Bio 1.8 Immune system
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
immune system
can be divided into:
innate
adaptive immunity
innate immunity
consist of defenses that are always active against pathogens but are not capable of targeting specific invaders
adaptive immunity
long response time but response targets a specific pathogen and maintains immunologic memory of the infection to mount faster response during subsequent infections
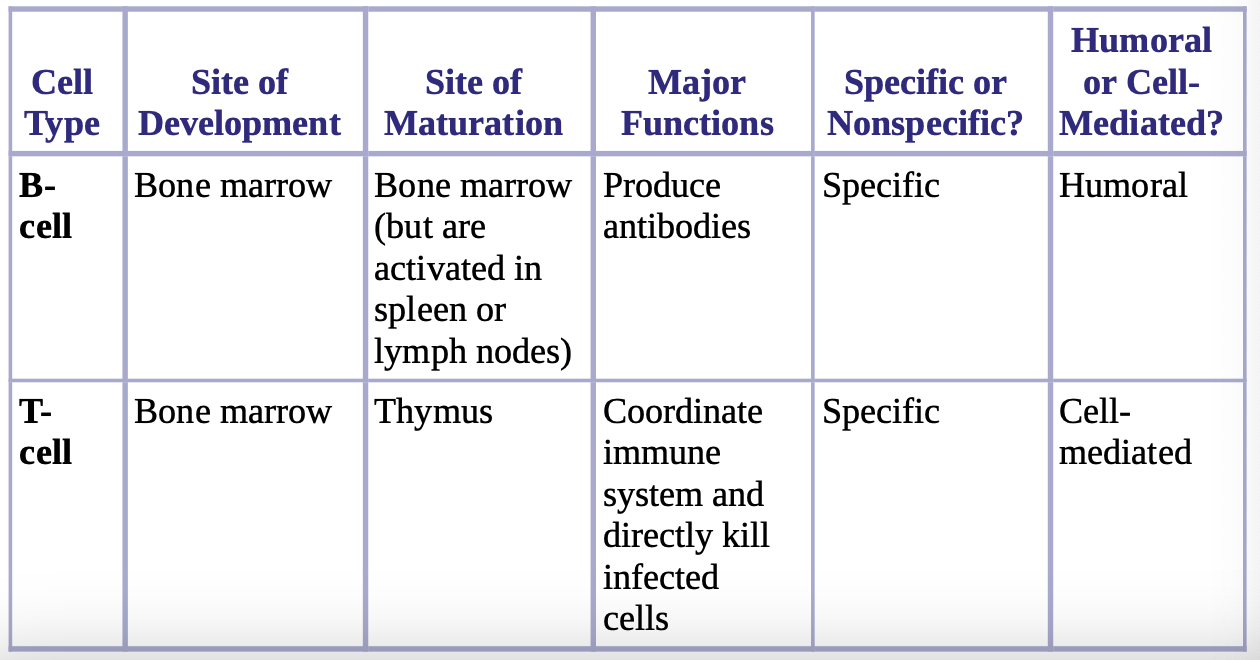
B-cell vs T-cell
humoral immunity driven by B-cells and antibodies, cell mediated immunity driven by t-cells
granulocytes
neutrophiles, eosinophils and basophils
agranulocytes
lymphocytes (B and T cells) and macrophages (monocytes)
immune system is found in
bone marrow [where immune cells come from]
spleen and lymph nodes are sites where immune response can be mounted and in which the B-cells are activated
thymus site of T-cell maturation
Gut associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) includes tonsils and adenoids
leukocytes
white blood cells
non-specific non-cellular defenses [innate immune system]
skin
mucus
tears and saliva [contain lysoszyme]
stomach
complement system
interferons
skin
acts as a physical barrier and secretes antimicrobial compounds like defensins
mucus
traps pathogens; in the respiratory system, the mucus is propelled upwards by cilla and can be swallowed or expelled
tears and saliva
contain lysozyme [an antibacterial compound]
stomach
produces acid, killing most pathogens.
colonization of the gut helps prevent overgrowth by pathogenic bacteria throiugh completion
complement system
punches holes in cell walls of bacteria making them osmotically unstable
interferons
given off by virally infected cells and help prevent viral replication and dispersion to nearby cells
non-specific cellular defenses
macrophages
MHC class 1
MHC class 2
dendritic cells
natural killer cells
granulocytes
neutrophils
eosinophils
basophils
mast cells
Macrophages
ingest pathogens and present them on major histocompatibility complex.
secrete cytokines (Cytokines signal the immune system to fight infections and injury)
MHC Class 1
presented in nucleated cells and displays endogenous antigen (antigen from within the cell) to cytotoxic t-cells (CD8+ cells)
MHC Class 2
present professional antigen-presenting cells (macrophages, dendritic cells, B-cells and certain activated epithelial cells) and displays exogenous (proteins from outside the cell) to helper T-cells (CD4+ cells)
dendritic cells
antigen presenting cells in the skin
Natural killer cells
attack cells not presenting MHC molecules, including viraly infected cells and cancer cells
Granulocytes
neutrophils, esinophils and basophils
neutrophils
ingest bacteria, opsonisation of bacteria (those that are marked with antibodies)
follow bacteria via chemotaxis
esinophils
used in allergic reactions and invasive parasitic infections.
release histamine causing inflammatory response.
basophils
used in an allergic reaction
circulate in the bloodstream
mast cells
used in an allergic reaction
reside in tissues in the body
adaptive immunity
humoral immunity
cell-mediated immunity
humoral immunity
centered on antibody production by plasma cells [which are activated B-cells]
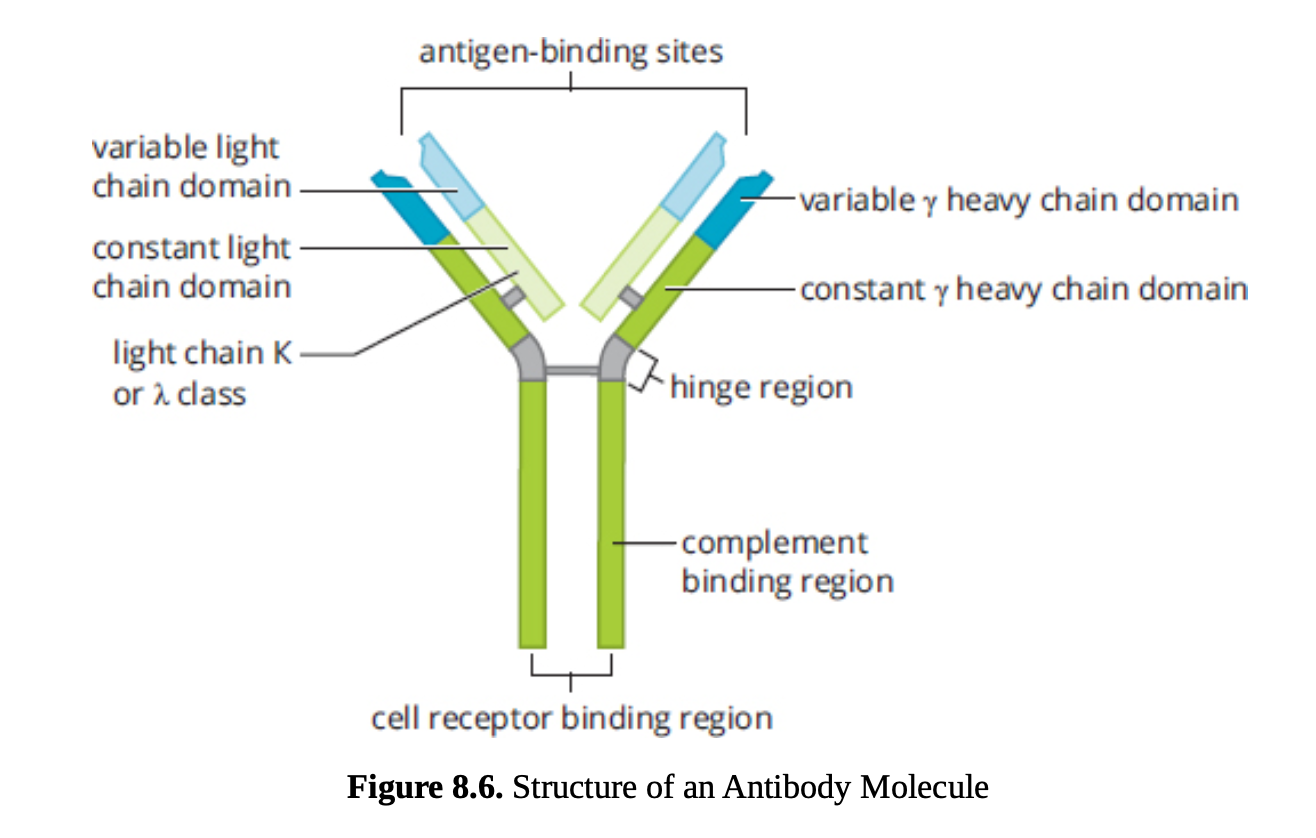
antibodies
target particular antigen
the tip of the variable region is the antigen binding region
when activated antigen binding region undergoes hypermutation to improve the specificity of the antibody produced
circulating antibodies can opsonize pathogens (mark them for destruction), cause agglutination (clumping) into insoluble complexes that are ingested by phagocytes or neutralise pathogens
antibody types
IgM
IgD
IgG
IgE
IgA
memory B-cells
wait for second exposure to a pathogen and can then mount a more rapid response (secondary response)
cell-mediated (cytotoxic) immunity
centered on T-cells
t-cells
undergo maturation in the thymus through positive selection (only that can react to antigen presented on MHC) and negative selection (causing apoptosis in self-reactive T-cells)
thymosin is a peptide hormone that promotes T-cell development
helper T-cell (CD4+/ Th)
respond to MHC 2 and coordinate the rest of the immune system
secretes lymphocytes to active various arms of defense
Th1 - secrete interferon to active macrophages
Th2 - activate B-cells in parasitic infections
Cytotoxic T-cell (Tc/ CD8+)
respond to antigen on MHC-1 and kill virally infected cells
suppressor T-cell
tone down response after an infection and promote self tolerance
autoimmune
self-antigen is identified as foreign and immune system attacks the body’s own cells
allergic reactions
non-threatening exposure that incite inflammatory response
immunization
inducing active immunity prior to exposure to a particular pathogen
passive immunity
transfer of antibodies to the individual
lymphatic system
circulatory system that consist of 1 way vessels with intermittent lymph nodes
connects to the cardiovascular system via the thoracic duct
equalises fluid distribution, transport fats and fat soluble compounds in chylomicrons and provides sites for mounting immune responses
hematopoietic cell
immature cells that develop into all types of blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. They are also known as blood stem cells.