final urinary test review
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
function of the urinary system
detox
blood pressure regulation
regulation of blood composition
inner fascia surrounding kidney
renal capsule
middle fascia surrounding kidney
layer of phrenic fat
outer layer fascia surrounding kidney
renal fascia (gerota’s fascia)
compensentory hypertrophy
only one kidney is present, it gets larger to accommodate increased workload
peripheral parenchyma
where filtration of blood occurs
made up of renal medulla and cortex
renal sinus
where urine is collected
made up of infundibulum and renal pelvis
renal cortex
outer portion of the parenchyma, contains renal corpuscle, proximal and diet convoluted tubule
column of Berlin
band of cortical tissue separating medullary pyramids from each other
renal medulla
inner, cone shaped portion of the peripheral parenchyma that drain into the minor calyces
renal papilla
apex of the medullary pyramid, indents into each minor calyx
renal sinus in kidney
collecting system, portion containing the infundibulum, renal pelvis and renal hilum
infundibulum
portion of renal pelvis that consists of the minor and major calyx
renal calyx
cavities within the renal infundibulum in which urine collects before flowing into renal pelvis
renal pelvis
upper basin or expanding end of the proximal ureter
renal hilum
medial portion of the kidney where RA/RV/ureter enter/exit
where the ureters lead the renal pelvis
UPJ
where the ureter pierces the bladder wall
UVJ
where the ureter kinks as it crosses the pelvic brim
pelvic inlet
3 strictures along the ureters
UPJ, UVJ, pelvic inlet
peristalsis of the ureters is based on
body state of hydration
there are _____ of smooth muscle that make up the detrusor muscle of the bladder
3 layers
female urethra has
membranous portion
the RA’s are bilateral branches of
AO just INF to the SMA
renal corpuscle consists of
glomerulus
Bowmans capsule
bowmans space
uremia
raised levels of urea and nitrogenous waste in the blood
uremia is elevated when___
kidneys are damaged
uric acid
formed from breakdown of nucleic acids
creatinine
waste product that comes from the normal wear and tear on muscles of the body
urine PH
important in kidney stone management
specific gravity
measures kidneys ability to concentrate urine
dark urine =
high specific gravity
light urine =
low specific gravity
blood-hematuria -presence of RBC’s
suggest trauma, neoplasm, renal dysfunction, vascular inflammatory process
blood-hematuria - presence of WBC’s
suggest infection, inflammation, necrosis
hemoglobin
present in urine whenever damage to RBC’s occur
injured kidneys lead to____
AKF
protein
found in urine when glomerular damage in present
protein is commonly found in ________
neoplasms, stones, chronic infection, pyelonephritis
sodium
should be elevated
HTC
occurs with hemorrhage secondary to disease or blunt trauma
serum albumin
decrease of albumin in blood with neoplasms, stones, chronic infection, pyelonephritis
BUN
concentration of urea nitrogen in the blood
serum creatinine
elevates due to renal dysfunction
sono eval of kidney vs. liver
most hyperechoic
renal sinus
sono eval of kidney vs. liver
isoechoic
cortex
sono eval of kidney vs. liver
mot hypoechoic
parenchyma
normal residual urine for adults
20 cc or less
renal variants
slight alterations on anatomy
prominent columns of Bertin
hypertrophied extensions of the normal columns
dormedary hump
bulge of cortical tissue in the lateral surface of the kidney
usually LK
fetal lobulation
cortex of kidney is scalloped
junctional parenchymal defect
triangular echogenic area along the cortex extending into collecting system
extrarenal pelvis
presence of the renal pelvis outside the confines of the renal hilum
duplex collecting system
2 separate collecting systems each with their own ureter
isthmus
connection bridge of renal parenchyma
bosniak classification system
classification of renal cyst for concerning characteristics
parapelvic cysts mimmic____
hydronephrosis
von hippel-lindau
autosomal dominant genetic disorder
bilateral renal cysts and masses
acquired cystic kidney disease
associated with dialysis pts
autosomal RECESSIVE polycystic kidney disease
rare genetic disorder on chromosome 6
perinatal
progresses to renal failure
massively enlarged echogenic kidneys
juvenile
present with HTN, renal insufficiency, nephromegaly, liver problems, carols disease
autosomal DOMINANT polycystic kidney disease
genetic disorder
bilateral disease
4-5th decade of life
most common dominant polycystic kidney disease
ADPKD1
Multicystic dysplastic kidney
nonhereditary
bilateral is incompatible with life
most common form of cystic disease in neonate
neonates with multi cystic dysplastic kidneys
multicystic kidneys with absence of renal parenchyma
adults with multi cystic dysplastic kidneys
echogenic atrophied kidneys
renal cell carcinoma is males
2x more common
nephroblastoma
wilm’s tumor
renal disease- end stage___
renal atrophy
renal disease- cortical thickness___
measure greater than 6 mm
acute renal disease
enlargement and hypoechoic cortical tissue
acute tubular necrosis
most common cause of AKI
damage due to lack of oxygen
is reversible
renal function improves in acute tubular necrosis=
echogenicity decreases
pre renal
secondary to hypofunction of kidney
renal
parenchymal disease
post renal
obstruction of urine flow
chronic kidney disease
loss of renal function due to renal disease
most common parenchymal disease
3 typed of chronic kidney disease
nephron
vascular
intersitial
chronic kidney disease kidneys are____
bilateral small, echogenic
pyonephrosis
associated with urosepsis
secondary to long standing obstruction
emphysematous
air is present
xanthogranulomatous
a staghorn calculi
nephrocalcinosis
increased echogenicity of renal cortex
medullary nephrocalcinisis
increased echogenicity of the medullary pyramids bilaterally
typical first location for renal transplant
RLQ
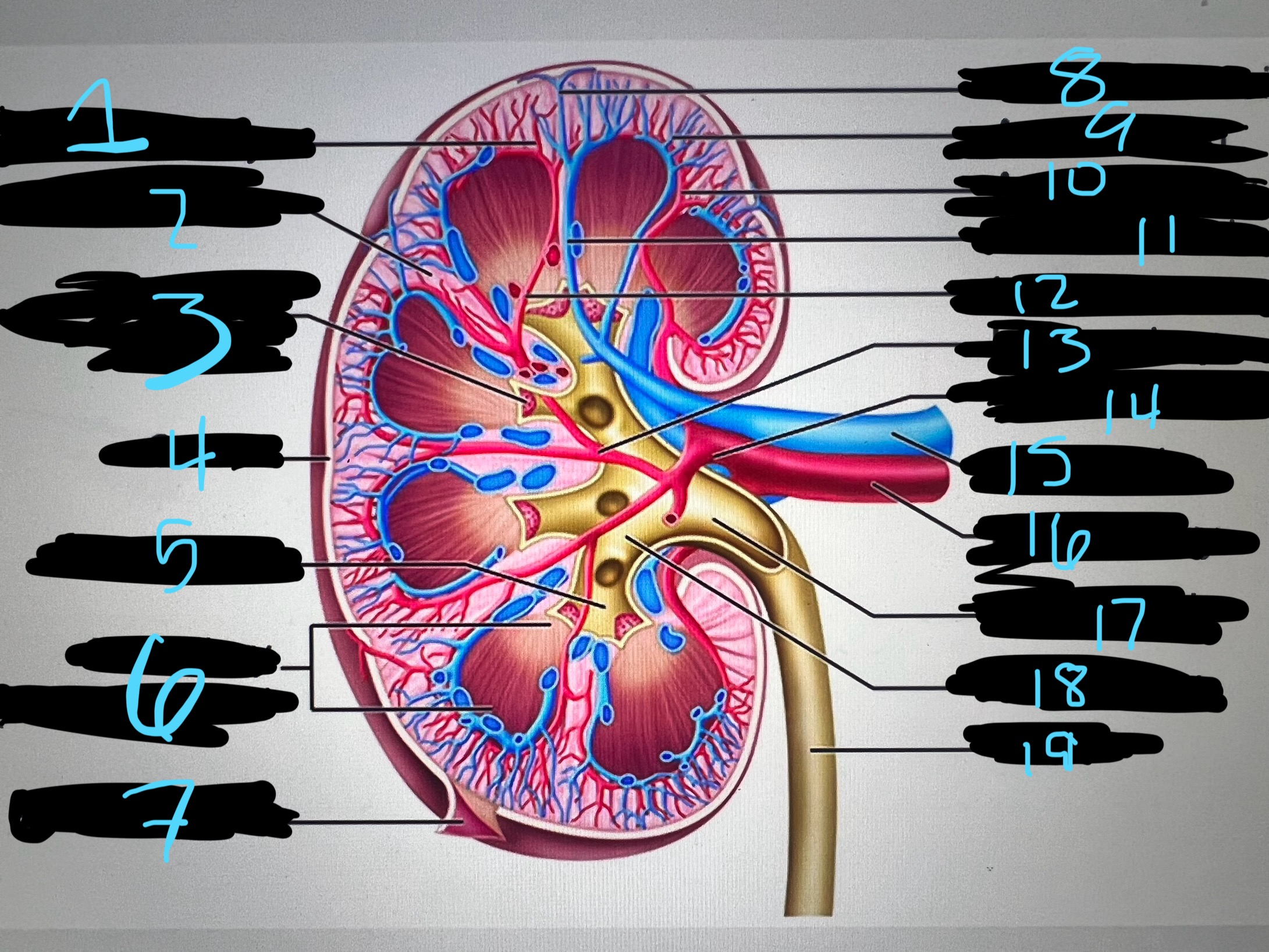
1
blue
intralobar artery
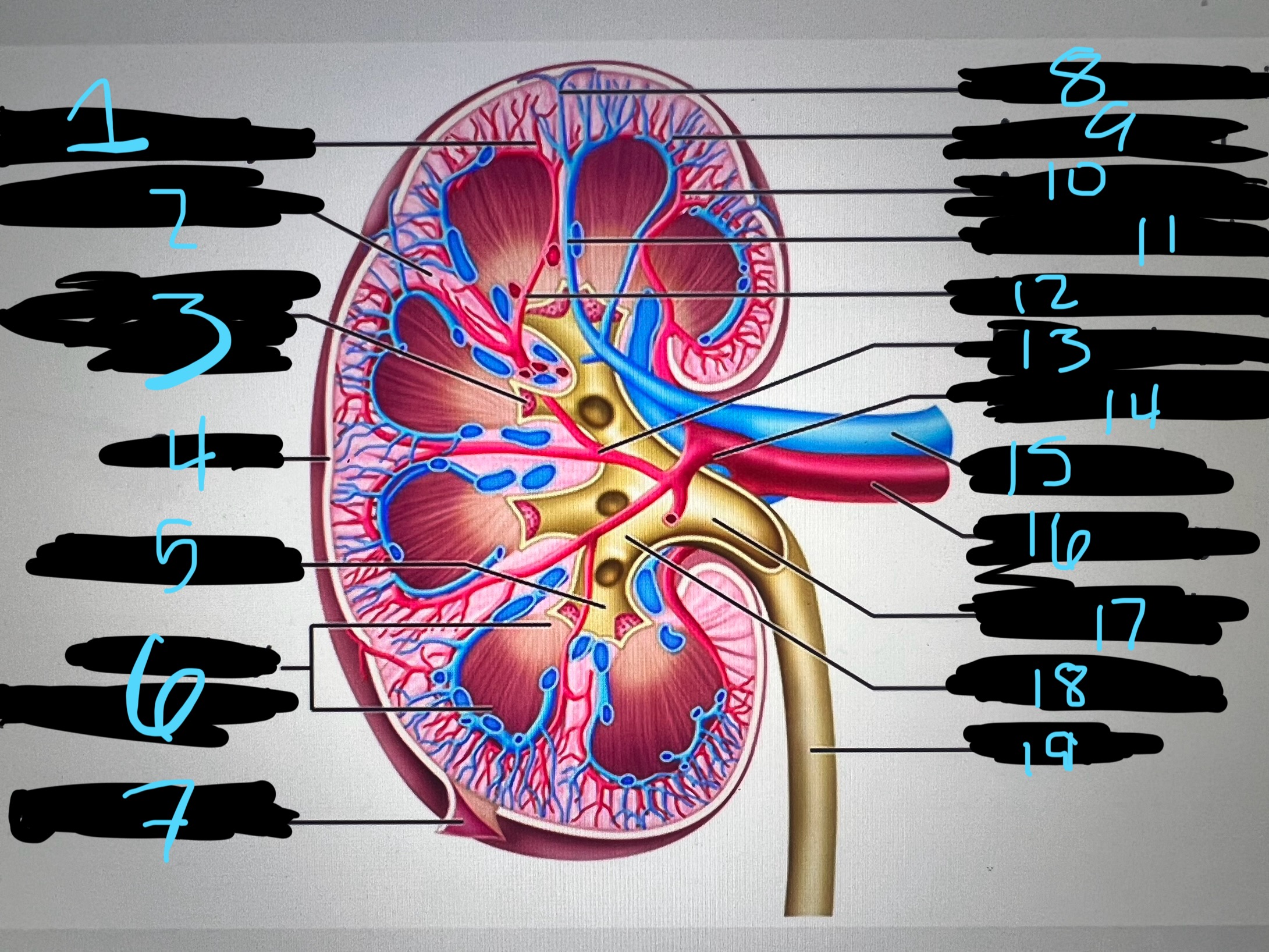
2
blue
renal column
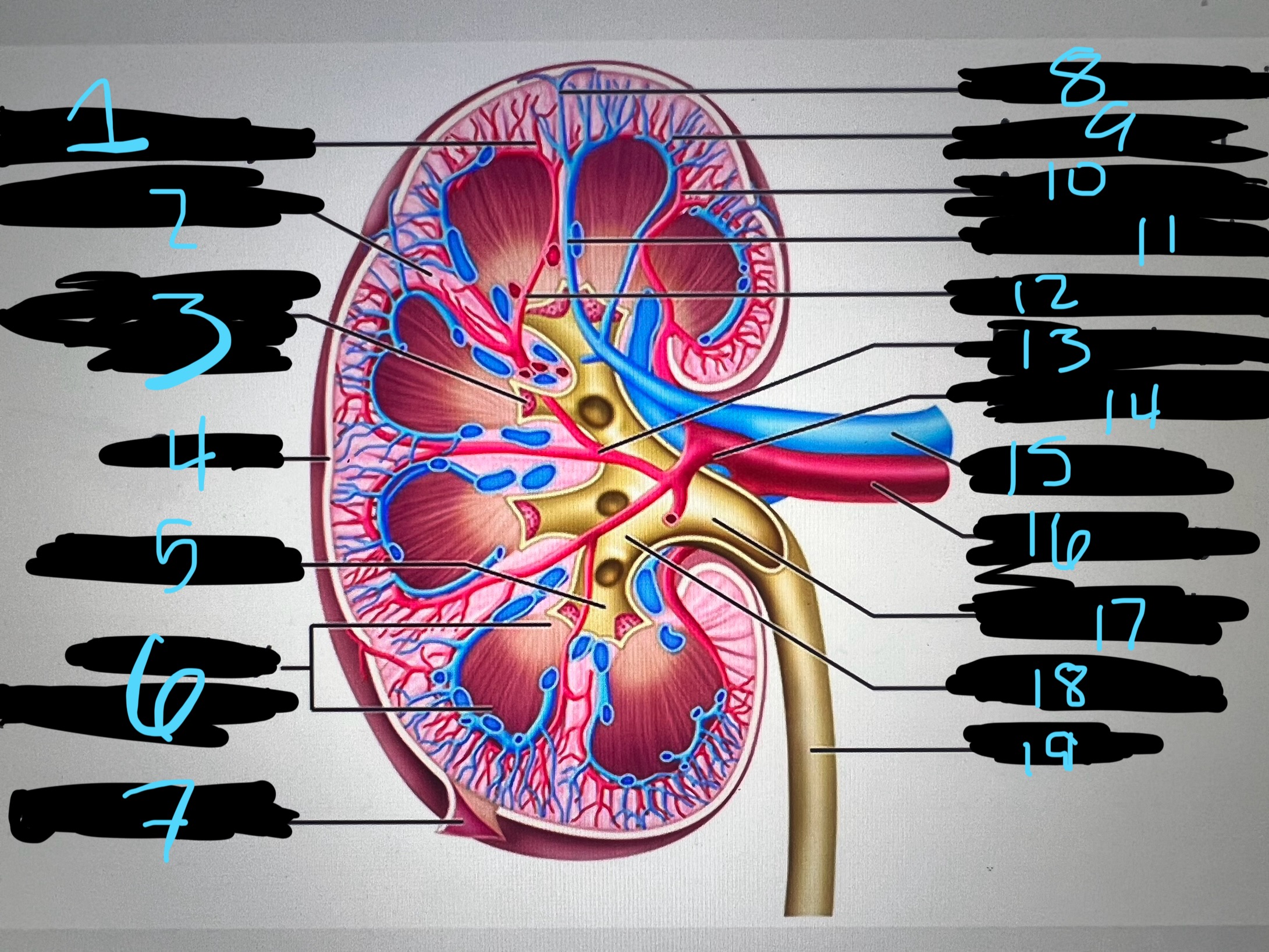
3
blue
papilla of pyramid
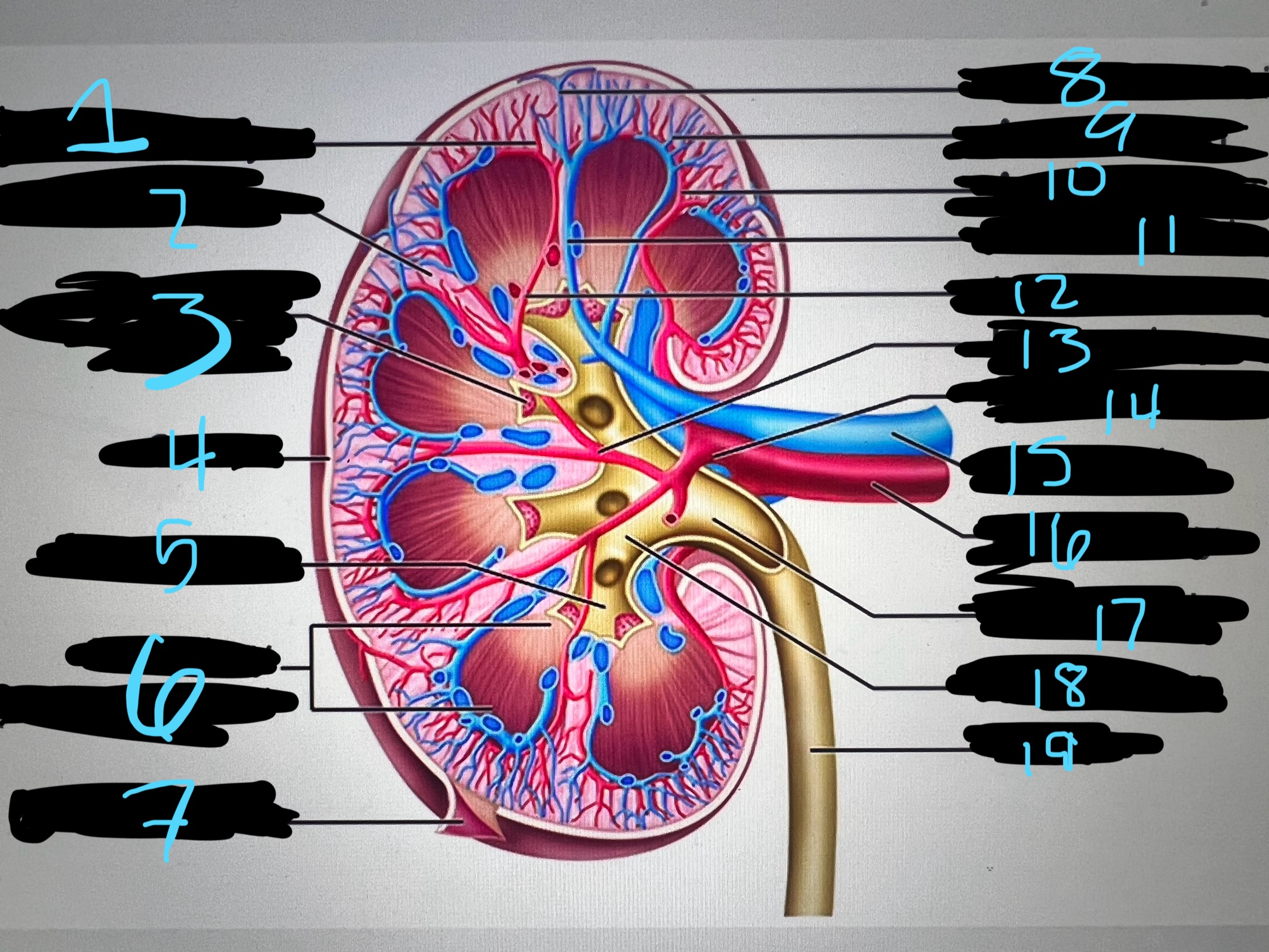
4
blue
cortex
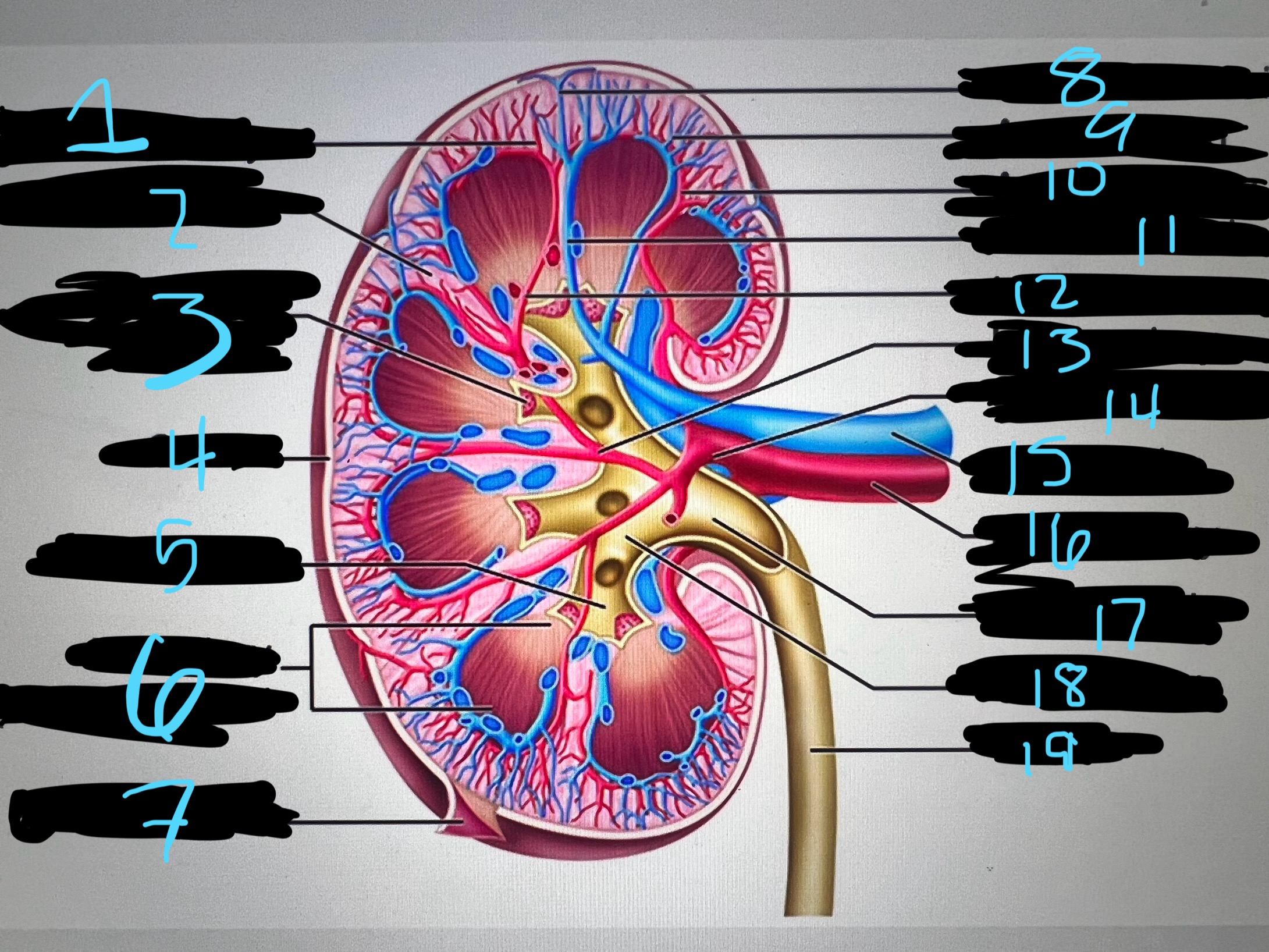
5
blue
minor calyx
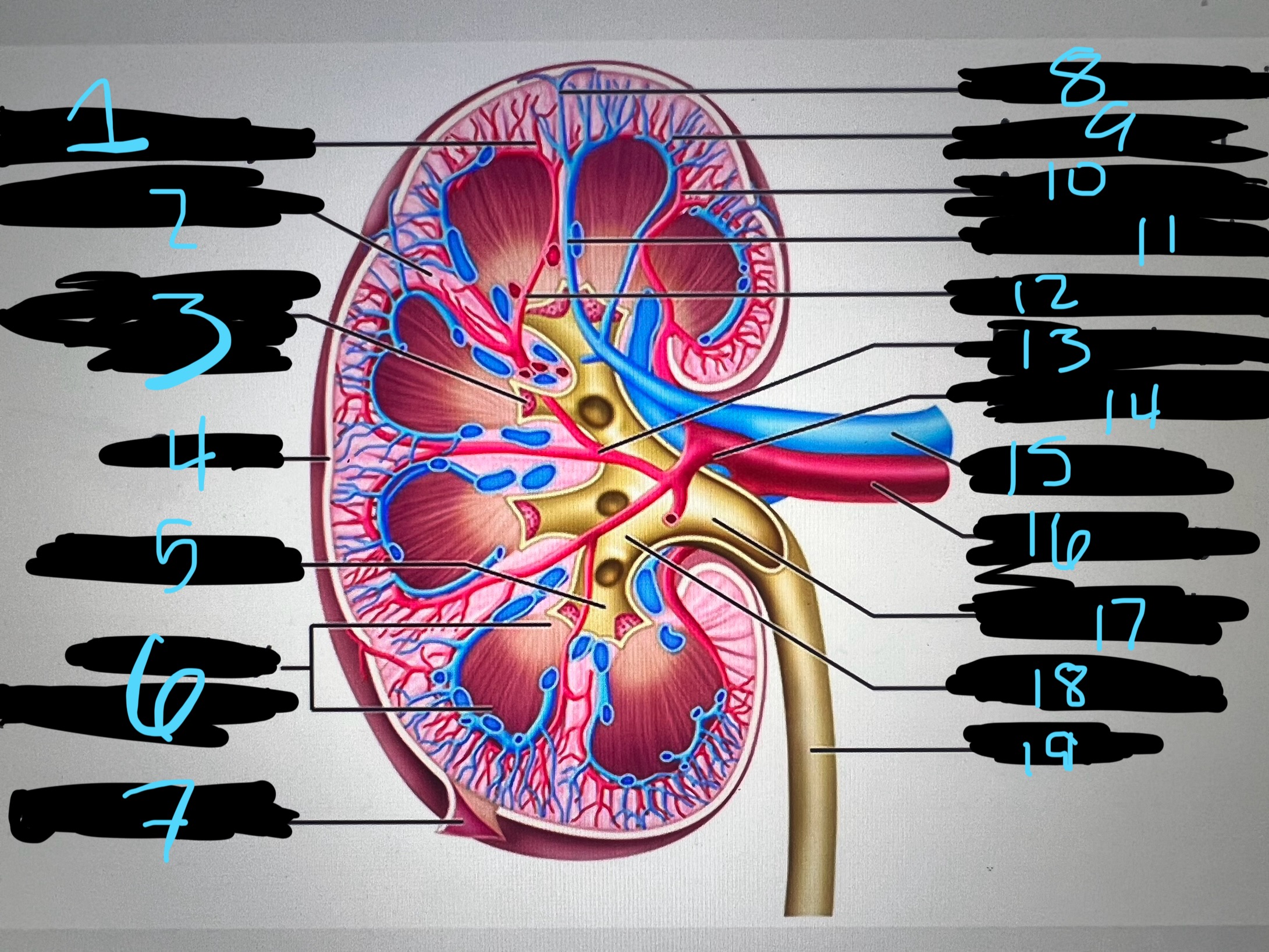
6
blue
medullary (renal) pyramid
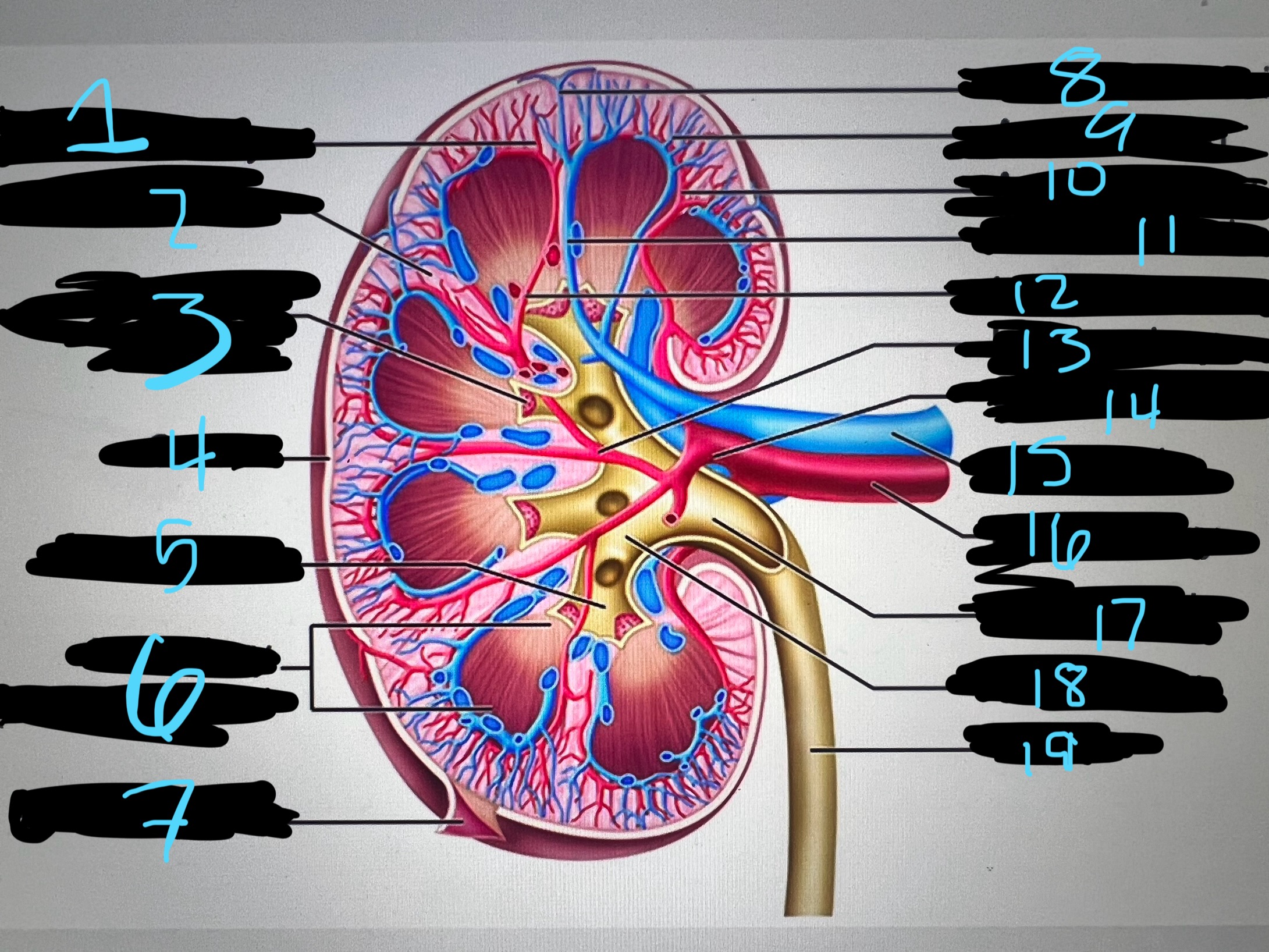
7
blue
renal capsule
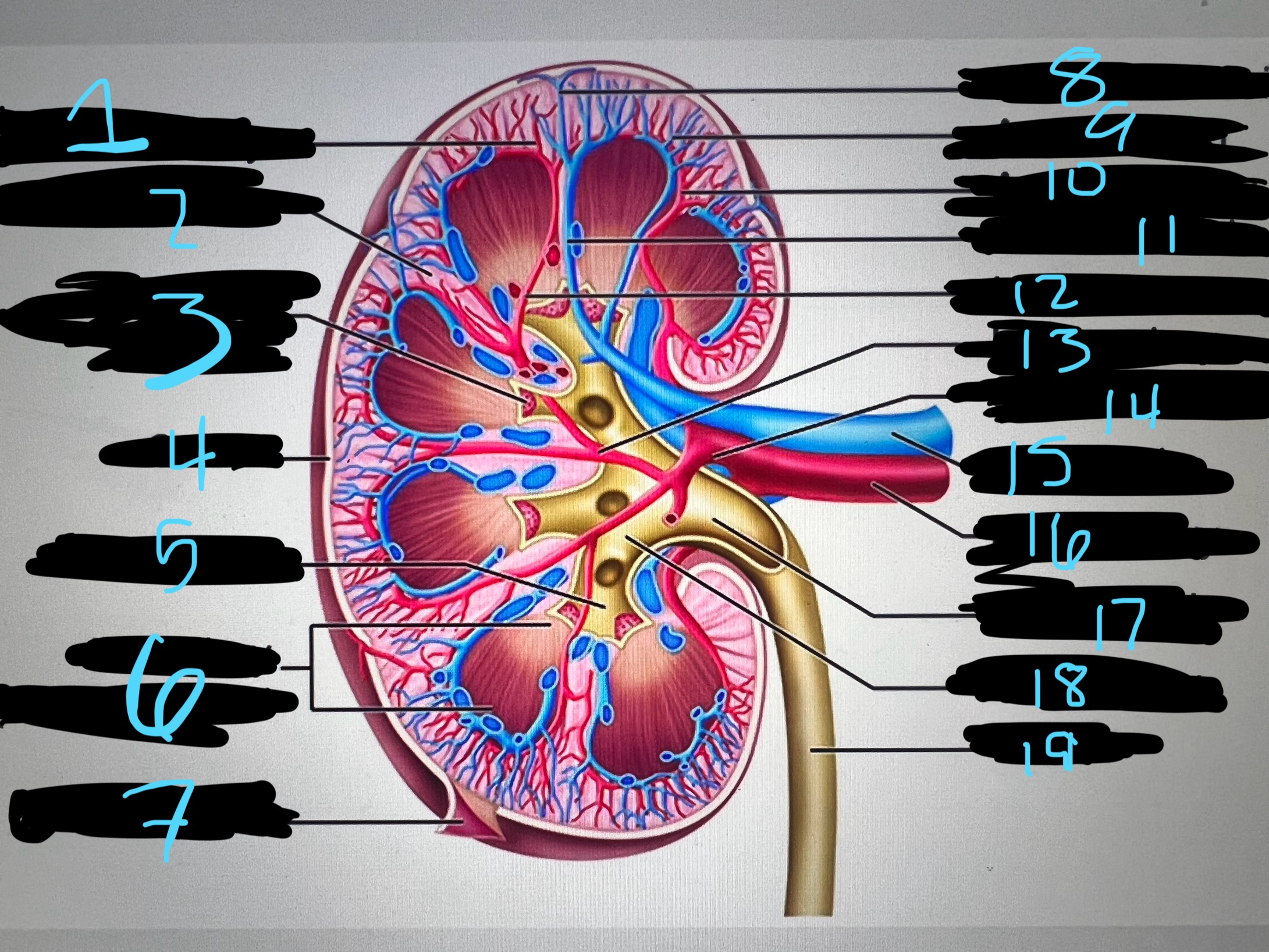
8
blue
interlobar top vein
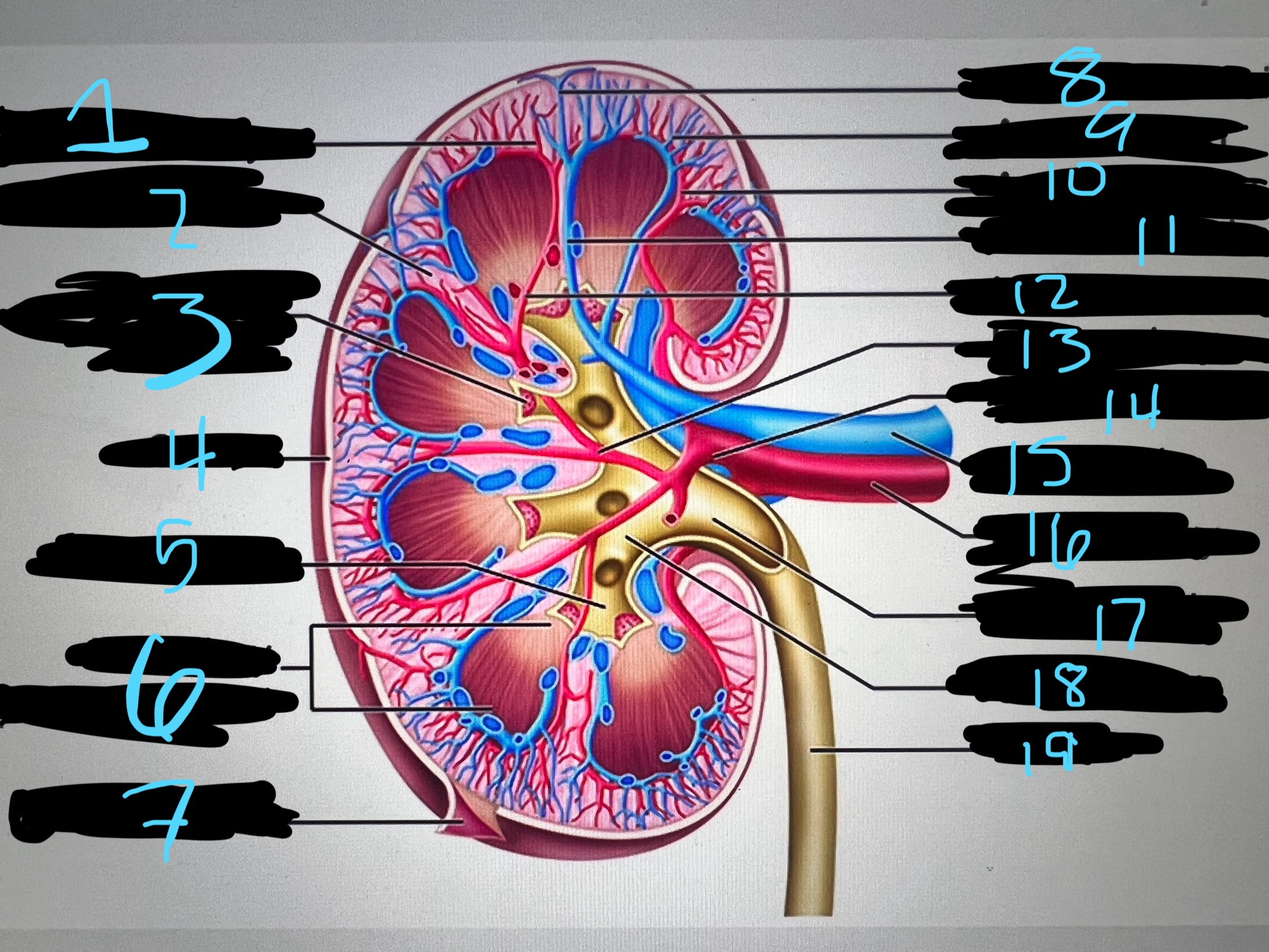
9
blue
arcuate vien
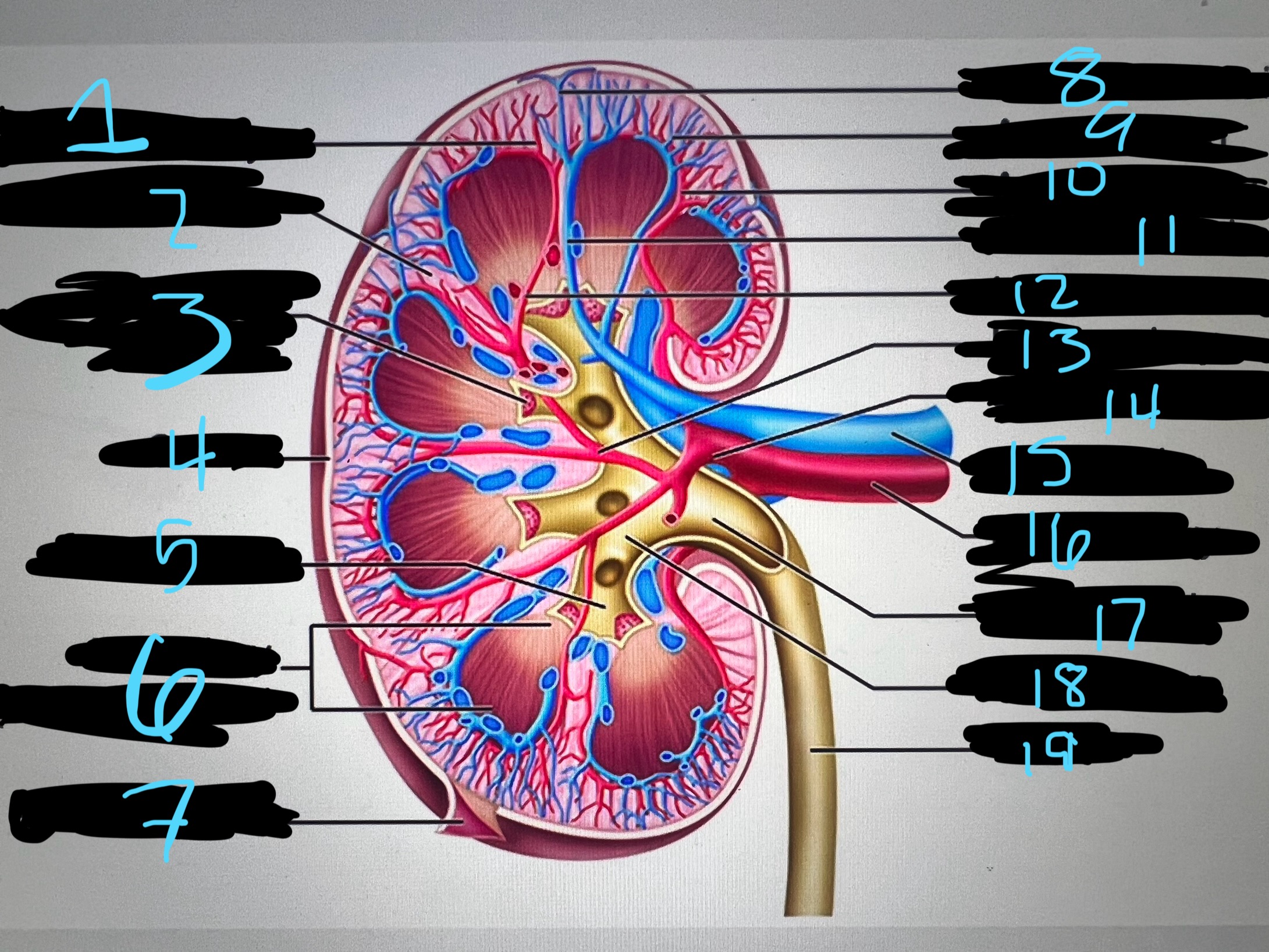
10
blue
arcuate artery
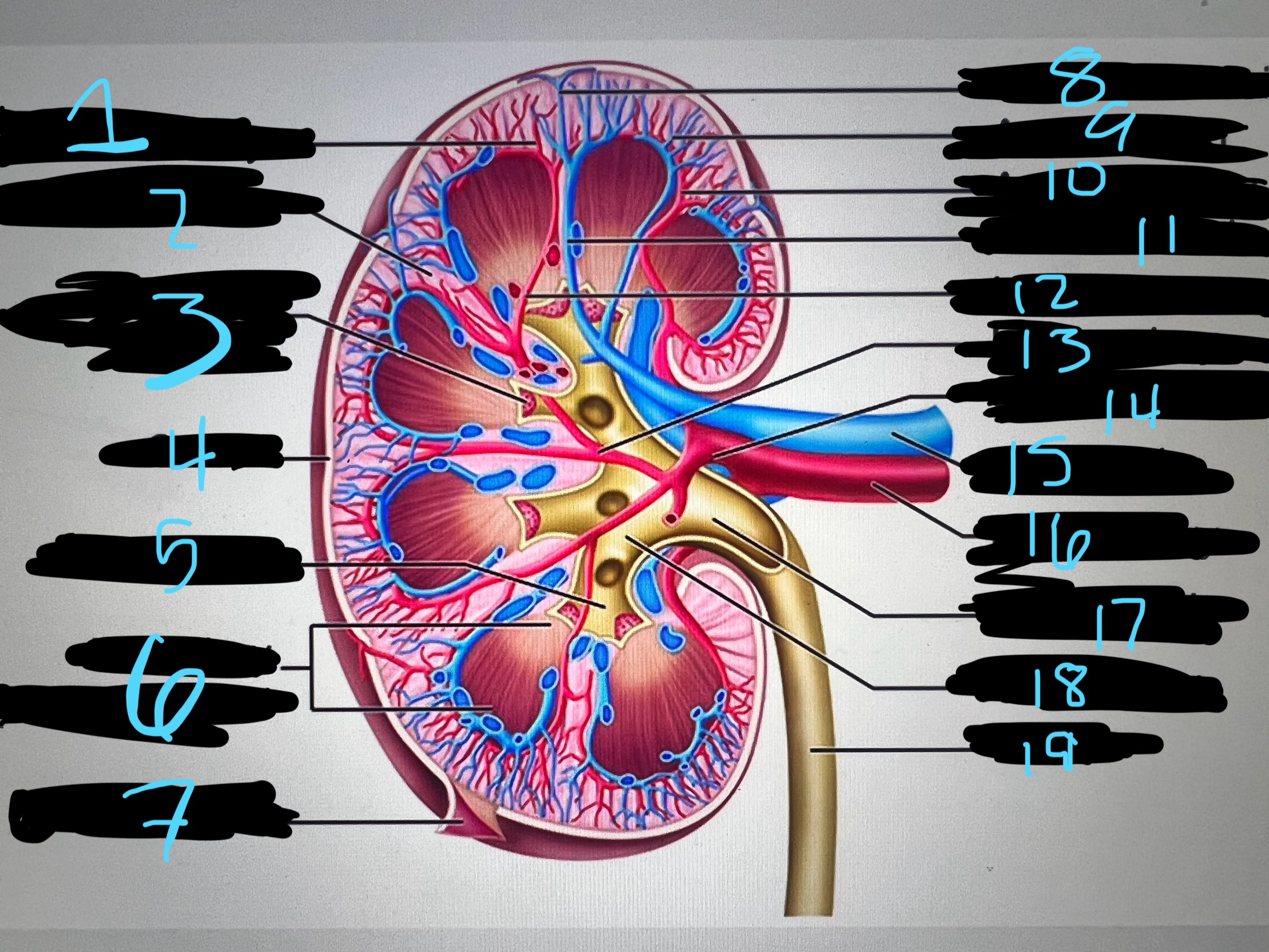
11
blue
interlobar bottom vein
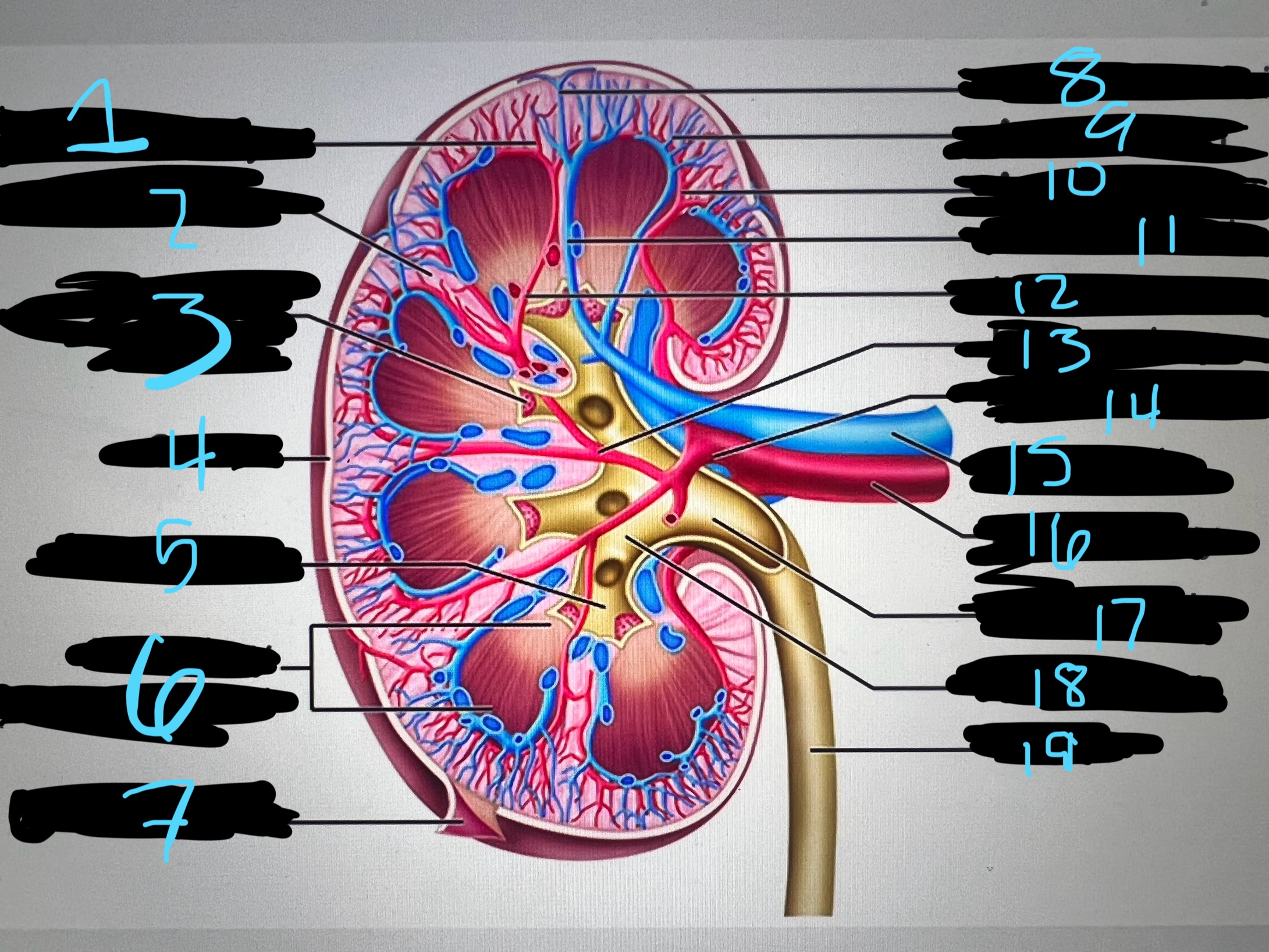
12
blue
interlober artery
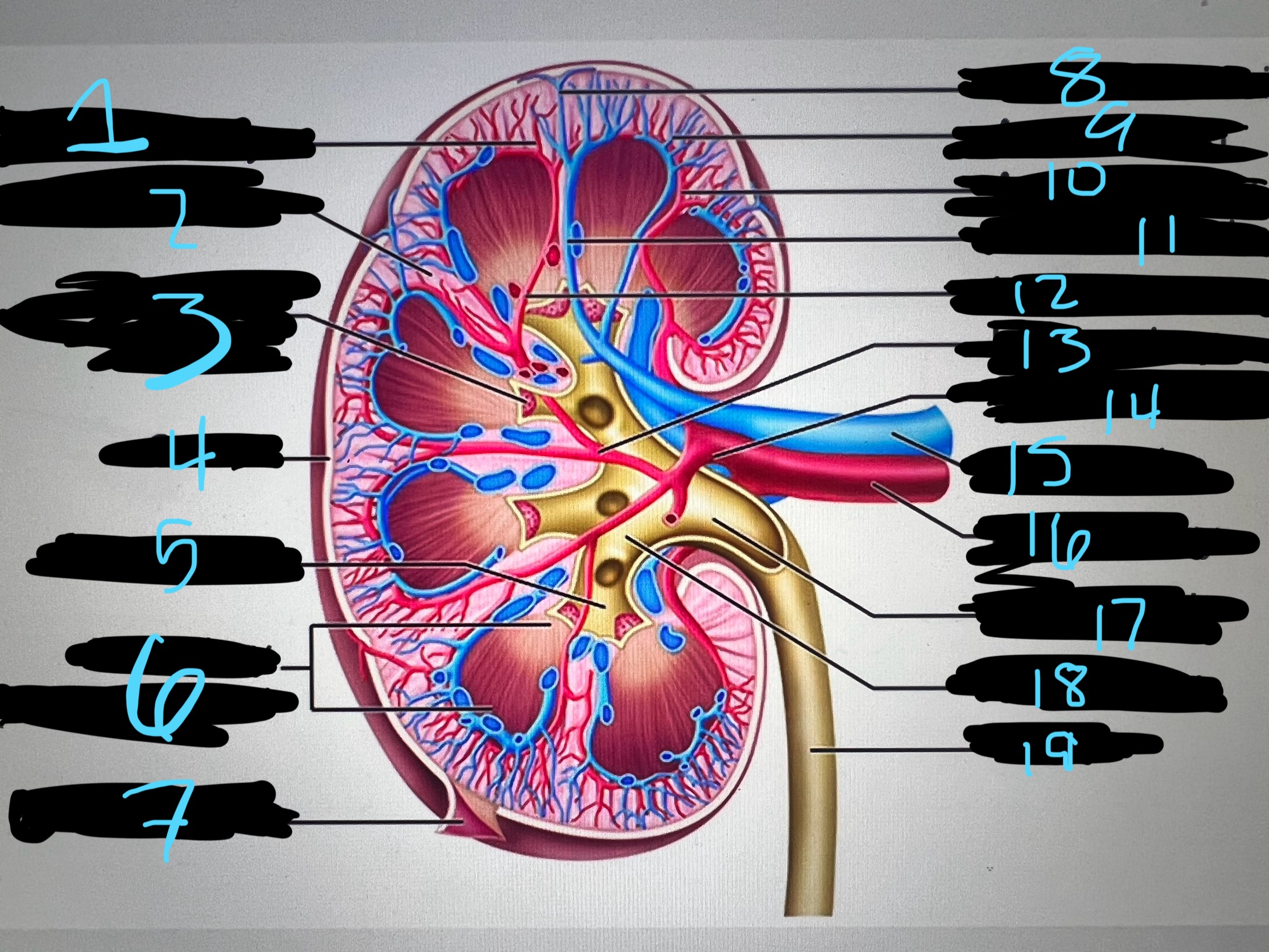
13
blue
lobar artery