Parts of the Brain video
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:45 AM on 3/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
3
New cards
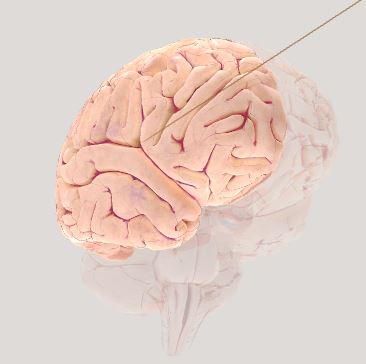
\
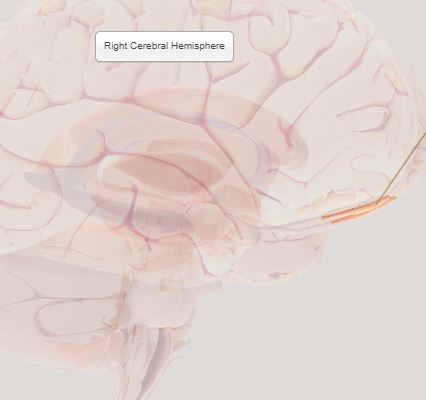
Right Cerebral Hemisphere
4
New cards
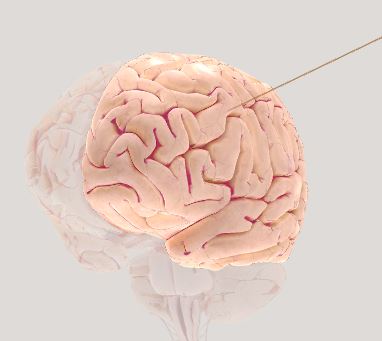
\
Left Cerebral Hemisphere
5
New cards
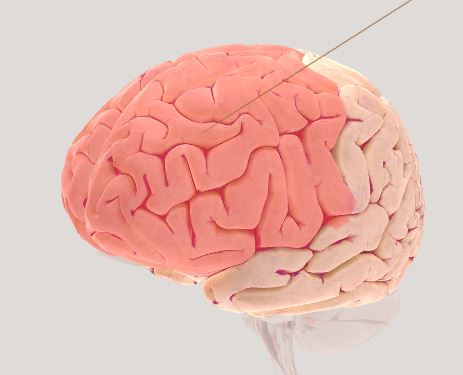
Frontal Lobe- working memory and behavioral traits
6
New cards
What is Phrenology and who is an example?
The detailed study of the shape and size of the cranium as an indication of character and mental abilities; Franz Joseph Gall
7
New cards
What makes the bodies big decisions? ai. command center
Central Nervous System
8
New cards
What are non-neutron cells that assist neutrons?
Neuroglia
9
New cards
What Part of the Body has sensory neurons that gather information and report it back to the body
Peripheral Nervous System
10
New cards
Who got a pole through their head and paved the way for connections between behavior and the brain?
Phineas Gage
11
New cards
Why is the 10% theory wrong?
Every region of the brain lights up during simple tasks like walking and talking.
12
New cards
What percentage of the body’s energy does the brain need?
20%
13
New cards
New Brain systems built upon old brain systems
Differences in minds of different animals.
14
New cards
What is the most basic part of our brain called and what is it anchored by?
“Old Brain”; Brain stem
15
New cards

The most ancient and central core of the brain. Spinal cord enters the skull.
Brain Stem
16
New cards
What controls automatic body tasks that don’ t require conscious effort ex. beating of heart?
Medulla
17
New cards
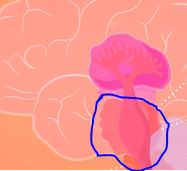
\
What helps coordinate movement, arousal, other automatic functions ex. sleep, and relying information between cerebellum and cerebral cortex in the old brain?
What helps coordinate movement, arousal, other automatic functions ex. sleep, and relying information between cerebellum and cerebral cortex in the old brain?
Pons
18
New cards
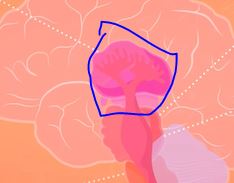
What part of the old brain takes in sensory information ex. hearing?
Thalamus
19
New cards
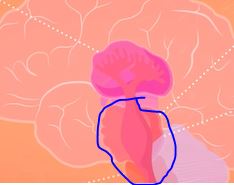
Finger shaped nerve that’s essential for arousal
Reticular Formation
20
New cards
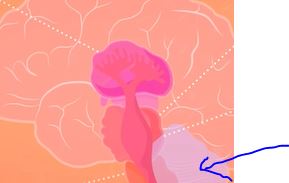
Responsible for non-verbal learning and memory, perception of time, voluntary movement, and modulating emotion
Cerebellum
21
New cards
What separates the old brain and the newer cerebral areas?
Limbic system
22
New cards
What is more complex and newer then the limbic system and the old brain?
Left and Right Hemispheres
23
New cards
Journalist and armchair phycologist use research showing the complexity of the brain to sell newspapers
Pop psychology
24
New cards
A thin layer of 20 billion interconnected neurons
Cerebral Cortex
25
New cards
Spiderweb of support that surrounds, insulates, and nourisihes the cerebral neurons.
Glial Cell
26
New cards
What are the four lobes of the Cerebral Cortex?
Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Temporal
27
New cards
Especially prominent folds that separate cerebral Cortex lobes.
Fissures
28
New cards
Processes incoming sensations in the frontal lobe; behind motor cortex
Somatosensory Cortex
29
New cards
Deals with higher mental function such as thinking (interpreting and linking sensory information to memories)- more subtle in all lobes
\
Association Areas
Association Areas
30
New cards
Sensory to CNS
Afferent
31
New cards
CNS to Sensory
Efferent
32
New cards
Study of drugs and their effects
Pharmacology
33
New cards
chief neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system, the part of the autonomic nervous system, that contracts smooth muscles, dilates blood vessels, increases bodily secretions, and slows heart rate. can stimulate a response or block a response and thus can have excitatory or inhibitory effects.
AcH
34
New cards
\#signals
Divergence
35
New cards
\#signals recived by target
Convergence
36
New cards
Send electrical and chemical signals
Neutrons
37
New cards
Supports, protects, and repairs neutrons
Glia/neuroglia
38
New cards
Parts of Neutron
\
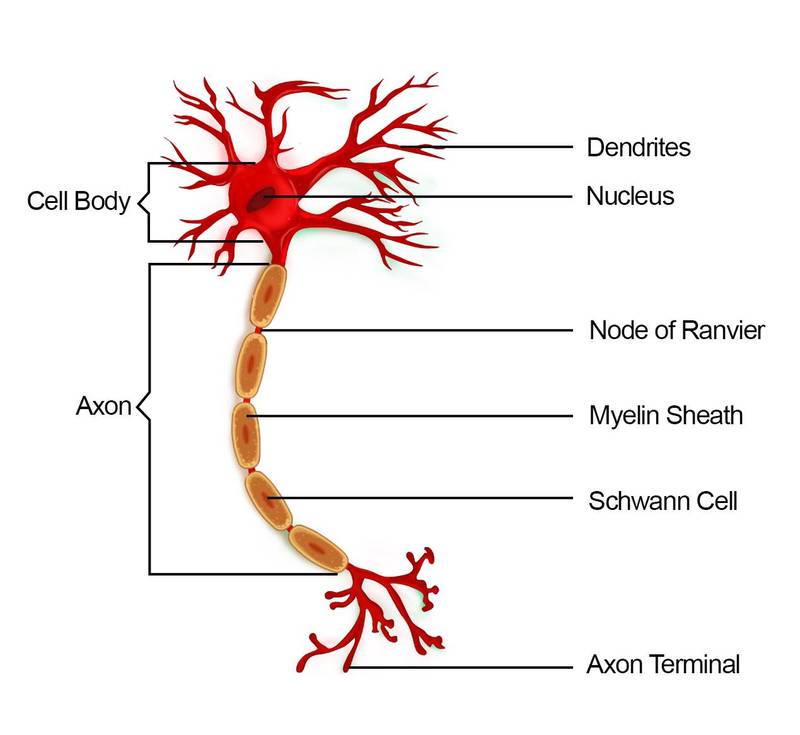
39
New cards
Learning to do things that we weren’t born with
Learning Circut
40
New cards
Part of the Brain that seeks rewards
Striatum
41
New cards
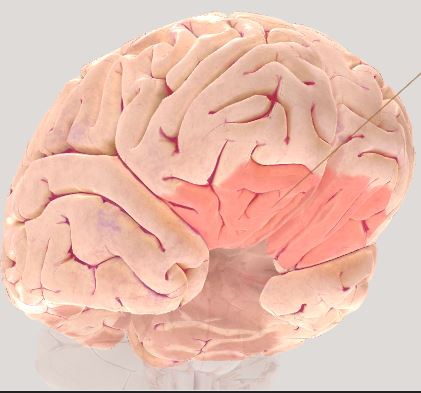
\
Orbitofrontal Cortex- understand complex behaviors
42
New cards
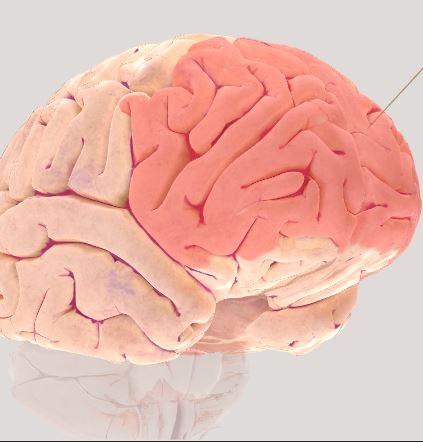
Prefrontal Cortex- complex decisions
43
New cards
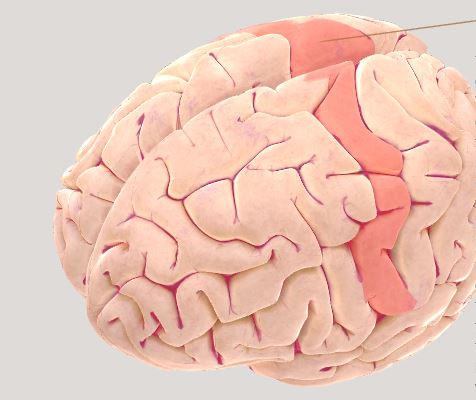
Motor Cortex- directs movement
44
New cards
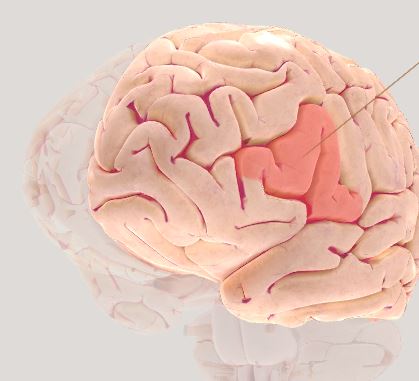
Broca’s area- coordination of speech
45
New cards
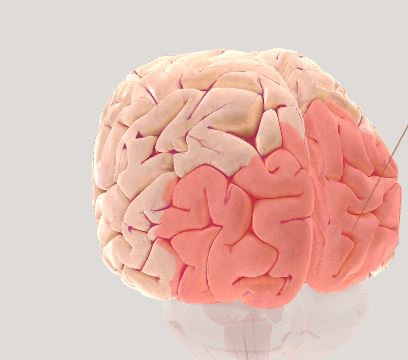
Occipital Lobe- visual
46
New cards
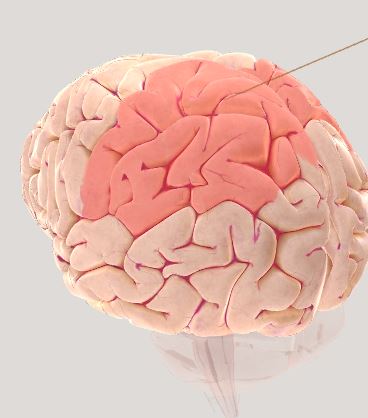
Parietal Lobe-information from senses
47
New cards
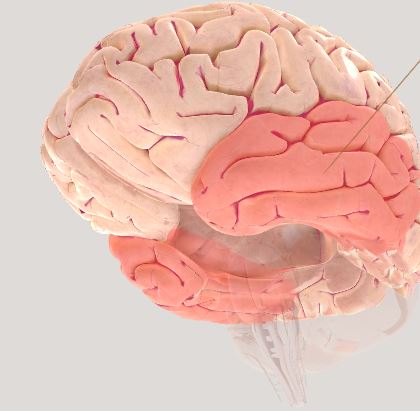
Temporal Lobe- memories, emotions, comprehension, recognition
48
New cards
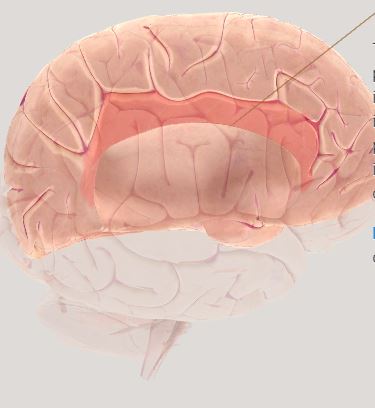
Cingulate Cortex- emotions, emotional distress of pain
49
New cards
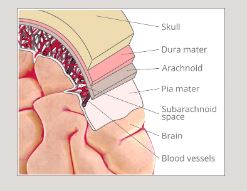
Meningeal Layers- envelop and protect the brain
50
New cards
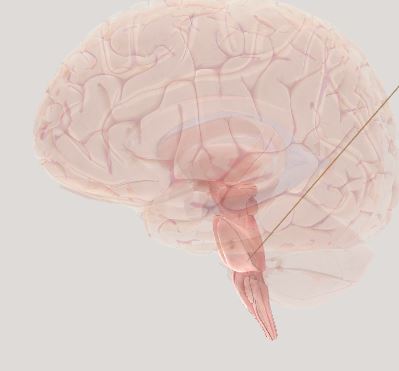
Brain Stem- essential activities; heart rate and breathing
51
New cards
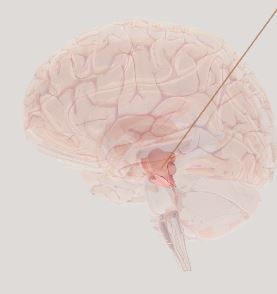
Midbrain- regulates movement and holds substantia nigral which helps regulate movement
52
New cards
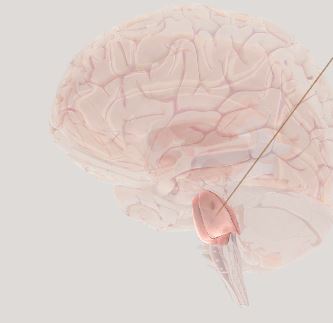
\
Pons- Attention
53
New cards
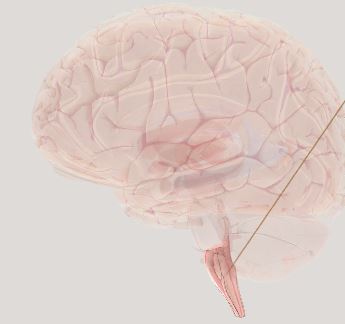
Medulla Oblongata- breathing control centers
54
New cards
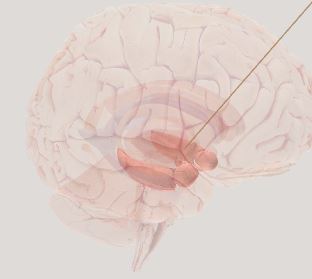
Limbic System- motivation, learning, memory, emotion
55
New cards
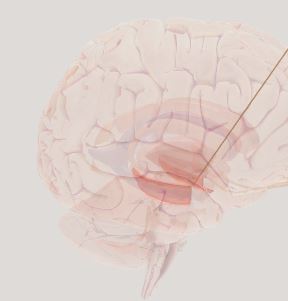
Entorhinal Cortex- funnel sensations into hippocampus for memory and have grid cells that help relate our location in space to the external environment
56
New cards
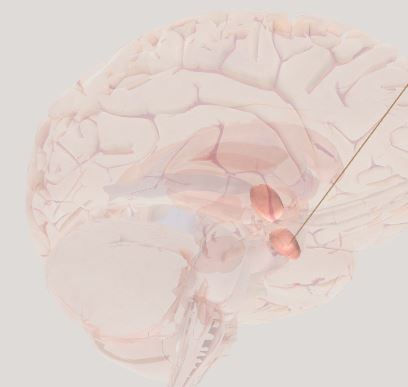
Amygdala- helps hippocampus create long term memories linked to emotion
57
New cards
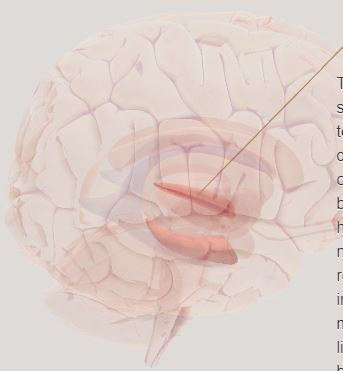
Hippocampus- long term memory
58
New cards
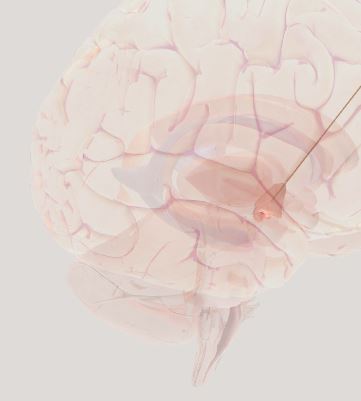
Hypothalamus- link between CNS and endocrine system. Controls Pituitary Gland. helps to bridge brainstem subconscious signals to the cerebral cortex
59
New cards
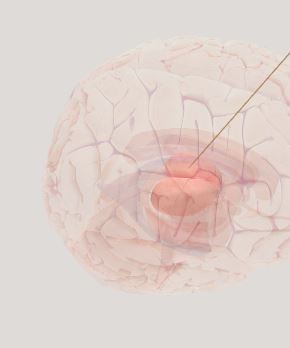
Thalamus- relays information about senses to rest of the brain
60
New cards
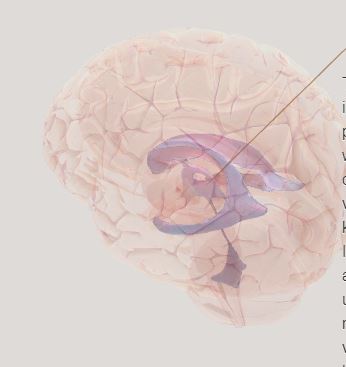
Ventricles- four cavities in the brain that produce cerebrospinal fluid to protect, nourish, and clean up the brain.
61
New cards
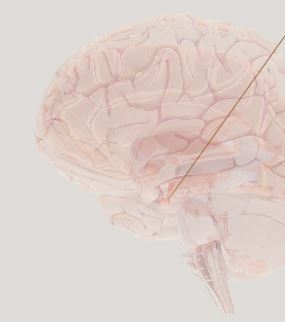
Pituitary Glad- produces and releases hormones to control various bodily functions and behaviors
62
New cards
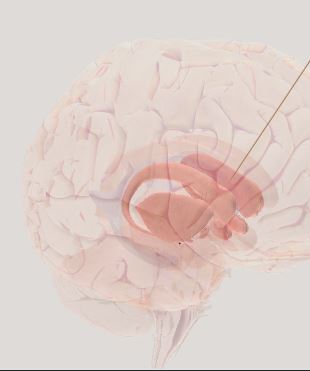
Basal Ganglia- control voluntary movements, habitual behaviors, and emotion
63
New cards
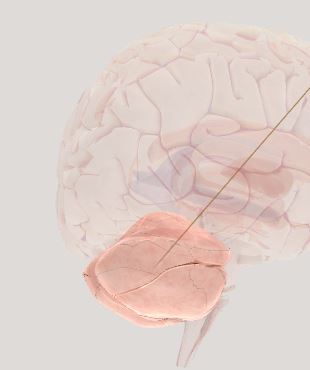
Cerebellum- hones the most practiced talents and helps improve motor skills
64
New cards
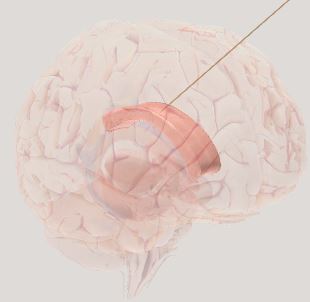
Corpus Callosum- links the left and right hemisphere of cerebral cortex (superhighway)
65
New cards
Olfactory Bulb- processes sense of smell
66
New cards
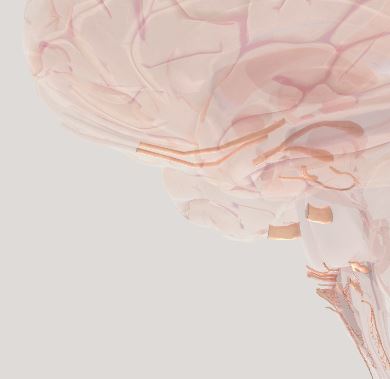
Cranial Nerves- 12 nerves controlling muscles in the neck and head.