[10] ANATOMY - Connective Tissues
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
Mesoderm
What is the embryonic origin of connective tissues?
Parenchyma
These are the functional elements of tissue/organ
True
TRUE OR FALSE: The following are the functions of connective tissues
Binds body parts but allows some degree of mobility
Forms the stroma/supporting framework
Envelopes muscles to protect against friction
Avenue for blood vessels and nerves
Venue for gas and substance exchange between blood & tissue
Provides arena & cells to protect the body
Extracellular Substance and Cells
What are the composition of connective tissue?
Ground substance
Amorphous (no shape), homogeneous, transparent, hydrated gel
Water
What is the main component of the connective tissue?
Proteoglycans, Hyaluronic acid (Hyaluronan), Mineral salts, Glycoproteins
What are the other components that stabilize water in the ground substance?
Water
Main component of ground substance. Abundant in the ground substance. Oxygen, nutrients and other materials diffuse easily from blood to connective tissue. Waste products of metabolism diffuse easily from connective tissue to the blood
Proteoglycans
Main structural constituent of extracellular substance. Responsible for the gelatinous character of the ground substance. Macromolecules that consist of a core protein with covalently attached disaccharides (glycosaminoglycans or GAGs)
GAGs (glycosaminoglycans)
Make the ground substance acidic due to the sulfate and carboxyl groups in sugar
Keratan sulfate, Chondroitin sulfate, Dermatan sulfate, Heparin sulfate
What are the common GAGs?
Hyaluronic Acid or Hyaluronan
A glycosaminoglycan. Most abundant GAG in the connective tissue. Backbone of proteoglycans to form bigger molecules called proteoglycan aggregates or complexes. Does not have any sulfate groups attached (unlike proteoglycans). Does not covalently attach to a core-protein
Glycoproteins
At least two of the glycoproteins are fibrillar in the form of microfibrils
Fibrillin
Larger of the 2 fibrillar glycoproteins. Non-sulfated; 10 to 12 nm in diameter. In an electron micrograph, it has an electron-lucent core surrounded by electron-dense area. An essential part of elastic fibers
Smaller microfibril
Not named. Not much is known. 3 to 5 nm in diameter
Fibronectin, Laminin, Thrombospondin
What are the other glycoproteins involved in cell adhesion and migration?
Cells (scarce)
These cells are not bound to each other and are scattered in the matrix
Extracellular matrix (abundant)
Further contains blood vessels and nerve fibers
Collagen fibers
Present in all connective tissues in varying amounts. Found especially in collagenous connective tissue (most commonly occurring type of connective tissue). Colorless (individually) but appears white if abundant (such as in tendons). 2 to 10 µm in diameter
Collagen
Accounts for approximately 25% of body’s dry weight. Family of structural proteins numbered I to XXVIII
Type I, II and III
Type of collagen fibers present in connective tissue
Type I
Type of collagen fiber that particularly only makes up collagen fiber
B, D, F, E, A, C
ARRANGE THE FOLLOWING BASED ON THE FORMATION OF COLLAGEN FIBERS:
A. Collagen microfibrils will group together to form collagen fibrils of collagen macrofibrils (0.3-0.5 µm)
B. Fibroblasts and mesenchymal cells produce the precursor protein of collagen fiber called procollagen (α-chain)
C. Collagen fibers are formed when collagen macrofibrils group together in a parallel fashion
D. Produced procollagen are secreted into the extracellular matrix where extra amino acids are enzymatically removed
E. Tropocollagen will aggregate to form collagen microfibrils (45-100 nm)
F. 3 right-sized procollagen will twist around each other are bound by hydrogen bonds to form tropocollagen
Elastic Fibers
Not as widely distributed as collagen fibers. Branch and anastomose with each other (which collagen fibers do not). Grossly impart a yellow color. Average 1 µm diameter
H&E stain
In elastic fiber staining, using this stain, it appear as refractile pinkish-yellow lines which are indistinguishable from collagen fibers
Orcein stain
In elastic fiber staining, using this stain, it appear blue to black
Resorcin-fuchsin and aldehyde-fuchsin
What other stains are used for elastic fibers?
elastin
Elastic fibers are made of ________ at its core, surrounded by longitudinal microfibrils, mostly fibrillin
Elastin
A highly insoluble protein but very elastic. Resistant to boiling and hydrolysis of acids, alkali and most enzymes
elastase (pancreatic enzyme)
Elastin can by hydrolyzed by a protease called?
elastic lamellae
Elastin appear in the form of elastic fibers or elastic sheets called?
Ligamentum flavum
Elastic cartilages of auricle and external acoustic meatus
External nose
Auditory tube
Epiglottis and larynx
Elastic Fibers are abundant in structures with frequent stretching like?
A, C, F, E, D, B
ARRANGE THE FOLLOWING BASED ON ELASTOGENESIS:
A. Fibroblasts and mesenchymal cells secrete microfibrils to the extracellular matrix → further aggregate to form bundles
B. In its development, more elastin and microfibrils are added once there is enough elastin
C. The same fibroblasts and mesenchymal cells produce tropoelastin, the precursor of elastin
D. Elastin is incorporated into the outer aspect of the microfibril bundles
E. Tropoelastin polymerizes to form elastin
F. Microfibrils and tropoelastin are secreted into the ECM
smooth muscle cells
Elastic fibers are formed by _______________ that lay elastin in fenestrated sheets or lamellae in concentric layers
Reticular fibers
Made of collagen type III. Surrounding structure of the parenchyma. Branch and anastomose like elastic fibers. 0.5 nm to 2.0 µm diameter. Stains black with silver salts
Kidneys, Lymph node, Spleen, Pancreas, Bone marrow
They are the main extracellular fibers of reticular tissue in?
lamina fibroreticularis
Fibrillar component of ____________________ of the basement membrane of epithelial tissues
False
TRUE OR FALSE: The formation of reticular fibers is similar to the of collagen fiber except they are produced by fibrilin.
Reticular cells
Special type of fibroblast that synthesize procollagen
Mesenchymal cells
Multipotent stem cells. Give rise to numerous cell types but are limited. They are scarce in adults but are present in most organs where they replace dead or damaged cells
zygote
The union of male and female gametes
totipotent stem cell
This can give rise to any human cell, placental cell, or cell of the fetal membranes (amnion and chorion)
Pluripotent stem cells
These arise from totipotent stem cells which can form any cell type of the body, but cannot produce a human being (i.e., they can no longer give rise to placental cells and cells of the fetal membrane)
stellate
Mesenchymal cells are ____________ (star-shaped) cells with delicate cytoplasmic processes and oval nuclei with fine chromatic and distinct nucleoli
Fibroblasts, Reticular cells, Adipocytes, Osteoprogenitor cells, Myoblast
Mesenchymal cells are stem cells of most connective tissue cells such as?
Fibroblasts
The most abundant cells in most connective tissues. Active. Responsible for synthesizing and marinating extra cellular components of connective tissue (e.g. proteins, glycoproteins, GAGs of the ground substance and precursors of collagen and elastic fibers)
Fibroblasts
They have a well-developed rER which are used for protein synthesis making their cytoplasm basophilic. Capable of mitosis, however, infrequently as they are sturdy and long-lived.
Fibrocytes
Fibroblasts that are not actively producing extracellular connective tissue components. Inactive.
wound healing
In appropriate conditions, they can become fibroblasts like in ________________ wherein extracellular connective tissue components are needed for wound closure.
a. pointed by arrow
What cell is inactive?
a. pointed by arrow b. circular
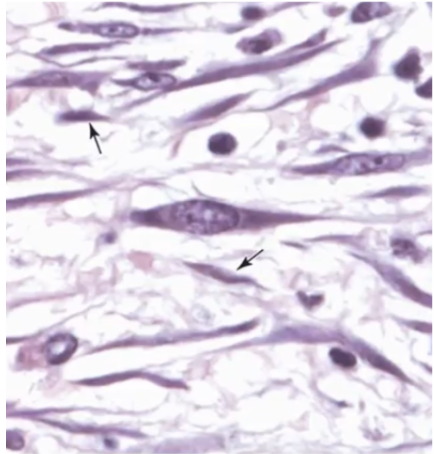
Reticular cells
Specialized fibroblasts that produce the precursor of type III collagen that make up reticular fibers
Adipose cells or Adipocytes
It can also be called a fat cells or lipocytes. It is a specialized cell that stores lipids or fats (mainly triglycerides) in its cytoplasm
lipoblast
Several fat globules in cytoplasm. usually seen in the young, and could be a malignancy if present in adults.
Adipocyte
Only one fast globule inside
signet ring
Due to the large droplet of fat in the cells the nucleus is pushed to one side, making the cell look like a?
glutaraldehyde or osmic acid
If adipocytes are fixed with these, they will be seen as grey or black globules.
brown adipose
A small population of fat cells stores fat in their cytoplasm as multiple small droplets. These fat cells are seen in _______________ (mostly in infants, disappear in adults).
False
TRUE OR FALSE: Adipocytes are capable of mitosis.
preadipocytes (pre-fat cells)
Adipocytes are sourced from mesenchymal cells called?
Mast cells
Also called mastocytes; histaminocytes. Large (15 to 20 µm), ovoid cells with centrally located nuclei and numerous cytoplasmic granules
toluidine blue
This stain is used so that mast cells can be recognized by their dark purple granules
Heparin
Anticoagulant. Thins out the blood by preventing coagulation
Histamine
Dilates blood vessels and makes it permeable. Stimulates smooth muscles especially bronchioles. Also an anticoagulant
True
TRUE OR FALSE: The following are the functions of mast cells
Involved in inflammation and immediate-type hypersensitivity reaction (allergic reaction)
Severe type is anaphylactic shock
Synthesize and release leukotrienes, prostaglandins and certain cytokines
Role in wound healing
Defense against pathogens
Colony Forming Unit Mast cell (CFU-Mast)
Mast cells come from this from the bone marrow
lamina propria of GI tract
Mast cells are abundant where?
Lamina propria
This is just under the mucosa so foreign substances will be caught
Macrophages
Are phagocytes derived from monocytes. Present in all tissues, not only the connective tissue. Have different names in different parts of the body.
Monocytes
are WBCs that migrate to connective tissue by crossing the wall of venules and differentiate to macrophages.
histiocytes
Macrophages that migrate to connective tissue
pulmonary alveolar macrophages
Macrophages that migrate in the lungs or alveoli
Kupffer cells
Macrophage that can be found in liver sinusoids.
True
TRUE OR FALSE: Macrophages are easier to recognize under the light microscope when they have phagocytosed materials in their cytoplasm
antigen presenting cells
The macrophage function as immune defense system and serves as what to lymphocytes?
Fixed macrophage
Attached to collagen fibers. Can become free macrophages once they have detached from collagen fibers
Free macrophage
Wandering freely in the extracellular matrix. Can become fixed macrophages if they attach themselves to collagen fibers
Resident macrophages
Permanently inhabit a given tissue. Less immunologically active. Increase in number by limited local proliferation or from monocytes in connective tissue
Inflammatory macrophages
Migrate to a site in response to stimulus (e.g., if there is infection in connective tissue). More immunologically active. Increase in number only from monocytes (they cannot do local proliferation)
Plasma Cells
Also known as plasmocytes. They are bigger than red blood cells (RBCs)
B lymphocytes (B cells)
Plasma cells differentiate into what type of WBC?
immunoglobulins or antibodies
Plasma cells produce these
True
TRUE OR FALSE: Plasma cells have a limited number in all connective tissues but numerous in connective tissues that are readily accessible to foreign proteins and bacteria (e.g. lamina propria of the digestive tract)
Leukocytes
They are also known as white blood cells (WBCs). These are the nucleated cells in the blood
False
TRUE OR FALSE: In post-natal life, all leukocytes are produced in the bone marrow except for the monocytes
thymus, lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils
Lymphocytes are also produced in the lymphoid tissues and organs such as the?
neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, lymphocytes
What are the types of white blood cells?
diapedesis
For the leukocytes to go to the connective tissue from blood vessels, they need to squeeze through the endothelial gaps in the blood vessels, this process is called?
amoeboid movement
Once in the connective tissue, the leukocytes exhibit
Collagenous Connective Tissue
Most abundant type of connective tissue in the body. Referred to as ordinary connective tissue or just connective tissue.
collagen fiber type I
What is the most abundant extracellular fiber?
type III collagen
What type of collagen can be seen in reticular fiber?
fibroblast
What is the most abundant cell in collagenous connective tissue?
Dense Collagenous Connective Tissue
Characterized by scanty ground substance. Abundant and closely packed collagen fibers. Relatively few cells embedded
Dense regular connective tissue
Collagen fibers arranged in a definite pattern (one direction). Comprises tendons, ligaments, and fibrous membranes
Dense irregular connective tissue
Collagen fibers run in various directions (haphazard). Comprises the dermis of skin, capsule of lymph nodes, liver, spleen & testes, nerve sheaths, periosteum and dura mater
Loose Connective Tissue
Abundant extracellular substance. Haphazardly arranged few collagen fibers. More cellular than Dense CT. Highly vascular. Seen in hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue), tunica adventitia of blood vessels, lamina propria & submucosa of digestive, respiratory & urogenital tracts
Adipose tissue
Represents the largest energy storage site. Functions as thermal insulator (poor heat conductor; can save heat in the body). Serves as shock absorber (kidneys & soles of feet)
Adipocyte
Specialized cell that stores fat which represents excess dietary calorie intake then released if needed in form of fatty acids
reticular fibers
In the lobules, the adipocytes are supported mainly by
yellow and brown fat
What are the two kinds of adipose tissue?