Early Christian and Byzantine Art
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Arch of Constantine
315 AD (IMPERIAL ROMAN ART)
Constantine converts to Christianity
makes the state religion of the Roman Empire
representing human form
short flat bodies —> Christian body
large heads —> Christian soul (emphasized)
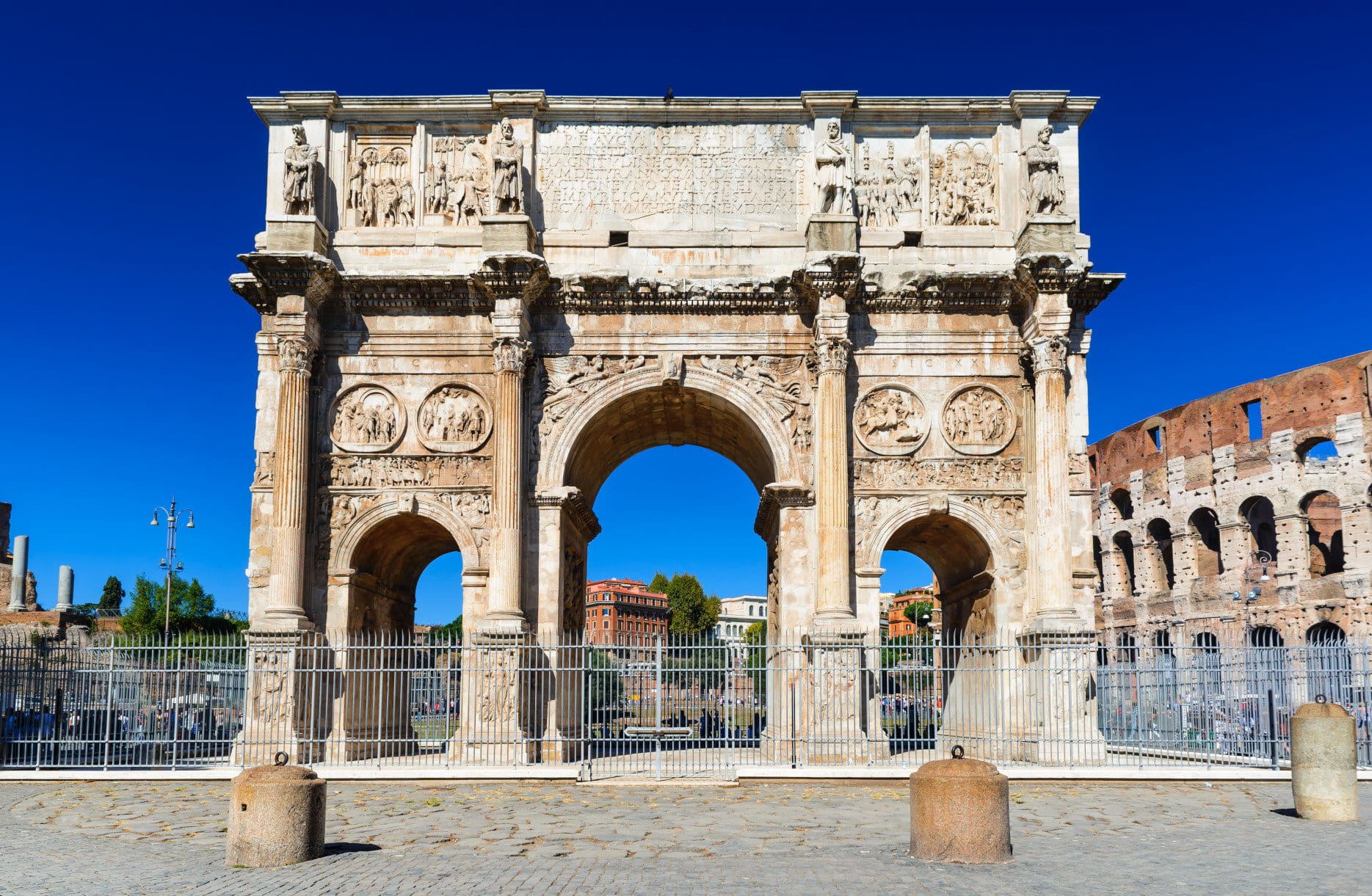

Catacombs
Rome, 3rd-4th c.
EARLY CHRISTIAN AND BYZANTINE ART
Loculi—> “shelves” of Christian bodies were entombed (estimated 4 million bodies entombed)
Orant figure—> prayerful pose (Christ, crucifixion, Christ in the temple)
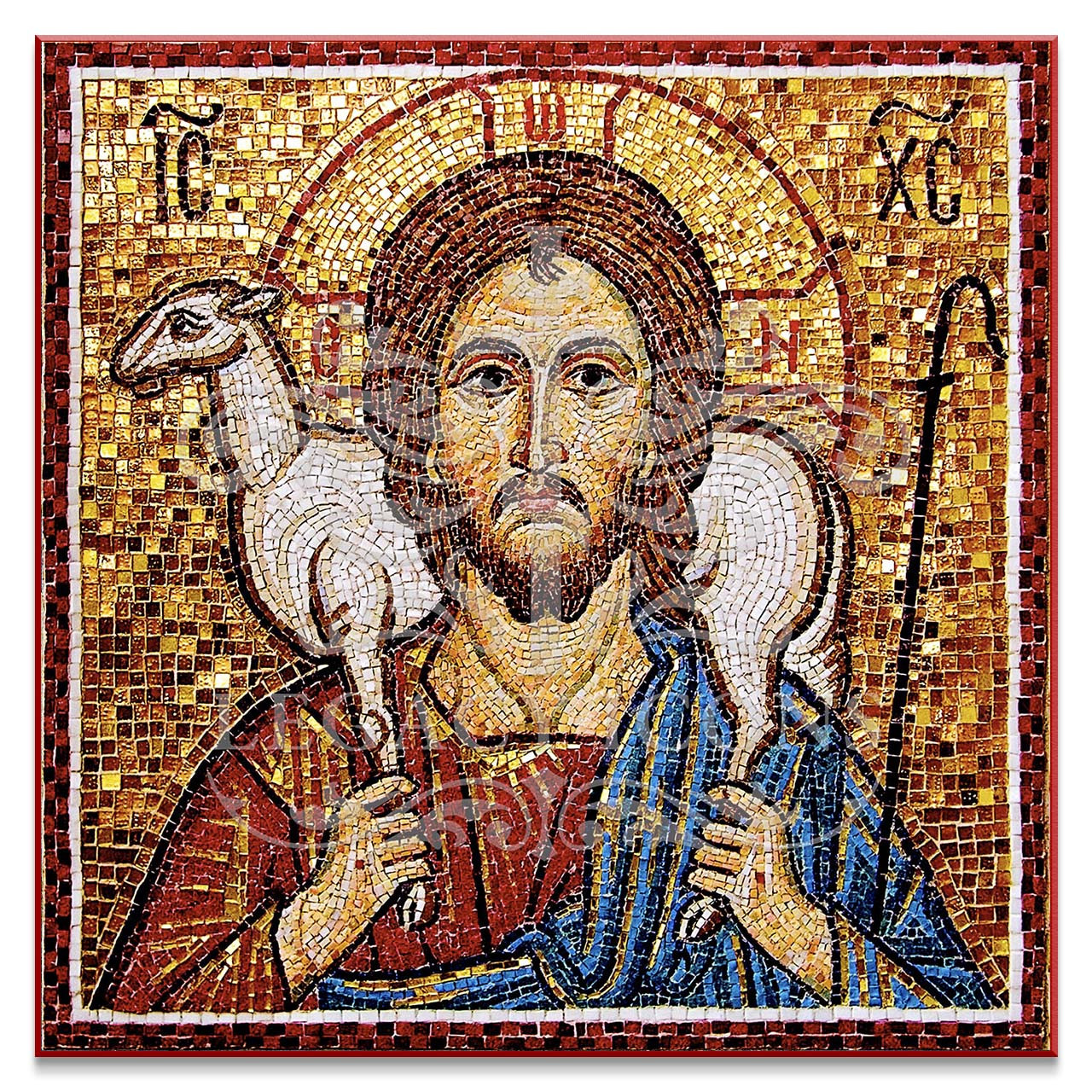
Good Shepherd—> figure of Christ, New Testament book of John

Loculi
“shelves” of Christian bodies were entombed (estimated 4 million bodies entombed)
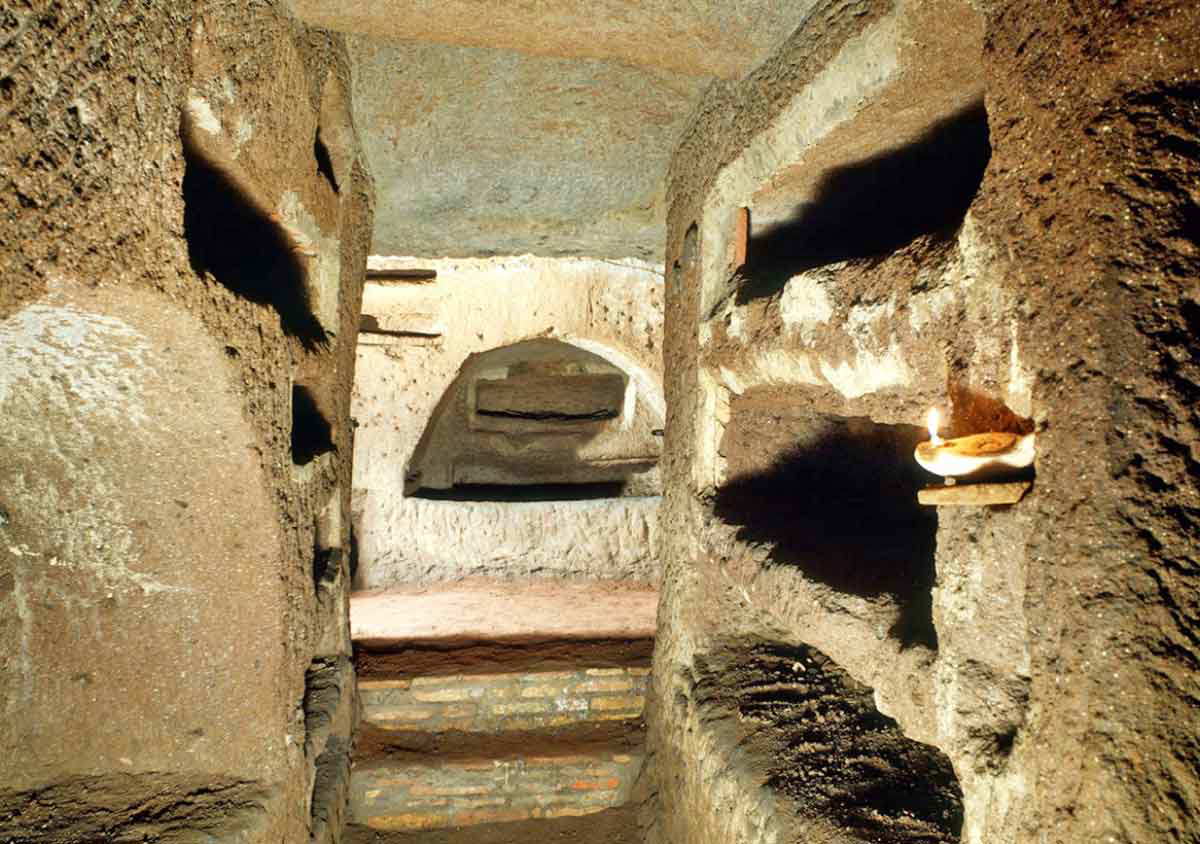

Orant figure
prayerful pose (Christ, crucifixion, Christ in the temple)
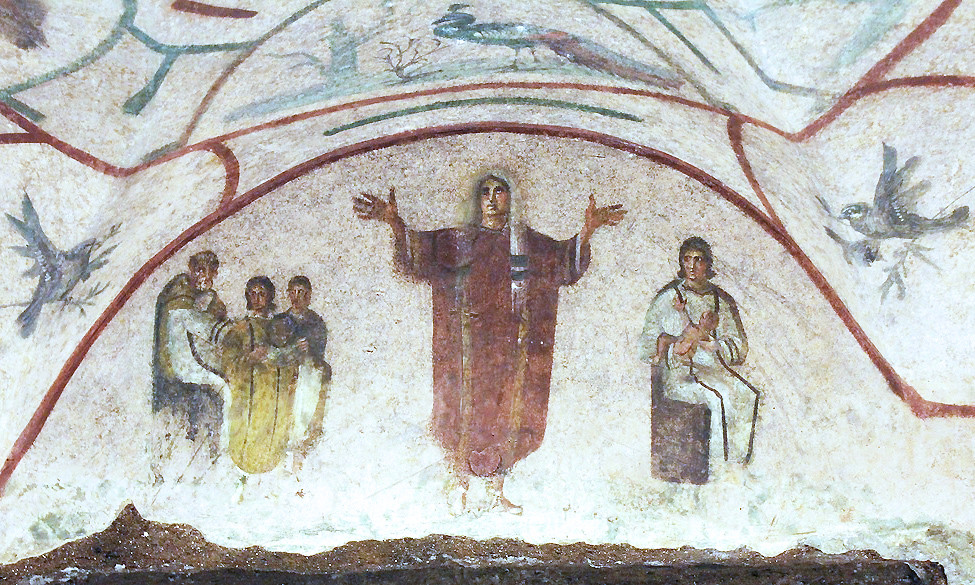

Good Shepherd
EARLY CHRISTIAN AND BYZANTINE ART
figure of Christ, New Testament book of John
youthful (“human”) large head —> de-emphasized body
rescues (salvation)
crucifixion story
avoids confusion of Christ with pagan gods

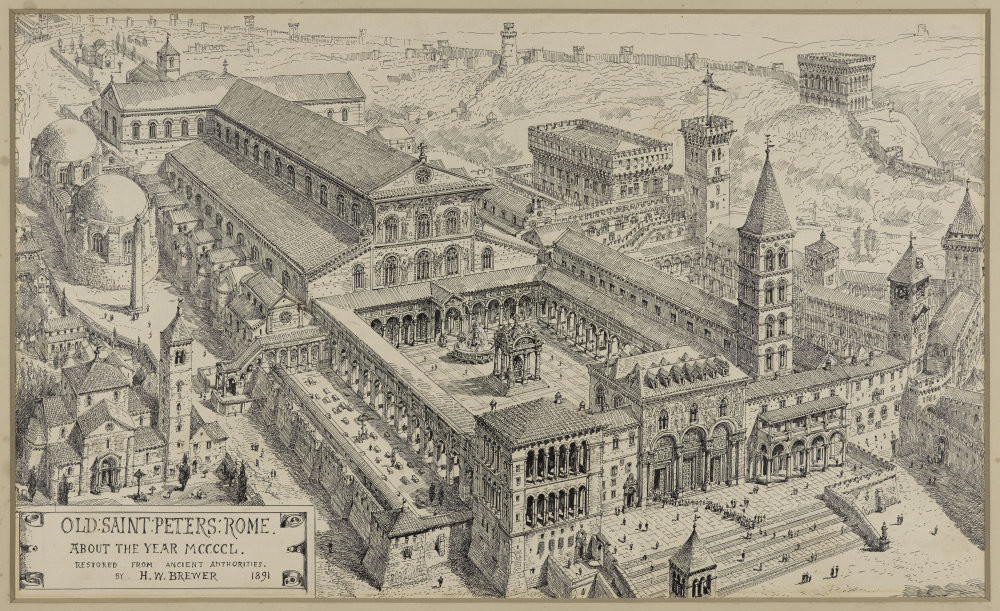
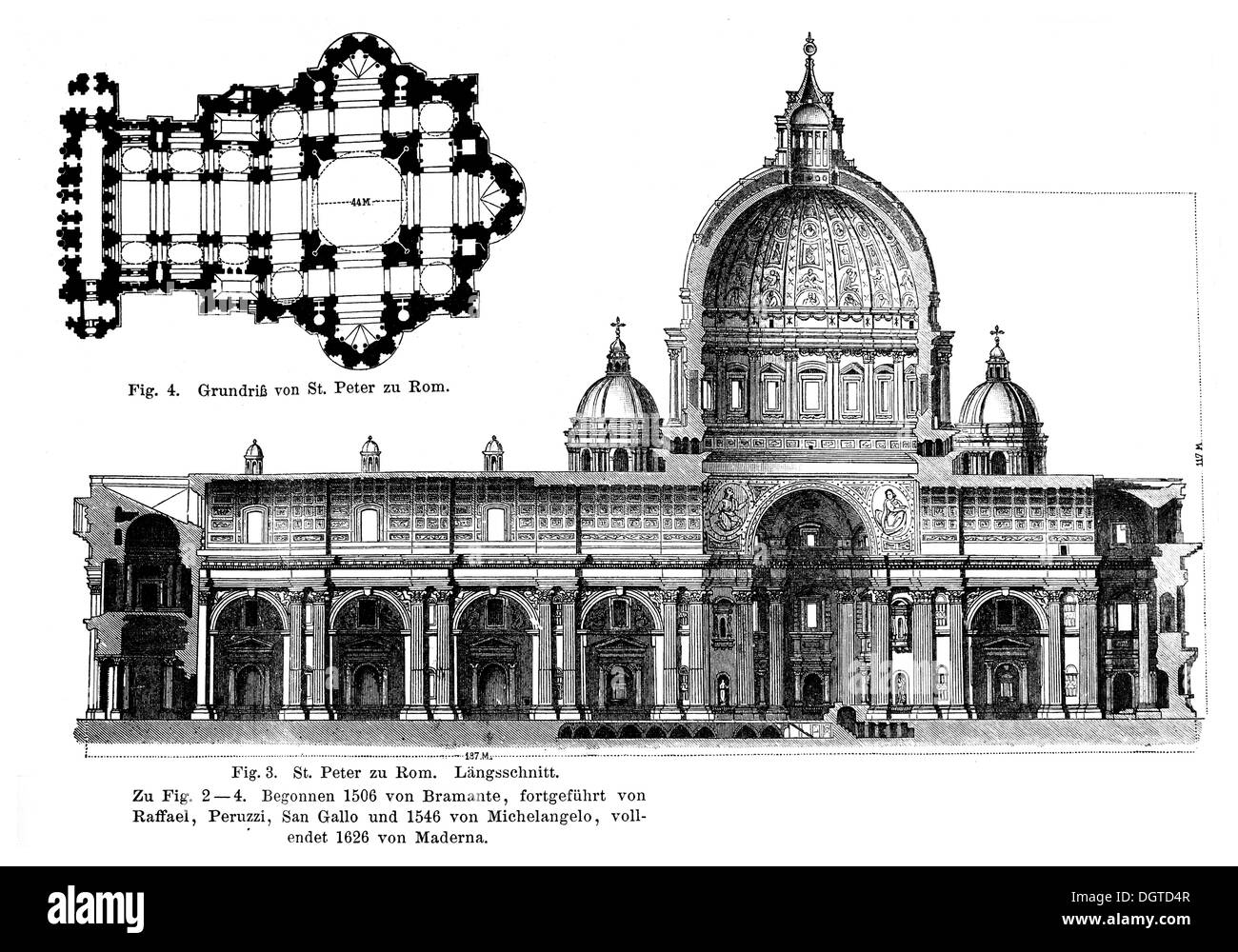
Old St. Peter’s
Rome, begun 320
*Early Christian church
provides public space for worship
teach rituals of Christian practice
avoid similarities to “pagan” temples to avoid confusion
pagan —> Christian
brick, wood, no column orders
*Basilica Plan Church
cruciform

Santa Pudenziana
Rome, 410
EARLY CHRISTIAN AND BYZANTINE ART
“Christ Enthroned” apse mosaic
brick, symbolic of the body
Central Plan Church
apse (altar) —> ambulatory (walkway)
central dome
height 60 m
mosaics of glass tesserae backed with gold
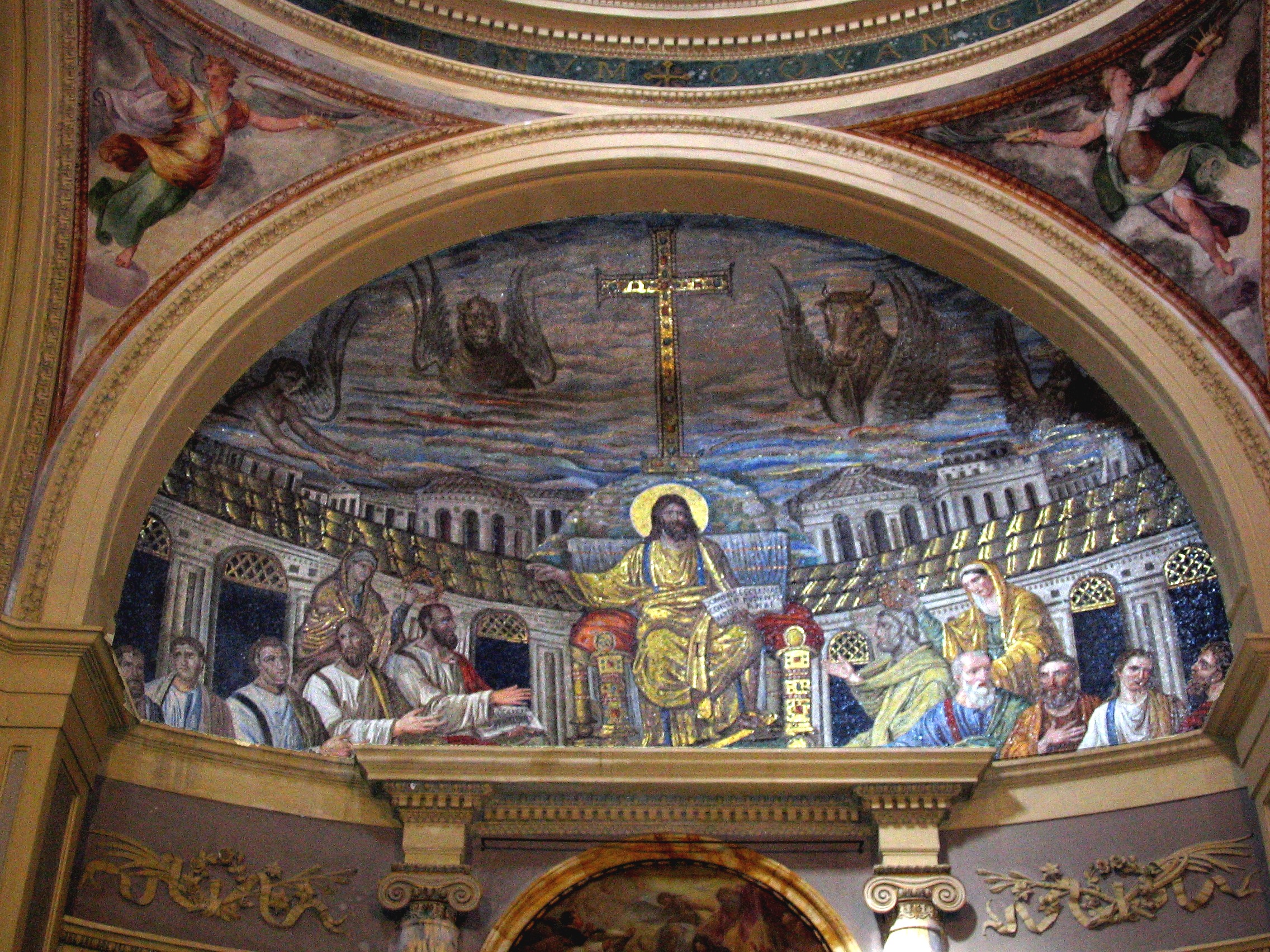

Apse mosaic “Second Coming”
EARLY CHRISTIAN AND BYZANTINE ART
Christ between two angels, St. Virtutis + bishop
Christ returns to judge and rule
crown —> earthly rule
book —> New Testament Doctrine
orb —> earth as circular planet “round earth

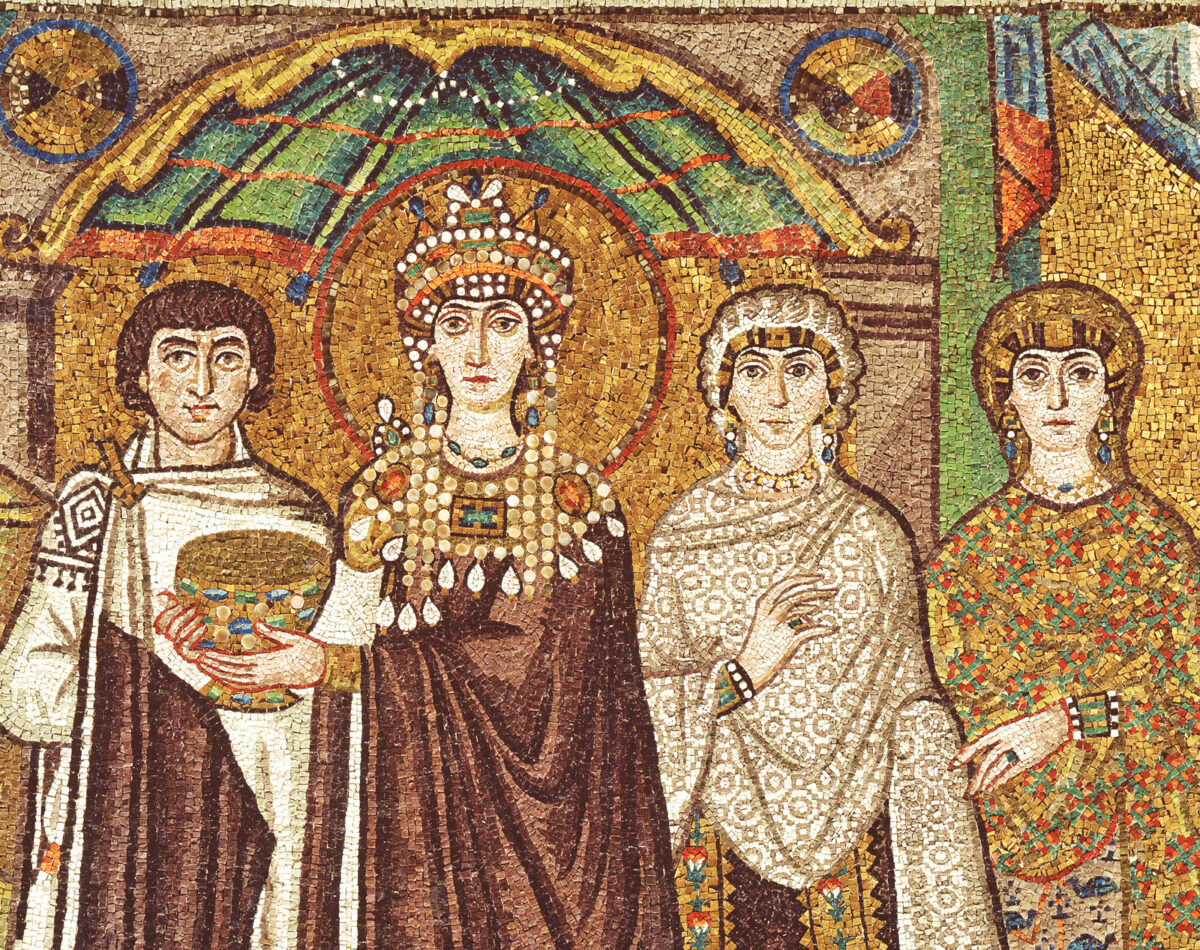
“Justinian” (Theodora) mosaics
EARLY CHRISTIAN AND BYZANTINE ART
San Vitale, Ravenna, 526-547
Justinian the Great emperor of the Eastern Roman Empire, 527-565

Sant’Apollinare in Classe
549 Byzantine
EARLY CHRISTIAN AND BYZANTINE ART
brick
Basilica Plan Church
Apse
orant figure—>
Apollinave: Christ-like
hand of God the Creator
alignment
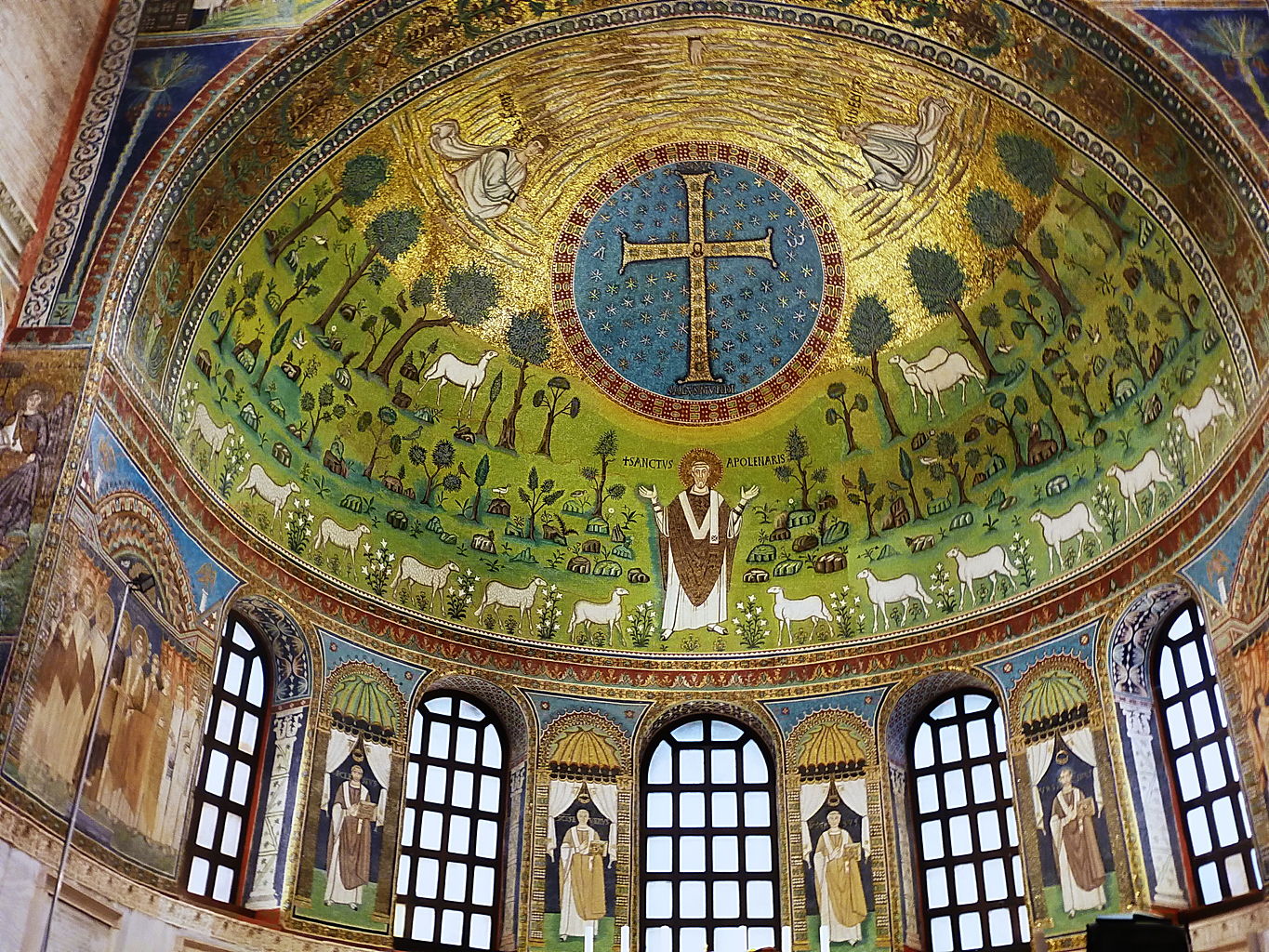

St. Apollinaris amid Sheep (Hand of God the Creator)
EARLY CHRISTIAN AND BYZANTINE ART
central image of apse in the Basilica of Sant’Apollinare in Classe
Transfiguration of Christ

Hagia Sophia (“Holy Wisdom”)
[Isidore of Miletus] Constantinople, 532-537
EARLY CHRISTIAN AND BYZANTINE ART
1453 turned into a mosque, then a museum
central plan church + basilica plan church
circle within a square
10,000 people + 5 years to complete
hemispheric dome
how to join circle + square
![<p>[Isidore of Miletus] Constantinople, 532-537</p><p>EARLY CHRISTIAN AND BYZANTINE ART</p><p>1453 turned into a mosque, then a museum</p><ul><li><p>central plan church + basilica plan church</p><ul><li><p>circle within a square</p></li></ul></li><li><p>10,000 people + 5 years to complete</p></li><li><p>hemispheric dome</p></li><li><p>how to join circle + square</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bb677ba1-b195-4eaa-a1b1-7415a7395228.jpg)
Figuras
character types
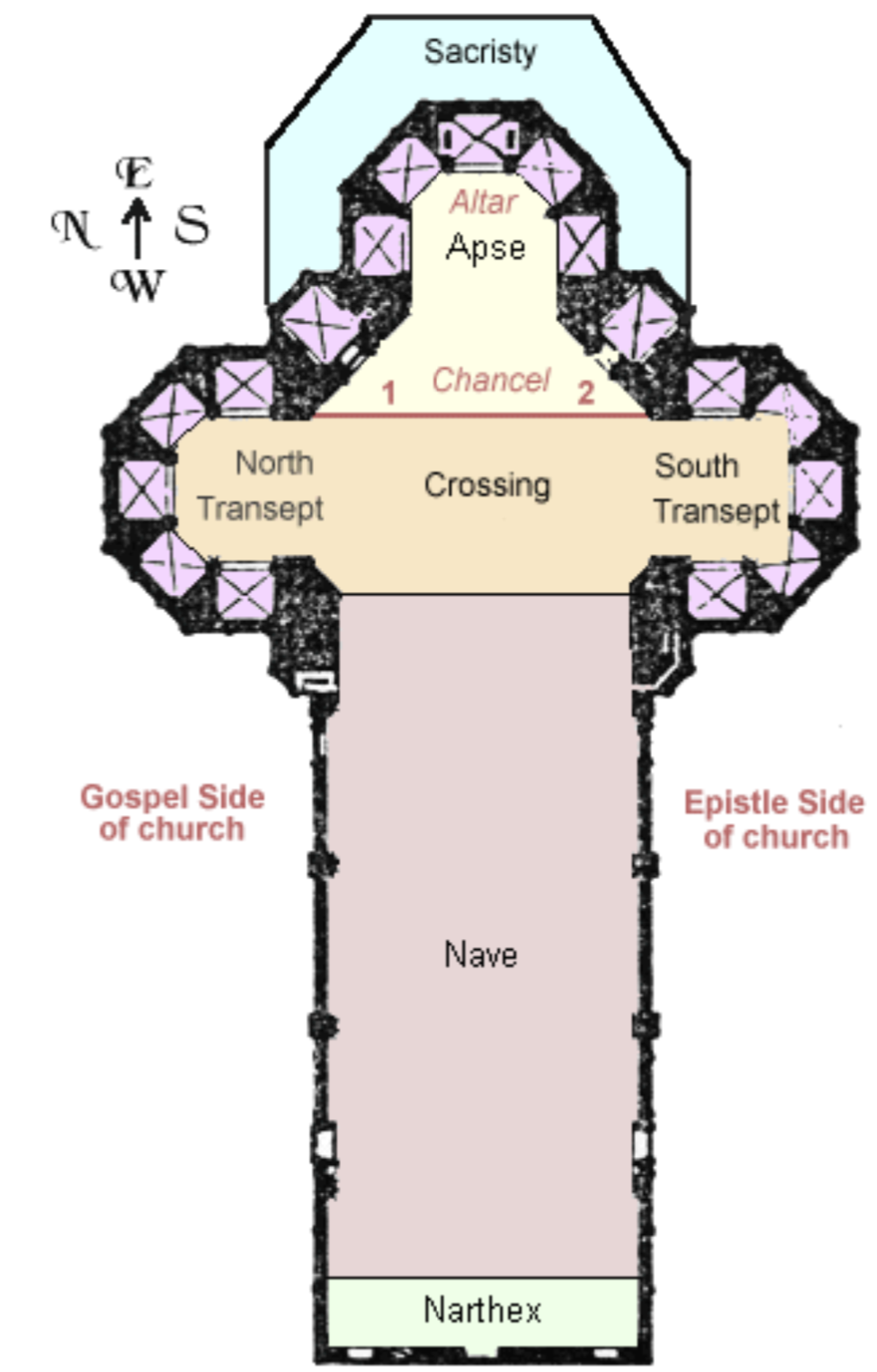
Basilica plan
cruciform
narthex
nave
apse (altar)
transept
aisle
apse
where the sacred altar is located

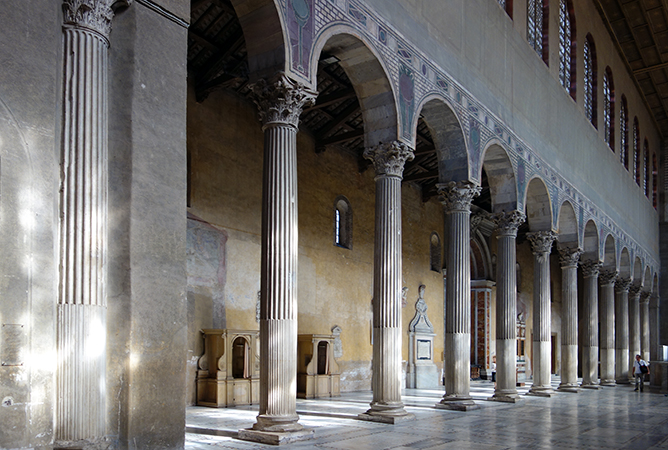
nave
processional way

aisle
3-part division

narthex
antechamber, distinct area at the entrance of churches
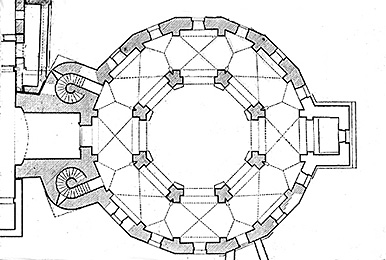
Central Plan
different from Basilica Plan
focused towards the center
ambulatory—> walking path along interior
gallery
brick (unadorned)
avoids Greek/Roman orders
Tesserae
small block of stone used in construction

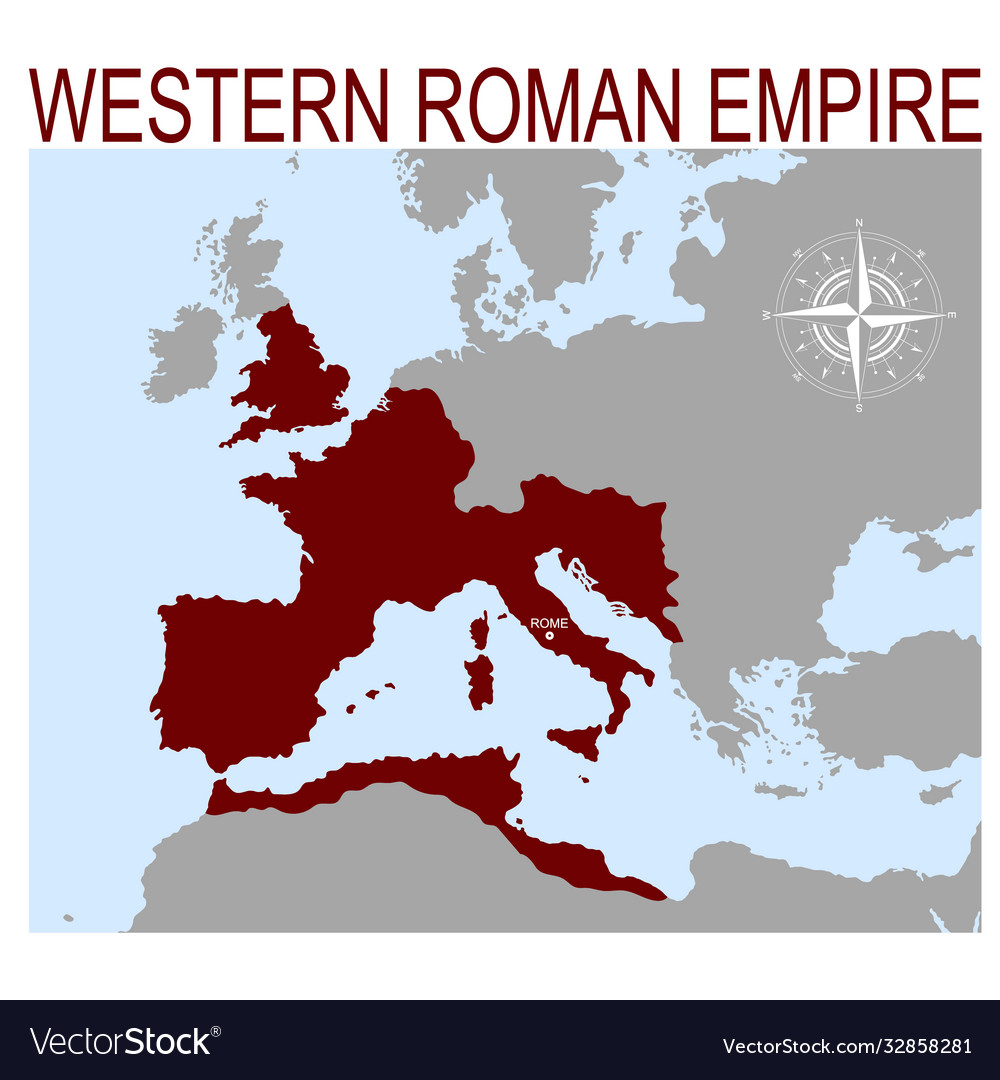
Western Roman Empire
285 AD
EARLY CHRISTIAN AND BYZANTINE ART
created to handle challenges in the west
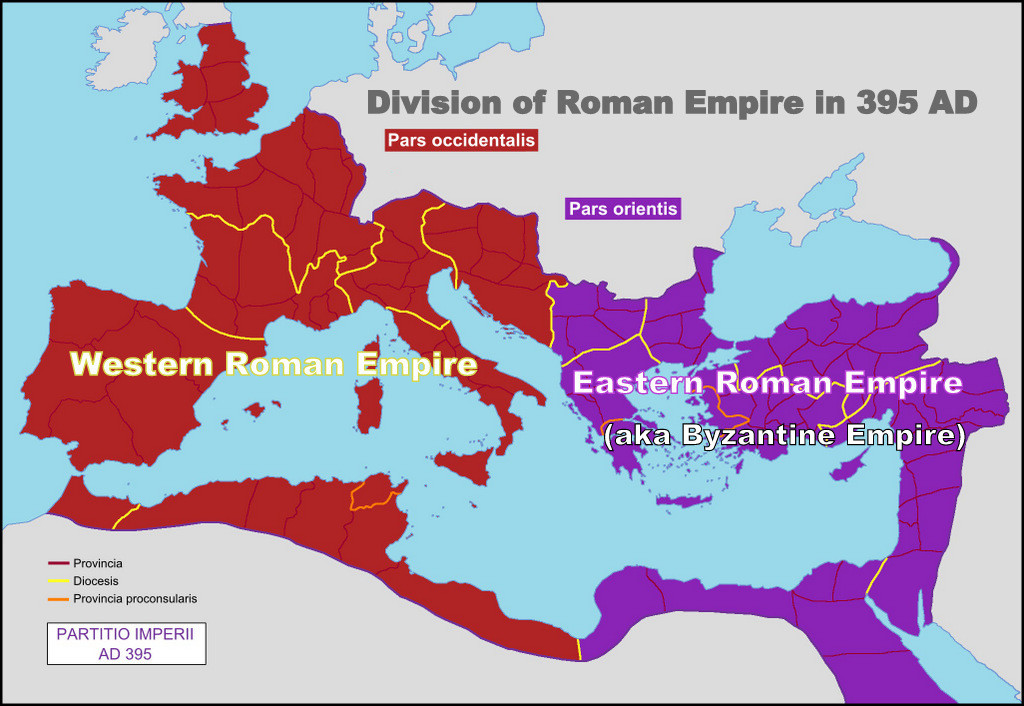
Eastern Roman Empire
285 AD
EARLY CHRISTIAN AND BYZANTINE ART
given its own administrative structure to deal with the problems in its territories
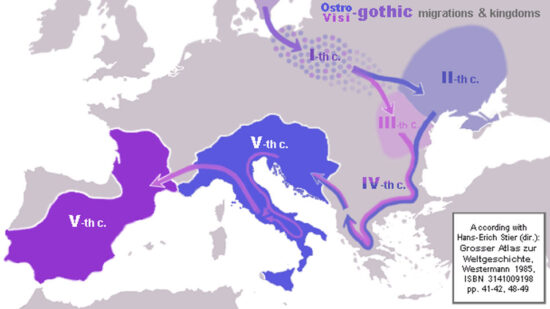
Visigothic invasion
Invade Rome: 410 AD
EARLY CHRISTIAN AND BYZANTINE ART
Kind Alaric sacked the city for 3 days after political negotiations failed
Hieratic Imagery
stylized, formal representations to convey religious importance, prioritizing spiritual meaning over naturalism
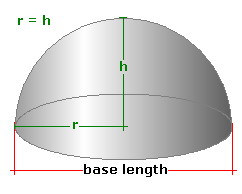
Dome (hemispheric)
A dome shape that is a perfect half-sphere
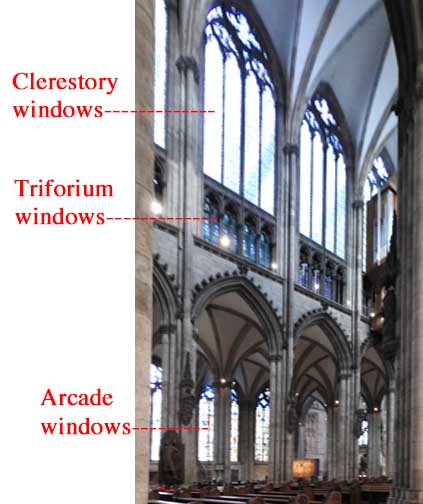
clerestory
The upper part of the church is made up of a series of windows
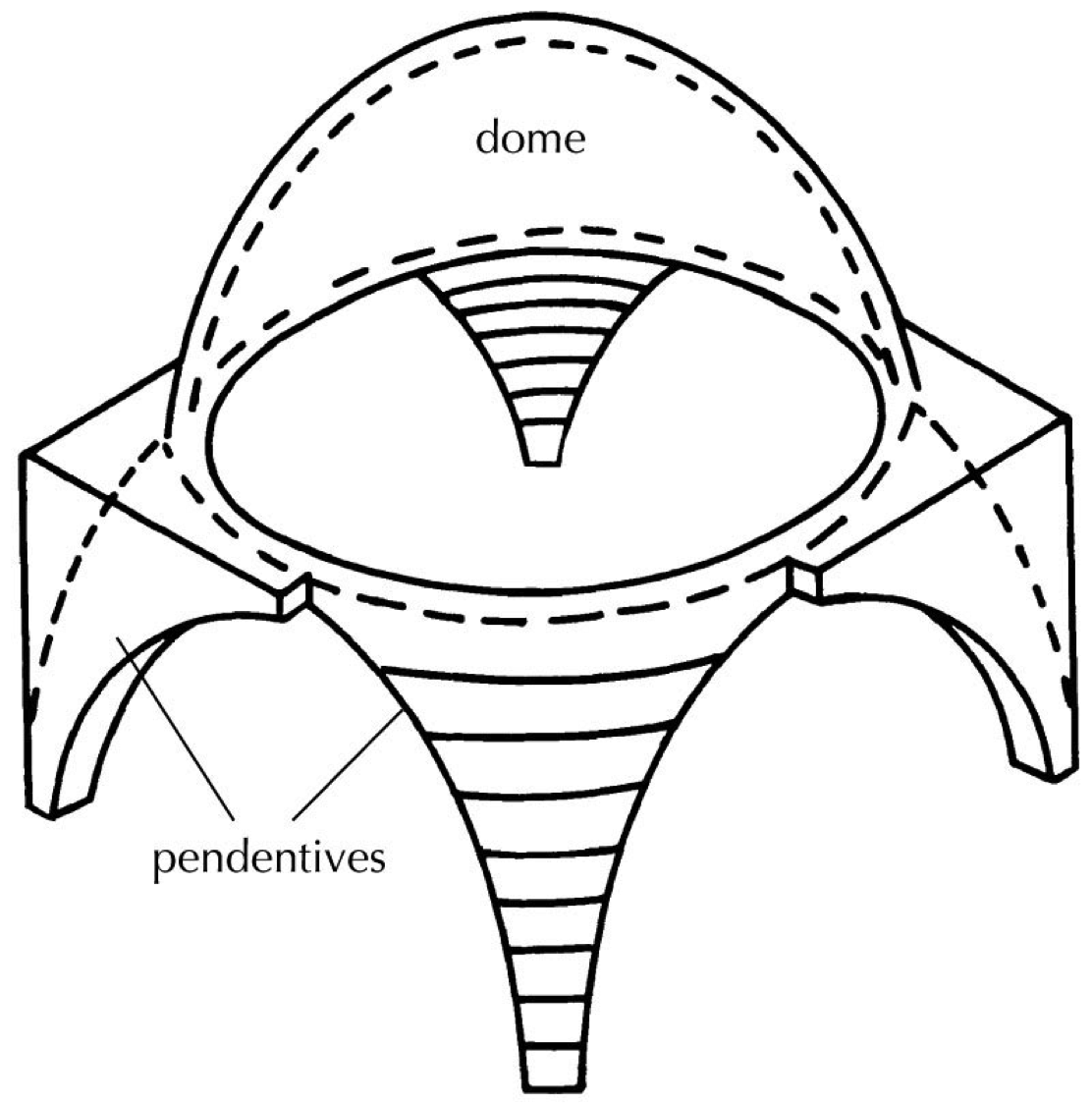
pendentives
triangular, spherical architectural elements that create a transition from a square or polygonal base to a circular dome
wall piers
structural wall that is supported by vertical piers or columns at intervals