14. therio- bovine abortion
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
what is the importance of accurately diagnosing the cause of abortion in cattle?
important since herd prognosis and prevention/control depend on it

how are tentative diagnoses of abortion made?
by evaluating clinical signs, herd history, and pathologic findings

what is the definition of abortion?
loss of a fetus between days 42-260 of gestation
tissues are not resorbed, but expelled

what defines early embryonic death?
death of an embryo/fetus before day 42 of gestation
what defines a stillbirth?
death of a fetus after day 260 of gestation
what is the typical incidence of bovine abortion?
around 10% from day 42-260 (decreases monthly with an increase during the last month of gestation)
4-5% are stillbirths

t or f: in most instances, an abortion outbreak is over by the time a diagnosis is made
true
why are most fetuses presented for examination in the second half of gestation?
likely because fetuses aborted earlier go unobserved
how are most cases of epidemic abortions diagnosed?
by laboratory procedures (need multiple samples to show a consistent etiology)
is it more difficult to diagnose sporadic or epidemic abortions?
more difficult to diagnose sporadic abortion
are current lab procedures helpful for diagnosing abortions due to non-infectious causes?
no, current lab procedures are of little use for diagnosing non-infectious abortions
what is the rate of abortion laboratory diagnostic success?
30-35%
why is the rate of diagnosis in cases of bovine abortion so low?
-abortion may result from an event that occurred weeks to months earlier
-the fetus is often retained in the uterus for hours or days after death and autolysis obscures diagnostic lesions
-incomplete diagnostic specimens available/submitted
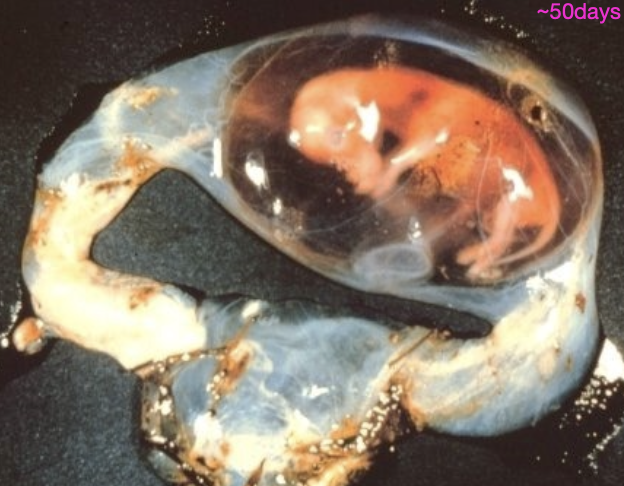
why may an aborted fetus not have any significant lesions?
due to autolysis or a rudimentary inflammatory response (immature immune system)

what samples from the fetus should be submitted to the lab for abortion diagnosis?
-weigh or estimate weight of fetus
-measure crown-rump length and note sex
gestation in days X = 2.5(CRL+21))
-submit entire fetus and placenta when practical (CRL < 25cm), chilled, not frozen
-note any gross lesions on fetus or placenta
what is the single most important diagnostic specimen for investigating cause of abortion?
placenta
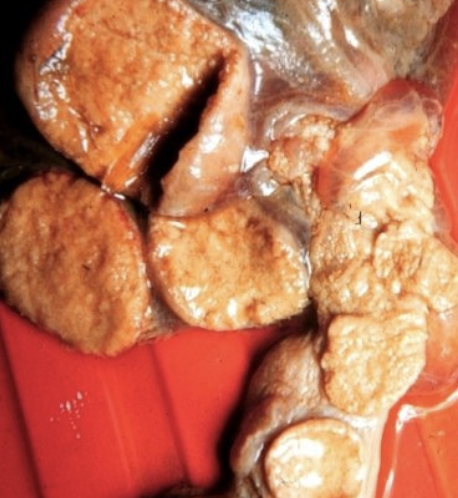
how should samples be submitted for abortion diagnosis for histopathology?
10% non-buffered formalin:
-placenta (multiple sections)
-lung
-liver
-heart
-skeletal muscle (tongue, diaphragm)
-kidney
-brain 1/2
-eyelid

what samples from the dam should be submitted to the lab for abortion diagnosis?
serum
urine
vaginal discharge (for trich/campylobacter)

how beneficial are submitting paired serum samples in providing a diagnostic cause of abortion?
rarely contribute additional significant diagnostic information (may be useful for lepto tho)
dams serum Ab to the abortigenic organism has usually reached max concentration by the time abortion occurs
how should paired serum samples be collected/submitted for diagnosis of abortion?
10 animals or 10% of herd should be sampled
-2-3 week sampling intervals
-4 fold rise in titer indicates infection is active in herd
what are the major categories of bovine abortigenic organisms?
1. bacteria (mainly opportunistic)
2. viruses
3. protozoal abortion
4. mycotic abortion
5. toxins
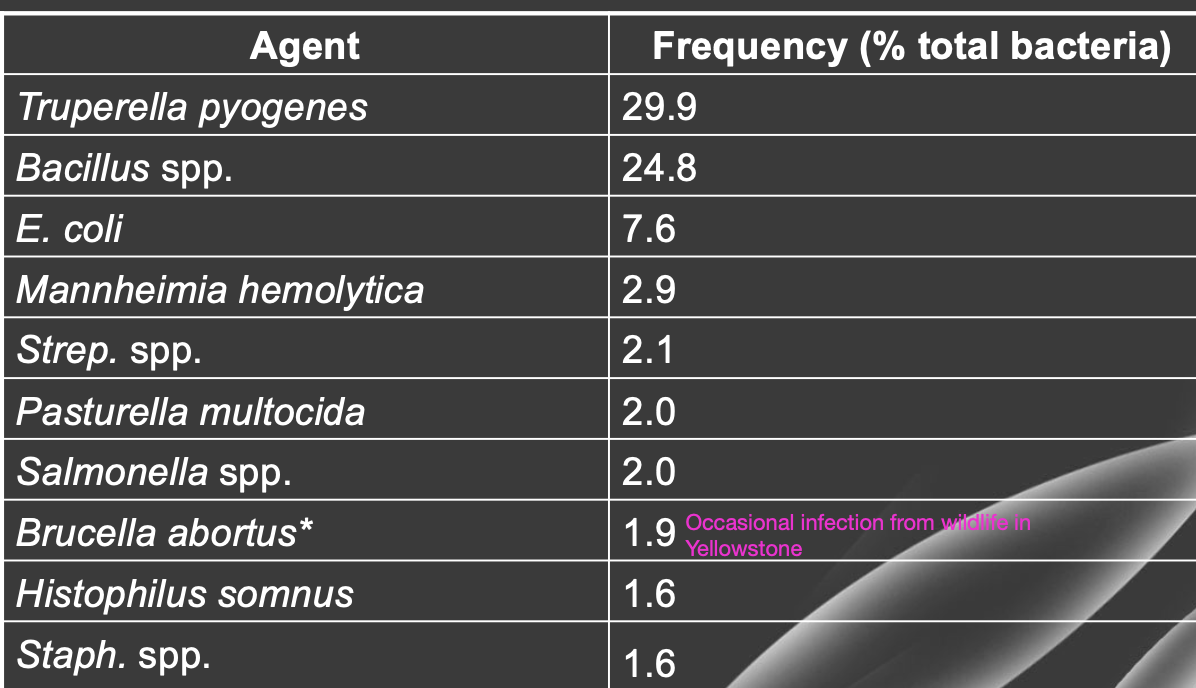
what are the most common bacteria isolated from cases of bovine abortion?
truperella pyogenes
bacillus spp.
e. coli
mannheima hemolytica
etc.
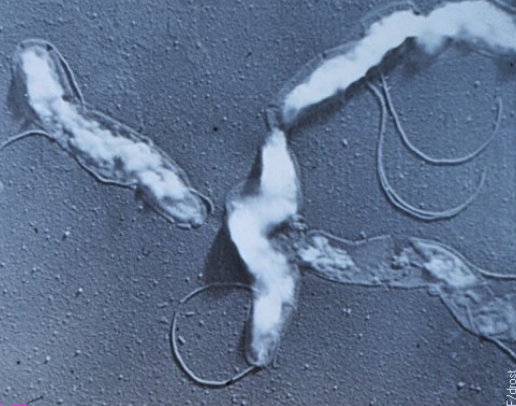
what is vibrio/vibriosis?
aka genital campylobacteriosis, infection caused by an obligate parasite of the bovine repro tract
organism: camplylobacter fetus venerealis
motile, gram-negative, curved or spiral, polar flagellated, microaerophilic bacteria
which animals are asymptomatic carriers of vibrio?
bulls
transiet in bulls under 4yrs (bc under-/non-developed crypts)
how is vibrio transmitted?
venereal (coitus) transmission
what are consequences of vibriosis in the cow?
-occasional abortions (EED or fetal death)
-endometritis, placentitis, salpingitis (pyometra is rare)
-irregular estrous cycles
-transient infertility
where does vibrio persist once infected in the cow?
persists in the uterus/uterine tubes for weeks to months
persists in the vagina for up to 24 months (these animals are carriers)
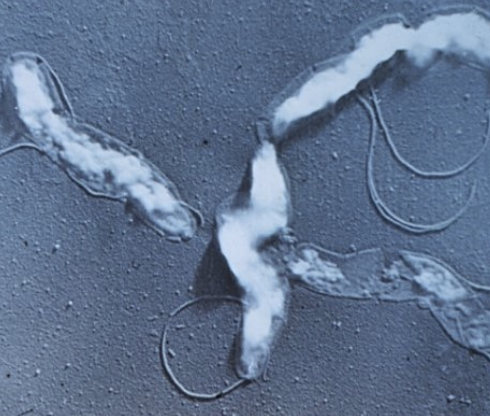
how is vibriosis diagnosed?
-herd history: irregular return to estrus, low pregnancy rate, or wide range of gestational ages
-culture or PCR
-ELISA on vaginal mucus
what samples are needed from the bull, cow, and calf/fetus for PCR/culture of virbiosis?
bull: preputial aspirates
cow: vaginal aspirates during estrus
calf: lung, spleen, placenta, abomasal fluid
use transport enrichment media (TEM) at room temp
how long after infection do cows and heifers clear vibrio infections?
cows and heifer mount immunity and clear infection in 4-8 months
issue is: if they are pregnant, abort, and become pregnant again, they are still carriers and can abort again
how is vibriosis controlled?
-vaccinate cows and bulls *vaccine can help prevent and treat!
-remove positive bulls
-use AI for 2 years

what is brucellosis?
caused by b. bovis, a gram negative coccobacillus that survives and multiplies within phagocytic cells and lymphocytes (stops lysosome-phagosome fusion)
how is brucellosis transmitted?
via ingestion
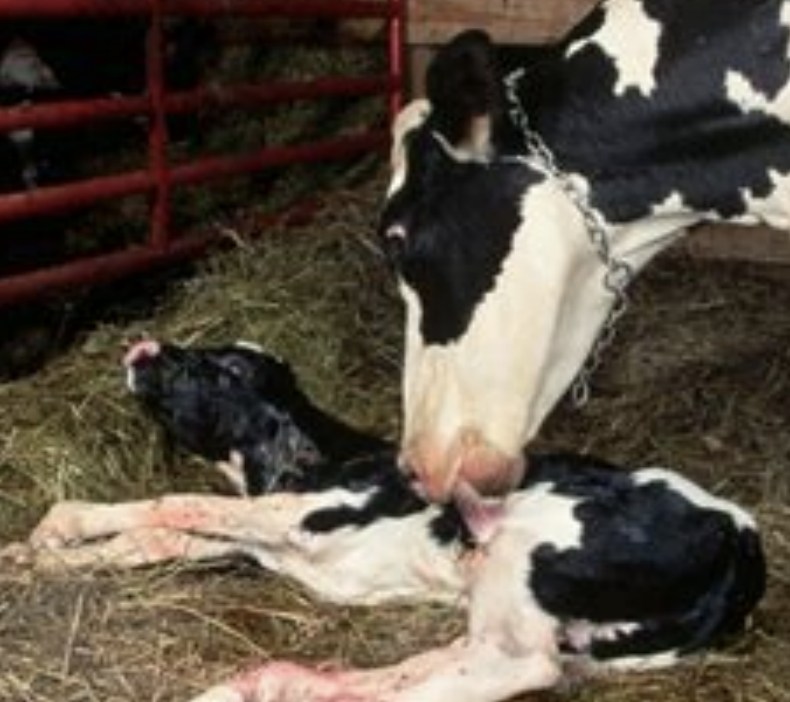

how long do infections with brucellosis last?
infection persists indefinitely
what do brucellosis infections in bulls and pregnant cows result in?
bulls: orchitis
pregnant cows: abortion after 5 months gestation
how is brucellosis controlled?
control based on surveillance and vaccination
what are the 2 types of strains of leptospirosis infections in cattle?
1. host adapted (maintenance) strains
2. non-host adapted strains
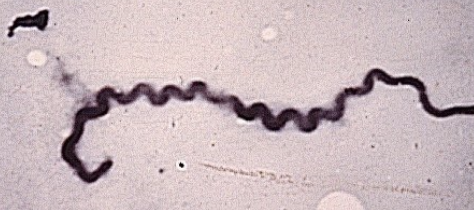
what type of disease do host-adapted strains of lepto cause?
have efficient transmission, chronic disease, persistent infection
low antibody response
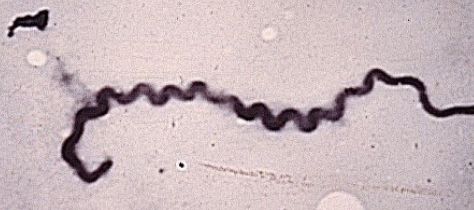
what are consequences of host-adapted strains of lepto in cows?
abortion
stillbirth
infertility
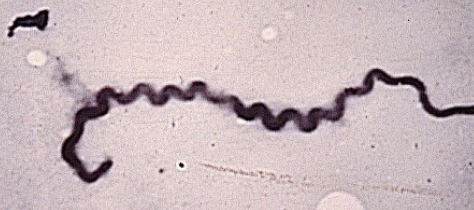
what type of disease do non-host adapted strains of lepto cause?
acute, sporadic disease
marked antibody response
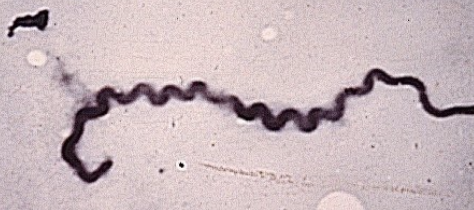
how do leptospirosis infections occur? where do organisms localize?
penetrates intact mucus membranes and survives outside of the host
localizes in renal tubules and uterus
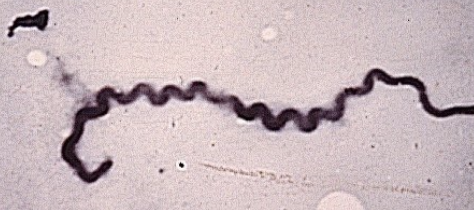
what is the nomenclature for leptospirosis (how is it named)?
generic name
followed by species name
followed by serovar
followed by strain or serogroup
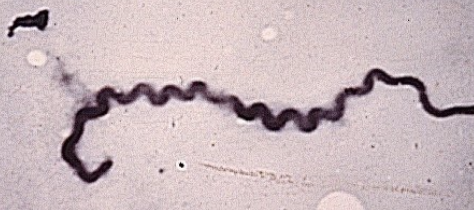
how does lepto hardjo (hardjo bovis) cause abortion?
causes unexplained infertility, including early embryonic deaths
what should you do if you find 1 positive cow for lepto hardjo in a herd?
vaccinate the whole herd with hardjo-bovis vaccine, including calves
does the lepto hardjo-bovis vaccine prevent and eliminate lepto?
the vaccine prevents, but does not eliminate lepto or prevent transient infection (shedding)
how are cows chronically infected with lepto hardjo-bovis treated to prevent obtaining permanent damage to repro tract?
antibiotics (oxytet) given during dry period
what is the most frequently diagnosed viral cause of bovine abortion?
BHV-1 (infectious bovine rhinotracheitis; IBR)
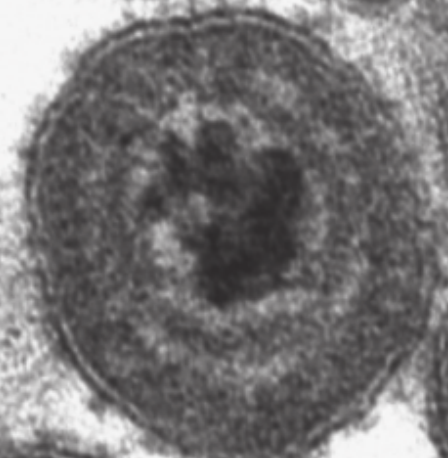
how is IBR transmitted?
direct contact and venereal transmission
when are abortions seen in cows infected with IBR?
may abort at any stage, most abortions occur in second half of gestation (fetal autolysis, RFM)
what pathologies occur when cows are infected with IBR at breeding by an infected bull?
necrotizing endometritis, IPV (infectious pustular vulvovaginitis), lysis of CL resulting in early embryonic death
how is IBR diagnosed?
detect viral antigen or virus in tissue (fluorescent antibody on fetal kidney)
why should you use caution with the IBR vaccine?
bc it is a modified live vaccine- if a heifer is vaccinated with the MLV while pregnant and has not previously been vaccinated for IBR, the rate of abortion in these animals is fairly high
what do the consequences of BVDV infections depend on?
depend on stage of gestation (can cause luteolysis or directly affect fetus)
what occurs to the fetus when the dam is infected with BVDV near conception?
embryonic death
what occurs to the fetus when the dam is infected with BVDV 42-125 days gestation?
infection with non-cytopathic biotype results in fetal death, or persistently infected calf
what occurs to the fetus when the dam is infected with BVDV after 100 days gestation?
congenital defects (cerebellar hypoplasia, ocular defects, stunted growth)
-cytopathic: + titer at birth, virus negative
-non-cytopathic: no titer, virus +
what occurs to the fetus when the dam is infected with BVDV 125-170 days gestation?
may abort
(+) titer (cytopathic)
(-) non-cytopathic
what occurs to the fetus when the dam is infected with BVDV after 170 days gestation?
normal calf, + titer (at this point, the calf's immune system is fairly developed)
what organisms most commonly cause protozoal abortion?
trichomoniasis
neosporosis
what organism causes genital trichomoniasis?
tritrichomoniasis foetus- a single celled protozoan
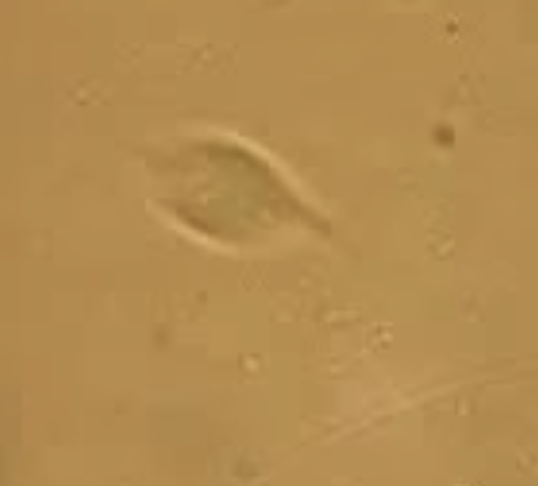
how is trichomoniasis transmitted?
venereal transmission (no systemic illness)
which animals are permanent carriers of trichomoniasis?
bulls, more commonly in bulls over 5 years old
mostly seen in beef cattle since breeding is done by natural service
what disease processes is trichomoniasis associated with?
-early embryonic death
-infertility (due to vaginitis, cervicitis, endometritis, salpingitis)
-rarely abortion during first half of gestation
-post-coital pyometra
how is trichomoniasis diagnosed?
via preputial scrapings/aspirates with rtPCR
collect in phosphate buffered saline, in-pouch TF, biomed TF tube
how is trichomoniasis controlled?
-vaccination of females stimulates antibody production
-vaccine is LIMITED in bulls
-test bulls, use AI, or use virgin bulls
how effective is the trichomoniasis vaccine in cows and bulls?
-causes females to clear infection in 6-10 weeks
-vaccines have limited efficacy in bulls
what is the treatment for trichomoniasis?
no approved treatment
is trichomoniasis reportable?
yes, its a reportable dz in oregon
what is neospora-associated abortion caused by?
protozoan parasite neospora caninum
this is a major cause of infectious bovine abortion

how does neosporosis cause abortion?
organism is maintained in cattle as a chronic persistent infection that is efficiently passed on to the fetus during pregnancy
once infected, animals are infected for life

what are the possible fates of calves congenitally infected with neosporosis?
may be aborted
but most are born alive and appear normal

how is neosporosis transmitted?
vertical: in utero from infected cows
horizontal: ingestion of sporulated oocysts in feces (from feces of dogs)
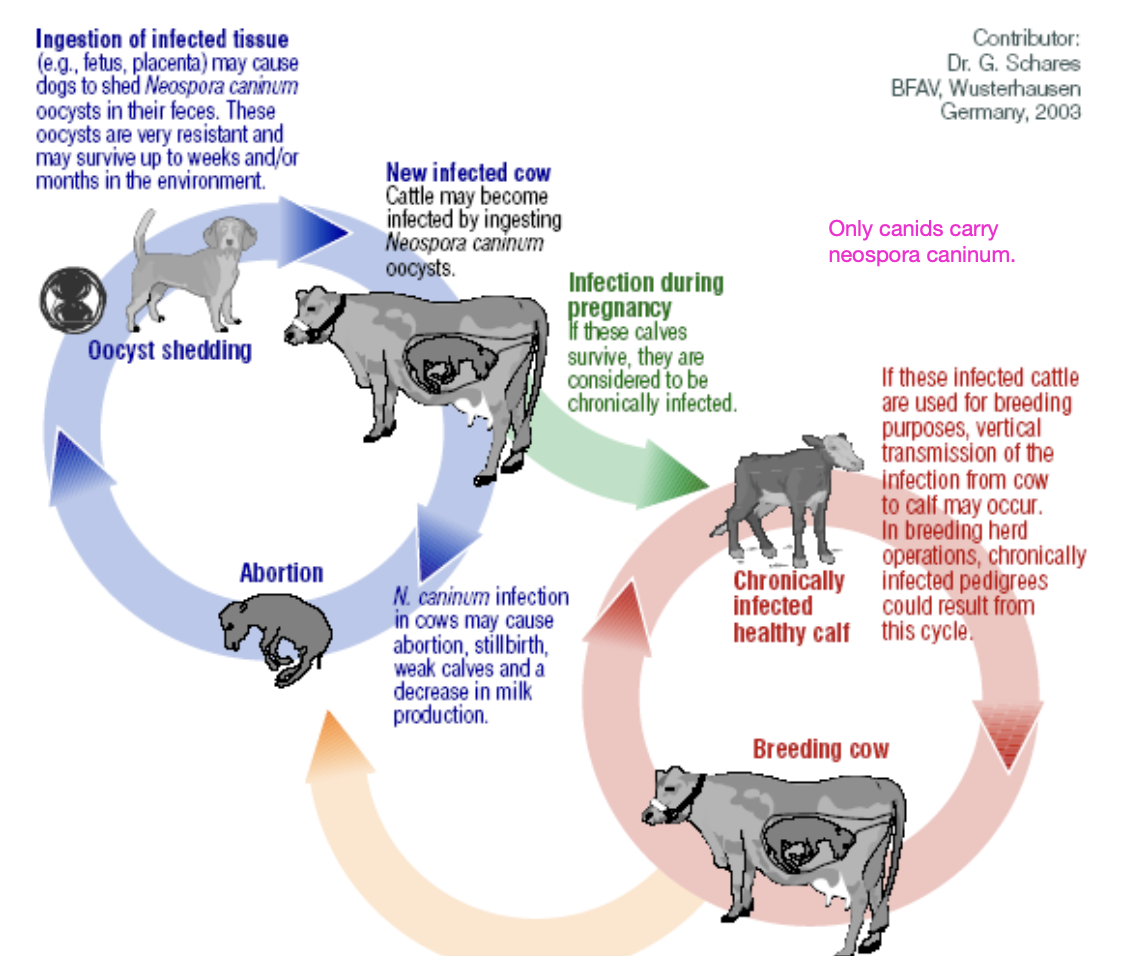
what is the primary manifestation of neosporosis?
abortion mid-gestation
how will aborted/live fetuses of neospora-infected dams present?
aborted: autolysed fetus (4-6 months), occasional mummification of younger fetuses
live calves may have neurologic disease (encephalomyelitis)

will neospora-infected dams show any clinical signs of illness?
no
what is the epidemiology of neospora-associated abortion in cattle?
abortions may be endemic or epidemic
-endemic: persistently elevated abortion rate of over 5%/year
-epidemic: high proportion of pregnant cattle abort over a relatively short period of time
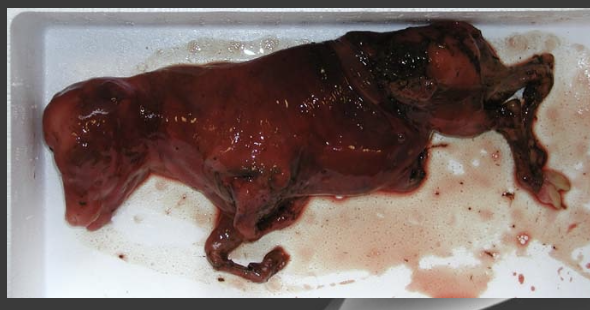
are cattle who abort fetuses due to neosporosis immune to the organism?
no, aborting cattle are not immune and are at increased risk of aborting subsequent pregnancies
how is neosporosis diagnosed?
-examination of aborted fetuses (gestational age, disseminated lesions of brain, lung, heart, muscle, placenta, presence of detectable parasites)
-serologic tests on dam and fetus (usually a diagnosis by elimination)
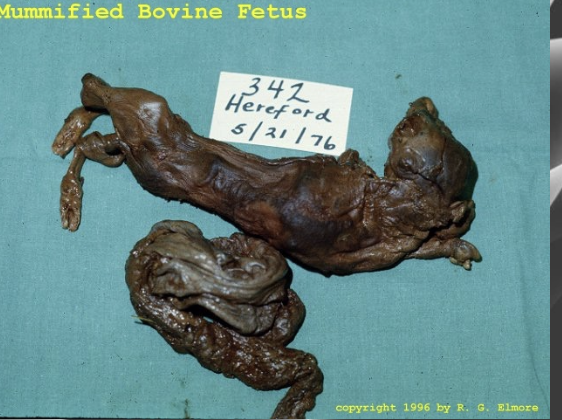
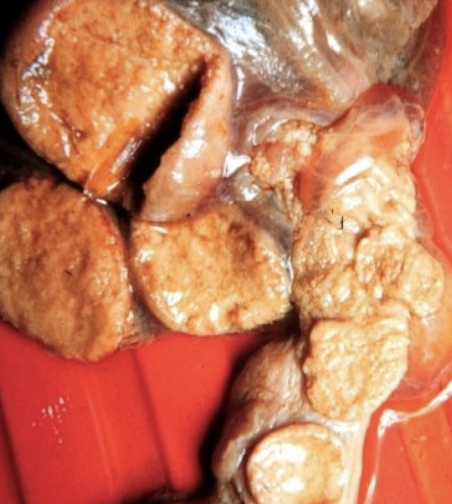
what is the cause of mycotic abortion?
caused by various molds and yeast, most commonly by aspergillus fumgatus
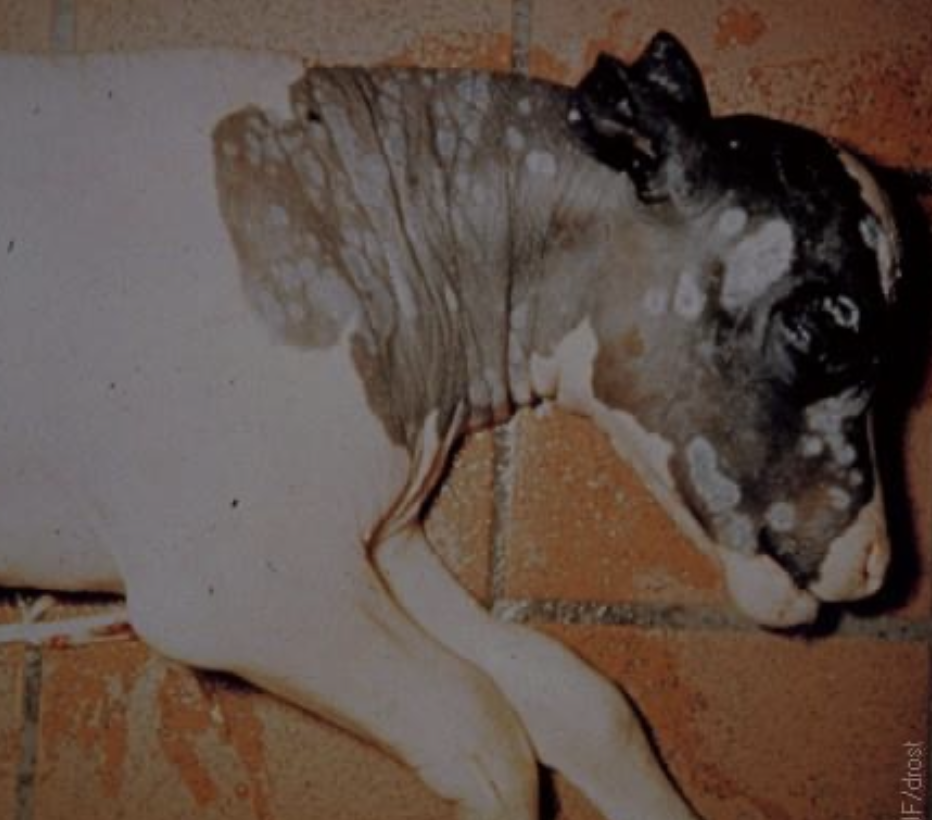
when are mycotic abortions seen?
seen when cattle are confined and fed hay, usually abort at 6-8 months gestation
will have RFMs
how are causes of mycotic abortions transmitted from cow to cow?
likely enters via GI or respiratory systems --> hematogenous--> placentomes
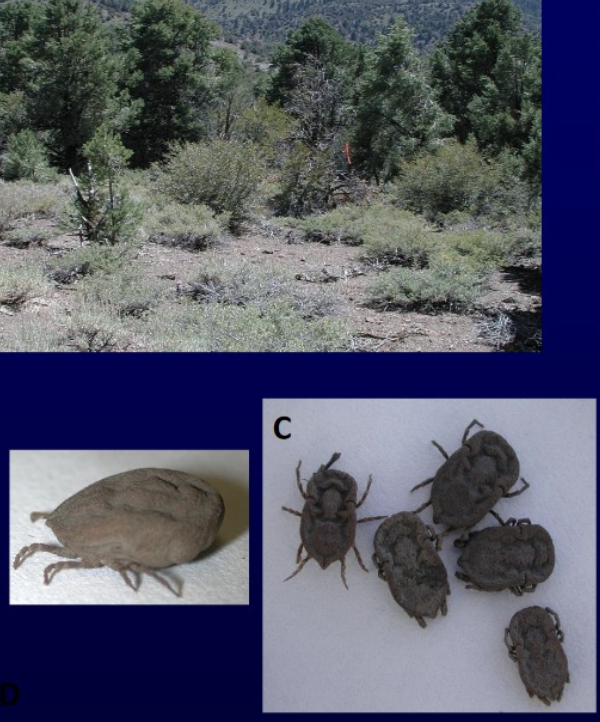
where does foothill abortion occur?
in the foothills and mountain areas of NV, CA, and southern OR
in bushy, wooded areas that provide deer habitat (bc transmitted by deer ticks)

which animals are affected by foothill abortion?
cattle can develop natural immunity so only naïve cattle are affected

when do abortions occur with foothill abortion?
late (6-9 months) term abortion
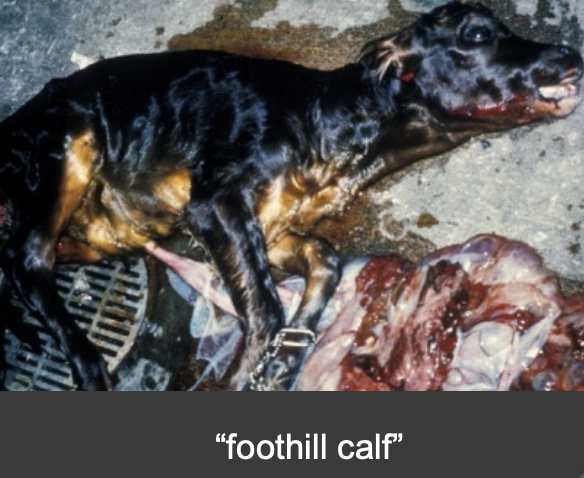

what is the vector of foothill abortion?
ornithodoros coriaceus (pajaroello ticks): feed on deer and cattle
bacteria: myxococcales- pajaroellobacter abortibovis

does foothill abortion cause systemic illness in cows?
no
what is the interval from exposure to abortion in cows infected with foothill aboriton?
3-5 month interval
so, only cattle exposed before 6 months gestation are affected (will never see early abortions)
what lesions are seen in aborted fetuses due to foothill abortion?
petechial hemorrhages and enlarged LNs, enlarged liver, hemorrhage and enlarged thymus
aborted calves have very high IgG

how is foothill abortion diagnosed?
-history, region, gross and microscopic lesions
-IHC
-PCR
-fetal serology in pre-colostral calves or aborted calves

how is foothill abortion controlled?
-minimize exposure of naive animals to ticks from 60 days pre-breeding
-expose heifers pre-breeding (to develop immunity)
-breed in winter months for fall calving

what are the consequences of poison hemlock ingestion in pregnant cows?
multiple congenital contractures, cleft palate

what are the consequences of lupine ingestion in pregnant cows?
arthrogryposis if exposed days 40-70

what are the consequences of locoweed ingestion in pregnant cows?
abortion, hydrops, teratogen

what are the consequences of snakeweed ingestion in pregnant cows?
premature, weak, dead calves

what are the consequences of fescue ingestion in pregnant cows?
decreased prolactin, lower conception rates
what are the consequences of gossypol ingestion in bulls and cows?
affects bull fertility, unknown for females
what are the consequences of phytoestrogen ingestion in pregnant cows?
like legumes/clover: cystic ovaries, anestrus
what are the consequences of pine needles ingestion in pregnant cows?
late term abortion (due to stress) or weak calves, abortion occurs 1-21 days after ingestion
ingestion of any stage pine needle causes abortion (isocupressic acid)

how does isocupressic acid cause abortion of calves?
causes constriction of caruncular arterial bed (starves calves of nutrients, causes hypoxia)