Biology - Chapter 12.1, 2: Animal & Plant Pathogens & Disease
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What are communicable diseases caused by?
Pathogens
What are the different types of pathogens?
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi and Protoctista
What is a vector?
A living or non-living factor that transmits a pathogen from one organism to another e.g. female malaria mosquito
Bacteria features
Prokaryotic
Do not have membrane bound nucleus or organelles
Not all are pathogen (only a small proportion are)
Why is gram staining bacteria useful?
The type of cell wall affects how bacteria reacts to different antibiotics
What color does gram positive and negative bacteria turn after staining?
Gram positive: Purple-Blue
Gram negative: Red
Differences between bacteria and viruses
1. Bacteria living, Viruses non-living
2. Bacteria don't require a host to survive, viruses entirely dependent on host
3. Viruses much smaller than bacteria (0.0.-0.3 micrometers)
4. Viruses consist of nucleic acid enclosed in protein coat, genetic material DNA or RNA, bacteria have circular strand of DNA
What are protista?
Eukaryotic organisms
Include single-celled organisms and cells grouped into colonies
Protists that cause disease = parasitic (may need vector to transfer them to host)
What type of fungi causes communicable disease?
Parasitic.
What happens when fungi reproduces?
Produces millions of tiny spores that can spread long distances, means fungal diseases can spread rapidly and widely through plants
What diseases do bacteria cause?
tuberculosis, bacterial meningitis, ring rot
What diseases do viruses cause?
HIV/AIDS (humans), influenza (animals), tobacco mosaic virus (plants)
What diseases do protoctista cause?
Malaria, potato/tomato late blight
What diseases do fungi causes?
black sigatoka (bananas), athlete's foot (humans)
Ring Rot
- Bacterial disease of potatoes, tomatoes
- Caused by gram positive bacteria
- No cure
- Once infects a field, cannot be used to grow for 2yrs
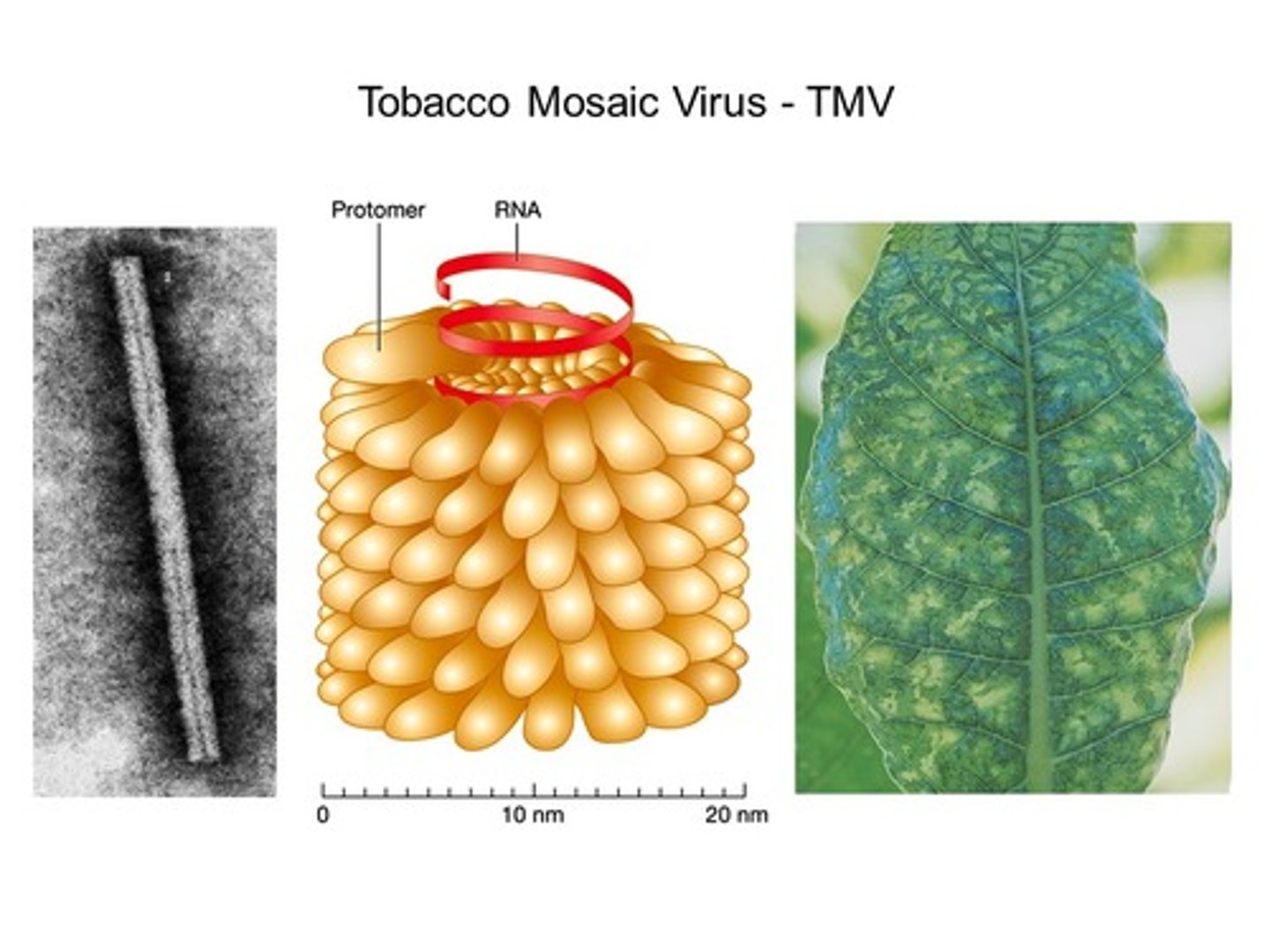
Tobacco Mosaic Virus
- Virus that infects tobacco plants and major crops (150 other species)
- Damages leaves, flowers & plants
- Stuns growth, reduces yield, can lead to crop loss
- No cure, but resistant crop strains exist
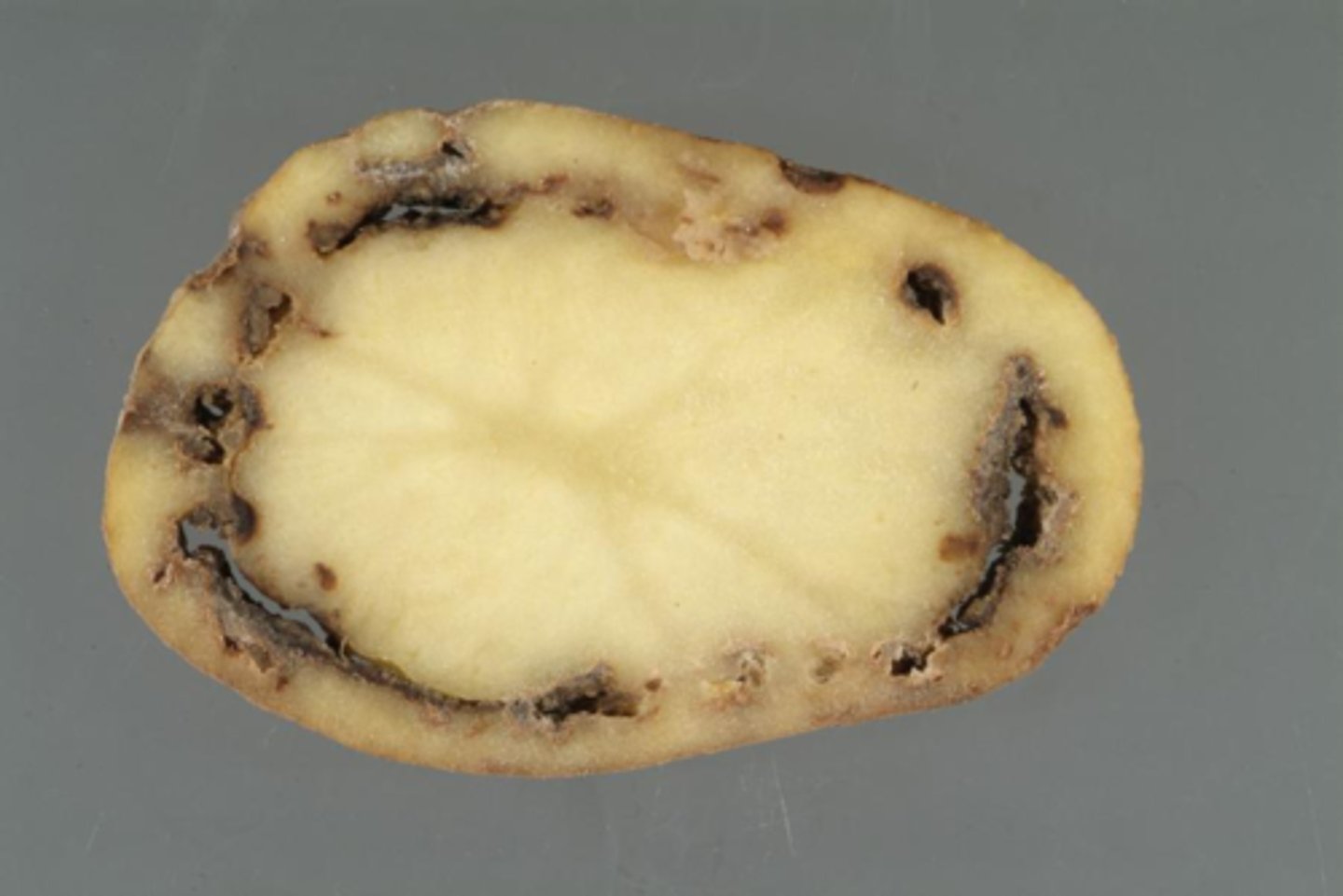
Potato/Tomato late blight
- Caused by fungus protoctist
- Hyphae penetrates host cells, destroying leaves, tubers and fruit
- No cure
- Resistant strains, careful management & chemical treatments can reduce infection risk
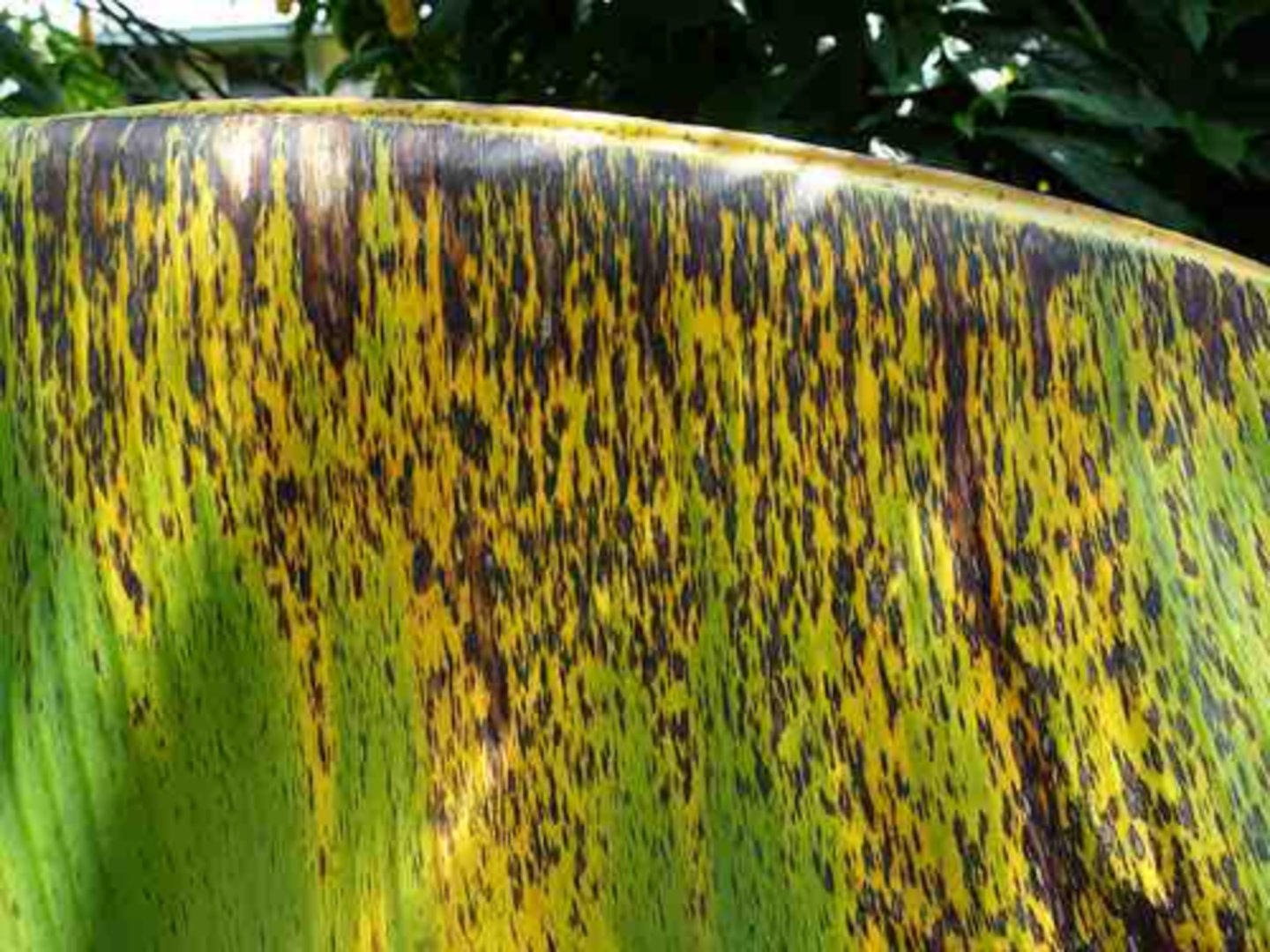
Black Sigatoka
- Fungal disease, affecting bananas
- Hyphae penetrate & digest cells ; turns leaves black
- Resistant strains being developed,
- Fungicide & good husbandry can control spread
- No cure

TB
- Bacterial disease that destroys lung tissue & suppresses immune system
- Affects humans, cows, pigs and badgers
- Curable by antibiotics
- Preventable by improving living standards & vaccination
bacterial meningitis
- Bacterial infection of meninges of brain which can spread to rest of body causing septicaemia & rapid death
- Mainy affects v. young children & teens 15-19
- If given early, antibiotics can cure disease
- Vaccination to prevent some form of bacterial meningitis
HIV/AIDS
- Viruses that causes aids ; targets T helper cells
- Gradually destroys immune system
- Transmission = Bodily fluids
- No vaccine, No cure
- Anti-retroviral drugs slow the progress of disease to give many years of healthy life
Influenza
- Viral infection of ciliated epithelial cells in gas exchange system
- Kills them, leaving airways open to secondary infection
- Vulnerable groups given vaccines to protect against changing strains
- No cure
Malaria
- Caused by protoctista Plasmodium, spread by bites of female Anopheles mosquito
- Invades RBCs, liver and brain
- No vaccine, limited cures
- Control the vector
Ring worm
- Fungal disease
- Different fungi infect different species
- Causes grey-white, crusty, infectious, circular areas of skin
-Antifungal creams are a cure
Athlete's foot
- Human fungal disease
- Form of human ring worm that grows on and digests the warm, moist skin between toes
- Causes cracking and scaling
-Antifungal creams are a cure
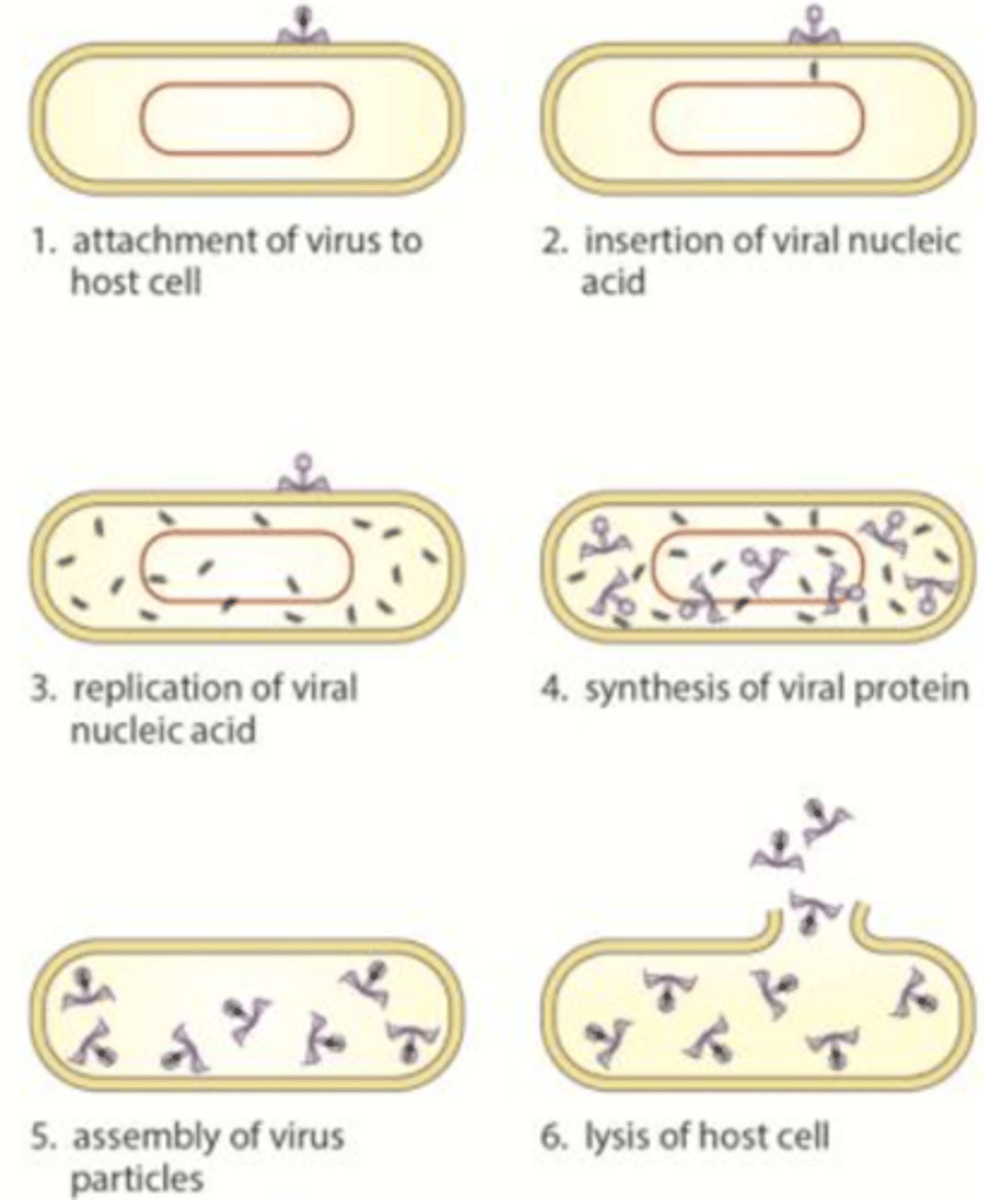
How do viruses attack and damage the host tissue?
-Take over cell metabolism
- Viral genetic material gets into host cell & is inserted into host DNA
-Virus uses host cell to make new viruses
- Eventually burst out of cell, destroying it & spread to infect other cells
How do protoctista attack and damage host tissue?
-Some take over cells & break them open as new gen emerge
- Do not take over genetic material of cell
- Digest & use cell contents as they reproduce
How do fungi attack and damage host tissue?
-Digest living cells an destroy them
- Combined with response of body to damage caused gives symptoms of disease
- Some produce toxins, affecting host cell & causing disease
How do bacteria attack and damage host tissue?
- Most produce toxins that poison or damage host cells, causing disease
- Some bacterial toxins break down cell membranes,
- Some damage or inactivate enzymes
- Some interfere w. host cell genetic material so cell can't divide
- Toxins are by-product