BIOL 3220 - Intro to Bioinformatics (Ch1-3)
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Iowa State University. Also known as: BCBIO 3220; List of questions from homework and daily quizzes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
The primary structural difference between pre-mRNA and mRNA is:
pre-mRNA contains introns but mRNA does not.
You were a geneticist working in cancer biology. You want to compare the expression of all genes between tumor cells and normal cells. To achieve a high coverage with lower cost, the best option is:
Illumina RNA-seq
Nucleotides are connected via phosphodiester bonds. Which structures are required for the extension of a nucleotide chain?
5’ P in the ribose and the 3’ OH in the ribose
Which step does not belong to PCR?
Annealing
Synthesis of new dNTPs
Denaturation
Extension
Synthesis of new dNTPs
During gel electrophoresis, longer DNA moves _____ than shorter DNA.
slower
During sequencing-by-synthesis, the modifications to dNTP do NOT stop DNA extension, because…
The modifications block the 3’OH end, but they are removed after releasing the fluorescent signals
In Sanger sequencing, how to end a DNA polymerization reaction?
By di-deoxy nucleotides that cannot react with the next dNTP
In modern Sanger sequencing, how to know the sequence of a DNA molecule?
Length of DNA fragments and fluorescent signals they produce
A 30x PCR will amplify the DNA template to _____ copies.
2^30
T or F: Classical Sanger sequencing can NOT distinguish four ddNTPs and therefore the sequencing reactions have to occur in 4 tubes.
True
T or F: Modern Sanger sequencing can distinguish four ddNTPs by fluorescent dyes, and therefore gel electrophoresis is not needed.
False
T or F: The positions of forward and reverse primers in a DNA template determine the size of the PCR product.
True
T or F: In PCR, reaction temperature often fluctuate between high and low, therefore one should provide excessive amount of polymerase in case the enzyme was denatured.
False
Illumina sequencing has four steps: sample preparation, cluster generation, sequencing by synthesis, and data analysis.
Which step is similar to PCR?
Cluster generation
Adaptors are NOT:
Sequences naturally present in the sample DNAs
Flow cell is:
A reaction platform for cluster generation and sequencing
The final product of illumina sequencing is:
Millions to billions of reads that contain the sequences of DNA templates
Illumina sequencing has four steps: sample preparation, cluster generation, sequencing by synthesis, and data analysis.
Which step is similar to Sanger sequencing?
Sequencing by synthesis
Abnormal alternative splicing is often detected in the developing tumors. You hypothesized that cancerous cells had transcripts that did not exist in the healthy cells. To validate this hypothesis, your best option is:
RNA sequencing by Nanopore or Pacbio
Which of the following correctly describes the workflow of mRNA-seq?
Total RNA extraction -> isolation of mRNAs -> Reverse transcription to generate ds cDNAs -> Sequence library preparation -> PCR amplification and sequencing
What is the purpose of PCR amplification in RNA-seq analysis?
Amplify the fluorescent signals such as even low-expressed genes are detectable
T of F: In fastq files, the sequencing quality of each nucleotide is represented by a number.
False
Temperature for Extension in PCR:
72 C
Temperature for Denaturation in PCR:
94 C
Temperature for Annealing in PCR:
56-60 C
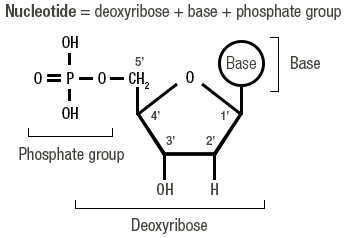
Which modification to dNTP will terminate the extension of DNA?
Replace the 3' OH with 3' H
Sanger PCR generates a series of DNA products decreasing by ____ in length.
one nucleotide
Gel electrophoresis separates DNA fragments by their…
lengths
If, from TOP to BOTTOM of the gel, the fluorescent signals read as "TGCAGTG" . The sequence of DNA template should be _____
GTGACGT
What is a barcode sequence?
A region within the adaptor to distinguish DNA templates
You are a biologist working in cancer genetics.
You have identified a gene involved in cancer cell migration. To obtain the sequence of this gene and avoid unnecessary cost, your best option is _____.
Sanger sequencing
You want to identify the genomic variations between cancerous cells and healthy cells, especially the variations in the protein-coding regions. To maximize the search results, the best option is ______.
100x whole-exome sequencing
In 2022, human genome project released the first complete human genome sequence, called “T2T” (telomere-to-telomere).
Which sequencing technology is likely used in T2T?
Pacbio and/or Nanopore whole genome sequencing
In RNA-seq, the reads come from…
RNAs transcribed from genes and cDNAs reverse-transcribed from RNAs
RNA-seq can be used to study…
gene expression differences between stem cells and immune cells and novel transcripts in the virus-infected tissues compared to the non-infected tissues
You are working on identifying SNPs that are only present in tumor cells. You have extracted total DNA from tumor cells and healthy cells, and used the extracts to perform 30x and 100x whole genome sequencing. 100x coverage identifies more cancer-specific SNPs than 30x, this is NOT due to:
100x coverage likely uses more input DNA, therefore SNP-rich regions are more targeted than the other regions
What sequences are NOT present in the raw reads of RNA-seq?
Introns and promoters
What sequences are removed by trimming?
Adaptors and low quality reads
The sequence of reads are mapped to the sequence of genome to obtain…
the coordinates of the reads
A GTF file includes…
the coordinates and strands of genes and their exons
The number of reads belonging to a gene is NOT influenced by…
the length of introns
To compare the expression level of gene A in sample X versus sample Y, one should…
use the read counts, but calibrated by total read count or calibrate by both length and total read count
You want to identify the differentially expressed genes between tumors and healthy tissues.
You performed the differential expression analysis with edgeR.
The contrast is specified as tumor - healthy
edgeR report the logFC of gene X is 2, which means:
X expression in tumors is 4-fold of its expression in healthy issues
To find the differentially expression genes between tumors and healthy tissues, I should use the following criteria: ____.
q-value < 0.05
To find the up-regulated genes in tumors and healthy tissues, I should use: ______.
logFC > 0 and q-value < 0.05
The reads of 3' QuantSeq should align to _____ (region) of an mRNA.
the region after the STOP codon
Many QuantSeq-based analyses avoid calibration by transcript length, and these analyses often use ____ as the expression unit.
CPM
What is required for RNA-seq data analysis?
Reference genome sequence, single-end or pair-end fastq files, GTF file, experimental design
Choose an appropriate analysis pipeline to find differentially expressed genes between the mutated cells and normal cells
Quality check and trimming -> genome alignment -> quantification -> differential expression analysis
Genome alignment requires…
genome sequence, genome annotation file, reads
Genome sequences are stored in ____ format.
fasta
Reads are stored in ____ format.
fastq
What is true about GTF files?
Used to match a read to a gene, lists transcript isoforms from a gene, contains the coordinates of full-length transcript
T or F: One RNA-seq dataset often contains millions of reads, it is possible that not every read has the same sequencing quality.
True
T or F: One should expect substantial variation in quality among reads, even with high-quality RNA-seq dataset.
False
T or F: The expression level of a gene is based on the expression of its transcript isoforms.
True
T or F: Without any calibration, read count of gene A is higher in the mutated cells than the healthy cells. Gene A is more expressed in the mutated cells.
False
T or F: You want to compare the expression of gene A and gene B in the cancerous cells. Because gene A has a longer transcript than gene B. You decide to calibrate the read count by the length of transcript. Because you want to compare the expression of two genes in the same sample, there is no need to calibrate by the total number of reads.
True
T or F: Your mentor argued that only one RNA-seq dataset from each cell type did not provide conclusive results. Therefore you grew more cell cultures and redid the RNA-seq. Because cell cultures and sequencing libraries were prepared under identical conditions, and sequenced by the same instrument, there is no need to calibrate by the total read count.
False
Differential expression analysis (by edgeR) requires…
non-calibrated read count of each gene in the sample, specify the contrast to calculate the fold change, and experimental design
In differential expression analysis, false discoveries are made because _____, and it can be avoided by _____.
too many genes are tested, having stronger cutoff on the q-values
TF ChIP-seq identifies the regulatory target genes by…
distance between peak and gene and using the antibodies to pull down the DNAs that are binding to TF
What is the primary purpose of motif analysis?
To identify recurring short sequences that likely have a biological function
What does the letter size of a motif logo represent?
The proportion of peaks having the same nucleotide at that position
Which genomic regions will have ATAC-seq reads but not RNA-seq reads?
Promoter
Which genomic regions will not have ATAC-seq reads?
Closed chromatin
The reads of Ribo-seq come from…
RNAs occupied by ribosomes
Ribo-seq combined with RNA-seq provides…
Translation efficiency of mRNAs and clues regarding post-transcriptional regulation
Differences between ChIP-seq and DAP-seq:
DAP-seq captures direct binding sites, while ChIP-seq captures both direct and indirect binding
For DAP-seq, the binding between TF and DNAs happens in a controllable environment; while for ChIP-seq, this happens within the cells.
You are working a research team that studies maize genetics. You identified two plant height-associated genes (Gene A and B). However, you don’t know the functions of these genes. You decide to align Gene A with the other known genes. Choose an appropriate method:
blastn
You are working a research team that studies maize genetics. You identified two plant height-associated genes (Gene A and B). However, you don’t know the functions of these genes.
You didn’t find any known gene showing high similarity to Gene A. You are curious whether you will get better results when using Protein A (product of gene A) as the query:
blastp
You are working a research team that studies maize genetics. You identified two plant height-associated genes (Gene A and B). However, you don’t know the functions of these genes.
You didn’t find any known protein matching Protein A. To expand your search, you decide to include all possible protein products from nucleotide database. You should use:
tblastn
You are working a research team that studies maize genetics. You identified two plant height-associated genes (Gene A and B). However, you don’t know the functions of these genes.
Gene B is computationally predicted to be a gene. You want to find the open reading frame of Gene B. Choose an appropriate method:
blastx
You are working a research team that studies maize genetics. You identified two plant height-associated genes (Gene A and B). However, you don’t know the functions of these genes.
The blastx search for Gene B is not successful. As a final check, you want to align all translations from Gene B against all possible products from the known genes:
tblastx