CHEMISTRY OCR A ORGANIC
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
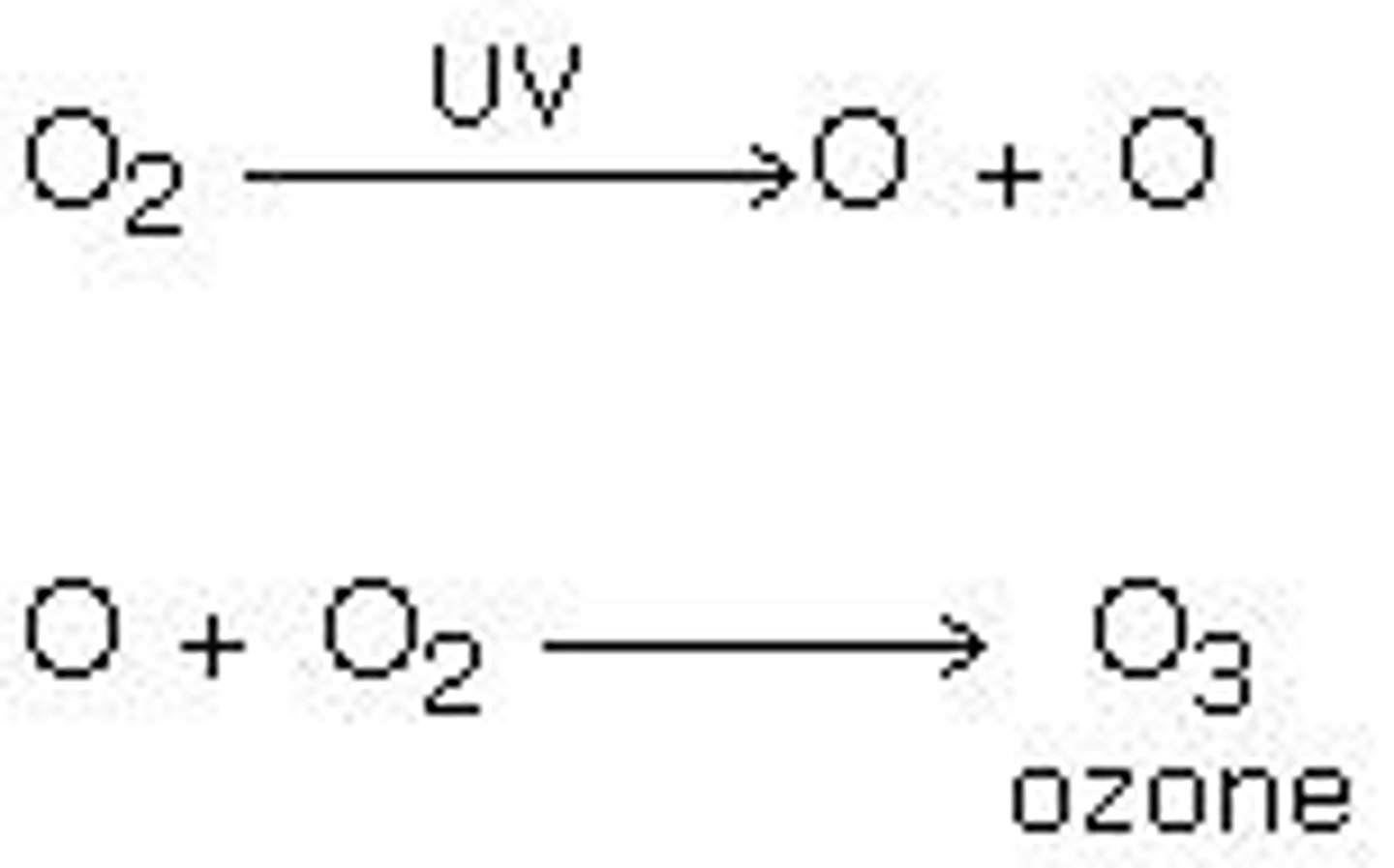
Equation showing showing formation and depletion of ozone
Equation showing the effect of chlorofluroalkanes on ozone
[will insert]
Equation showing the effect nitric acid on ozone
[will insert]
What are haloalkanes named based on?
They are named based on the original alkane with a prefix indicating the halogen atom.
What prefixes are used for halogen atoms in haloalkanes?
Fluoro for F; Chloro for Cl; Bromo for Br; Iodo for I.
How are haloalkanes classified?
Haloalkanes can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon atom adjacent to the halogen.
What defines a tertiary haloalkane?
A tertiary haloalkane has three carbons attached to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen.
What defines a primary haloalkane?
A primary haloalkane has one carbon attached to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen.
What defines a secondary haloalkane?
A secondary haloalkane has two carbons attached to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen.
What is a nucleophile?
A nucleophile is an electron pair donor, such as :OH-, :NH3, or CN-.
What does the mechanism of nucleophilic substitution involve?
It involves the nucleophile attacking the positive carbon atom and swapping a halogen atom for another atom or group.
How does bond strength affect the rate of substitution reactions in haloalkanes?
The weaker the C-X bond, the easier it is to break and the faster the reaction.
Which haloalkane is the fastest to substitute?
Iodoalkanes are the fastest to substitute due to the weak C-I bond.
What is hydrolysis in the context of haloalkanes?
Hydrolysis is the splitting of a haloalkane molecule by a reaction with water.
What is the result of hydrolysis of haloalkanes?
The result is the formation of an alcohol and a halide ion.
What happens when aqueous silver nitrate is added to a haloalkane?
The halide leaving group combines with a silver ion to form a silver halide precipitate.
What is the effect of CFCs on the ozone layer?
CFCs contribute to the depletion of the ozone layer by releasing chlorine radicals that catalyze the breakdown of ozone.
What is the role of ultraviolet light in ozone formation?
UV light causes O2 molecules to split into free radicals, which can then form ozone.
What is the overall reaction for ozone depletion by chlorine radicals?
O3 + O. → 2 O2.
What are HFCs and why are they used?
HFCs (Hydrofluorocarbons) are used as safer alternatives to CFCs because they do not contain the C-Cl bond.
What is the environmental concern regarding CFCs?
CFCs have a long lifetime in the atmosphere and continue to enter the atmosphere from disused items.
What is the significance of the ozone layer?
The ozone layer filters out harmful UV radiation, protecting life on Earth.
What is the consequence of the continuous cycle of ozone formation and depletion?
There is a constant amount of ozone in the atmosphere, balancing formation and removal.
What are the precipitate colors formed when haloalkanes react with silver nitrate?
AgI forms a yellow precipitate, AgBr forms a cream precipitate, and AgCl forms a white precipitate.
What is the mechanism used to show the movement of electrons in reactions?
Curly arrows are used to indicate the movement of two electrons in reaction mechanisms.
What is the relationship between bond enthalpy and reactivity of haloalkanes?
The lower the bond enthalpy, the higher the reactivity of the haloalkane.
What conditions are necessary for nucleophilic substitution with aqueous hydroxide ions?
The reaction occurs in aqueous solution and requires heating under reflux.
What happens when the solvent is changed to ethanol during nucleophilic substitution?
An elimination reaction occurs instead of substitution.