Soil Functions, Conservation, and Human Impact in Agriculture and Ecosystems
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What early civilizations developed along the floodplains of the Yellow River?
The Chinese civilization.
What major environmental event in the 1930s significantly impacted soil fertility in North America?
The Dust Bowl.
What were some agricultural practices that contributed to the Dust Bowl?
Over-plowing of native prairie, lack of cover crops and rotation, and no conservation tillage practices.
What were the human impacts of the Dust Bowl?
Widespread farmer displacement, health issues like dust pneumonia, and economic collapse in rural areas.
What was established in 1935 to address soil conservation?
The Soil Conservation Service.
What are the four essential needs of individual plants from soil?
Anchorage, water, oxygen, and nutrients.
How does soil aeration affect oxygen dynamics for plants?
Soil aeration allows for the exchange of gases, with roots and soil organisms consuming oxygen and releasing CO₂.
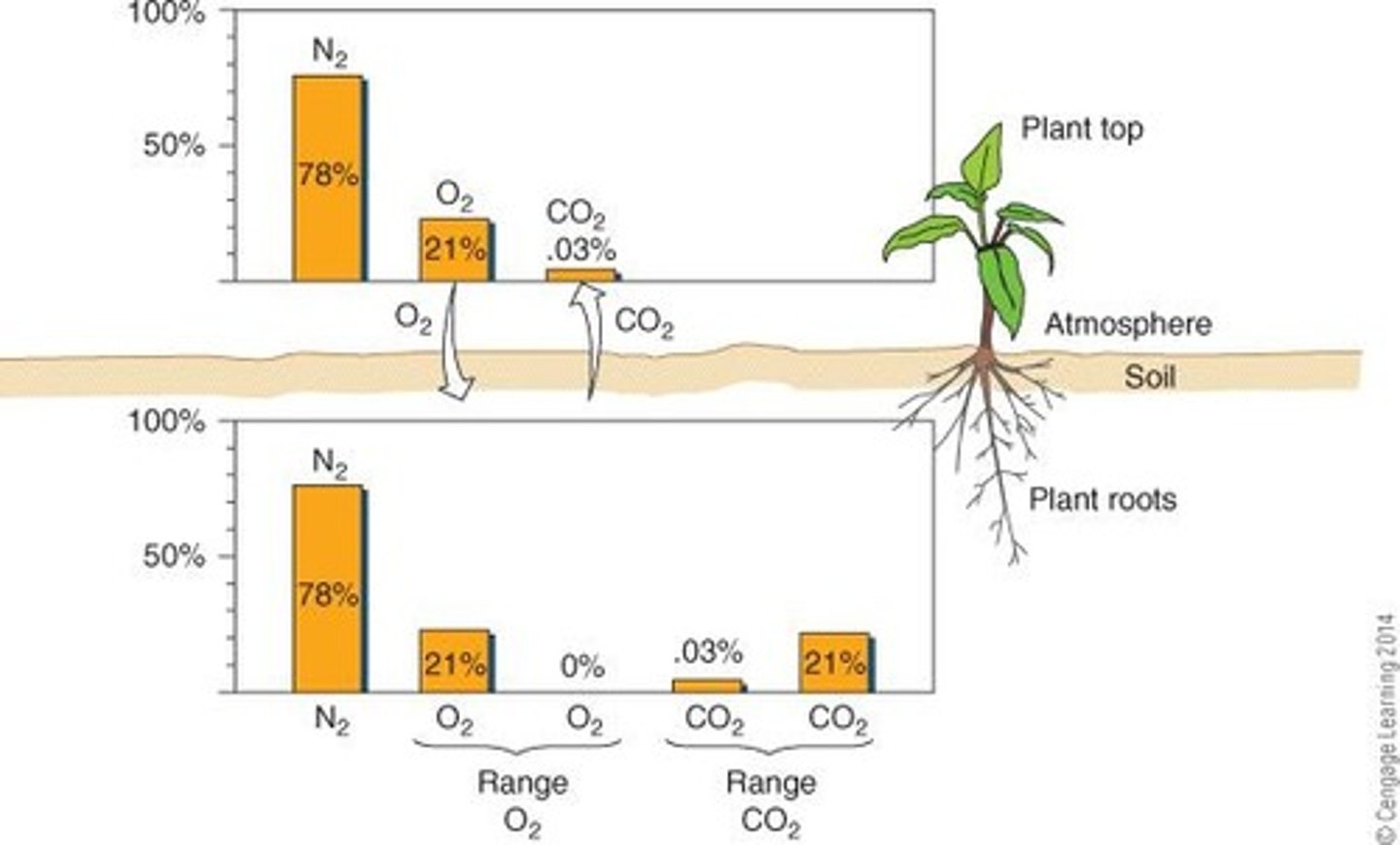
What is the significance of root hairs in plants?
Root hairs absorb nutrients from soil water, a process that requires energy from root respiration.
What are the three phases of soil?
Solid particles, pore spaces, and liquids (water).
How does soil compaction affect tree growth?
Compacted soil can lead to stunted growth, while open soil allows for vigorous growth.
What is a hardpan in soil?
A hard subsoil layer caused by cementation by carbonates or other chemicals that limits root spread.
What are some non-agricultural uses of soil?
Recreation, engineering, waste disposal, and building materials.
What are the effects of soil on construction?
Soil affects building stability, retaining walls, and the integrity of roads, bridges, and sewer lines.
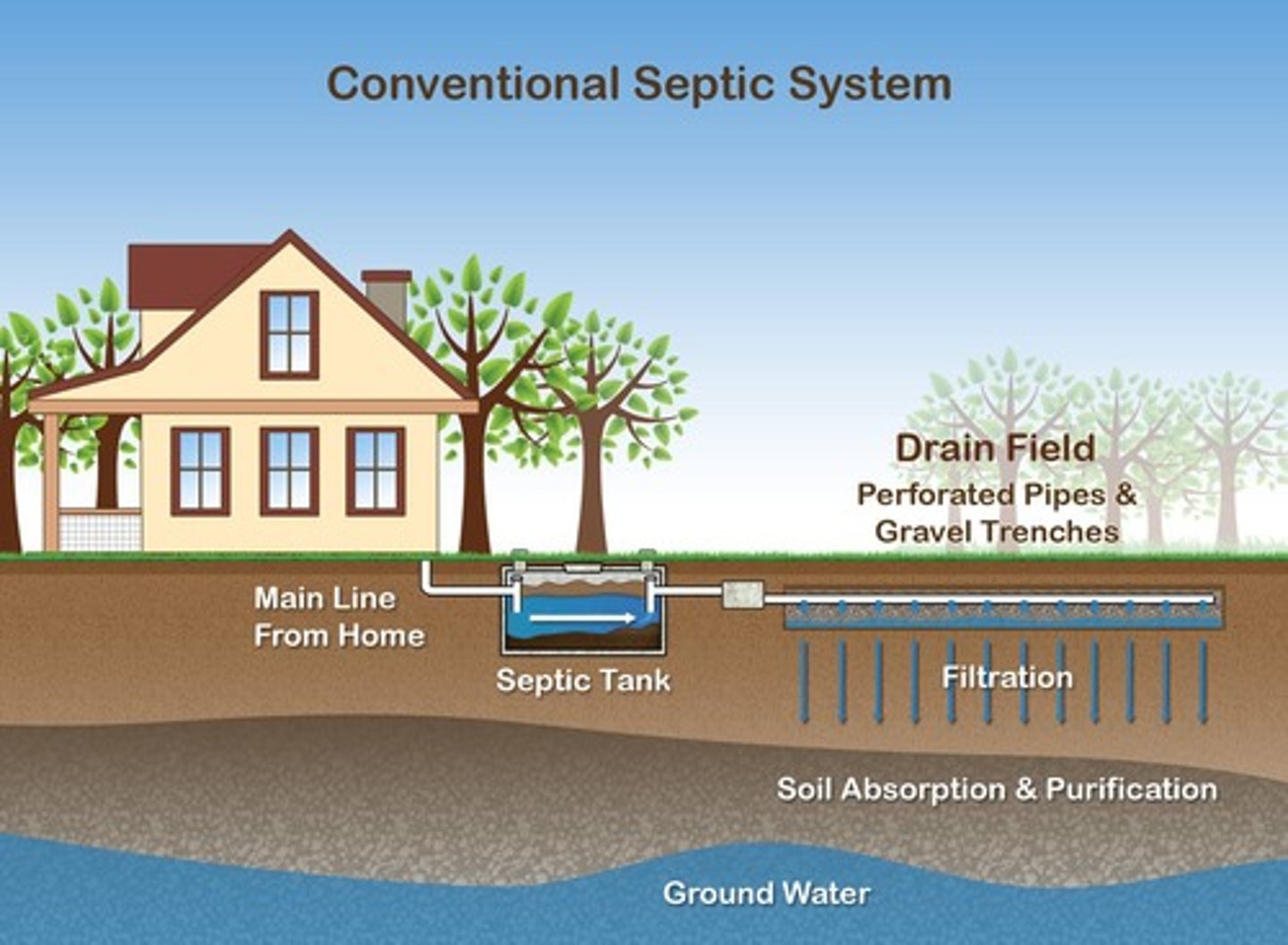
How does soil filter and treat waste?
Soil microbes break down organic waste in septic systems and can help treat sewage sludge.
What is soil quality also referred to as?
Soil health.
What are some causes of soil degradation?
Erosion, pollution, desertification, changes in soil chemistry, salinization, and loss of organic matter.
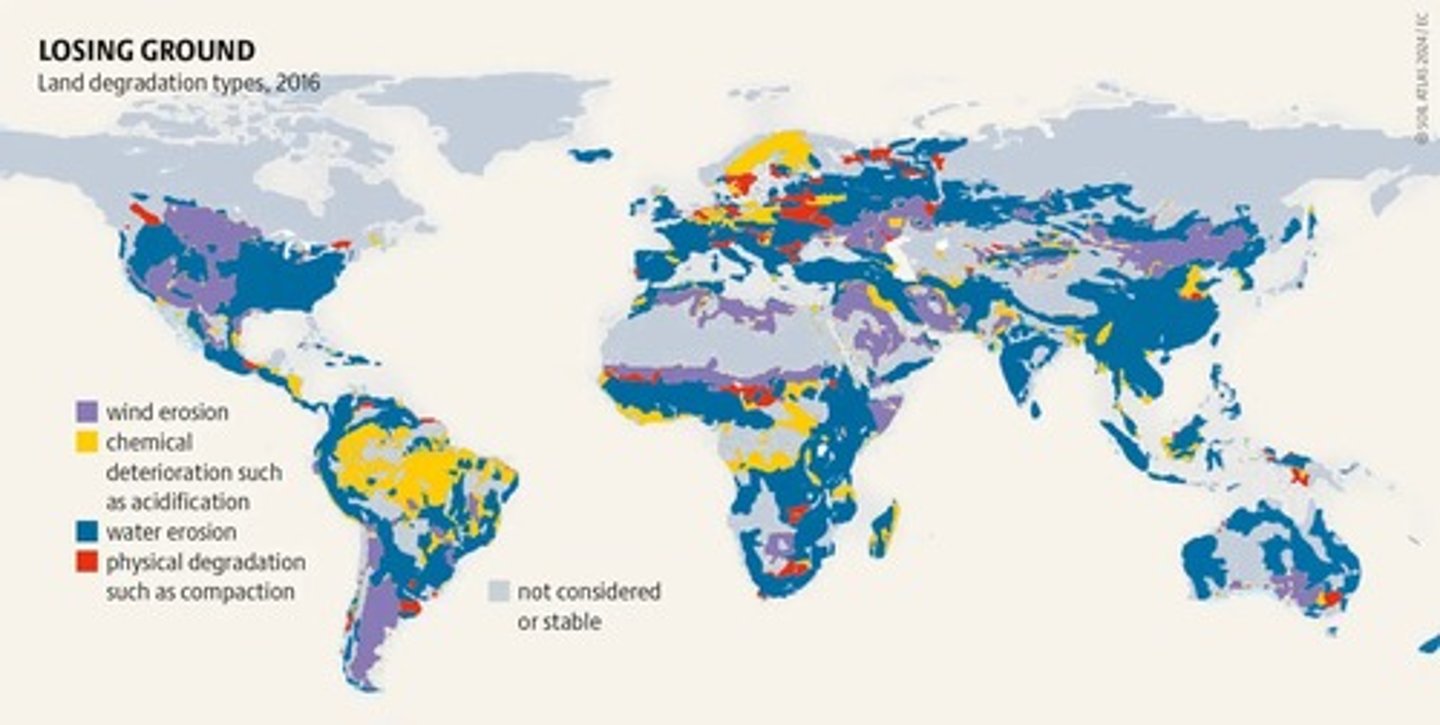
What best management practices (BMP) can help preserve soil and water quality?
Cover crops, mulching, and conservation tillage.
How does soil interact with climate change?
Soil management can increase or decrease greenhouse gas concentrations, affecting climate change.
What is carbon sequestration in relation to soil?
The process of storing carbon in soils or plants to mitigate climate change.
What role does organic matter in soil play in carbon storage?
Organic matter is one of the planet's largest reservoirs of carbon; its loss increases atmospheric CO₂.
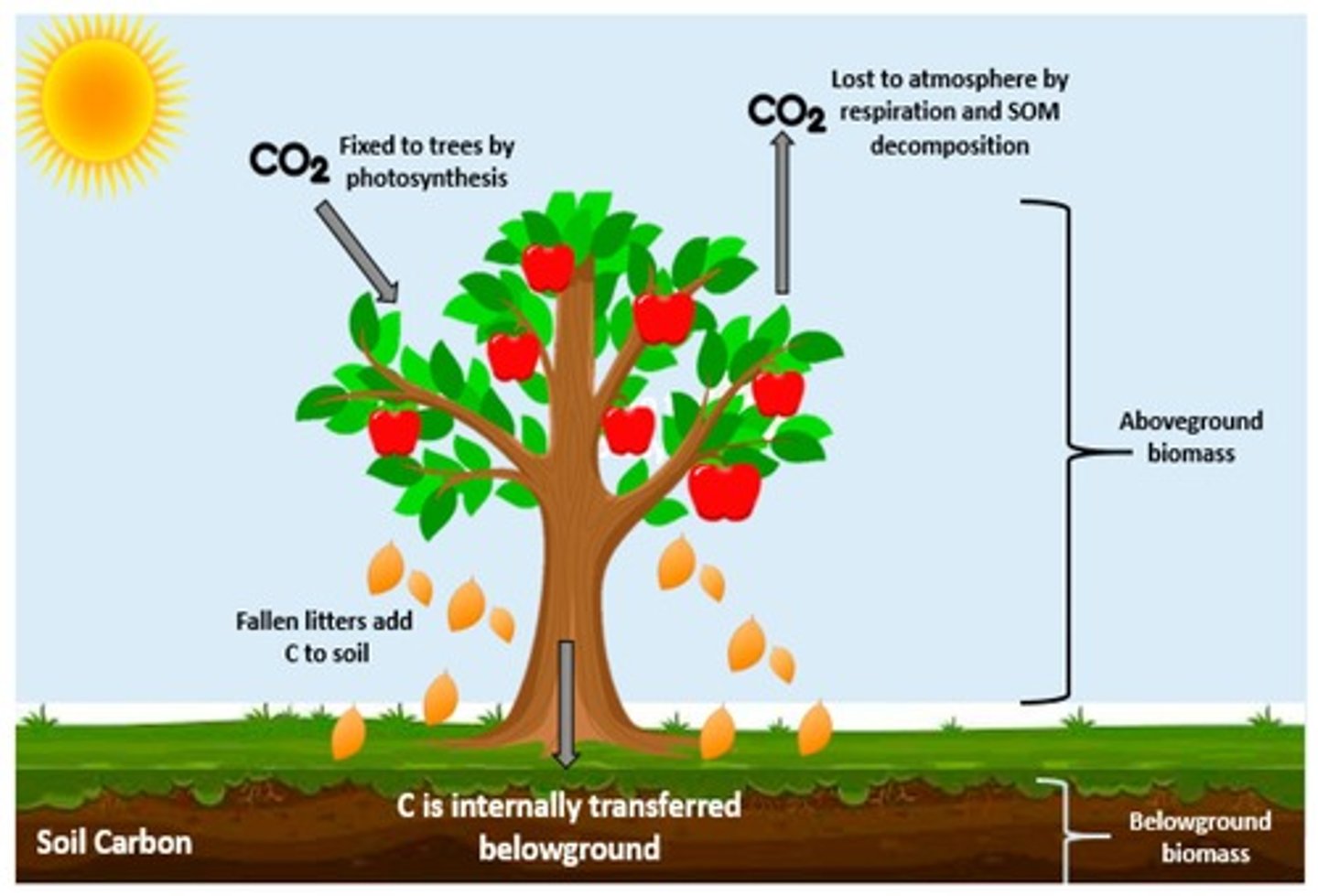
What are the consequences of losing organic matter from fields?
More CO₂ is released into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change.
What is the impact of conservation tillage on soil carbon?
Conservation tillage helps build soil carbon and improve crop productivity.
What is the significance of soil moisture and nutrients in determining plant communities?
Soil moisture and nutrients influence which plant communities can thrive in specific locations.
What are the essential nutrients that plants need from soil?
Plants need 17 essential nutrients, 14 of which are absorbed from the soil.
What is the role of soil in recreational uses?
Soil is used in recreational areas like golf courses, where it must be managed for optimal conditions.
What is the effect of urban agriculture on soil management?
Urban agriculture requires specific soil management practices to ensure healthy crop production.