RNR2102 Exam 2
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
GIS
Geographic Information System
GPS
Global Positioning System
DGPS
Differential Global Positioning System
PDOP
Position Dilution of Precision
NAD27
North American Datum of 1927
NAD83
North American Datum of 1983
WGS84
World Geodetic System 1984
UTM
Universal Transverse Mercator
DEM
Digital Elevation Mode
DOQQ
digital orthophoto quarter quadrangle
SA
Selective Availability
LiDAR
Light Detection and range
GMT
Greenwich Mean Time
WAAS
Wide Area Augmentation System
GIS is a computerized system for making and storing maps.
False. it handles, projects, and manages geographic area
GIS is a computer-based system to store, manipulate, and output geographical data.
True.
GPS units used by the military have higher PDOP than normal GPS units.
False
GPS works better during the day, when the clouds help improve the signals
False. Clouds make it more difficult.
GPS cannot work at all in the forests, even if the canopy is sparse.
False. Heavy canopies and tall trees can cause errors to your GPS readings, but it can be done.
The signals we obtain with normal GPS today contain random error introduced by the military.
False.
Post-processing requires a special kind of GPS called Differential GPS.
False. Post processing is done after readings are taken while Differential GPS is used during real time.
Measurements of Cartesian coordinates are in meters
True
Measurements of geographic coordinates are in degrees.
True
DOQQs are digital aerial photographs.
True. It is a square image of an aerial relief that is orthorectified.
A raster model consists of pixels and therefore can require a large amount of storage.
True
A vector model consists of objects (points, lines, and polygons) that take up less storage.
True
Metadata are a huge database that consists of both vector and raster models.
False
Selective availability allows the GPS user to select the proper frequency (L1 or L2).
False.
What is GPS?
Allows you to know your location thru satellite triangulation using a signal sent from between 4-7 satellites
What are measurement offsets?
measure distance and direction from a known location to an object of interest
What range would you ideally maintain PDOP in?
1 to 6, but the lower the PDOP the more accurate
The process of first collecting GPS data in the field and later applying corrections to those data is often termed ______________.
Post processing.
What is selective availability?
It is a random error that was in GPS systems before 2000. It kept military/political positions hidden from enemy GPS.
What is multipath error? How do we correct for it?
This error occurs when the signal from the satellite bounces off of large objects around you such as trees or buildings and gives the GPS unit an incorrect or off reading. This kind of error cannot be corrected, only avoided.
Differential GPS
Relies on the use of base stations in addition to the GPS receiver.
The GPS data are adjusted in real time.
Generally results in increased accuracy of geographic fixes.
A ___________ is a smooth, mathematical representation of the Earth’s surface that best fits the global mean sea level.
Geoid
A __________ is a set of referenced points against which position measurements were made.
Datum.
A ____________ is a mathematical representation of the Earth’s surface that considers mountains and valleys.
Geodetic Datum
What are the main differences between NAD27 and NAD83?
NAD27 is based off of 25,000 reference points with a center at the geographic center of the U.S. at Meeds Ranch, Kansas.
NAD83 is based off of 270,000 reference points with a center at Earth's center.
What are the three most common projections used in North America? What are the differences among these projections?
Mercator, Conic, and Robinson.
Convert 40^20’50” latitude into decimal degrees
40.3472 degrees
Convert 40.3472 degrees into degree-minute-second format.
40^20’49.92
List two types of coordinate systems. What are their units?
Cartesian Coordinate System (m), Geographic Coordinate System (degrees)
UTM divides the earth into _____ zones and the contiguous US into _____ zones.
60 zones, 10 zones
A GIS provides four basic capabilities. What are they?
1. Input of data
2. Management of Data
3. Manipulation and Analysis
4. Output in many forms
What is a dangling arc?
An arch with no end point.
What is an island?
A polygon inside of another polygon.
What is a raster model?
map divided into square cells or pixels; each cell has a condition that is represented
What is a vector model?
objects or conditions represented by points and lines that define boundaries; geographic objects are represented by points, lines, and polygons
What are metadata?
Information about data.
Name four of the elements that can be used to recognize an object in an aerial photo.
shape, size, patterns, shadows
Map scale: 1:24,000. What is the area in acres of a tract measuring 1.5” x 2” on the map?
275.48 ac
PDOP <_ x: under 1m accuracy,
PDOP = x to y: open area,
PDOP<_ z: under forest canopy.
What are the values of x, y, and z?
x: 4, x to y: 4-6 z: 8
The mean is a measure of the _________ of the distribution.
center
The variance is a measure of the _________ of the distribution.
spread (no unit)
The standard deviation is a measure of _________ of the distribution.
spread (unit)
What is the Central Limit Theorem?
x ~ any distribution (mu, sigma²)
xbar ~ N(mu, s²/n)
What is the significance of the Central Limit Theorem?
A large sample means xbar is normal and you can test hypothesis.
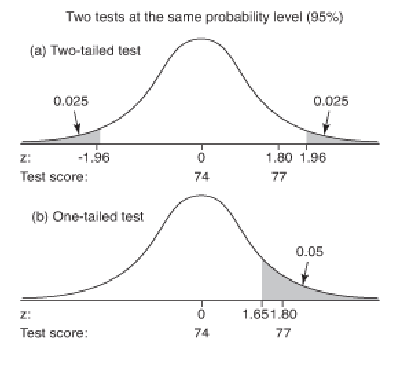
What are the null and alternate hypotheses for the two tests depicted on the right?
a. H0 = 1.96 Ha =/ 1.96
b. H0 <= 1.651 Ha > 1.651
What is the difference between Accepting H0 and Failing to Reject H0?
you cannot accept H0, only fail to reject it
If you fail to reject the null hypothesis, what else can you do be able to reject H0 at the same alpha level (changing from a two-tailed test to a one-tailed test does not count)?
increase sample size
True or False: For a two-tailed test, the null hypothesis is rejected when |t_calculated| < ttabulated.
false
True or False: For a large sample, the distribution of X is approximately normal.
false, xbar is normal
True or False: When the 95% confidence interval for mu contains c, a test if mu = c will be rejected at the 5% level
false
The _________________ (calculated, tabulated) t value is required to compute the 95% confidence interval.
tabulated
At the same alpha level, it is ________ (easier, more difficult) to reject H0 for a one-tailed test as compared to a two-tailed test
easier
For a two-tailed test, if the critical t value from the t-table is 2.01, and the calculated t value is –2.34, then we should ______ (reject, fail to reject) the null hypothesis.
reject
Explain why an average of a few GPS readings is better than a single GPS reading.
The average of a few GPS readings is more accurate than a single GPS reading.
A sample of 41 catfish was caught, and the average length is 16.1 inches. If the variance is 30, perform the 5% test that the average length is equal to 14.5 inches.
tcalc = 1.869 - Reject H0
For a 5%, two-tailed test, t values from the table are:
df = 40; t = 2.021
df = 60; t = 2.000
What is the t value for n=47?
2.015
From a volume table, for a 6” tree, volumes for 20’ and 30’ of merchantable height are 0.039 and 0.053 cords, respectively. What is the cord volume of a tree 6” and 26’?
0.0446 cords
A regression equation, 𝑦̂𝑖 = 𝑎 + 𝑏𝑥𝑖 , is developed.
a. We can assume that _____ (x, y) is easy/cheap to measure and _____ (x, y) is difficult/expensive to measure.
b. The _________________ method is used to estimate a and b of that regression model.
a. x then y; b. least squares method
To estimate coefficients of regression models, we need to minimize
Sum of (yi - y^i)²
Define streamflow.
flow rate of water along a natural channel
Define watershed.
an area of land that collects and discharges water through one outlet
The average velocity of a stream is 0.1 ft./second. If the stream is 6 feet wide and averaging 2 feet deep, what is the average flow of the stream?
1.2 ft³/s
Give an example of a unit of measurement for Load and Concentration
Load: Mass/time in tons/day; Concentration: mass/volume in lbs/m²
Give examples of some common problems with water quality:
- Inorganic Sediment:
- Organic Sediment:
- Dissolved oxygen:
- Chemical pollutants:
- Nutrients:
1. trash, plastic, or chemicals
2. fertilizer runoffs from farms
3. can result in hypoxia and etc.
4. heavy metals from factories
5. nitrogen cause alge blooms
Give an example each for point source pollution and non-point source pollution.
point source- factory waste pipe being drained into stream or river
non-point source fertilizer runoff into a river or stream form a farm
BMP stands for _______________. Define.
Best Management Practices - prevent or reduce water pollution.
TMDL stands for _______________. Define.
Total Maximum Daily Load - amount of a pollutant that a water body can receive and still meet water quality standards.
If a single rainstorm of 3.2 inches over 2 days fell on a 40-ha watershed, what is the average rainfall rate in mm/hr and in cfs(ft3/s)?
1.69 mm/hr; 6.65 cfs
What is hypoxia? It happens when the level of ________________ is __________________ (higher, lower) than __________________.
dissolved oxygen, lower, nitrogen levels in the water
Secchi disk is used to measure water
Turbidity
Secchi disk is considered an __________________ (estimate, index) because
_______________________________________________________________.
index, it does not give an exact answer
(T or F) Result from electrofishing can be considered as an estimate of fish density.
False, its a fish index
(T or F) The pulse frequency of electrofishing can be selected to target a certain fish species or size.
True
(T or F) Toxicants such as rotenone are appropriate in fast moving water because they can be spread quickly.
False
(T or F) Rotenone kills fish that cannot be consumed later because of poisonous residue.
True
(T or F) Primacord is the brand name of a toxicant for killing fish.
False
Identify the following as active or passive nets.
a. Seines
b. Gill nets
c. Hoop nets
d. Trawls
e. Fyke nets
a. active
b. passive
c. passive
d. active
e. passive
Dissolved oxygen ____________ (increases, decreases) with increasing temperature.
decreases
What is measured by a hydrolab?
Water temperature, Conductivity, pH, and Dissolved Oxygen
Flow Rate
Q=VA
V= Velocity
A= Cross sectional area. Divide by 2
Unit = ft³/s