Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Treatment
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
chlamydia trachomatis
obligate, intracellular parasite of eukaryotic cells
cannot replicate extracellularly or synthesize ATP
humans are the only known natural host
chlamydia trachomatis incubation for symptomatic infection
7-21 days (1-3 weeks)
chlamydia life cycle
chlamydia infects host mucosal epithelial cells (may kill cells)
0-6 hrs: elementary body (EB) (extracellular chlamydia) attaches and enters the host cell
EBs are infectious
6-12 hrs: EB becomes reticulate body (RB)
RBs are non-infectious, but replicating form
12-24 hrs: RB replication
24-36 hrs: RBs reorganize back to EBs
36-48 hrs
48-72 hrs: lysis or extrusion occurs; RBs and EBs escape from cell
if untreated, infection can become chronic

chronic chlamydia timeline
lasting months to 1 yr+
chlamydia overall transmission rate
~55%
chlamydia transmission rate per act of sex
~10%
chlamydia transmission - higher rate of transmission from ____ to _____ (genders)
higher rate of transmission from males to females
percentage of chlamydia transmitted perinatally
20-50%
diagnosis of Ct (chlamydia) and GC (gonorrhea)
NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Test)
urogenital
urine (M/F)
vaginal swab (F)
urethral swab (M)
rectal
swab (M/F)
oropharyngeal
throat swab (M/F)
swabs can be self-collected
Ct & GC screening for women
annual screening
pregnancy
prn based on reported sexual activity
Ct & GC screening for women - annual screening
annual screening:
all sexually active women younger than 25 yo
highest incidence
asymptomatic
severe health/reproductive complications if undiagnosed
sexually active 25+ yo women, if at increased risk
new or multiple partners
not monogamous
partner has STI
Ct & GC screening for women - pregnancy
at first prenatal visit and in third trimester
same criteria as annual screening:
all sexually active women younger than 25 yo
highest incidence
asymptomatic
severe health/reproductive complications if undiagnosed
sexually active 25+ yo women, if at increased risk
new or multiple partners
not monogamous
partner has STI
Ct & GC screening for women - prn based on reported sexual activity
rectal and oropharyngeal screening prn based on reported sexual activity
Ct & GC screening for men
men who have sex with women only
MSM (men who have sex with men)
Ct & GC screening for men - men who have sex with women only
no routine screening recommended
low risk
no data to support
increased risk should be considered
high chlamydia setting
correctional facilities
STD/sexual health clinics, etc.
Ct & GC screening for men - MSM
at least annual testing for all sexually active MSM
rectal and urethral based on reported sexual activity
routine oropharyngeal not recommended for chlamydia but can be picked up on GC NAAT if tested
more frequent testing based on risk
chlamydia presentation in men - urethretis
discharge - clear to mucopurulent; dysuria
how it likely presents itself (scale of 1-3)
1/3 chance symptomatic presentation
3/3 chance asymptomatic presentation
chlamydia presentation in men - epididymitis
scrotal and flank pain, inguinal flank, urethral discharge (any type of groin pain)
how it likely presents itself
3/3 chance symptomatically
1/3 chance asymptomatically
chlamydia presentation in men - anorectal
irritation, painful defecation, purulent discharge, pruritis, scant bleeding
how it likely presents itself
1/3 chance symptomatically
3/3 chance asymptomatically
chlamydia presentation in men - oropharyngeal
pharyngitis, tonsillitis, fever, cervical adenitis
how it likely presents itself
1/3 chance symptomatically (mild)
3/3 chance asymptomatically
chlamydia presentation in women
cervicitis
urethritis
PID (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease)
anorectal
oropharyngeal
chlamydia presentation in women - cervicitis
non-specific vaginal discharge, spotting/bleeding, abdominal discomfort
site of infection in 75-80% of women
how it likely presents:
1/3 chance symptomatically
3/3 chance asymptomatically
chlamydia presentation in women - urethritis
dysuria, urinary frequency
how it likely presents:
1/3 chance symptomatically
3/3 chance asymptomatically
chlamydia presentation in women - PID
lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, dyspareunia, intermenstrual bleeding, fever
20% infertile
30% develop chronic pain
1% experience ectopic pregnancy if they conceive
likely presentation:
3/3 chance symptomatic
1/3 chance asymptomatic
chlamydia presentation in women - anorectal
irritation, painful defecation, purulent discharge, pruritus, scant bleeding
may be due to sex or autoinoculation from vaginal secretions
likely presentation
1/3 chance symptoms
3/3 chance asymptomatic
chlamydia presentation in women - oropharyngeal
pharyngitis, tonsillitis, fever, cervical adenitis
likely presentation
1/3 chance symptomatic (mild)
3/3 chance asymptomatic
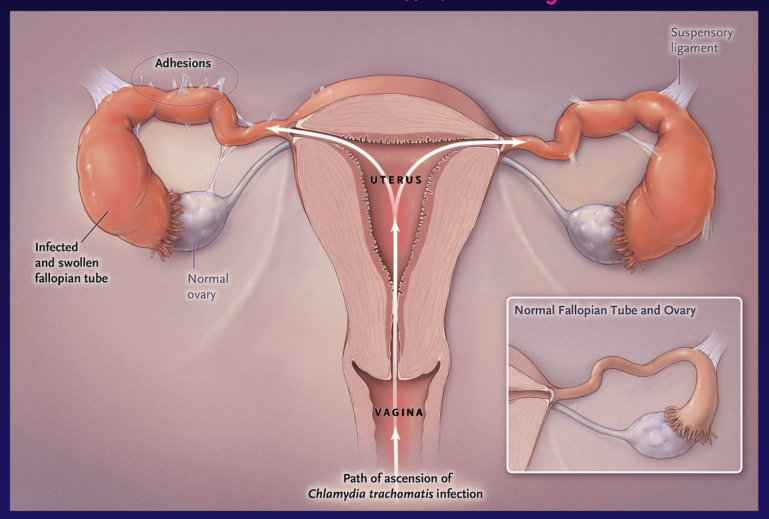
PID
fallopian tube is infected and swollen
infertility
adhesion
vagina = path of ascension of chlamydia
Chlamydia trachomatis conjunctivitis sx
redness, not much discharge tbh
treatment of urogenital, rectal, and pharyngeal chlamydia (general/nonpregnant)
doxycycline 100mg po BID x 7 days
alternative:
azithromycin 1000mg po x 1 dose
levaquin 500mg po q24h x 7 days
treatment of urogenital, rectal, and pharyngeal chlamydia (pregnancy)
azithromycin 1000mg po x 1 dose
urogenital/rectal/pharyngeal chlamydia follow-up for patient
retesting for lack of CL of sx or for recurrence of sx
repeat testing @ 3 months
routine test of cure @ 7-14 days is not recommended
urogenital/rectal/pharyngeal chlamydia follow-up for partners
evaluate and/or treat all partners within the last 60 days from onset or dx
last partner > 60 days = evaluate and treat
no sexual activity for 7 days after end of tx
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
gram-negative diplococci
resistance mechanisms
many carry a plasmid that produces TEM-1 type of beta-lactamase (penicillinase)
PCN is no longer accepted as tx
cephalosporins are stable to beta-lactamase
FQ resistance increasing
third world countries = 30-60%
USA = 0-30%
N. gonorrhoeae transmission methods
M to F (if male infected)
M to F (if female infected)
oropharyngeal
perinatally
anorectal?
N. gonorrhoeae transmission rate of infection - M to F (if male infected)
50-70% per episode of sex
N. gonorrhoeae transmission - M to F (if female infected)
~20% per episode of sex
N. gonorrhoeae transmission rate - oropharyngeal
lower rates
N. gonorrhoeae transmission rate - anorectal
rates not quantified
N. gonorrhoeae transmission - perinatally
can be transmitted perinatally
GC presentation in men - sites
urethritis
epididymitis
anorectal
oropharyngeal
GC presentation in men - incubation & sx presentation (timeline)
incubation = 1-14 days
sx = most sx present within 2-5 days
GC presentation in men - urethritis
mucopurulent discharge, dysuria
likely presentation
3/3 sx
1/3 asymptomatic
GC presentation in men - epididymitis
scrotal and/or inguinal and/or flank pain, urethral discharge
likely presentation
3/3 sx
1/3 asx
GC presentation in men - anorectal
irritation, painful defecation, purulent discharge, pruritis, scant bleeding
likely presentation
1/3 sx
3/3 asx
GC presentation in men - oropharyngeal
pharyngitis, tonsillitis, fever, cervical adenitis
likely presentation
1/3 sx (mild)
3/3 asx
GC presentation in females - incubation and sx presentation (timeline)
incubation = variable
most sx present within 10 days
GC presentation in females - sites
vaginitis/urethritis/cervicitis
PID
anorectal
oropharyngeal
GC presentation in women - vaginitis/urethritis/cervicitis
non-specific vaginal discharge, intermenstrual bleeding, dysuria, lower abdominal pain, dyspareunia
likely presentation
1/3 sx
3/3 asx
GC presentation in women - PID
lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, dyspareunia, intermenstrual bleeding, fever
long term can impact fertility and pregnancy
likely presentation
3/3 sx
1/3 asx
GC presentation in women - anorectal
irritation, painful defecation, purulent discharge, pruritis, scant bleeding
may be due to sex or perineal contamination from cervical secretions
likely presentation
1/3 sx
3/3 asx
GC presentation in women - oropharyngeal
pharyngitis, tonsillitis, fever, cervical adenitis
likely presentation
1/3 sx (mild)
3/3 asx
gonococcal conjunctivitis sx
redness
discharge
disseminated gonococci can lead to ___ and ___
rash
arthritis
tx of GC (general/non-pregnant)
resistance issues with GC
FQs
only give oral cefixime if ceftriaxone is unavailable in uncomplicated pt
otherwise, it is no longer recommended
tx of GC alone (urogenital/rectal/pharyngeal) (and if they’re allergic)
ceftriaxone 500mg IM x 1 dose
if pt weighs more than 150kg, dose 1000mg IM
highly allergic alternative:
gentamicin/azithromycin
240mg IM/2000mg po
tx of GC including chlamydia
often with vaginal, cervical, urethral infections, there is a co-infection with chlamydia
^ must tx both organisms
ceftriaxone 500mg IM x 1 dose and doxycycline 100mg BID x 7 days
tx for disseminated GC
ceftriaxone 1000mg IM or IV q24h
cefotaxime 1000mg IV q8h
tx of GC only in pregnant pts
ceftriaxone 500mg IM x 1 dose
tx of GC with chlamydia in pregnant pts
ceftriaxone 500mg IM x 1 dose and azithromycin 1000mg po x 1 dose
GC f/u - urogenital or rectal
repeat testing at 3 months
retesting for lack of CL of sx or for recurrence of sx
GC f/u - pharyngeal
test-of-cure recommended between 7-14 days
retesting for lack of CL of sx or for recurrence of sx
GC f/u - partners
evaluate and/or treat all partners within last 60 days from onset or dx
last partner > 60 days = evaluate and tx
no sexual activity for 7 days after end of tx
syphilis bug name
Treponema pallidum
syphilis
Treponema pallidum; spirochete
syphilis transmission methods
sexual transmission
congenital syphilis (mother to child)
syphilis transmission - sexual transmission
contagious throughout primary/secondary stages
contact with lesions or rash
enters through skin or mucous membranes
syphilis transmission - congenital syphilis
mother to child
generally occurs via transplacental passage of T. pallidum during maternal spirochetemia
may also be transmitted at birth if contact with genital lesions
T. pallidum stages
play role in determining tx
primary
secondary
latent
early (less than a year)
late (more than a year)
unknown
tertiary
T. pallidum stages - primary syphilis
incubation period: 10-90 days (average 21)
chancre appears @ site of spirochete penetration
painless and resolves spontaneously within 1-8 weeks
highly infectious
T. pallidum stages - secondary syphilis
develops 4-8 weeks (1-2 mo) after onset of primary
hematogenous or lymphatic spread of organism → results in rash (especially skin lesions; often on palms of hands and soles of feet)
spontaneously resolves in 4-6 weeks
sx:
lymphadenopathy
malaise
fever
alopecia
rashes (body, palms, soles, penis, scrotum)
T. pallidum stages - latent syphilis
individuals with positive serologic test
no other signs of disease related to primary, secondary, or tertiary stages
can remain asxtic for life or can develop tertiary disease
less likely to transmit in this phase than others
T. pallidum stages - tertiary syphilis
can affect any organ of the body
gummas
neurosyphilis
CV
T. pallidum stages - tertiary syphilis → gummas
granulomatous lesions
often affect bone, skin, upper respiratory tract
can involve any organ
T. pallidum stages - tertiary syphilis → neurosyphilis
general paresis
deafness
optic atrophy
blindness
dementia
can actually occur @ any stage
T. pallidum stages - tertiary syphilis → CV
aortic insufficiency
aortic aneurysms
congenital syphilis
80% due to lack of screening or appt tx :(
situations in which outcomes of congenital syphilis are worse
more likely worse outcomes in 1st/2nd trimester
outcomes less likely to be worse in 3rd trimester but still could present with issues post-nataly
if conception occurs during early syphilis
increased risk of fetal death with acute infection — mom/fetal inflammatory response?
untreated syphilis
does treatment entirely eliminate congenital syphilis?
no :(
early congenital syphilis manifestations (neonates/young children)
early = less than 2 yo
small for gestational age
liver issues
spleen issues
lymphadenopathy
rash
bone
potential CV
neurologic
ophthalmic issues
late manifestations of congenital syphilis (neonates/young children)
late = older than 2 yo
orofacial issues
bone
ophthalmic
deafness
syphilis screening tests
non-specific screening
specific screening
syphilis non-specific screening
measure IgM/IgG antibodies NOT specific to T. pallidum, but to cellular breakdown products
VDRL (venereal disease research laboratory)
RPR (rapid plasma regain) - reactive or dilution (ex., 1:32)
specific syphilis screening
measure antibody specific to T. pallidum
FTA (fluorescent treponemal antibody)
TP-PA (T. pallidum particle agglutination)
traditional syphilis screening algorithm
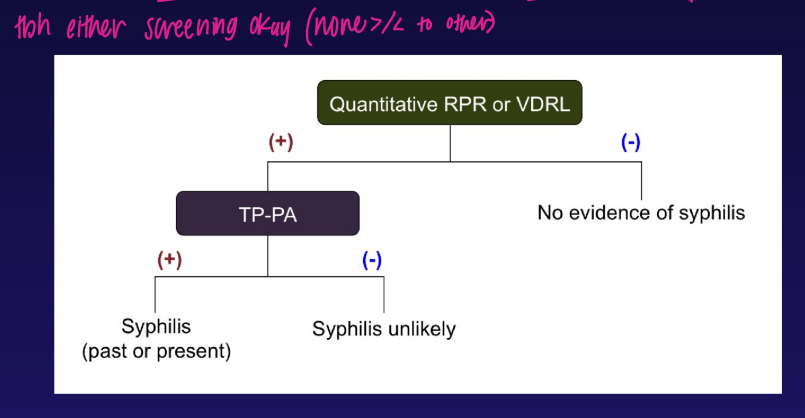
syphilis screening algorithm - reverse sequence algorithm
EIA = Enzyme Immunoassay
CIA = Chemiluminescent Immunoassay

when do you screen for syphilis in pregnancy?
first prenatal visit
third trimester/after 28 weeks
@ delivery
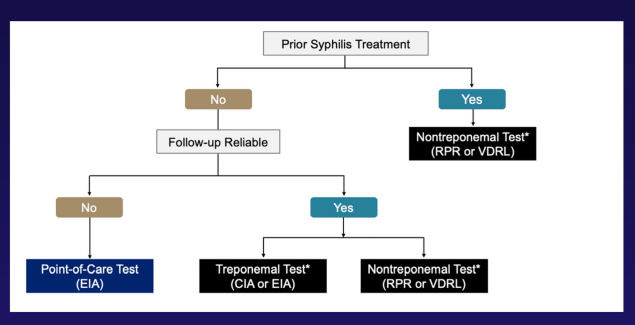
how to screen for syphilis in pregnancy
“Follow-up reliable” just means:
👉 Can we trust that this patient will come back for follow-up labs and treatment if needed? / Will this person actually show up again?
primary, secondary, and early latent syphilis - timeline
12+ months
how to treat primary, secondary, and early latent syphilis
benzathine PCN G 2.4 MU IM x 1 dose
(MU = million units)
benzathine PCN G
depot IM injection
slow release
how to treat tertiary and late latent or unknown duration of latency syphilis
benzathine PCN G 2.4 MU IM qweek x 3
how to tx neurosyphilis
aqueous PCN G 3-4 MU q4h
continuous infusion if possible
how to treat syphilis in pregnancy
PCN
desensitize to PCN if allergic
Jarish-Herxheimer rxn
not an allergy to PCN
rxn seen soon after tx w/PCN for syphilis (usually a few to 24 hrs after the dose) in early stage
due to high bacterial burden?
Jarish-Herxheimer rxn sx
fever
malaise
N/V
rash or worsening rash
less often chills
hypotension
treatment of Jarish-Herxheimer rxn
self-limiting w/in 24 hrs
supportive care
primary syphilis follow-up
resolution of sx/signs
check RPR at 6 and 12 months
RPR titer should drop 4+ fold
if not seen, reassessment and retreatment may be necessary
secondary syphilis follow up
resolution of sx/signs
check RPR at 6 and 12 months
RPR titer should drop 4+ fold
if not seen, reassessment and retreatment may be necessary
latent syphilis follow up
resolution of sx/signs
check RPR at 6, 12 and 24 months
RPR titer should drop 4+ fold
if not seen, reassessment and retreatment may be necessary
primary syphilis - partners testing
evaluate and tx all partners within last 90 days from onset or diagnosis
last partner > 90 = evaluate and tx if positive serology
no sex for 7 days after end of tx