Bio - Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
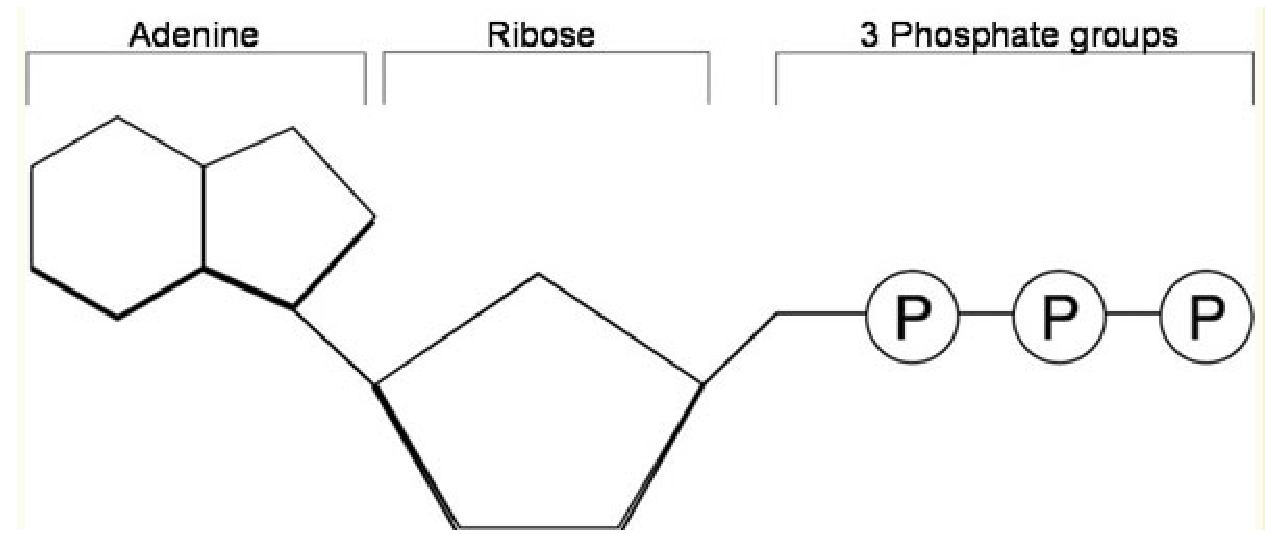
What are the three parts of ATP?
Adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups
Where is the energy of ATP stored?
The phosphate bonds
What happens to ATP when it loses energy?
It becomes ADP.
What are some high energy molecules?
ATP, NADPH, NADH, FADH2
What are some low energy molecules?
ADP, NADP+, NAD+, FAD+
What are the parts of a chloroplast?
Stroma: “cytoplasm” empty space
Thylakoids: little membrane disks
Grana: stacks of thylakoids
What does chlorophyll reflect?
most yellow and green light
What are accessory pigments?
Pigments that absorb the colors chlorophyll reflects (green and yellow)
What is the purpose of photosynthesis?
To use sunlight to make glucose
Where does it happen?
In the chloroplasts.
What are the reactants in photosynthesis?
H2O, CO2
*Sunlight is NOT a reactant
What are the products of photosynthesis and what happens to them?
O2 (released as waste)
C6H12O6
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O ——> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What are the steps involved in photosynthesis?
Light dependent reactions
Light independent reactions (Calvin Cycle)
Where do light dependent reactions take place?
Thylakoids. (they need the chlorophyll)
What goes into light dependent reactions?
Sunlight, H2O
What is produced by light independent reactions, and what happens to them?
ATP and NADPH go to light independent reactions, and O2 is released as waste
Describe light dependent reactions.
Sunlight energy strikes the chorophyll pigments of photosystem II (chlorophyll).
Electrons are boosted through the energy from photosystem II to a carrier molecule, the first primary electron acceptor, now at high energy.
H2O (reactant) molecule is split, forming 2e-, H+, and O2.
As the electrons go away from Photosystem II (chlorophyll) they are replaced by 2e- from the split water molecule.
H+ are released inside the thylakoid membrane.
O2 (product) is released as waste.The electrons in the primary electron acceptor go bouncing down the electron transport chain from high to low (energy). They reach photosystem I (chlorophyll).
As they travel down the electron transport chain, their energy is used to transport H+ ions across the thylakoid membrane.
The H+s move from the thylakoid to the stroma through a protein ATP synthase, causing it to spin and combine ADP with P, making ATP (product).
In photosystem I, sunlight’s energy boosts the electrons to another electron acceptor, while electrons from the first electron transport chain replace them as they leave photosystem I.
NADP+ and H+ combine with the 2e- (2 negative charges) to make NADPH (product)
Where does the Calvin Cycle, or light independent reactions, take place?
Stroma
What is used in the Calvin Cycle, aka light independent reactions?
CO2, ATP, NADPH
What is produced by the Calvin Cycle, or light independent reactions? Where do these products go?How many turns of the cycle are necessary to finish making all products?
6 turns to create 1 glucose.
ADP and NADP+ are also created, and they go back to the light independent reactions to get charged back up (into ATP and NADPH)
Describe the light independent reactions.
A 5-carbon molecule called RuBp (ribulose biphosphate) combines with CO2 (reactant) to make a 6-carbon molecule.
The 6-carbon molecule splits into 2 PGAs, each of which is 3-carbon.
The PGAs use the energy from the ATP (reactant) and NADPH (reactant) created in the light-dependent reactions to convert into 2 PGALs.
The PGALs combine and drop 1 carbon, resulting in a 5-carbon RuBp again.
The cycle restarts and runs 6 times, dropping 1 carbon each time - making C6H12O6 (product)
*note: this process is simplified
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
To make ATP from glucose
Where does cellular respiration happen?
In the mitochondria
What is the correlation between the equations of photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
They’re opposites!
What are the reactants in cellular respiration?
O2 and C6H12O6
What are the products of cellular respiration?
CO2 & H2O
What is the overall chemical equation of cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ——> 6H2O + 6CO2
What are the steps involved in cellular respiration?
Glycolysis
Krebs Cycle
Electron Transport System
Where does glycolysis take place?
In the cytoplasm.
What is used in glycolysis?
Glucose, ATP
What is produced in glycolysis, and what happens to it?
ATP, NADH, and pyruvic acid. NADH goes to the electron transport system, ATP gets used by the cell, and pyruvic acid goes to the Krebs Cycle (or fermentation, if there isn’t oxygen).
Describe the process of glycolysis.
Glucose (reactant) uses the energy from 2 ATP (reactant) (turning them into ADP, as usual) to split into 2 PGALS (phosphoglyceraldehyde). Each PGAL turns into pyruvic acid (product), releasing energy and turning NAD+ into NADH is well as the 2 ADP back into 2 ATP (product). 2 NADH (product) and 4 ATP (product) is the total.
What are the energy gains in glycolysis?
2 ATPs used, 4 ATPs created: Net gain = 2 ATP
Where do the products of glycolysis go?
ATP is used by the cell, and NADH is sent to the electron transport system. Pyruvic acid goes to Krebs Cycle if oxygen is present, but if it’s not it goes to fermentation.
How many carbons are in a pyruvic acid?
3
Where does the Krebs Cycle take place?
In the matrix of the mitochondria.
What is used in the Krebs Cycle?
Pyruvic acid
For each glucose molecule, how many times does it turn? Why?
Twice, once for each pyruvic acid the glucose produces.
What are the total energy gains and products of the Krebs Cycle? What happens to them?
3 CO2
1 ATP
3 NADH
1 FADH2
The CO2 is waste (we exhale this)
ATP is used by the cells
NADH and FADH2 are sent to the electron transport system
Describe the Krebs Cycle.
Basically, a 4-carbon molecule starts the cycle by combining with a 2-carbon molecule to make a 6-carbon molecule. Stuff happens to the 6-carbon to make it 4-carbon again, restarting the cycle.
The 3-carbon pyruvic acid (reactant) releases a CO2 (product) and becomes the 2-carbon molecule.
The 2-carbon molecule binds to the 4-carbon molecule already from the cycle, resulting in a 6-carbon molecule.
The 6-carbon loses a carbon atom, releasing a CO2 (product) to become a 5-carbon molecule.
The 5-carbon drops a CO2 (product) again, becoming a 4-carbon molecule.
The energy released from releasing all these carbons is stored in ATP (product), NADH (product), and FADH2 (product)
Where does the electron transport system take place?
In the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
What is used in the electron transport system?
NADH, FADH2, O2, H+
What is produced by the electron transport system?
ATP and H2O. ATP is used by the cell and water is a waste product.
Also FAD+, NAD+ and ADP which return to the Krebs Cycle.
Describe the electron transport system’s purpose and process.
Purpose: make high-energy electrons into ATP.
High-energy molecules NADH (reactant) and FADH2 (reactant) give up their (high-energy) electrons to carrier molecules which pass them down the electron transport chain.
As they go they release energy which is used to pump the H+ (reactant) ions from the matrix to the inner membrane space.
The H+ ions move through the ATP Synthase on the inner membrane, which then spins and makes ATP (by combining ADP + P)
Oxygen (reactant) is the final electron acceptor, combining with the H+ ions to make H2O (product): H+ + H+ + O + e- = H2O
When does fermentation happen?
When there isn’t enough oxygen.
What is used in fermentation?
Pyruvic acid
What is produced by alcoholic fermentation?
CO2 and alcohol
What is produced by lactic acid fermentation?
Lactic acid, NAD+
NAD+ returns to glycolysis to get charged (into NADH)
How much more ATP does aerobic respiration (glycolysis, krebs cycle, electron transport system) make than anaerobic (glycolysis, fermentation)>?
Aerobic: 36 ATP
Anaerobic: 2 ATP