Module 1 Kinematics
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Scalars are quantities that only have…
Magnitude (or size)
Vectors have both magnitude and…
Direction
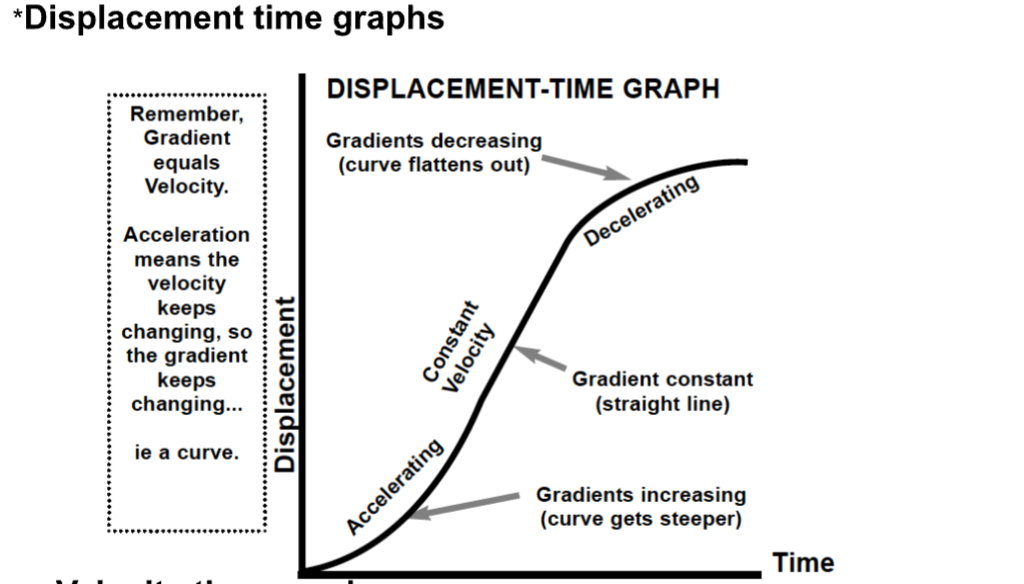
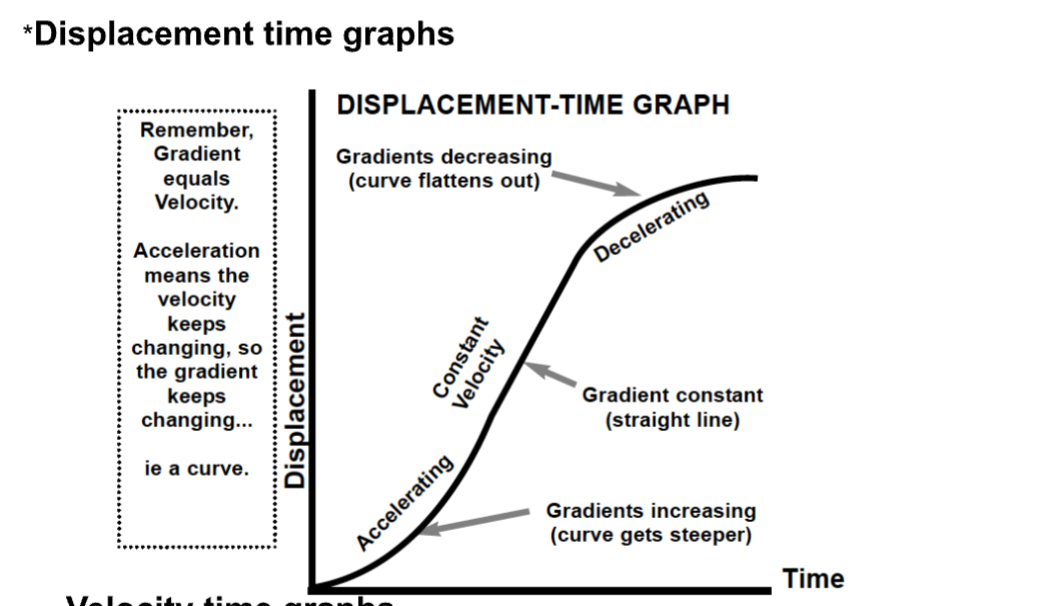
On a displacement time graph, gradient equals…
Velocity
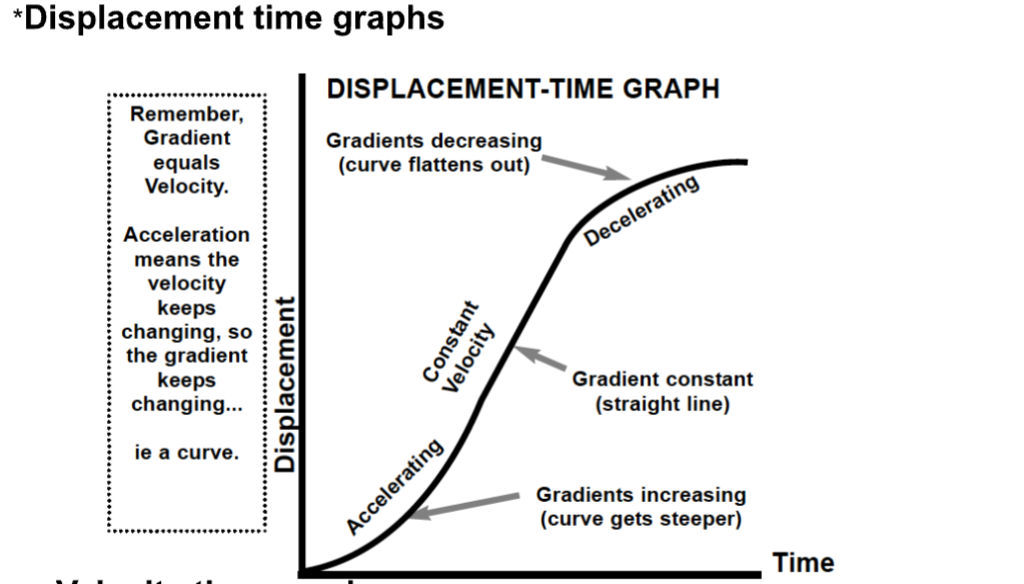
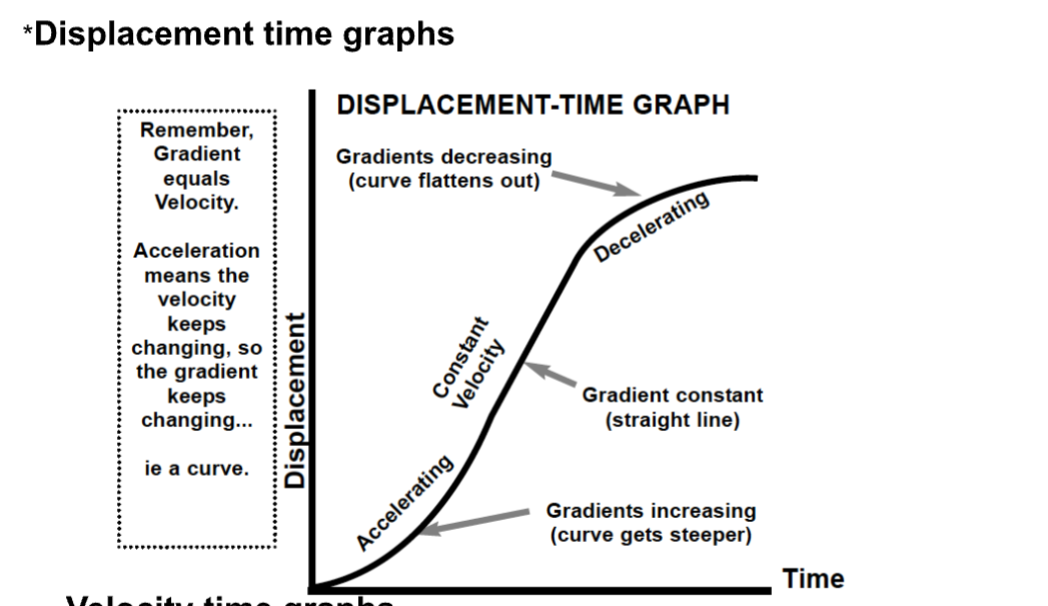
On a displacement time graph, acceleration is represented by…
A curve.
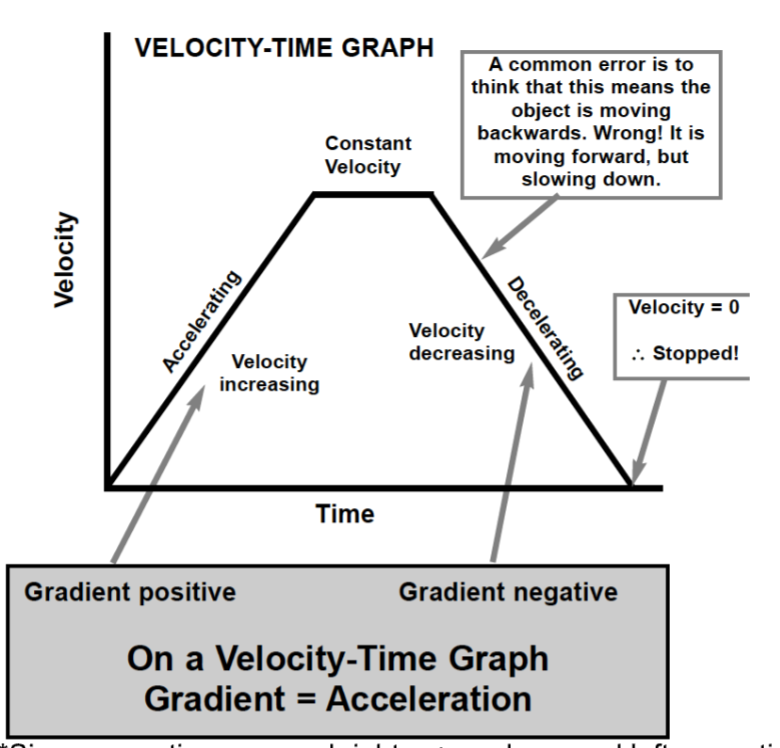
On a velocity time graph, acceleration, constant velocity and deceleration is represented by…
Positive gradient, horizontal line and negative gradient.
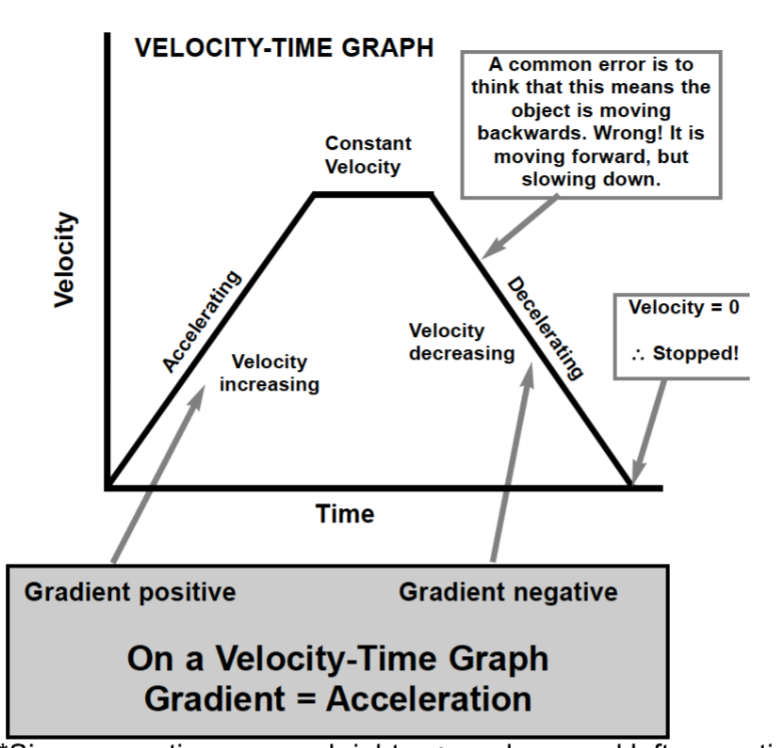
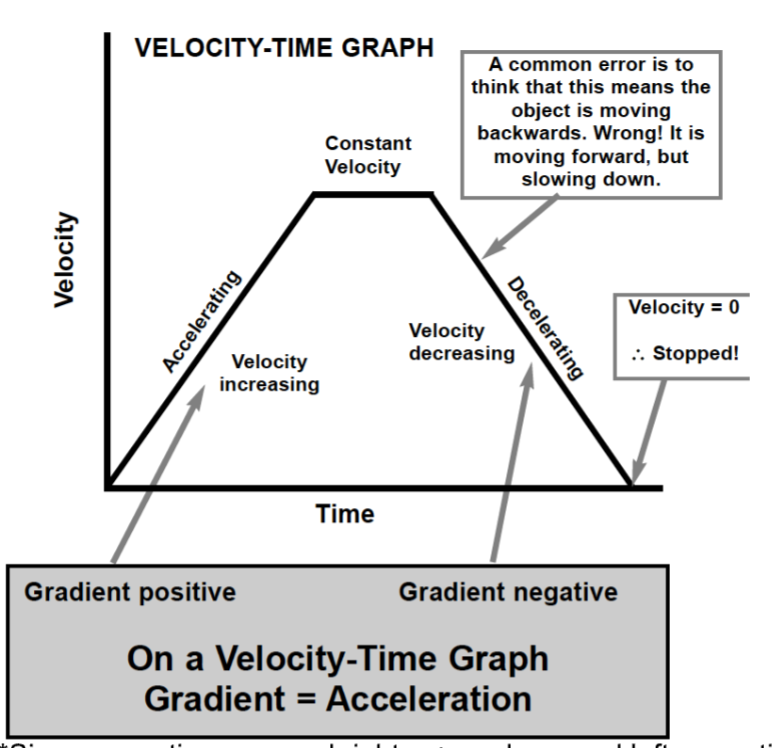
On a velocity time graph, area under graph equals…
Total displacement.
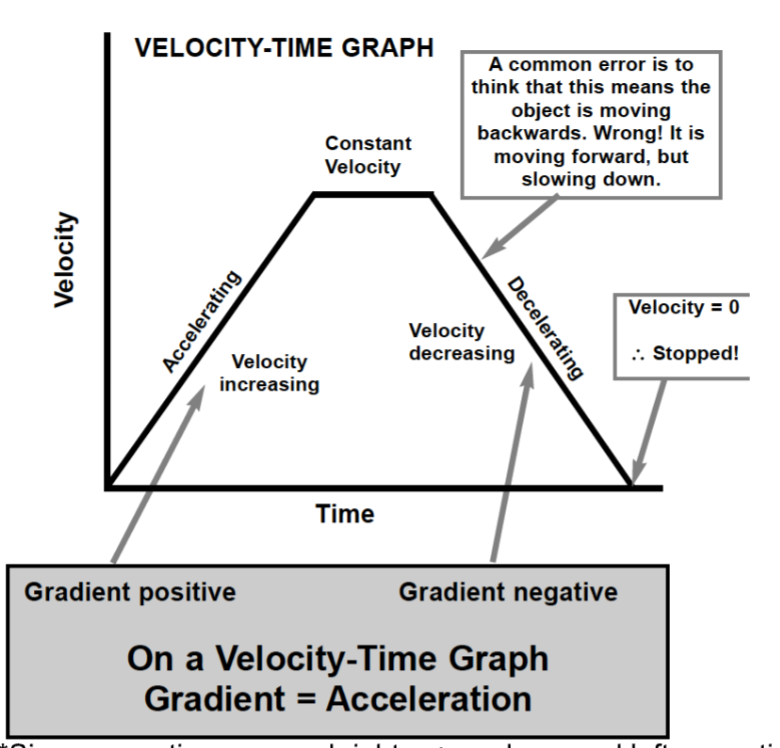
Average velocity formula?
Total Displacement/Total Time
When adding areas of a graph both over and under the x axis, you must remember to…
Have area under x axis have negative sign. E.g 18 m under x axis = -18 m
In Ticker Timer Prac, the space between each dot represents…
One fiftieth of a second 0.02 sec.
Intervals are made every ____ dot
Fifth. (Five spaces may look like six dots due to one at the bottom.)
In Ticker Timer Prac, average speed (velocity) equals…
Distance of interval / 0.1 (Remember to convert size to m.)
In Ticker Timer Prac, acceleration is…
(Final Speed - Initial Speed) / Time Taken
Final Strip Speed - First Strip Speed / 0.4
0.4 because the speeds are averages. Therefore half of two strips on the end plus the ones in the middle (in this case three, therefore equates to 4.) Adjust accordingly for the number of strips you have, which means you just - 1 from amount of strips.
Resultant vector is…
The sum of the vectors- drawn from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector
How do you find relative velocity in 1D
VBA = VB-VA
Flip the sign of the object that the other is moving relative to.
For example, when in a car your perception is that everything is moving relative to you. Flipping the sign is considerate of this, and cancels your velocity making you stationary so that everything is moving relative to you.
Instantaneous Velocity is…
The gradient of a tangent at a particular point in time.
Remember pick two points on tangent and use rise/run y2-y1/x2-x1
How do you draw vectors in 2D
The two perpendicular vectors are drawn so that the head of one joins
the tail of the other.
In 2D Vectors, if the question involves relativity to a moving object…
Flip the “relative to _____” vector
In 2D Vectors, if the question involves relativity to the ground (or bank)…
Don’t flip the vector.
In 2D Vectors, the resultant vector, x, joins…
The tail of the first to the head of the second vector.
In 2D Vectors, the angle to determine direction/bearing is…
Between the tail of the resultant and the tail of the adjacent vector.
In 2D Vectors, to work out resultant…
Use Pythagoras.
a squared + b squared = c squared
you will often use x = Root a squared + b squared
In 2D Vectors, to work out angle…
Use Pythagoras
Tanø = opp/adj
You will often use ø = Tan-1(opp/adj)
Remember! Angle must be from vertical.
Example answer
25 m/s North 75º West
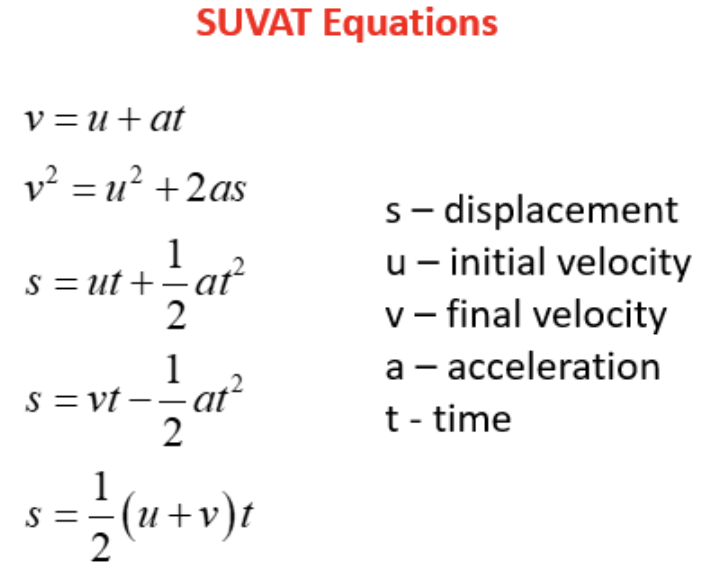
What does each letter of SUVAT stand for?
S = Displacement
U = Initial Velocity
V = Final Velocity
A = Acceleration
T = Time
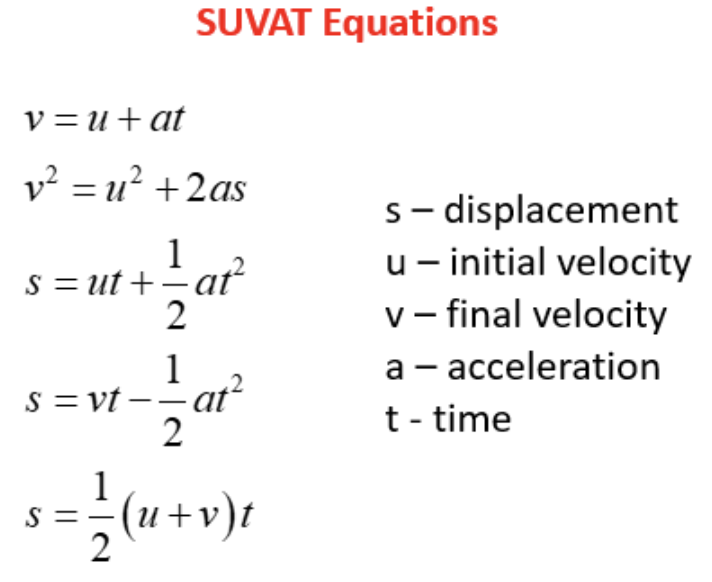
In reaction time prac time equals…
t= √(2s/a) where a= g (gravity)
What do we need to resolve horizontal and vertical vectors?
Hypotenuse (Resultant) and Angle.
Generally, the angle will be on the horizontal. If so formulas are…
Horizontal = Hypotenuse x Cos ø
Vertical = Hypotenuse x Sin ø
Always check hyp, opp and adj all makes sense.
If the angle is on vertical. Formulas are…
Horizontal = Hypotenuse x Sin ø
Vertical = Hypotenuse x Cos ø