molecules and membranes
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Water
Most abundant molecule in cells
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars
Dehydration reactions
Join together glucose forming glycosidic bonds
Polysaccharides
Polymers of many sugars
Oligosacchrides
Polymers of few sugars
Glycogen, starch, cellulose, chitin
Examples of polysaccharides
Stores glucose in animal cells, alpha config
Glycogen
Stores glucose in plant cells, alpha config
Cellulose
Main structural component of plant cell walls, beta config
Cellulose
Forms exoskeletons of crabs and insects
Chitin
Energy storage, cell signaling, messenger molecules
Main functions of lipids
Long hydrocarbon chains with carboxyl group at one end
Fatty acid
Fatty acid with no double bond
Saturated fatty acid
Fatty acid with at least 1 double bond
Unsaturated fatty acid
3 fatty acids linked to glycerol molecule
Triglycerides/fats
Principal components of cell membranes
Phospholipids
Polymers of 20 different amino acids
Proteins
Transport+storage of small molecules, transmit information between cells, defense against infection, enzymes
Functions of proteins
Secondary structure of protein
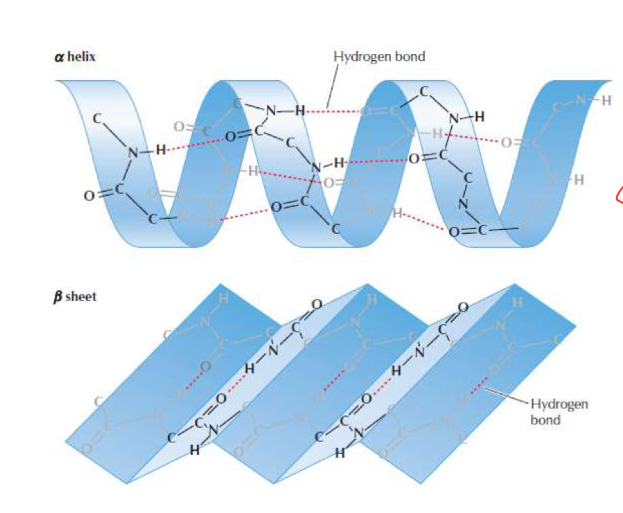
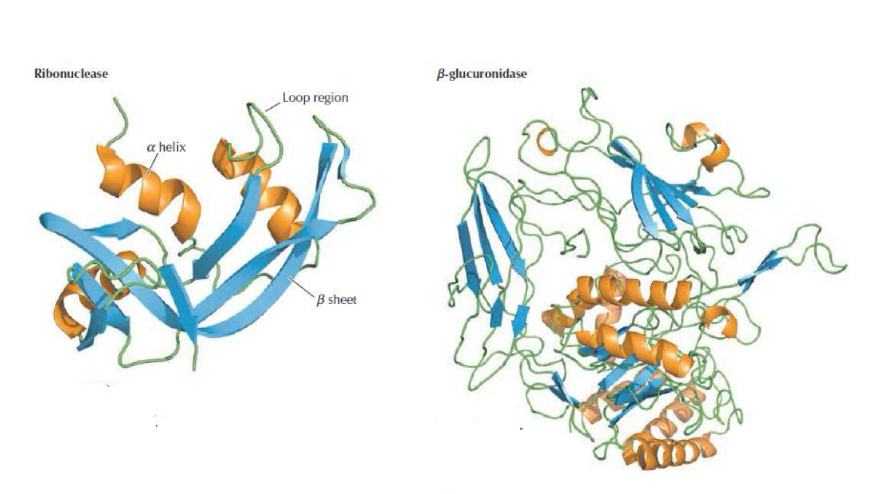
Tertiary structure of proteins
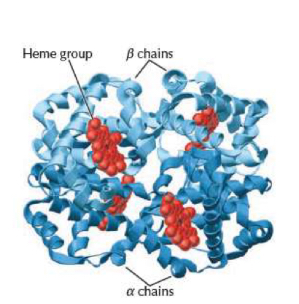
Quaternary structure of proteins
Principal information molecules of the cell
Nucleic acids
MRNA
Carries information from DNA to ribosomes
RRNA and tRNA
Nucleic acids involved in protein synthesis
Purines
Adenine and guanine
Pyrimidines
Cytosine, thymine/uracil
Oligonucleotides
Polymers of few nucleotides
Polynucleotides
Polymers of many nucleotides
Enzymes
Catalysts that increase the rate of all chemical reactions in cells
Enzymes work by lowering what
Activation energy
Activation energy
Energy required to reach transition state
Lock-and-key model
Substrate fits precisely into the active site
Induced fit model
Conformation of both enzyme and substrate is modified
Serine proteases
Enzymes that cleave peptide bonds adjacent to specific types of amino acids
Active sites
Serine, histidine, aspartame
Chymotrypsin
Serine protease produced by pancreas that hydrolysis peptide bonds of tryptophan, leucine, and phenylalanine
Nicotineamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
Coenzyme that carries electrons in oxidation-reduction reactions
Prosthetic groups
Small molecules bound to proteins that have critical functional roles
Critical group in myoglobin and hemoglobin, carries oxygen
Heme
Allosteric regulation
Enzyme activity is controlled by the binding of small molecules to regulatory sites on the enzyme
Feedback inhibition
Changes the conformation of the enzyme and alters the active site
Phosphorylation
Phosphate groups are added to the side chain OH groups of serine,threonine or tyrosine ; common mechanism of enzyme regulation (stimulate/inhibit)
Phospholipid structure in cell membrane exposed to water
Polar head groups
Phospholipid structure in cell membrane buried in interior of the membrane
Hydrophobic tails
What chemical helps determine membrane fluidity because of its ring structure
Cholesterol
How does cholesterol maintain membrane fluidity at lower temperatures
By reducing interaction between fatty acids
Can diffuse freely through a phospholipid bilayer
Gases, hydrophobic and small uncharged molecules
Molecules the phospholipid bilayer is impermeable to
Large polar molecules including glucose, amino acids, and ions
Channel proteins
Form open pores through which molecules of the appropriate size such as ions can cross the membrane
Carrier proteins
Selectively bind the small molecules to be transported and the undergo a conformational change to release the molecule on the other side of the membrane