Lecture 17-Targeting proteins to Peroxisome and Nucleus
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Single membrane bound oxidative organelles
Peroxisome
Contains enzymes (oxidases) that use molecular oxygen to oxidize various substrates such as fatty acids, breaking them down into smaller components to use in biosynthetic pathways
Peroxisome
Peroxisome Generates
hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
enzyme catalase that converts H2O2 to
oxygen and water
Peroxisome are most abundant where
liver cells
Switches from monomeric (composed of a single unit, such as a protein with one polypeptide chain or a small molecule that can form a polymer) soluble form to an oligomeric (molecule composed of a small number of repeating structural units, known as monomers, which are linked by covalent bonds) form embedded in peroxisomal membrane forming a complex with membrane protein Pex14
Pex5
Unlike the ER and Mitochondria, peroxisomes can import what
folded proteins
one of a group of four related diseases called peroxisome biogenesis disorders
Zellweger Syndrome
genetic material and associated protein (histones)
Chromatin
ribosomal RNA production and assembly of ribosome components
Nucleolus
non-nucleolar regions of the nucleus
Nucleoplasm
lamin filaments and associated proteins
Form scaffolding/structural support
Nuclear matrix
What is connected to the ER
Nuclear outer membrae
What perforate the nuclear envelope
Nuclear Pores
Nuclear pores are composed multi-protein structure
called
Nuclear Pore Complex
How many nuclear membranes does the Nuclear Pore Complex span
Both
Which size molecules and proteins can diffuse through passively (<40 kDa)
Small
Which size proteins need to be actively transported with the help of soluble transport proteins that interacts with the cargo and components of the nuclear pore
Large
Membrane embedded ring-structure with an aqueous pore
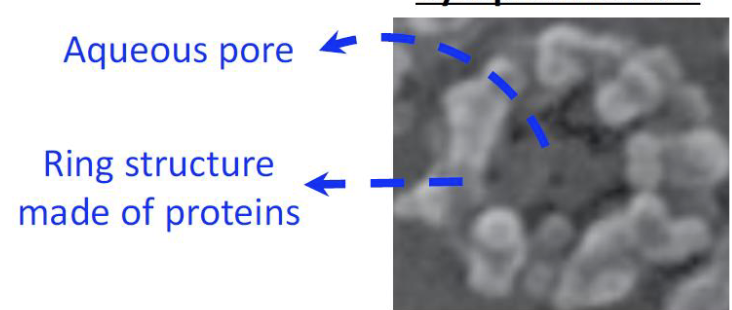
Cytoplasmic face
Distal Ends of the filaments joined by a terminal ring forming a nuclear basket structure
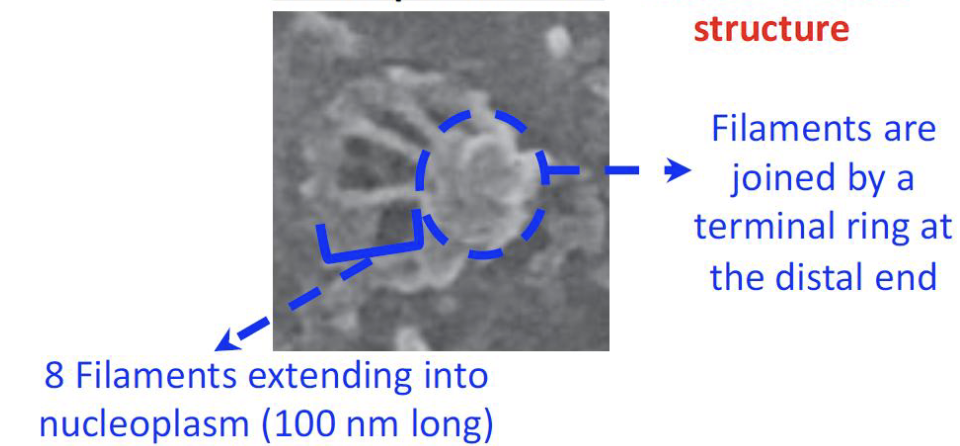

Nucleoplasmic face
Forms the scaffold of the nuclear pore
Forms an octagonal ring
Spans both inner and outer membranes
Seven structural nucleoporins form a Y- shaped structure known as the Y-complex
Sixteen copies of the Y-complex form the basic structural scaffold of the pore
Structural nucleoporins
The inner and outer membranes of the nuclear envelope are connected at the NPC by a highly curved region of membrane
This region contains the embedded membrane nucleoporins
Membrane nucleoporins associate with both the scaffold (structural nucleoporins) and the nuclear membrane
Membrane Nucleoporins
Contain multiple repeats of short hydrophobic sequences rich in phenylalanine (F) and glycine (G) residues
Line the channel of the NPC
Also found associated with the nuclear basket and cytoplasmic filaments
Forms a gel-like matrix
-Allows small molecules to diffuse
Blocks unchaperoned translocation
of proteins >40 kDa
Intrinsically disordered protein
FG-Nucleoporins
Targets protein for import through nuclear pores into nucleus
Stretch of basic amino acids (e.g., Pro-Lys-Lys-Lys-Arg-Lys-Val)
Nuclear localization signal
Located: N-terminus
6-12 hydrophobic residues,1 basic residue
Leucine, Isoleucine, Valine, Phenylalanine, Methionine, Alanine, Tryptophan,
Lysine, Arginine, Histidine
ER
Located: N-terminus
3-5 (non-consecutive) Arg, Lys
Mitochondria
Located: N-terminus
Ser & Thr rich
Chloroplast
Located: C-terminus
Ser-Lys-Leu
Peroxisome
Located: Internal
Leucine, Isoleucine, Valine, Phenylalanine, Methionine, Alanine, Tryptophan,
Lysine, Arginine, Histidine
Nucleus
Cytosolic components required for Nuclear-localization signal (NLS)
Nuclear transport receptors (importin) and RanGTPase
Binds to NLS on the cargo protein
Has affinity for FG-repeats on nucleoporins
By binding to cargo protein and interacting with FG-nucleoporins they facilitate the transport of cargo across the nuclear pore
Nuclear transport receptors (importin)
Small monomeric G-protein
Exists in either a GTP-bound or GDP-bound confirmation
Cycling of Ran between GTP-bound and GDP-bound conformations by hydrolysis of GTP→GDP provides energy to drive unidirectional transport through the nuclear pore
Ran GTPase
found in PKI (an inhibitor of Protein Kinase A) and Rev protein in HIV
Leucine Rich sequence
Precise structural features that determine recognition of these NES remain poorly understood
Heterogenous ribonucleoproteins
Binds to NES on the cargo protein
Has affinity for FG-repeats on nucleoporins
By binding to cargo protein and interacting with FG-nucleoporins they facilitate the transport of cargo across the nuclear pore
Nuclear Transport Receptor (Exportin 1)
In the nucleus, mRNA is associated with specific proteins and form a complex known as
Messenger Ribonuclear Protein Complex (mRNP)
mRNP is exported from the nucleus with the help of
mRNP Exporter
Heterodimeric protein
Large subunit called nuclear export factor 1 (NXF1)
Small subunit called nuclear export transporter 1 (NXT1)
Multiple NXF1/NXT1 dimers bind to mRNP
mRNP Exporter