirms the expectation; evidenced in a study by Rosenthal and Jacobsen at an elementary school where students performed to the teacher's expectation, AKA Pygmalion Effect
Self-Monitoring
part of attitude; tendency for an individual to observe the situation for cues about how to react; do you match your actions to your attitude or do you override your attitude in order to behave properly in a given situation; high self-monitors look at the situation for cues on how to react whereas low self-monitors express and act their attitudes with consistency regardless to situational cues

Social Psychology
Scientific study of the ways in which the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of one individual are influenced by the real, imagined, or inferred behavior or characteristics of other people;