Trophic Levels in an Ecosystem
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What does a food chain show?
It describes the feeding relationships between organisms and the resultant stages of biomass transfer.
What are trophic levels?
The stages in a food chain.
How are trophic levels represented?
Trophic levels are represented by numbers, starting from 1. After 1, trophic levels are numbered according to how far along the organism is in the food chain.
What is trophic level 1?
Plants and algae which make their own food (through photosynthesis) – called producers.
What is trophic level 2?
Herbivores which eat producers – called primary consumers.
What is trophic level 3?
Carnivores that eat herbivores – called secondary consumers.
What is trophic level 4?
Carnivores that eat other carnivores – called tertiary consumers.
What is an apex predator?
A carnivore with no predators.
How do decomposers break down dead matter?
Decomposers release enzymes which catalyse the breakdown of dead material into smaller molecules. Soluble small food molecules then diffuse into the microorganisms.
What is biomass?
The dry mass of all of the living organisms in an area.
Why is dry mass used for biomass?
Because the wet mass varies as the volume of water in the organism varies.
How do you calculate the efficiency of biomass transfer?
Efficiency = (energy transferred / total energy available) × 100.
What percentage of the incident energy from light for photosynthesis do producers transfer?
1%.
What percentage of the biomass from one trophic level is transferred to the level above it in feeding?
Approximately 10%.
Why are biomass transfers not 100% efficient?
Energy is lost through:
- Egestion (removal of faeces)
- Excretion (removal of waste products e.g., urine containing urea and water)
- Respiration (loss of carbon dioxide and water) in which large amounts of glucose are used
- The production of inedible bones and shells.
How does the efficiency of biomass transfers affect the number of trophic levels in a biomass pyramid?
The less efficient the transfers, the fewer trophic levels and the fewer organisms in higher trophic levels.
What is a biomass pyramid?
A pyramid that shows the total dry mass of organisms at each trophic level. Trophic level 1 is at the bottom of the pyramid.
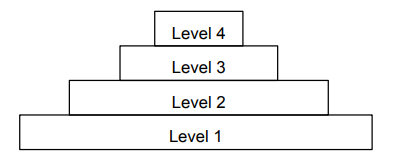
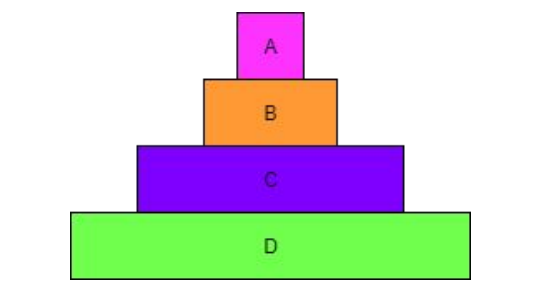
Identify the producer in this pyramid of biomass.
D is the producer.
What is a pyramid of numbers?
A pyramid of numbers shows the number of organisms at each trophic level.
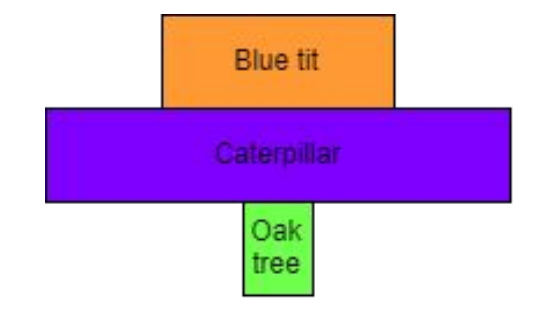
Why is this pyramid of numbers not pyramid shaped?
Pyramids of numbers don’t take size and mass of organisms into account.
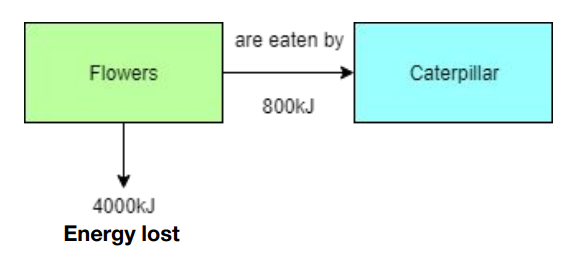
Calculate the efficiency of the biomass transfer from the flowers to the caterpillar.
Efficiency = (energy transferred / total energy available) × 100.
Total energy available = 800 kJ + 4000 kJ = 4800 kJ.
Energy transferred = 800 kJ.
800/4800 × 100 = 16.67%.