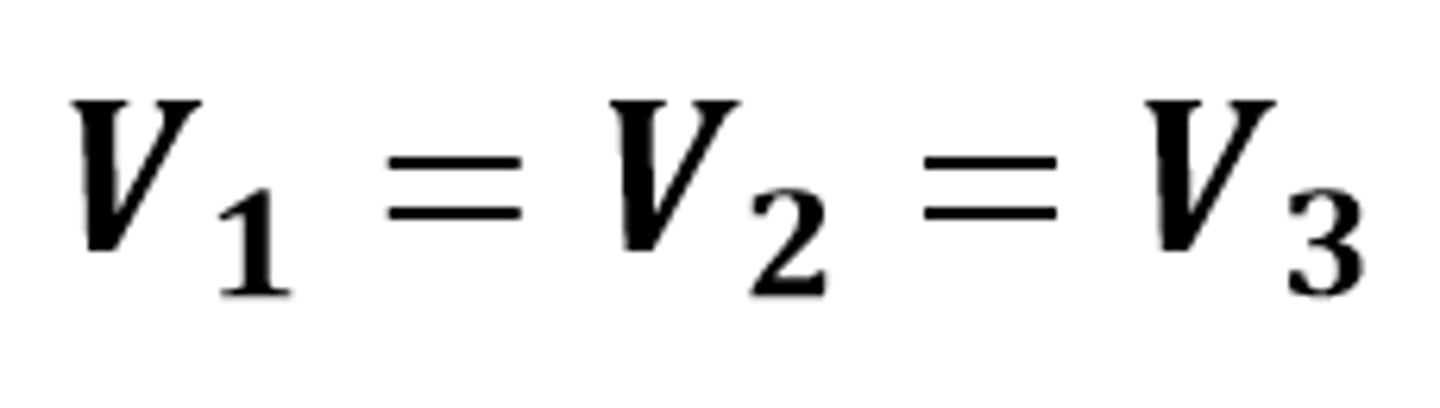Series and parallel circuits: Electricity: Physics: GCSE (9:1)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Series circuit
A circuit where electrical components are connected one after another in a single loop (a circuit that only has one path for the current to flow through)
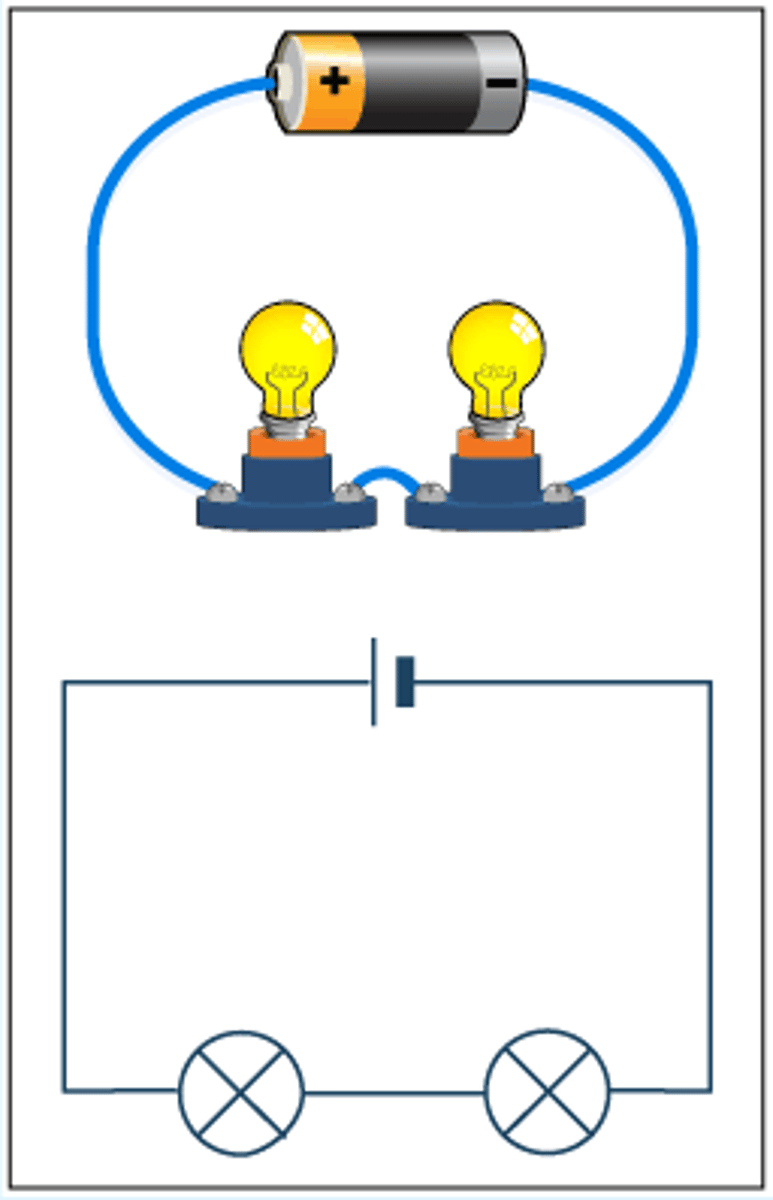
What happens when one component breaks in a series circuit?
The current will not be able to flow round the circuit; if one component breaks, then all of the other components stop working
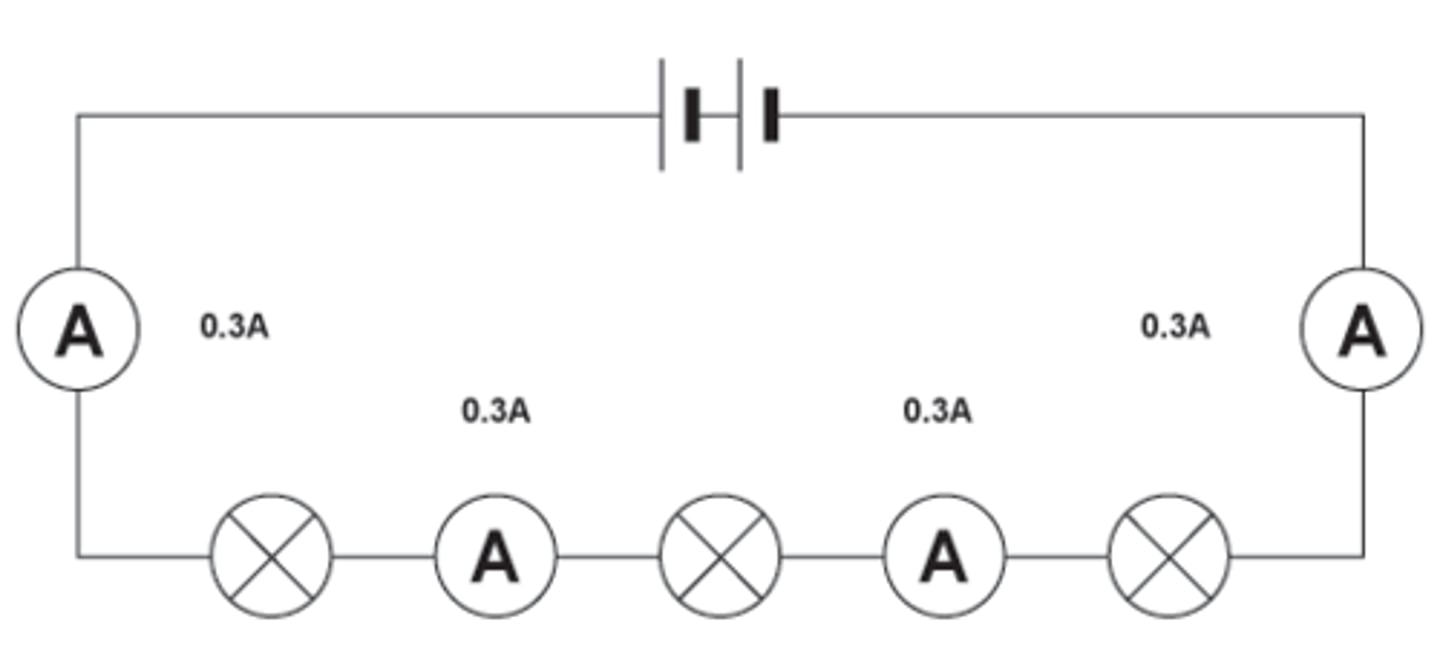
Rule for current in series
The same current passes through each component connected in series
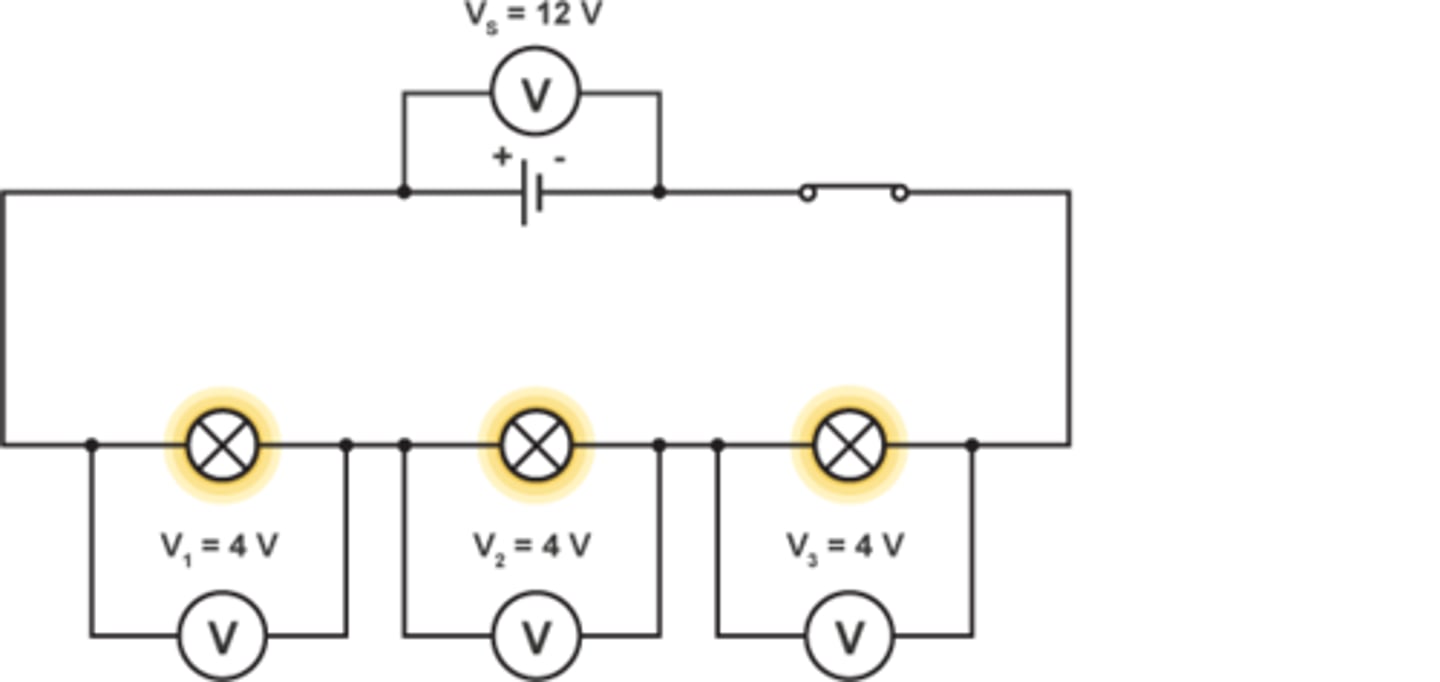
Rule for potential difference in series
The total potential difference of the power supply is shared between components connected in series
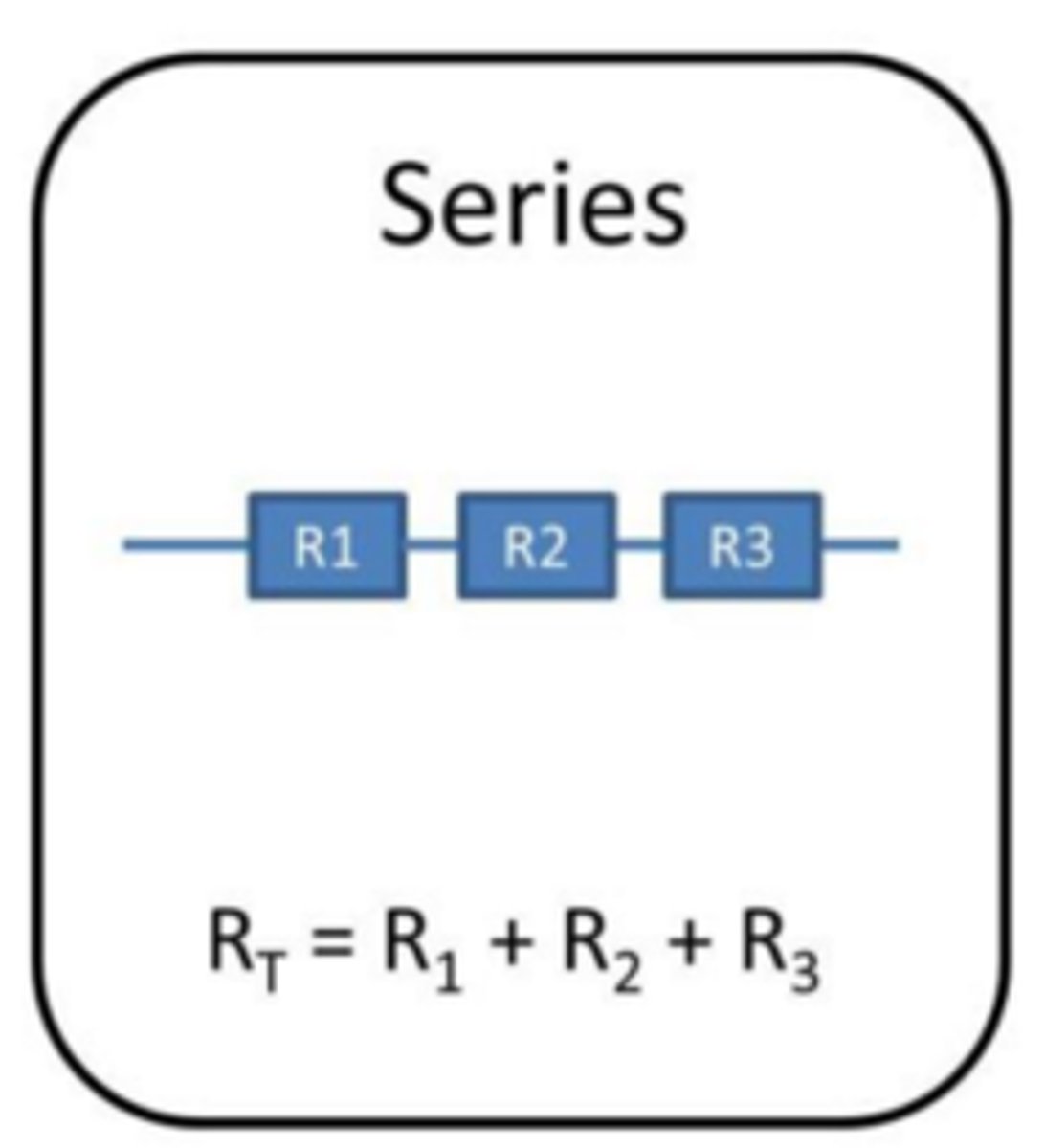
Rule for resistance in series
The total resistance of two components connected in series is the sum of the resistance of each component
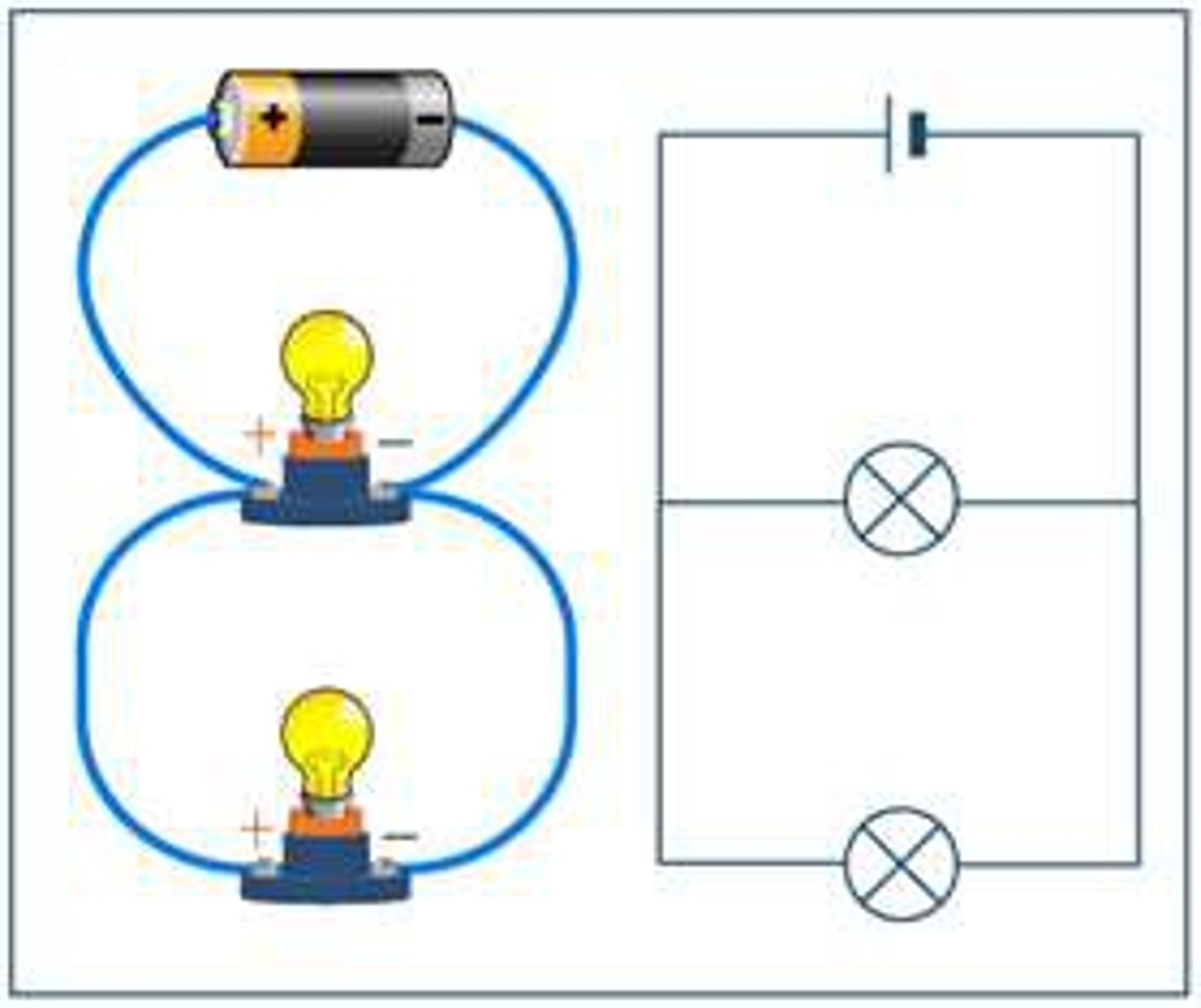
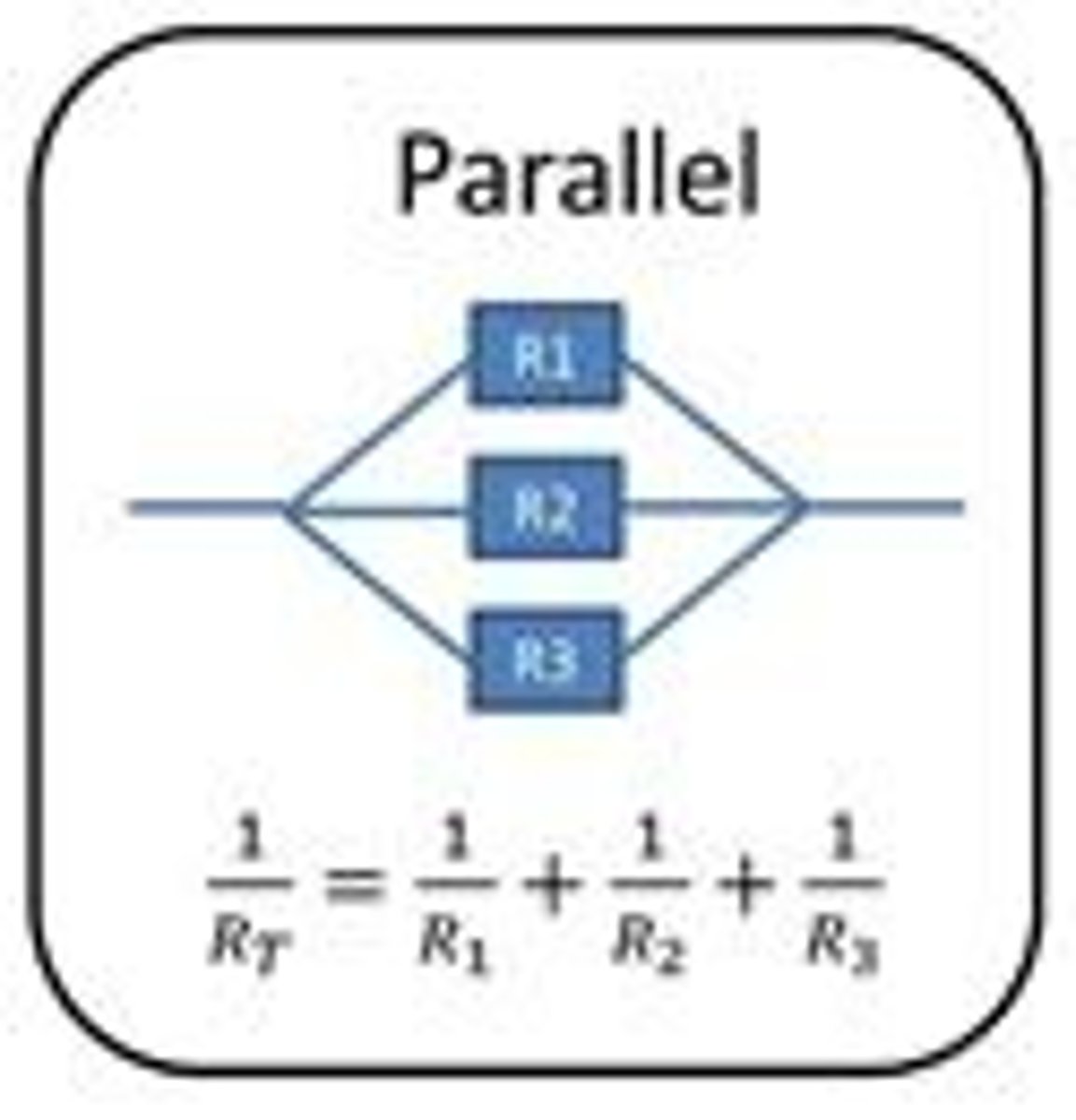
Parallel circuit
A circuit where electrical components are connected alongside each other on multiple loops; a circuit that has multiple paths for the current to flow through
What happens if one component breaks in a parallel circuit?
The current can still flow round the circuit through one of the other paths; if one component breaks, the other components still work
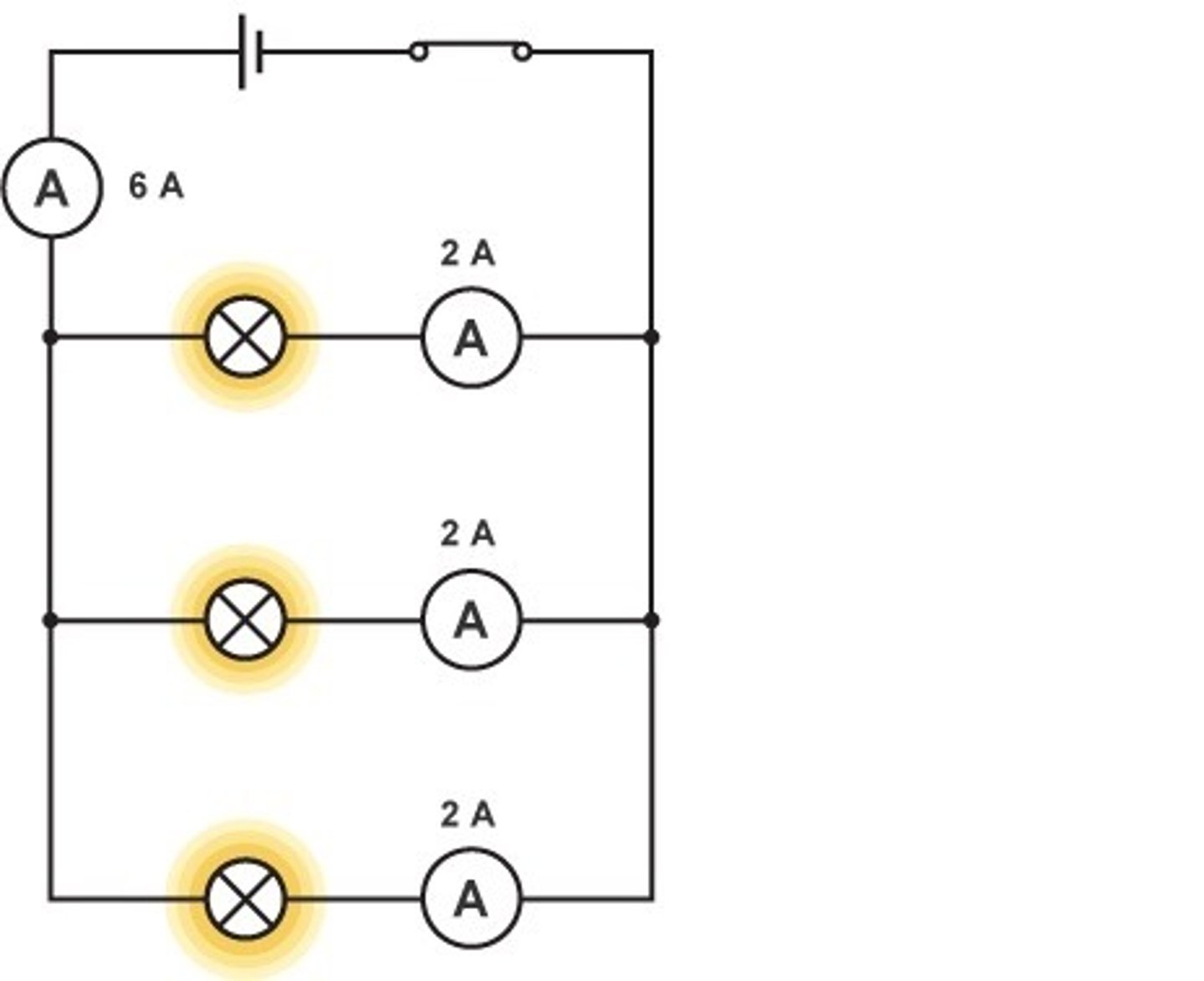
Rule for current in parallel
The total current through the whole circuit is the sum of the currents through the separate components
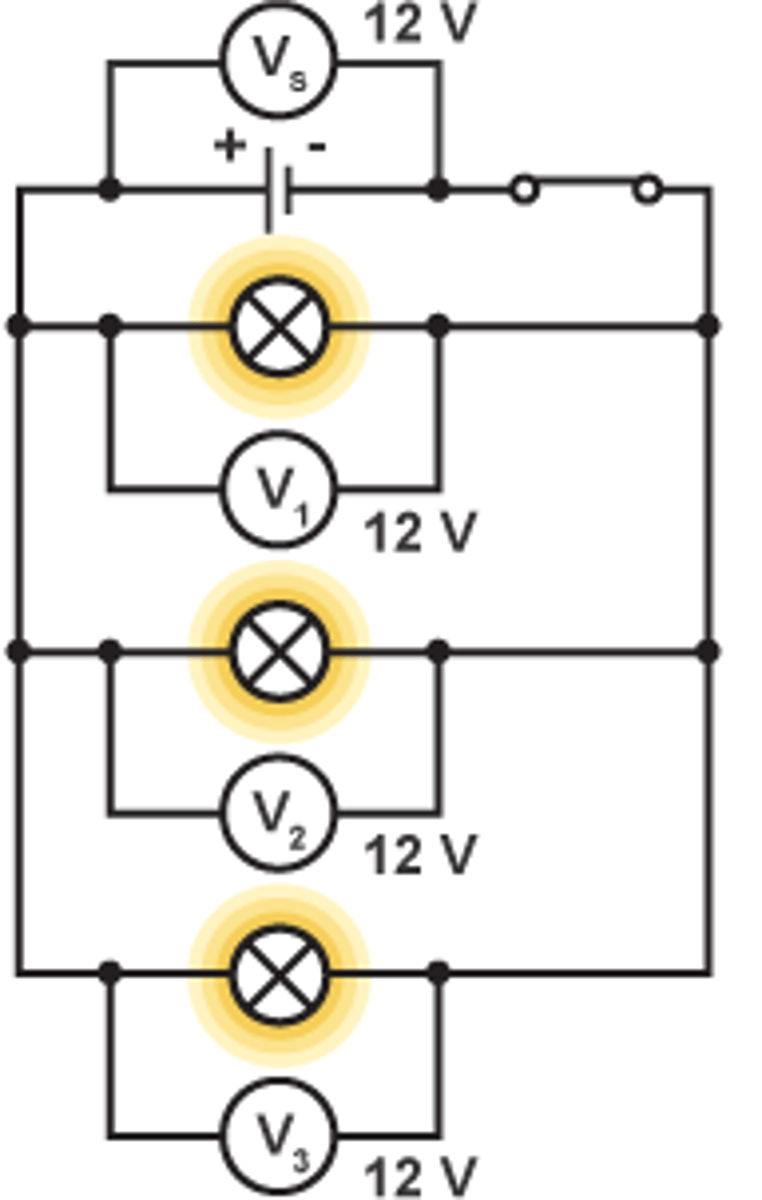
Rule for potential difference in parallel
The potential difference across each component is the same
Rule for resistance in parallel
The total resistance of two resistors is less than the resistance of the smallest individual resistor
I(1) = I(2) = I(3)
The mathematical relationship for the current through components connected in series
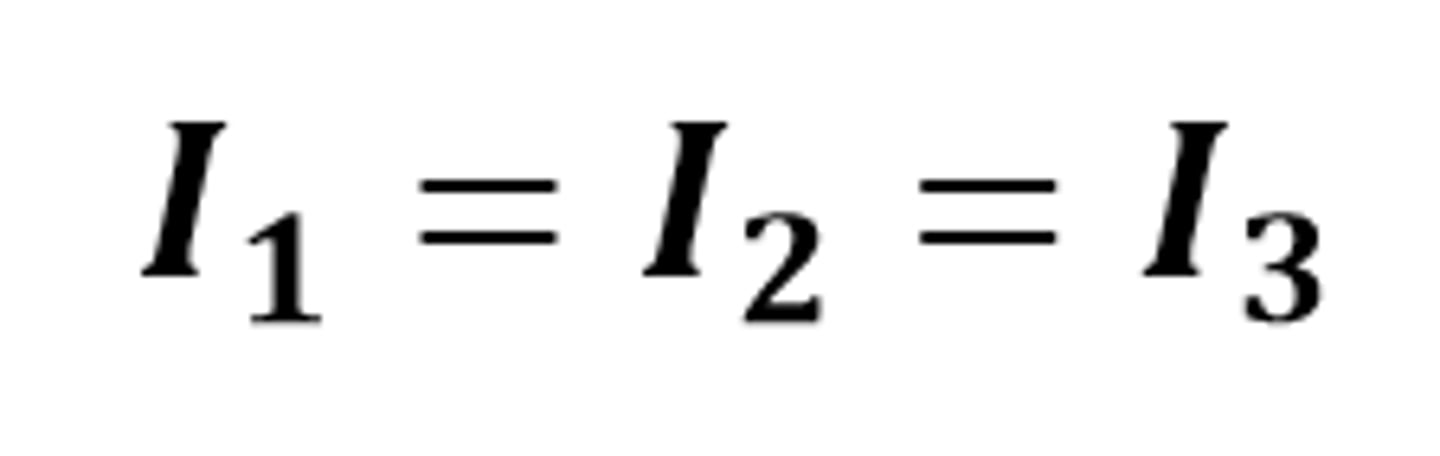
V(total) = V(1) + V(2)
The mathematical relationship for the total potential difference in a circuit when components are connected in series
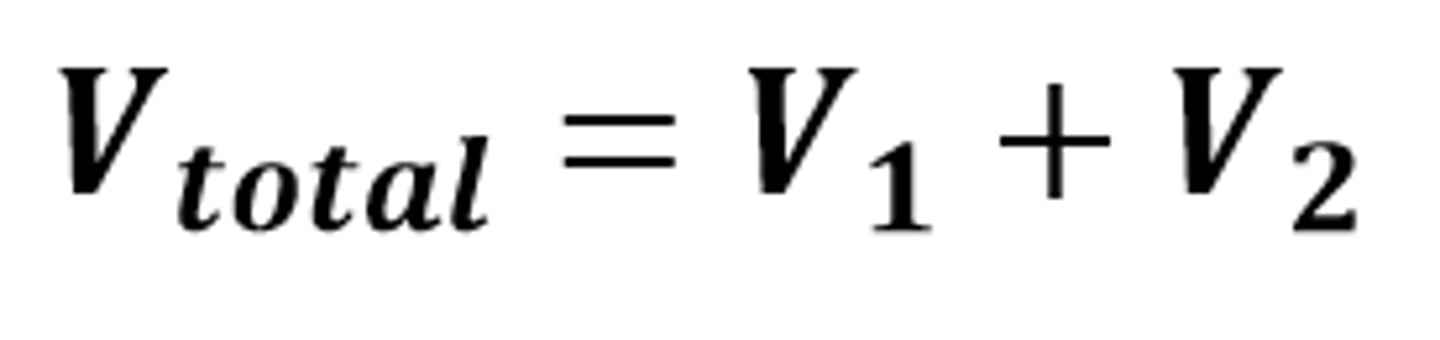
R(total) = R(1) + R(2)
The mathematical relationship for the total resistance in a circuit when components are connected in series
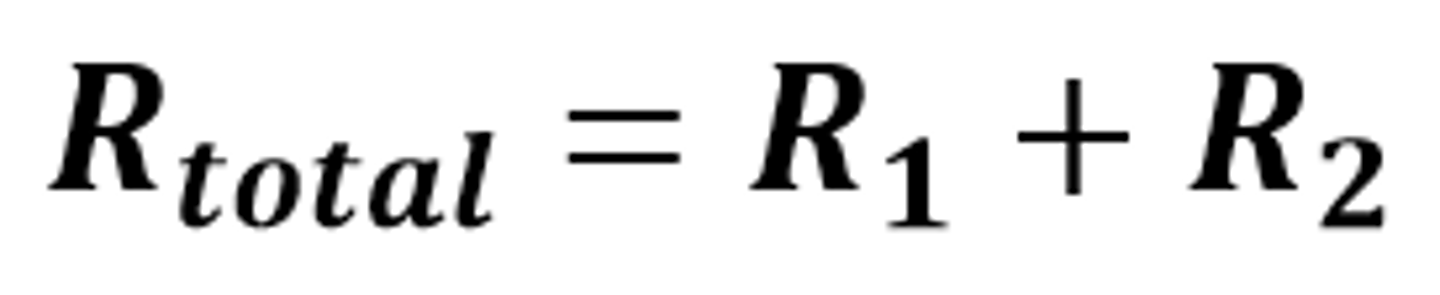
I(total) = I(1) + I(2)
The mathematical relationship for the total current in a circuit when components are connected in parallel
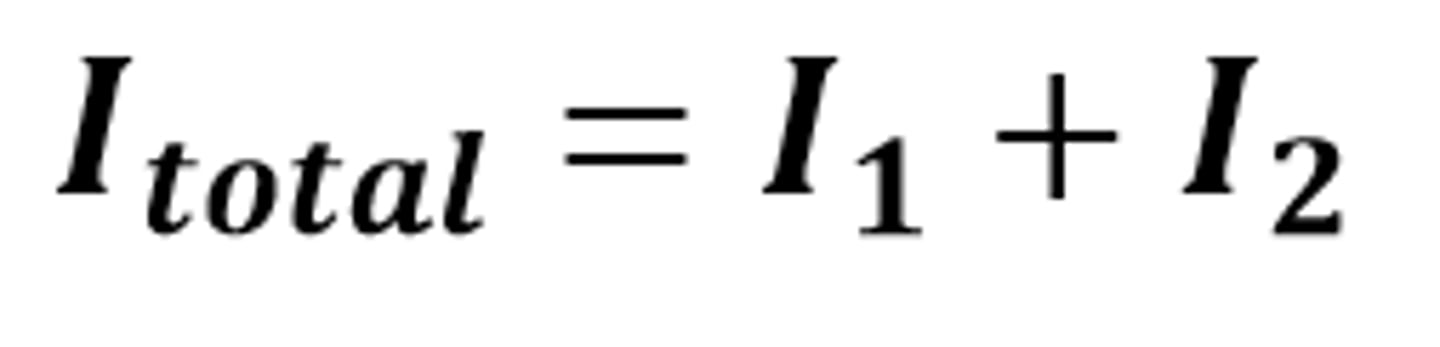
V(1) = V(2) = V(3)
The mathematical relationship for the potential difference across components connected in parallel