Biomolecules: Essential Macromolecules in Biology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Why is water less dense as a solid than as a liquid?
Ice has a structured lattice that makes it less dense than liquid water.

What is the primary product of photosynthesis in plants?
Glucose
What is a reducing sugar?
A sugar that can donate electrons and reduce other substances.
What are the functions of proteins?
They store energy, provide structural support, and act as enzymes.
What is collagen?
A type of structural protein found in connective tissues.
What is the term for the attraction between molecules of the same substance?
Cohesion
What is the term for the attraction between molecules of different substances?
Adhesion
What is the role of water in temperature regulation?
High heat capacity allows it to absorb and release heat without significant temperature changes.
What is a glycosidic bond?
A bond formed between monosaccharides during a condensation reaction.
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Amino acids
What is the primary function of lipids?
Energy storage and forming cell membranes.
What type of biomolecule is RNA?
Nucleic acid
What is the function of ribose in nucleic acids?
It is a core component of RNA.
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
Deoxyribose has one less oxygen atom than ribose.
What reaction forms disaccharides from monosaccharides?
Condensation reaction
Why are glycogen and starch suitable as storage materials?
They are insoluble in water, large molecules, and easily hydrolyzed.
What is hydrolysis?
A reaction that breaks down larger molecules into smaller ones using water.
What is the role of amylase in digestion?
Amylase cuts starch into maltose.
What happens when a reducing sugar is boiled with Benedict's solution?
It produces a brick-red precipitate if a large amount is present.
What are the main components of lipids?
Glycerol and fatty acid chains.
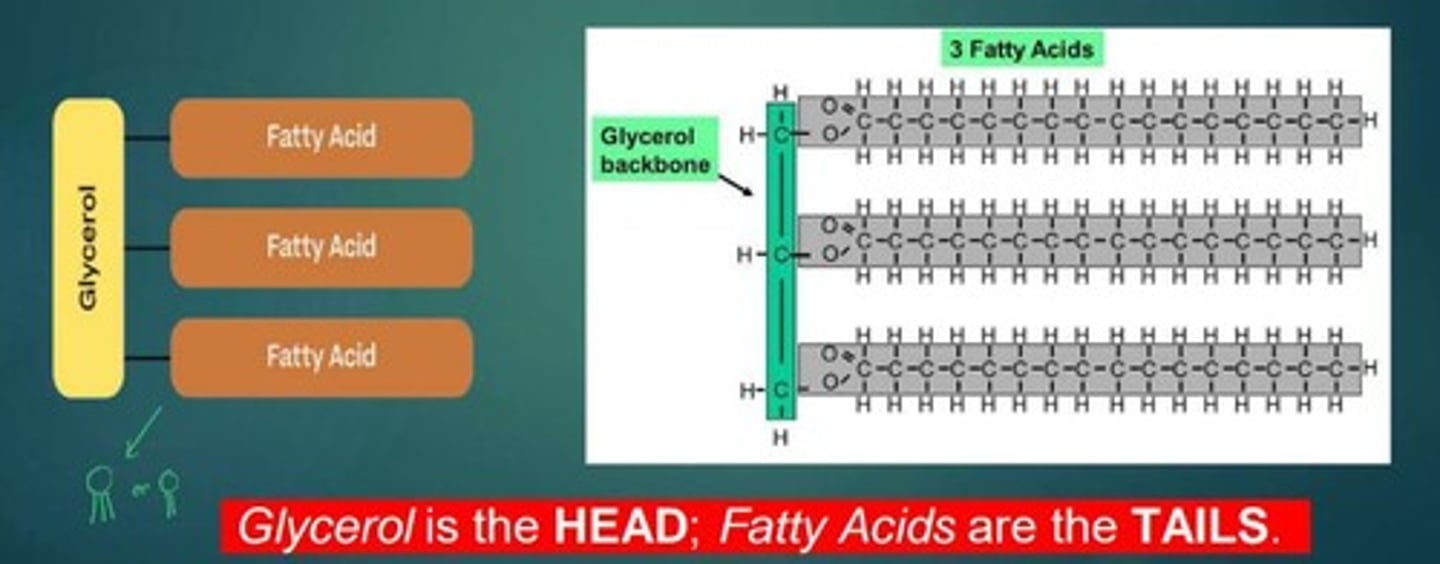
What distinguishes saturated fats from unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats have no double bonds between carbon atoms, while unsaturated fats do.
What is the structure of phospholipids?
They have a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic fatty acid tails.
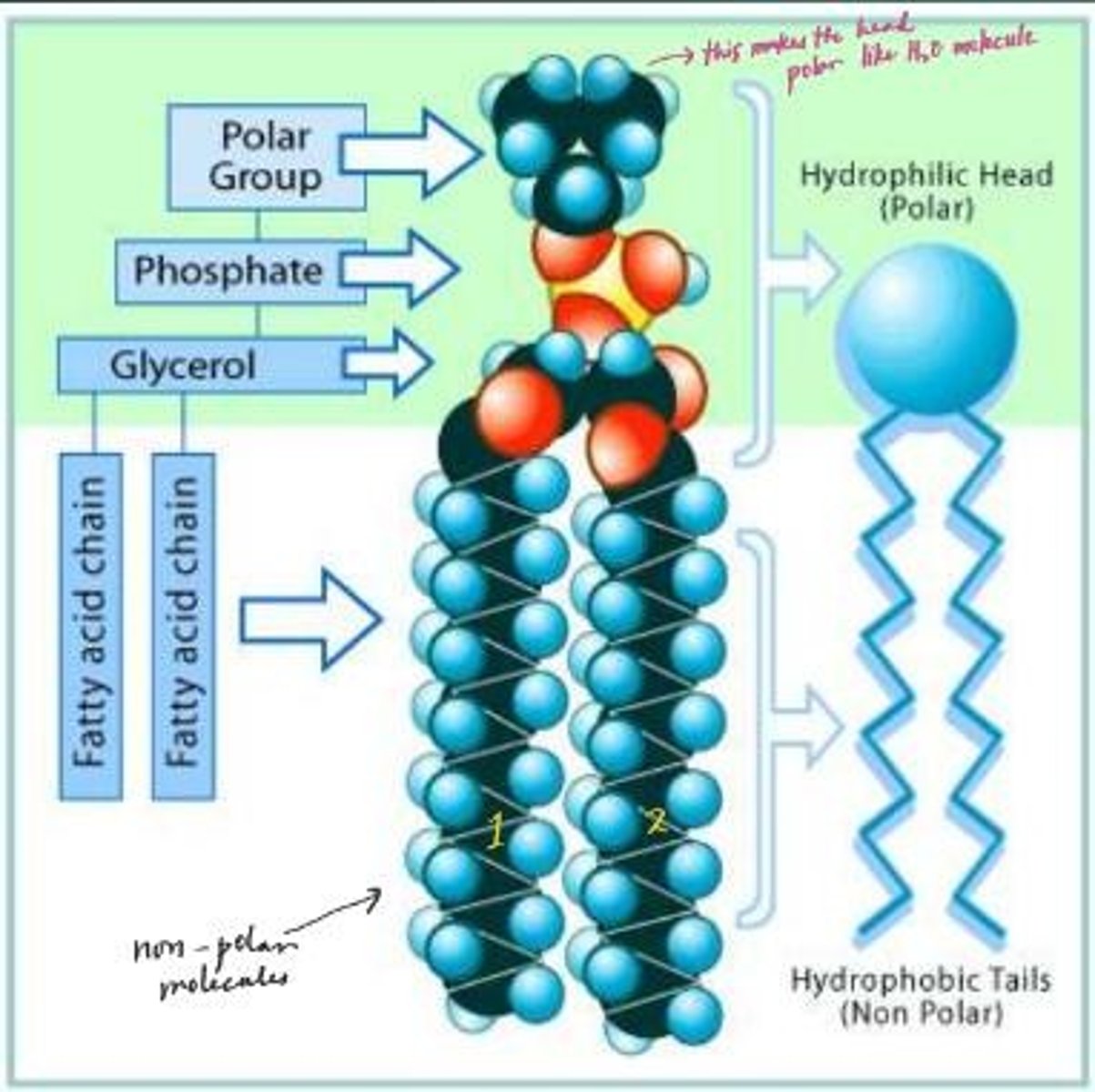
What is the primary function of triglycerides?
They serve as a concentrated source of energy.
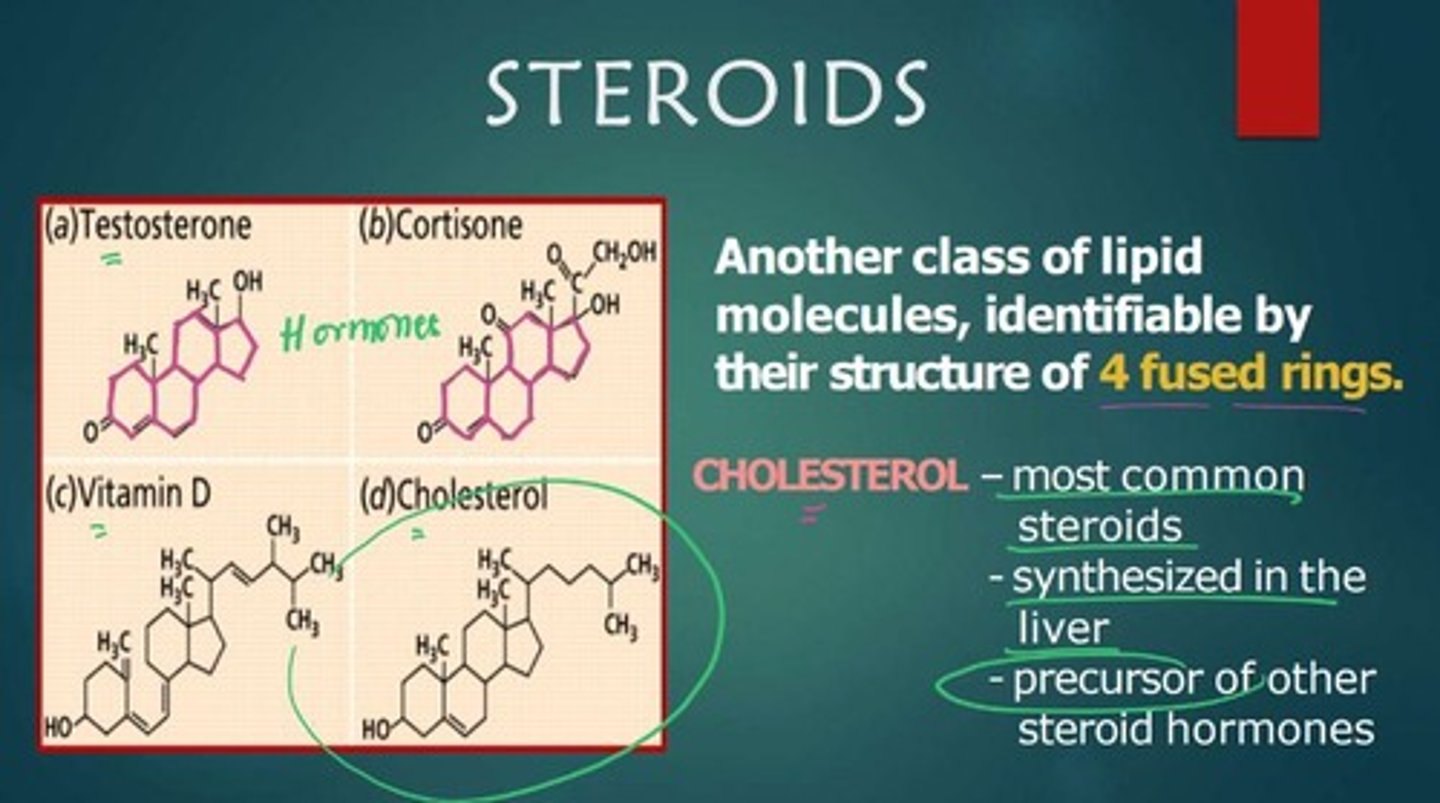
What are steroids?
A class of lipid molecules characterized by a structure of four fused rings.
What is the main component of cell membranes?
Phospholipids
What is the role of cholesterol in the body?
It serves as a precursor for other steroid hormones.
What are structural proteins?
Proteins that provide support and shape to cells and tissues.
What is keratin?
A structural protein found in hair, nails, and skin.
What is the importance of lipids in insulation?
Lipids provide insulation and protect organs from shocks.
How do lipids contribute to energy storage?
They are concentrated sources of energy, providing approximately 36 kJ/gram.
What are the four major types of biomolecules?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
What is the primary function of carbohydrates?
Immediate source of energy
What are lipids commonly known as?
Fats
What are proteins made from?
Amino acids
What are nucleic acids responsible for?
Carrying genetic information (DNA and RNA)
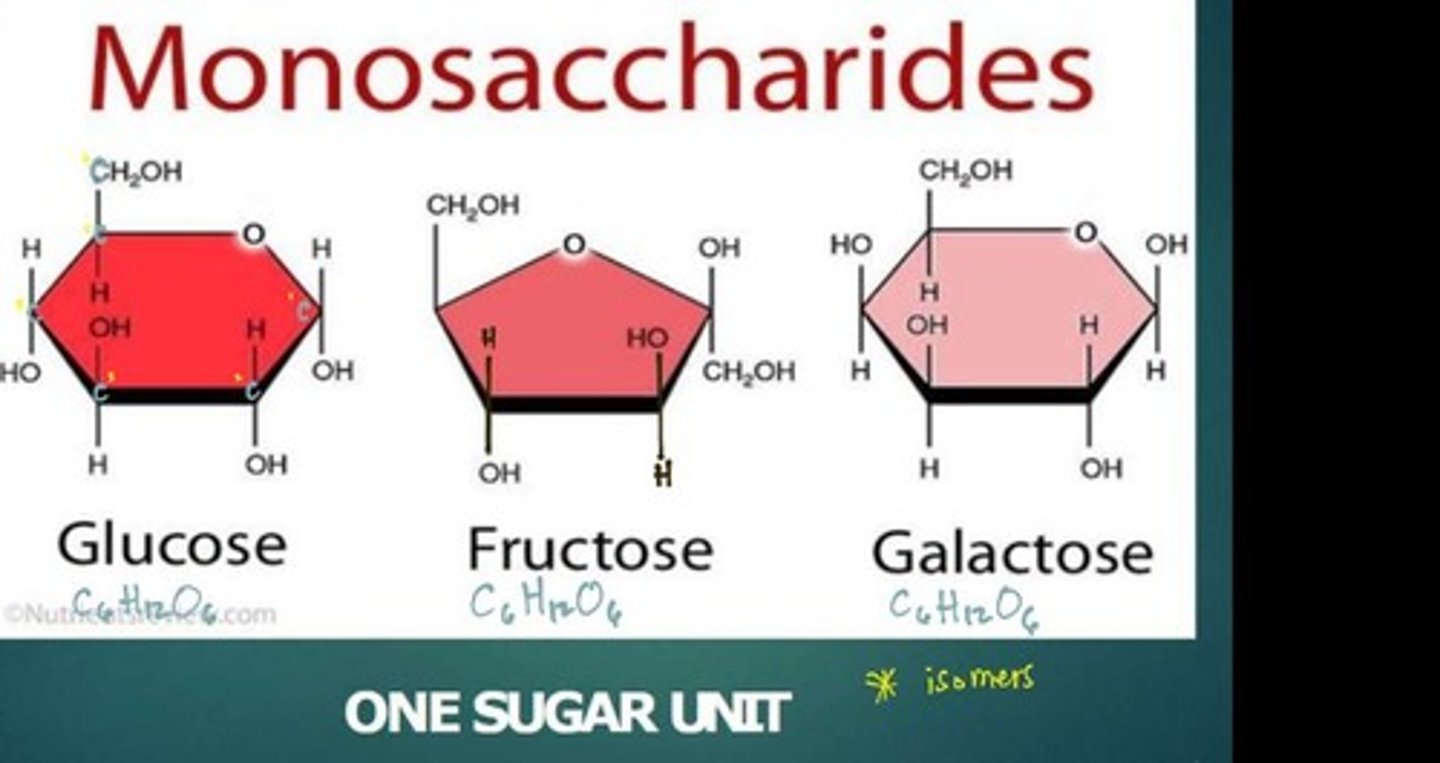
What is the chemical formula for monosaccharides?
C6H12O6
What is a disaccharide?
A sugar molecule composed of two monosaccharides
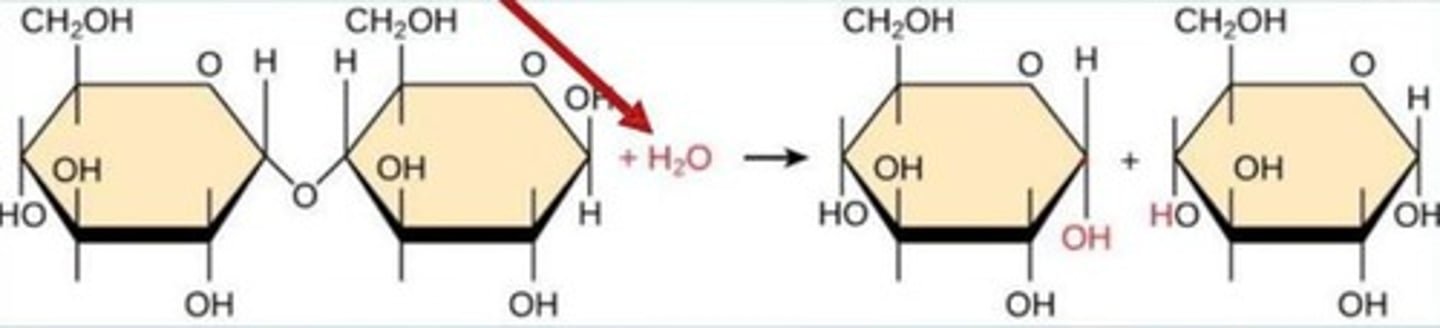
Give an example of a disaccharide.
Sucrose (glucose + fructose)
What is the general formula for polysaccharides?
(CH2O)n where n is the number of carbon atoms
What is the role of water in biological systems?
Universal solvent, key component of tissues, regulates temperature, and transports dissolved substances
What property of water allows it to dissolve many substances?
Polarity
What is the significance of hydrogen bonds in water?
They give water important properties like high heat capacity and cohesion.
What is the process of polymerization?
The joining of monomers to form polymers, often through condensation reactions.
What is a monomer?
A small, simple molecule that can join together to form polymers.
What is the difference between amylose and amylopectin?
Amylose is a linear form of starch, while amylopectin is branched.
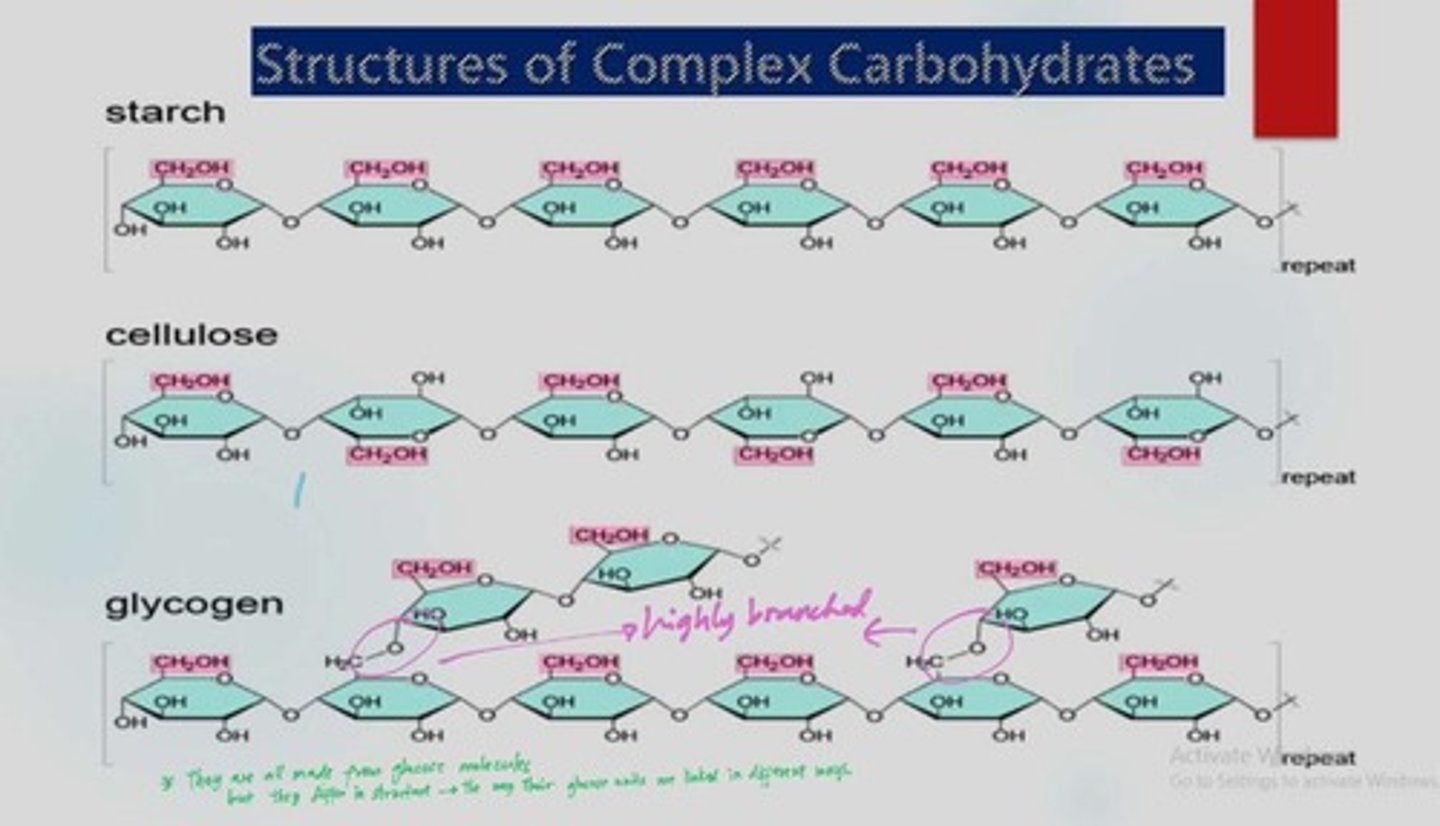
What is glycogen and where is it stored?
A polysaccharide that stores glucose in the liver and muscle cells.
What is the role of cellulose in plants?
Provides strength and rigidity to plant cell walls.
What is the process of hydrolysis?
The breakdown of polymers into monomers by the addition of water.
What is the significance of valence electrons in carbon?
Carbon has 4 valence electrons, allowing it to form four bonds with other elements.
Still learning (30)
You've begun learning these terms. Keep up the good work!