principles of chemistry
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
describe the structure of solids
particles arranged regularily and packed closely together
vibrate in fixed positions
strong forces between particles
small amount of kinetic energy
describe the structure of liquids
particles are mostly touching with some gaps
particles move about at random
medium forces between particles
moderate amount of kinetic energy
descrive the structure of gases
particles move at random and quickly
particles are far apart
weak forces between particles
high amount of kinetic energy
collide with eachother and sides of container
what is the proper name for the conversion of solid to liquid?
melting
what is the proper name for the conversion between liquid and gas?
boiling / evaporating
what is the proper name for the conversion between liquid and solid?
freezing
Describe what happens when water vapour cools to form liquid water
particles lose kinetic energy
particles move closer together
particles move slower and less randomly
describe what happens when liquid water boils to form water vapour
particles gain kinetic energy
particles move further apart
particles move quicker and more randomly
describe what happens when liquid water cools to form ice
particles lose kinetic energy
particles move closer together
particles move slower and less randomly
describe what happens when ice melts to form liquid water
particles gain kinetic energy and vibrate more
particles move further apart as forces of attraction are overcome
particles move quicker and more randomly
how does evaporation occur?
particles in liquid have differing amounts of energy
particles with the greatest amount of kinetic energy break away from surface of liquid
average kinetic energy of remaining particles is lowered
in a closed container both evaporation and condensation occur simultaneously
define diffusion
net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
how can diffusion be demonstrated experimentally?
use cotton wool soaked in ammonia (NH3) and hydrochloric acid (HCl)
white ring forms closer to HCl end
tells you that NH3 diffuses faster
NH3 has a lower Mr, so is lighter
diffuses more quickly than HCl
Define solvent
liquid in which a solute dissolves
Define solute
a solid which dissolves in a solvent
define solution
mixture of a solute and a solvent
define a saturated solution
a solution where no more solute can dissolve in the solvent
what is an element?
a substance which contains one type of atom only
cannot be split into anything simpler by any chemical means
what is a compound?
a substance made up of two or more elements chemically combined
what is a mixture?
a substance made up of two or more elements NOT chemically combined together
what are some examples of elements?
iron, lead, sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen
what are some examples of compounds?
calcium carbonate, ammonia, carbon dioxide, water, iron sulfide
what are some examples of mixtures?
honey, air, sea water, blood, soup
what is a pure substance?
contains one type of material only
eg. one type of element or molecule
describe the melting and boiling points of pure substances
fixed
eg. boiling point of pure water is exactly 100 degrees celcius
eg. melting point of pure water is exactly 0 degrees celcius
describe the melting and boiling points of mixtures
melts over a range of temperatures
boils over a range of temperatures
what method is used to separate an insoluble solute from a solvent?
filtration
what method is used to seperate a soluble solute from a solvent?
evaporation or distillation
what method is used to seperate liquids of different boiling points?
fractional distillation
what method is used to seperate pure water from sea water
simple distillation
what method is used to seperate petrol and water and why is this used?
seperating funnel
petrol and water are immiscible (dont mix)
what is paper chromatography used to seperate?
dyes/inks ie. liquids with different solubilities
how do you carry out paper chromatography?
use a pencil line as reference line
add spots of ink/dye to pencil line
place filter paper in solvent
make sure solvent level is below pencil line
leave until solvent nearly reaches top of paper
allow to dry
furthest dot has the greatest solubility
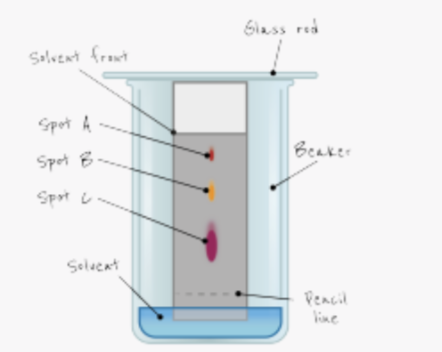
why should the line be drawn in pencil?
pencil does not contain ink so does not run
explain why it is important for the solvent level to be below the spots of dye
to prevent spots dissolving in the solvent
how do you calculate the Rt value?
Rt = distance travelled by component / distance travelled by solvent