Semester 1 Final Honors Biology 9th Grade (copy)
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
independent variables
A variable that a scientist changes to find out how this change affects other variables in the experiment.
dependent variables
The outcome factor -- the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable
control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
experimental group
In an experiment, the group that is exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable.
scientific method
1. ask a question- observation
2. form a hypothesis
3. setting up a controlled experiment
4. record and analyze an experiment
5. draw a conclusion
characteristics of living things
organized
respond to stimuli
growth and development
use energy
adaptation
reproduce
homoeostatic
classification of living things
kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
organization of living things
atom, molecule, cell, tissue, organ, body system, organism, population, community, ecosystem
3 types of bonds?
covalent ionic hydrogen
covalent bond
-chemical bond in which atoms share one pair of electrons
-strong bond
types- polar and nonpolar
ionic bond
-when an electron is transferred from one atom to another
-strong
hydrogen bond
-when the polarity in a water molecule causes the hydrogen in one molecule to attract the oxygen atoms in another water molecule
-weak
what is the chemical formula for water?
H2O
what are all the properties of whater?
High specific heat
High heat of vaporization
Has both cohesive and adhesive behaviours
High surface tension
Expansion upon freezing
Solvent of life
common household ph items
acidic
- stomach acid
- lemon
- soda
base
Oven cleaner
Baking soda
what is the ph of blood?
7.18
what is the definition of ph?
measurement of the concentration of H='s compared to OH in a solution
what pulls apart monomers and polymers?
hydrolysis
what are the 4 types of macromolecules?
lipids, carbohydrates, nucleuic acids, protein
what brings together monomers and polymers?
polymerization
what are three common polymers that are carbohydrates?
monosacchrides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
hydrophobic
do NOT like water
hydrophilic
do like water ( soluble in water)
what is a peptide bond?
a chain of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds
what is the function of a peptide bond?
bond together polypeptides or a chain of amino acids
what is the function of amino acids?
they make protein
what is the difference between RNA and DNA?
dna- double helix which has less oxygen, lacks 1 sugar in the oxygen
rna- 5 oxygen all available, has urisile instead
centrioles
cell organelle, existing in pairs, that occurs on the centrosome and may help organize mitotic spindle for chromosome movement during animal cell division
chloroplast
Membranous organelle that contains chlorophyll and is the site of photosynthesis
chromatin
network of fibrils consisting of DNA and associated proteins within a nucleus, wound up form
cytoplasm
contents of a cell between the nucleus and the plasma membrane that contains the organelles
eukaryote
type of cell that has a membrane-bounded nucleolus and organelles
golgi apparatus
organelle, consisting of flattened saccules and also vesicles, that processes, package, and distributes molecules within or from the call
endoplasmic reticulum
2 types rough and smooth make proteins and ship things out
lysosome
membrane-bounded vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes for digesting macromolecules
nucleoid
region of prokaryotic cells where DNA is located; it is not bounded by a nuclear envelope
nucleus
membrane-bounded organelle within a eurkaryotic cell that contains chromosomes and controls the structure and function of the cell
mitochondria
membrane bounded organelle in which ATP molecules are produce during the process of cellular respiration
plasma membrane
membrane surrounding the cytoplasm that consist of a phosopholipid bilayer with embedded proteins; regulates the entrance and exit of molecules form the cell
ribosome
RNA and protein in two subunits; site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm
vacuole
membrane-bounded sac that holds fluid and a variety of other substances
cell wall
Cell wall located outside the plasma membrane, joined together by peptide chain and is mostly found in plant cell to keep bacteria out
prokaryote
bacteria, no nucleus,
what are the organelle found in prokaryote
cell wall, cell membrane, nucleoid region, ribosome
DNA function
DNA contains the genes and the genetic material
genotype
An organism's genetic makeup
phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
dominant trait
Will always show up in an offspring when its allele is present
recessive trait
A trait that is apparent only when two recessive alleles for the same characteristic are inherited
what are the steps in the cell cycle?
Prophase, metaphse, anaphase, telopahse
cell cycle
This consists of interphase G1, S, G2, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis
in what stage does replication occur in a cell?
Interphase
what is the plasma membrane made of?
made of phospholipid bi layer and proteins
what can cross over the membrane?
passive transport
- oxygen, CO2, water, small non polar objects
what are the types of passive transport?
diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
osmosis
Diffusion of water
hypertonic
HIGH solute
LOW solvent
hypotonic
LOW solute
HIGH solvent
isotonic
Having the same solute concentration
endocytosis
Active transport process where a cell engulfs materials with a portion of the cell's plasma membrane and releases the contents inside of the cell. ( think IN )
exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material ( think EXIT )
types of exocytosis
phagocytosis and pinocytosis
bulk transport
Used to transport large particles and macromolecules.
exocytosis and endocytosis
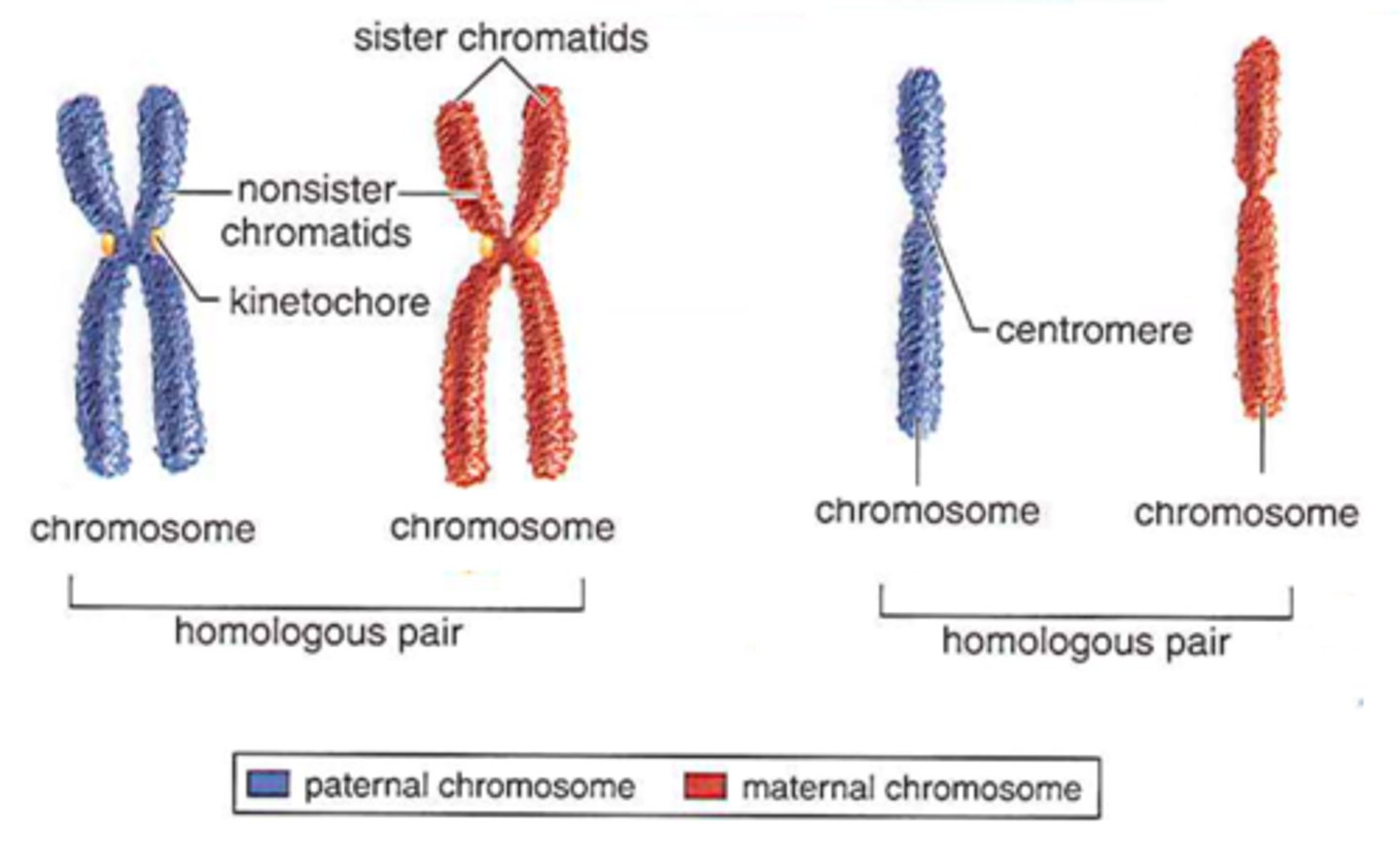
chromosome
chromatid
sister chromatids
homologous pairs
centromere
chromatin
What do plant cells contain in addition?
-their difference from animal cells
Cell wall
Chloroplast
Central vacuole