Chapter 6: Aggregates in the Community
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Chapter 6: Aggregates in the Community
Aggregates = Groups with a common characteristic.
Also called target populations.
Basis of Definition
May be based on:
Special interests (e.g., support groups, cultural groups)
Geographic locations (e.g., neighborhoods, rural areas)
Key Nursing Role
Community health nurses must identify aggregates when planning targeted health interventions.
Examples of Aggregates Served
Individuals across the lifespan (infancy to death)
Families
Groups within the community
Management of Care
Advocacy: Act as a client advocate.
Case Management: Plan individualized care for client based on needs.
Health Promotion and Maintenance
Health Promotion/Disease Prevention: Plan and/or participate in community health education.
Health Screening: Perform health history, health, and risk assessments.
Children (Birth to 12 Years) and Adolescents
Influences on Health
Income level of caregivers affects child health
Low-income = ↑ risk for food insecurity, homelessness, learning difficulties, cognitive delays
Access to care supported by:
Affordable Care Act (ACA)
Medicaid
Children’s Health Insurance Plan (CHIP)
(Helps reduce health disparities)
Health Concerns and Leading Causes of Death
Children
Perinatal conditions & congenital anomalies
Sudden Unexplained Infant Death (SUID)
Motor vehicle & other unintentional injuries
Infant mortality linked to maternal health, socioeconomic status, and access to care
Adolescents
Motor vehicle & other unintentional injuries
Homicide
Suicide
Screening and Preventive Services for Children
Height & weight
Vision & hearing
Dental health
At birth: hemoglobinopathy, phenylalanine level, T4, TSH
Immunization status (per CDC schedules)
Lead exposure
Cholesterol & triglyceride levels
Nutrition assessment
Physical activity assessment
Screening and Preventive Services for Adolescents
Height & weight
Vision & hearing
Dental health
Rubella serology & immunization history
Substance use disorders (including tobacco)
Immunization status
Mental health screenings
Cholesterol & triglyceride levels
Nutrition assessment
Physical activity assessment
National Health Goals (QEBP) for Children
Reductions in:
Dental caries
Obesity
Infant mortality
Exposure to secondhand smoke
Increases in:
Newborn blood spot screenings & follow-up testing
Access to a medical home (SDOH)
Schools that require health education
Childhood immunizations
Use of child safety restraints
Physical activity
Number of infants who are breastfed
National Health Goals (QEBP) for Adolescents
Reductions in:
Violent crimes
Use of alcohol, marijuana, and illicit drugs
Deaths related to motor vehicle crashes
Mental health concerns
Increases in:
Schools with a breakfast program
Participation in extracurricular activities
Wellness checkups
Physical activity
Community Education for Children
Anticipatory guidance
Breastfeeding
Sleeping positions
Nutrition
Physical activity
Substance use disorders
Dental hygiene & health
Skin protection
Injury prevention (car, fire, water safety, helmet use, poison control, CPR training)
Community Education for Adolescents
Anticipatory guidance
Substance use disorders
Sexual behavior
Nutrition (especially calcium intake for female clients)
Physical activity
Skin protection
Injury prevention (car, fire, firearm safety)
Factors Influencing Health of Adults
Genetic makeup (sex-linked risks for disease)
Environment (influences risk factors)
Societal & cultural expectations (gender influences disease risk and care)
Social determinants of health: major concerns are chronic conditions > infectious diseases
Screening recommendations are general but must consider individual client factors
Note: Despite high U.S. health expenditures, life expectancy is lower than in many other developed countries.
Health Concerns and Leading Causes of Death
Heart disease
Diabetes mellitus
Mental health disorders
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Colorectal cancer (and other cancers as public health concerns)
Stroke
Obesity
Health Concerns and Leading Causes of Death of Females
Reproductive health
Childbearing
Menopause
Preconception counseling
Malignant neoplasms (breast, cervix, ovaries)
Osteoporosis
Health Concerns and Leading Causes of Death of Males
Unintentional injuries
Erectile dysfunction
Malignant neoplasms (prostate, testes)
Screening and Preventive Services for Adults
Height & weight
Dental health
Blood pressure
Cholesterol (ages 45–65)
Fecal occult blood test / sigmoidoscopy (≥45 years)
Immunization status
Diabetes mellitus
HIV/STI
Skin cancer
Nutritional screening (obesity)
Depression screening
Screening and Preventive Services for Females
Pap test
Mammogram & clinical breast exam
Rubella serology & vaccination history (childbearing years)
Screening and Preventive Services for Males
Digital rectal exam
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing
National Health Goals for Adults
Reductions in:
Bone diseases (e.g., osteoporosis)
Death from cancer
Sexual violence
Incidence of HIV/AIDS
Fatal & nonfatal injuries
Unplanned pregnancies
Excessive alcohol & tobacco use
Increases in:
Use of both barrier & hormonal contraception
Pregnant clients receiving early & adequate prenatal care
Ability to identify warning signs of heart attack & stroke
Abstinence from alcohol, nicotine, & other substances during pregnancy
Community Education for Adults
Nutrition
STI prevention
Substance use disorders
HIV prevention
Injury prevention (car, fire safety, violence)
Breast & testicular self-examination
Older Adults
Fastest growing aggregate in U.S. population
Proportion of older adults living alone continues to rise → nurses must ensure access to healthcare & assistance (SDOH)
~1/3 of U.S. prescriptions are for older adults
Most have ≥1 chronic condition; many have multiple, with ↑ vulnerability due to aging changes & ↓ recovery ability
Administration on Aging (Older Americans Act): promotes services via states & local nonprofit agencies
Healthy People: has topic areas specific to older adult health
National Health Goals for Older Adults
Reductions in:
% with moderate to severe functional limitations
Hospitalizations due to heart failure
Inappropriate medication use (esp. with disability)
Hospitalizations due to pressure injuries
Emergency visits due to falls
Increases in:
Use of clinical preventive services
Use of “Welcome to Medicare” benefit
Public awareness of elder abuse, neglect, exploitation
Physical activity among adults with reduced physical/cognitive function
Access to diabetes self-management benefits
Healthcare professionals with geriatric certifications
Community Education
Community resources & programs
Healthy meals, snacks, nutritional supplements
Exercise
Dental health
Injury prevention
Car & fire safety
Fall prevention
Abuse & mistreatment awareness
Medication safety
A public health nurse is planning an in-service on older adult health. Which of the following information should the nurse include?
a
The percentage of older adults in the population is decreasing.
b
The proportion of older adults who live alone is increasing.
c
Older adults take one-half of all prescription medications.
d
Older adults have a decreased recovery time following injury.
b The proportion of older adults who live alone is increasing.
Since 1990, the likelihood of older adults living alone has grown.
Families
Family as a client = central to community-oriented nursing practice
Families provide emotional, financial, and/or physical support
Nurses help families through assessment, planning, development, and evaluation focused on family issues
Home visits allow nurses to observe the environment, identify barriers, and support risk reduction
Approaches to Family Nursing Care
Family as a Component of Society
Examines family interactions with institutions (schools, healthcare, finance, congregations)
Used for population-focused interventions (e.g., immunization campaigns for disadvantaged groups)
Family as a System
Studies how family member interactions affect overall functioning
Promotes health by guiding interventions toward family interactions
Family as a Client
Examines family unit functioning first, then individual needs
Assesses how family health is influenced by each individual’s reaction to a health event
Family as Context
Focuses on an individual first, then family next
Promotes recovery/health of an individual with family as support system
A home health nurse is planning care with a client and their family following a stroke. Match each approach to family nursing care with a strategy for using it to plan care.
Family as a component of society
Family as a system
Family as a client
Family as context
View the client as the focus of care. with the family members viewed as a source of support for the client.
Ask the family members how their family function overall has changed following the client’s stroke.
Ask individual family members how their life has changed following the client’s stroke.
Examine how the family unit interacts with other parts of society, such as with medical facilities or financial institutions.
Family as a component of society
Examine how the family unit interacts with other parts of society, such as with medical facilities or financial institutions.
Family as a system
Ask individual family members how their life has changed following the client’s stroke.
Family as a client
Ask the family members how their family function overall has changed following the client’s stroke.
Family as context
View the client as the focus of care. with the family members viewed as a source of support for the client.
Crisis and Transitions
Family Crisis
Occurs when family resources are inadequate to cope with a situation.
Common triggers (transitions):
Birth or adoption of a child
Death of a family member
Child moving out of the home
Marriage of a child
Major illness
Divorce
Loss of main family income
Impact of Transitions
Families must:
Change behaviors
Make new decisions
Reallocate family roles
Learn new skills
Use new resources
Characteristics of Healthy Families
Communicate well & listen to each other
Provide affirmation & support
Teach respect for others
Create trust
Share play & humor
Interact with one another
Participate in leisure activities together
Share a religious foundation
Respect individual privacy
Share responsibility
Maintain traditions & rituals
Seek help for problems when needed
Family Health Risk Appraisal
Biological Health Risk Assessment
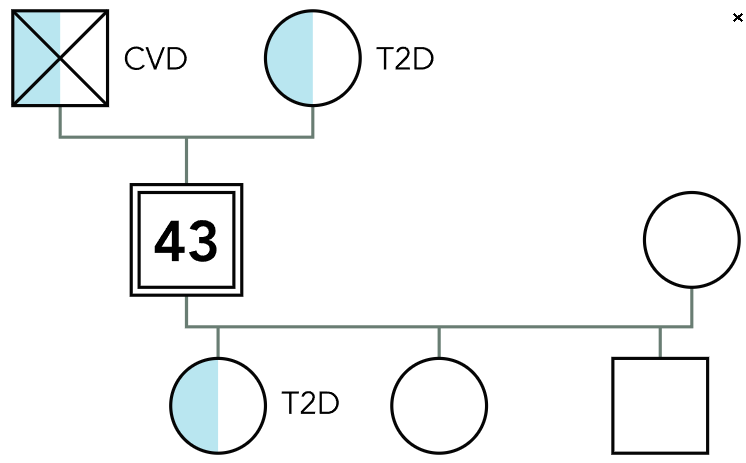
Genograms: Gather information about family structure, relationships, health/illness patterns.
Identify genetic risks (e.g., cancer, heart disease, diabetes mellitus).
Genomic information helps with targeted prevention.
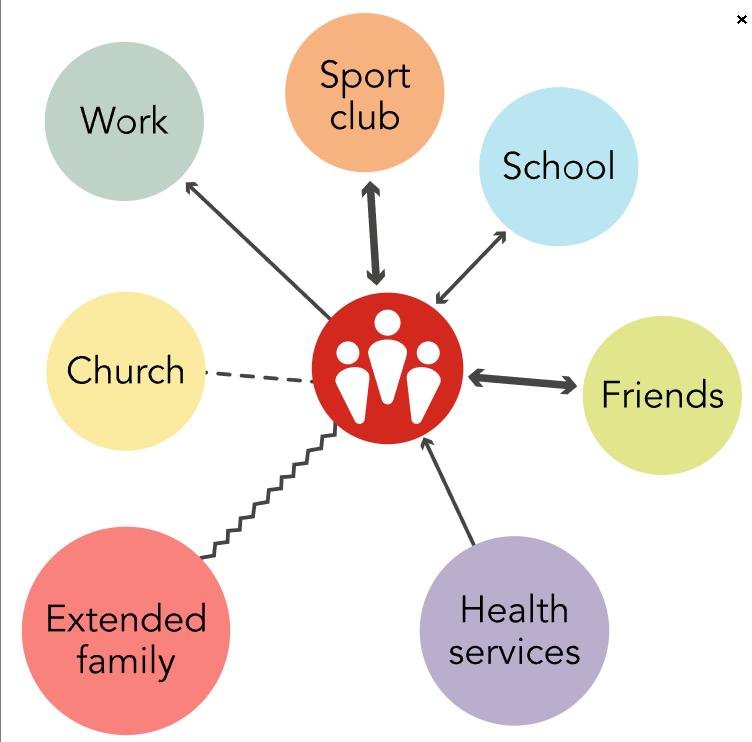
Ecomaps: Visual diagram of family’s relationship with external systems (school, work, church, friends, extended family, health services).
Shows family’s role in the community & social supports.
Environmental Risk
Ecomaps also assess family interactions with groups/organizations.
Provides information on support network and social risks.
Behavioral Risk
Gathers info about:
Health behaviors
Health values
Health habits
Risk perceptions
SDOH Example: Economic stability & access to nutritious food.
Children: Anemia, poor cognition, anxiety, asthma, poor oral health
Adults: Depression, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, sleep disorders
Senior Adults: Poor physical health, depression
Genogram (Image)
Ecomap (Image)
A community health nurse is using tools to conduct a family assessment. Sort the following information gathered by the nurse by whether it is more likely to be included in a genogram or an ecomap.
Family history of heart disease
Family involvement in church activities
Ages of everyone in the family
Birth order of children
Occupations of family members
History of family violence
Relationships with neighbors
Schools the children in the family are attending
Genogram
Ecomap
Genogram
Family history of heart disease
Birth order of children
History of family violence
Occupations of family members
Ages of everyone in the family
Ecomap
Relationships with neighbors
Schools the children in the family are attending
Family involvement in church activities
National Health Goals of Families
Reductions in:
Barriers to access
Allergens within the home
Families unable to have/maintain a pregnancy
Passive smoke exposure
Household hunger
Intimate partner violence
Increases in:
Positive parenting
Health education from agencies (Head Start, schools, colleges, employment sites, health departments)
Home testing for radon
Health insurance coverage
Individuals with a usual primary care provider
Family health literacy
A nurse is planning interventions for populations of different age groups in the community. Sort the following educational topics by the population in which it is a major concern.
Dental health
Pneumococcal vaccine
Preconception counseling
Accessing Medicare benefits
Congenital anomalies
Managing osteoporosis
STI Prevention
School-Age Children
Adults
Older Adults
School-Age Children
Congenital anomalies
Dental health
Adults
STI Prevention
Preconception counseling
Older Adults
Pneumococcal vaccine
Managing osteoporosis
Accessing Medicare benefits
Genograms vs Ecomaps
“Who’s in the family and their health history” (biological risk)
Purpose: Shows family structure, relationships, and health/illness patterns.
Focus: Biological and hereditary risks (e.g., cancer, heart disease, diabetes).
Use: Identifies genetic tendencies and intergenerational health problems.
Appearance: Family tree diagram with symbols for members, relationships, and medical history.
“How the family interacts with the outside world” (environmental/social risk)
Purpose: Shows family connections to external systems (school, work, church, friends, healthcare, community).
Focus: Environmental and social supports/stressors.
Use: Identifies resources, stressors, and support networks influencing family functioning.
Appearance: Central family unit connected outward to external groups with lines showing strength/quality of relationships.