Meiosis + haploid cells T3 W3
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Meiosis definiton
Meiosis is a process of cell division that produces gamete cells for sexual reproduction
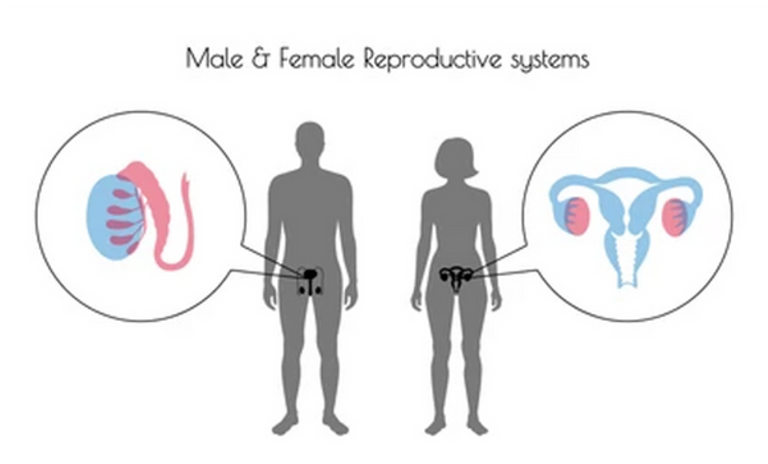
Meiosis purpose and where it occurs
To produce gametes for sexual reproduction. Humans have two types of gametes – sperm cells in the male and egg cells in the female.
Meiosis occurs in specialised tissue in the human body called the gonads. In the male the gonads are called the testes, and in the female the gonads are called the ovaries.
2 gametes types
Sperm cells - male
Egg cells - females
Haploid cells (N)
Happens in gametes, haploid number of chromosomes referred to as n
Humans n = 23
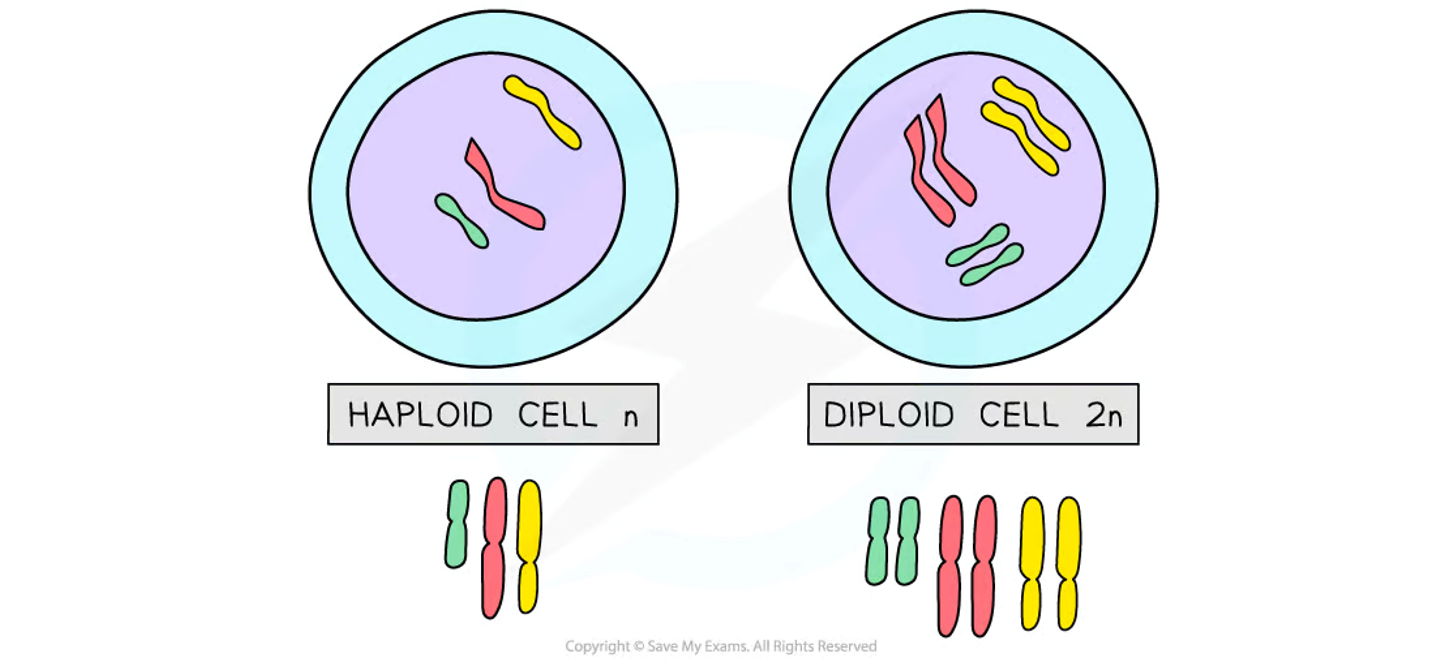
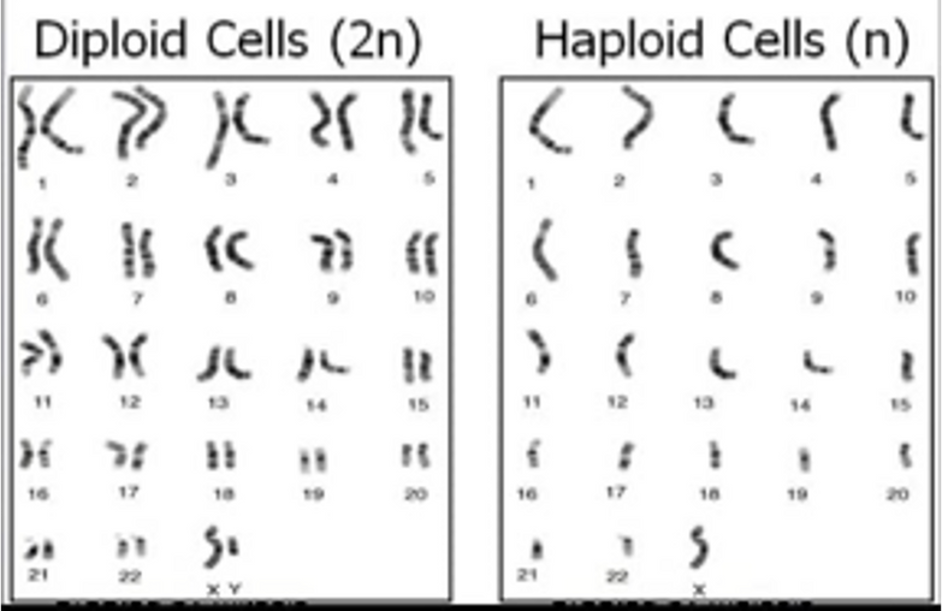
Meiosis aim
Produce haploid cells, from diploid body cells, so that they can go on to meet another haploid cell in fertilisation and become a diploid cell.
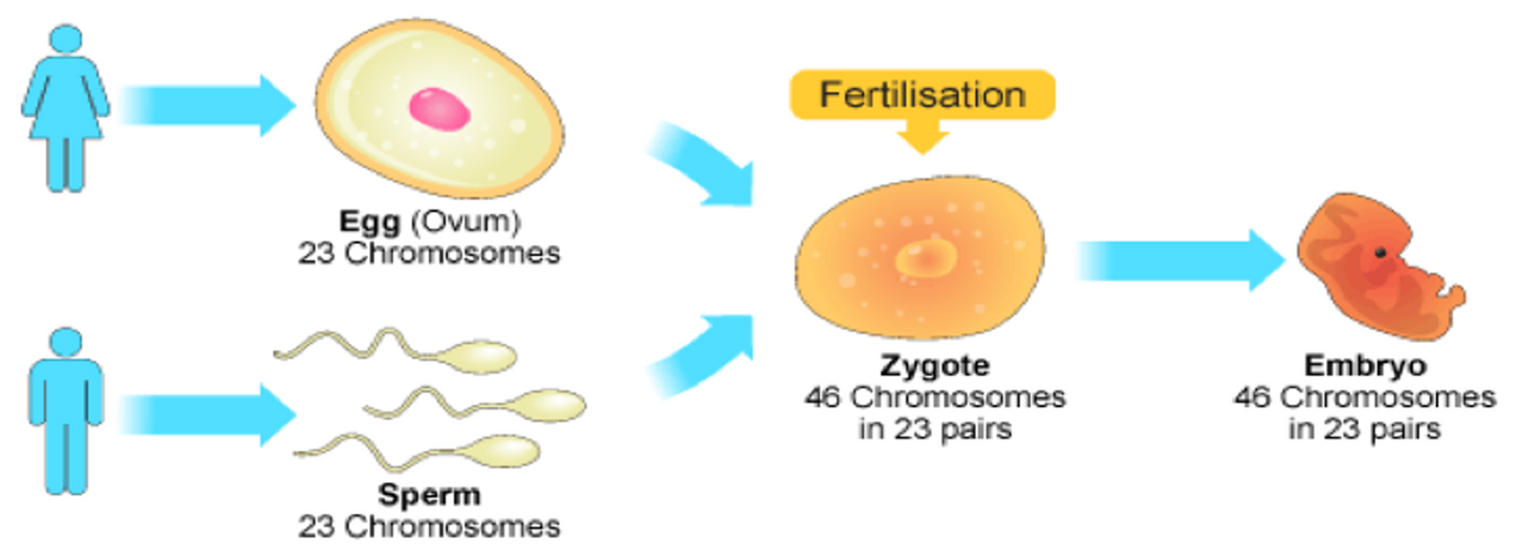
Meiosis parent cells location
testes/ovaries
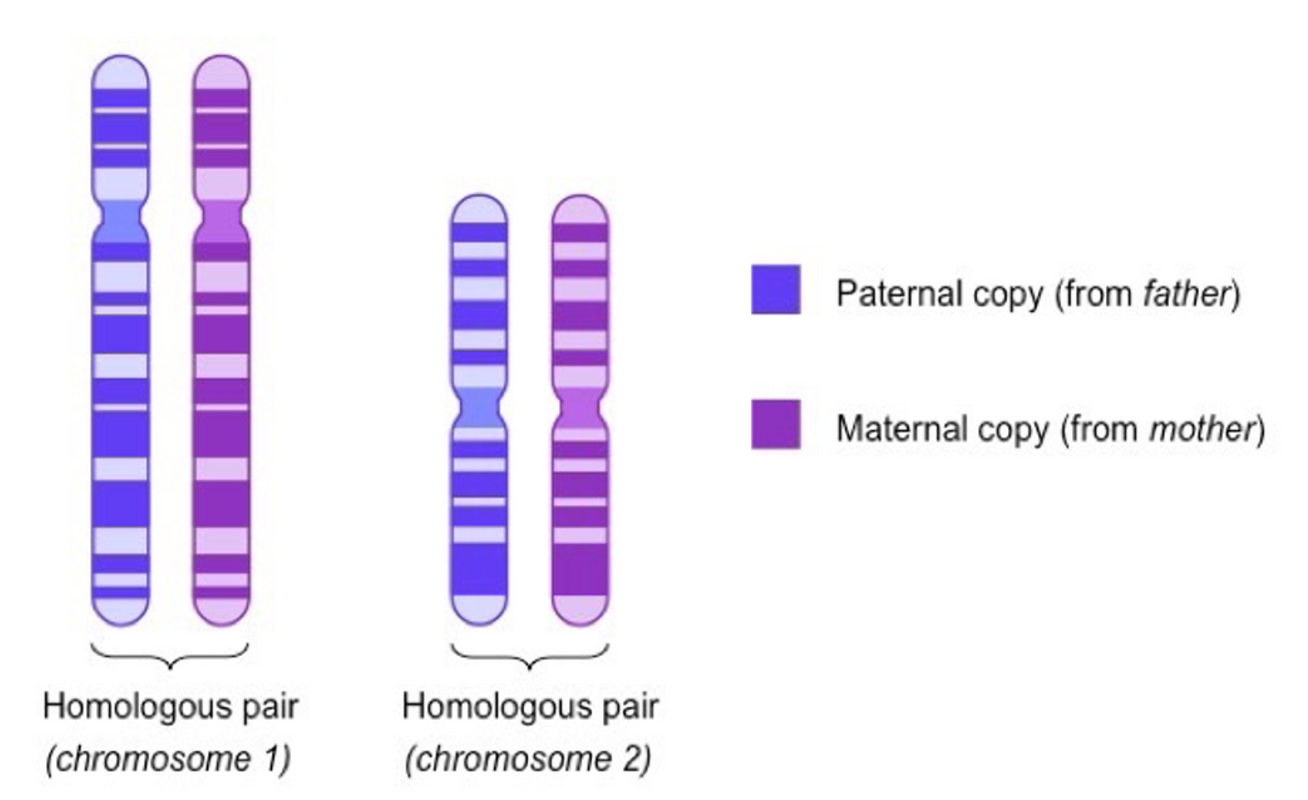
parental chromosome
inherited chromosome form father
maternal chromosome
inherited chromosome from mother
Homologous chromosomes
•Pairs of chromosomes that are identical in size, shape and they have the same genes located in the same position.
•Each member of a pair of homologous chromosomes carries genetic information that influences the same characteristics.