CHEM 403: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
what do nucleotides do for cellular metabolism?
provide energy; help respond to stimuli or hormones; structure; building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
gene
segment of DNA that codes for a protein or RNA
classes of RNA
ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) → components of ribosomes
messenger RNAs (mRNAs) → carries genetic info from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis
transfer RNAs (tRNAs) → translate mRNA to an amino acid sequence
noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) → many functions
what are nucleotides made of?
nitrogenous base (pyrimidine or purine), pentose, 1+ phosphates
nucleoside
nucleotide but without a phosphate group (has a sugar and base)
N-β-glycosyl bond
joins pentose (sugar) to base
purine bases
adenine (A) → DNA and RNA
guanine (G) → DNA and RNA
pyrimidine bases
cytosine (C) → DNA and RNA
thymine (T) → only in DNA
uracil (U) → only in RNA
nucleotide and nucleic acid nomenclature
-ine = nucleoside // -ate = nucleotide
deoxyribonucleotides
structural units of DNA
ribonucleotides
structural units of RNA
phosphodiester linkage
connects bases together (in both DNA and RNA)
hydrolysis of DNA vs RNA
RNA is rapidly hydrolyzed
DNA is not rapidly hydrolyzed
oligonucleotide
short nucleic acid
polynucleotide
longer nucleic acid
what kind of test do we use for aromatic structures?
UV-vis tests
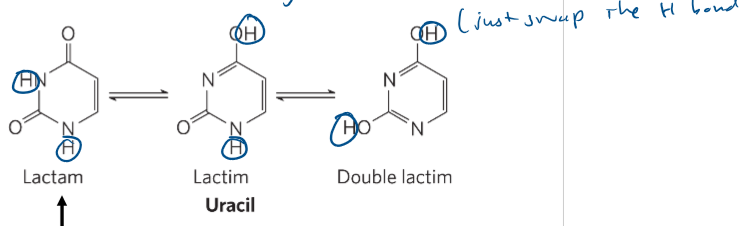
tautomers (know how to draw these given a base)
interconverted form of a base
base pairs
H-bonding patterns between complementary strands of nucleic acids
A → T or U (2 H bonds)
G → C (3 H bonds)
hierarchical levels of nucleic acid structure
primary = nucleotide sequence
secondary = regular, stable structure taken up by some or all of the nucleotides
tertiary = complex folding of chromosomes or folding of tRNA/rRNA structures
“Watson-Crick” model of DNA structure
offset pairing of the 2 strands creates a major groove (open: better interactions) and a minor groove (closed)
are DNA strands parallel or antiparallel?
antiparallel → 3’, 5’ -phosphodiester bonds in opposite directions (parallel strands would run in the same direction)
how many base pairs are in between helical turns?
10.5
how is the double helix stabilized?
metal cations shield (-) charges of backbone phosphates
base stacking interactions between base pairs (G-C stronger bc they have more H bonds)
how is DNA replicated (simple)?
parent strands split → strands serve as templates and complementary daughter strands are formed
three forms of DNA
B-form: “Watson-Crick” structure; right-handed; most stable; in our body
A-form: right-handed; wider; solutions with no water; not in our body
Z-form: left-handed; zig-zag appearance; for special cases; in our body (unsure of why)
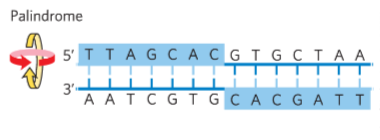
palindrome
section of DNA that is the same backward and forward
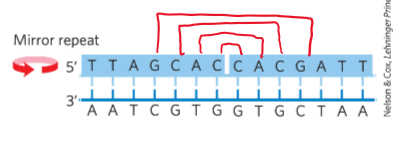
mirror repeat
sequence when the inverted repeat occurs within each individual strands
hairpin and cruciform structures
form from inverted repeat sequences
hoogsteen positions
participate in H bonding with a third DNA strand
hoogsteen pairing
non-Watson-Crick pairing; forms triplex DNAs (when 3 DNA strands pair)
tetraplex DNAs
occurs when 4 DNA strands pair; G tetraplex is very stable
transcription
mRNAs formed as copies of DNA template
monocistronic mRNA
codes for one polypeptide
polycistronic mRNA
codes for 2+ different polypeptide
how is the double helix denatured?
pH extremes or high temperatures; this disrupts H bonds and base-stacking interactions;
an open/denatured helix means higher UV-vis
anneal
two strands spontaneously rewind; can wind again when environment returns to normal
hypochromic effect
decrease of UV absorption when complementary strands are paired
hyperchromic effect
increase in UV absorption when helix is denatured
how does the denaturation temperature change with base pairing?
more G-C pairings increases it, meaning it is harder to denature with more G-C pairings because it has more H bonds than A-T
stability of duplexes
RNA duplex > RNA-DNA > DNA duplex)
mutations
alterations in DNA that make permanent changes in genetic information
deamination
spontaneous loss of exocyclic amino groups; happens all the time with cytosine → uracil (since U is not in DNA, the base is then removed)
sodium nitrite + nitrate → deamination
depurination
hydrolysis of the N-β-glycosyl bond between the base and sugar
alkylating agents
can change base-pairing or stop it
what does oxidative stress do?
damages DNA
cloning vectors
small DNAs capable of autonomous replication
recombinant DNA
composite DNA molecules made of covalently linked segments from multiple sources
origin of replication (ori)
sequence where replication starts
resistance enzymes
cut the plasmid so we can insert DNA
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
replicate DNA using thermophilic enzymes
can trace evolution, be used in forensics, detecting infections, etc.
sanger sequencing
remove the ability of one base to have something added to it
on the gel: smallest piece at the bottom and largest at the top
nucleotide-bonding fold
single protein domain that binds adenosine
second messengers
compounds made in the cell after extracellular chemical signals interact with receptors